International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1Assistant Professor, Global Academy of Technology 2,3,4,5Undergraduate Student, Global Academy of Technology ***
Abstract An essential step in the processing of medical image data is the classification of images of brain tumours. The idea of biomedical imaging is significant because doctors may utilize it to create precise diagnoses and treatment plans. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the most widely used imaging methods for examining brain tissue (MR imaging). A tumour forms when malfunctioning cells group together and solidify into a mass of tissue. Tumors can develop in bones, skin, tissue, organs, and glands. Benign and malignant tumours can be further divided into meningioma, glioma, and pituitary tumours. The purpose of this study is to present an AI based method for categorising multigrade tumours in the human brain. As we move forward with this study, we'll be using the four models U net, VGG 16, AlexNet, and ResNet50 for datasets that are small and medium sized. We found that AlexNet's accuracy for normal classification was 99 percent, and that for multigrade classification, we attained an average IOU of 77.5 percent.
Keywords Unet, AlexNet, ResNet, Vgg16, Meningioma, Glioma, Pituitary tumor
Biomedical imaging is a group of techniques that can be used to look inside a body's internal organs without performing surgery on it. Image segmentation is used in medical imaging processing to identify tumours and providehelpfulinformationforadditionaldiagnosis.
Theobjectivesofpicturesegmentationinmedicalimaging processing include tumour identification and effective findings for further diagnosis. A brain tumour is an abnormal growth of brain cells that may be cancerous, non cancerous, or both types of cells. The two most prevalent types of cancer are benign and malignant. A brain tumour that is malignant begins in the brain and swiftlyspreadstothetissuesaroundit.Ontheotherhand, benigntumoursdevelopgradually.Dependingonthetype, size, and location of the brain tumour, there are different treatment options available. Therefore, it is crucial to
classifybraintumoursinordertodeterminewhichformof braintumourapatientactuallyhas.Planningthecourseof treatmentisthereforeacrucialstepinenhancingpatients' quality of life. As a result, we suggest a system for classifying multigrade cancers. In this work, we present a useful system for classifying and identifying brain tumours.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Sl. No Author
Year of Publication Methodology
1 Nudrat Nida, et Al [3] 2021 CNNarchitecture
2 EmrahImarak,et Al [4] 2021 Convolutional neural network
3 Tobias Hinz, et Al [5] 2018 DeepCNN
4 JiaweiLai,etAl[6] 2019 U net,CNN
5 Asma Naseer, et Al [7] 2021 DeepLearning
6 Awwal Muhammad Dawud,etAl[8] 2019
CNN, AlexNet, and AlexNet SVM
Results obtained
Deep features combined with ELM classifiers produce accurate melanomarecognitionmodels.
Hyperparameter optimization in CNN
The hyperparameters can be optimised on a series of smaller representations that grow in size until the original data size is reached.
TheIBSR18dataset'sexperimental brainMRIresultsdemonstratedthe efficiency of GMMD U on segmentationtasks.
The average accuracy is roughly 98.8%.
“CNN, AlexNet, and AlexNet SVM attained accuracies of 90.65%, 92.13 percent, and 93.48 percent, respectively.”[8]
7 QIANGLI,etAl[9] 2021
AlexNet,GoogleNet, VggNet,DenseNetResNet,Squ eezeNet, ShuffleNet,MobileNet,
A brain tumour is a neurological condition that can manifest as a malignant or non cancerous mass, or as the growth of a tumour. AlexNet, Vggnet, and DenseNet all have results above 0.95. ResNet.On anoise freeimage,it'sa0.7663.
8 MortezaEsmaeili, etAl[10] 2021
9 Kai Klinker, et Al [11] 2019
GoogLeNet, MobileNet,DenseNet 121
AugmentedReality
10 Muhammad Sajjad, etAl[12] 2018
InputCascadeCnn,VGG 19
On the testing dataset, the considered models had the precision of 92.1%, 87.3%, and 88.9%.
ImprovedDiagnosisPrecision
For grades 1,2,3, and 4, the accuracy utilising the radiopaedia dataset is 90.03 percent, 89.91 percent, 84.11 percent, and 85.50 percent,respectively.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2338

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
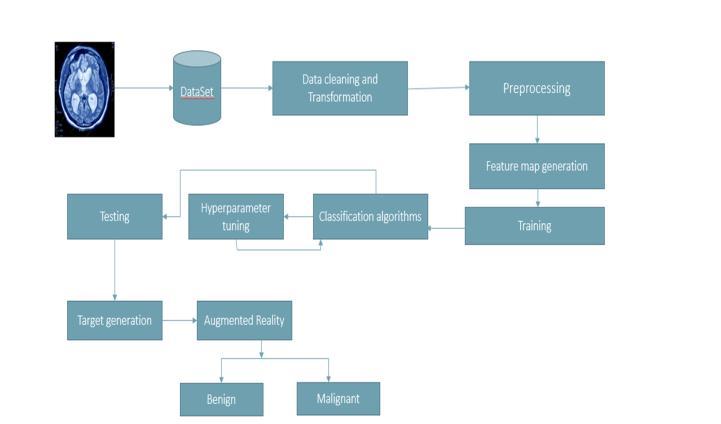
The suggested model aims to increase the precision and accuracy of the outcomes. We are working to improve the accuracyofthesysteminanefforttolowerthehighdeath rate caused by cancers. Our project's initial phase is the acquisition of the dataset, which consists of MRI pictures, followed by data cleaning and transformation, which is mostly done to convert the collected dataset into the necessary format. To remove noise and undesirable data components,thenextstepistopreprocessthedata.Inthis step, the image is enhanced and the undesired text and noise are removed. Additionally, the data is segmented to separate the tumor, cerebrospinal fluid, whitematter, and gray matter. After the preprocessing stage, the clean data is obtained. After that, we start the classification training, which involves teaching the system how to categorize a multigrade brain tumor. The classification algorithms offered by the CNN architecture are used in this step. The system must then be tested to ensure that the results are exactandaccuratewhenthetrainingprocessiscomplete
Dataaugmentationisamethodforintentionallyincreasing the volume and complexity of already existing data. To increase the size of training sets and give developers access to more representative training data, data augmentation techniques have been used. The fundamental idea is to artificially boost the quantity of training instances. It can function as a regularizer to stop neural networks from overfitting. However, although the study says data augmentation is not fully recommended for medical imaging experimentation, in our work due to acute shortage of data the experiments have been carried out using synthetic data keeping in mind the positional invariant features capture which would significantly enhancemodels’performance.
Image pre processing techniques aim to enhance images for the sake of further processing (generally object recognition).Pre primaryprocessing'sobjectivesarenoise reduction (the source of noise is typically digitizing and transmission), the elimination of distortion caused by the scanning device, and finally, the suppression or highlighting of other attributes that are crucial for subsequentprocessing,segmentation,andedgedetection.
Inthisstudy,weproposeaclassificationmodelthatwould allow us to use the patient's MRI pictures as an input and compute whether a brain tumor is present or not as an output. We used Kaggle, which makes MRI scans of the brainavailabletothepublic.
The suggested approach includes identification of the region for analysis, drawing out the feature maps,electing the right prominent feature value, and diagnosing them intotherightclass.Allthefeaturesthatareretrievedmake up the feature subset which includes most of the distinguished features supplied for classification and the experiment was progressive until a drop in the performance was seen. In order to compare these three pattern classification techniques: U net, AlexNet and Vgg16.
The methods were applied to a class of MRI images, historicallyidentifiedasBenignorMalignantandclassified using U net, AlexNet, and Vgg16 architectures to record the contrast between their performances. The accuracy of Vgg16modelwasfoundtobe66%formediumdatasetand 90% for small dataset, for U net model it was 74% for medium dataset and 92% for small dataset and AlexNet showed an accuracy of 99% model for both small and mediumdatasets.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The following Neural Network architectures have been experimentedandtheirperformancehasbeen recorded:
4.1. U net:
Fig.4.1.1Accuracygraphformediumdataset
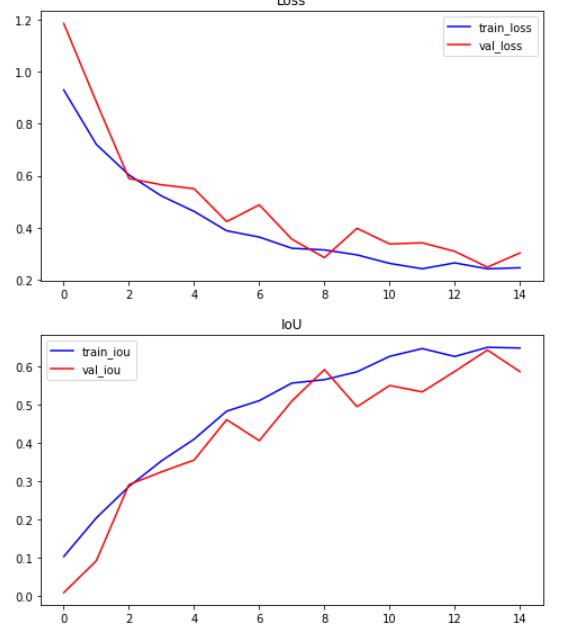
Fig.4.1.2Accuracygraphforsmalldataset
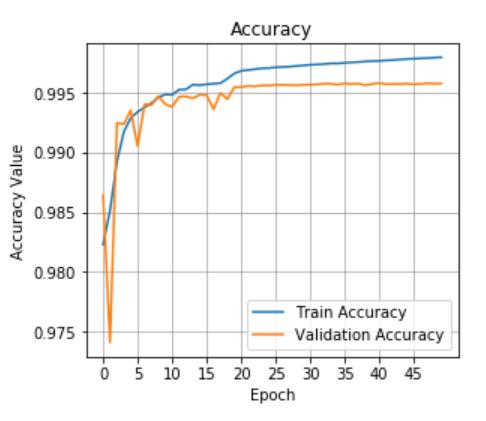
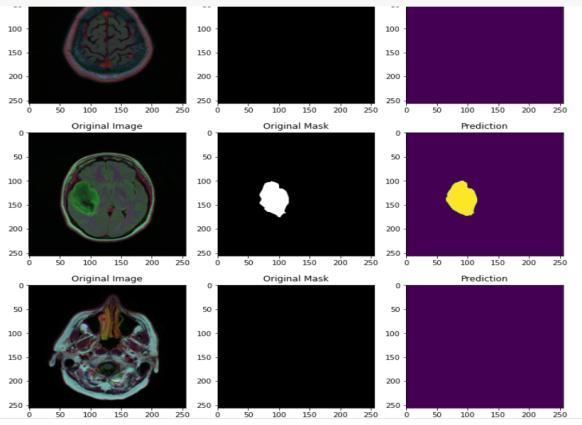
Fig.4.1.3Predictionformediumdataset
Fig.4.1.4Predictionforsmalldataset
The small dataset consisted of 250 images with 155 that showed the presence of tumor and 98 that did not show anytumor.Forthemediumdatasetweconsideredaround 4000imageswith2556imagesthathadtumorsand1373 thatdidnotshowanytumor.
Onadatasetofroughly4000MRIimagesforbraintumour detection, the proposed approach was examined and tested.
Inorder to improvethe performance ofthe network, data augmentation aims to increase the original training data's volume. There have been many different data augmentation methods applied. Simple transformations like flipping, rotating, shifting, and zooming can cause displacementfields toimagesbutdonotresultintraining samples with significantly altered shapes. Because tumours lack a defined structure, shear surgery can only

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
slightly affect the tumor's general form in the horizontal direction, which is not enough to offer enough varied trainingdata
To minimize the cost function with regard to its parameters, stochastic gradient based optimization is needed when training deep neural networks. Adam typically updates and corrects the moving average of the current gradients using the first and second moments of the gradients. The Soft Dice metric, as opposed to the cross entropy based or the quadratic cost function, was employed as the network's cost function throughout the trainingprocess.
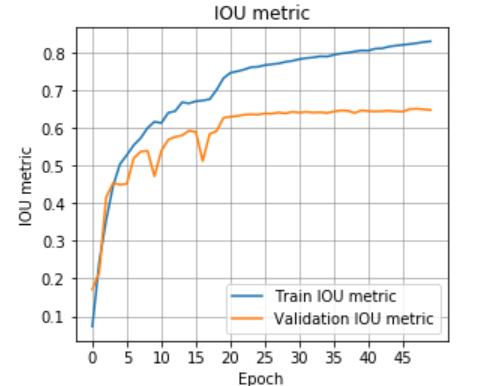
Fig.4.2.1Accuracygraphformediumdataset
Fig.4.1.2Accuracygraphforsmalldataset
4.2.1.
Fig.4.2.3Predictionformediumdataset
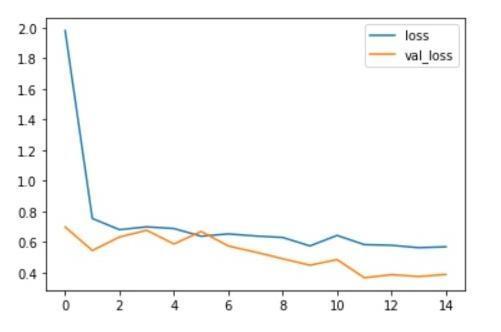
Fig.4.2.4Predictionforsmalldataset
Thesmalldatasetconsistedof2000imageswith1085that showed the presence of tumor and 980 that did not show anytumor.Forthemediumdatasetweconsideredaround 6000imageswith3255imagesthathadtumorsand2940 thatdidnotshowanytumor.
(IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Using the VGG 16 model, we studied how to correctly evaluate performance while detecting brain tumours. The first step will be to resize the data set's images to (224x224)andpre processtheminordertopreparethem as inputs for the VGG 16 model. Every image in the data set has undergone pre processing. Here weare using pre processingtechniqueslikenormalization,resize,label and shuffle .The first step in pre processing is normalization where the Brain image is cropped from the MRI. The second step of pre processing is to identify the highest contour so that here the edges of the brain are found and thisimageistakenasapre processedimage.
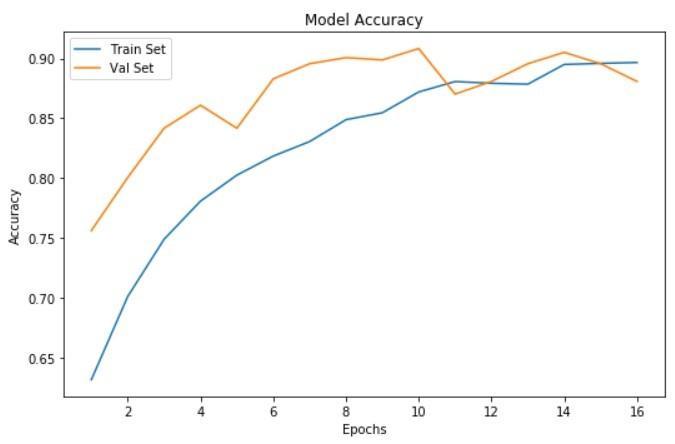
The images were enhanced and produced for pre processing before they were sent to training. The training set is utilized to develop and fit the model, the validation set offers an overall analysis of the trained model and finally the model's hyper parameters such as epoch, learning rate are considered for improving the performance oftheclassifier. Herewehaveusedadapting learningratewithepoch40,60,80,90.Thetestsetoffersan accuratereviewofthefinishedmodel.
A pretrained VGG 16 model with all the parametric weights needed for the imagenet classifier set has been feeded considering one particular parameter to add the weights. Since the experiment here is carried out to classifyintotwoclassesonly,thecustomclassifierisbeing devisedwiththetwoclassesaccordingly.Edges,lines,and blobs are low level picture elements that are extracted, and the fully connected layer then divides them into two groups. After the creation of the model ,the accuracy is checked and we test whether the model predicts the tumourornot.
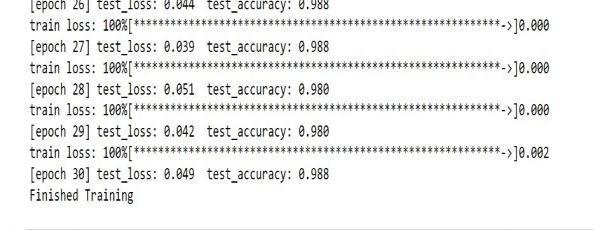
Fig.4.3.1Accuracyforepoch60
Fig.4.3.2Accuracyforepoch40
Fig.4.3.3Accuracyforepoch50
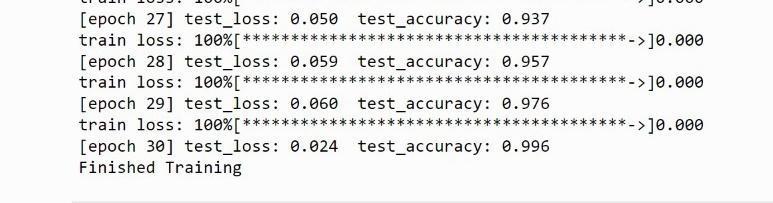
On a dataset of roughly 6000 MRI images for brain tumor detection, the proposed approach was examined and tested.The goal of data augmentation is to increase the amount of synthetic data which is essentially needed in order to track and increase the performance of modelAlexNet employs two methods for data augmentation. The first feeds random input image cropping,rotations,andflipsintothenetworkasitisbeing trained.Duetothepresenceoffullyconnectedlayers,input sizeisfixed.
To obtain steps with a high degree of precision, preprocessing is necessary. Patient specific artefacts include ring, staircase,and volume effectartefacts,aswell as MRI and CT scans. All of these are eliminated before analysis utilising some preprocessing techniques. The suggestedapproachshowshowasetofMRIimagescanbe categorised using transfer learning to retrain the AlexNet convolutional neural network. Following the creation of the network structure, training options are discussed. Stochastic momentum gradient descent optimization model, histogram equalisation, starting learning rate, and epochs which denotes the entire training period on the training dataset are some of the training options. By trainingthedatasetswithdifferentepochs,suchas40,50, and 60, hyper parameter tuning is accomplished. The network was trained using preset training datasets, layer designs, and training choices. The classification module receives the test image and uses a trained network to forecast or classify the supplied image into various categories.
4.4.1.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The input photos and their associated segmentation maps are used to train the network using Caffe's version of stochastic gradient descent. The unpadded convolutions cause the output image to be a constant border width smaller than the input image. We reduce the batch to a singleimagetoreduceoverheadandmakethemostofthe GPURAMbyprioritisinglargeinputtilesoveralargebatch size. We pre compute the weight map for each ground truth segmentation to take into account the fluctuating frequencyofpixelsfromacertainclassinthetrainingdata set and to force the network to learn the small separation barriers that we impose between touching cells. A good initialization of the weights is crucial in deep networks with numerous convolutional layers and varied network routes. Otherwise, some sections of the network could activatetoomuchwhileotherpartsneverdo.
Sincethereisashortageoftrainingsamplesforanymodel toadaptandlearn,dataaugmentationwassoughttoteach the neural network to handle invariance and flexibility of features. On a rough 3 by 3 grid, we produce smooth deformationsusingrandomdisplacementvectors.
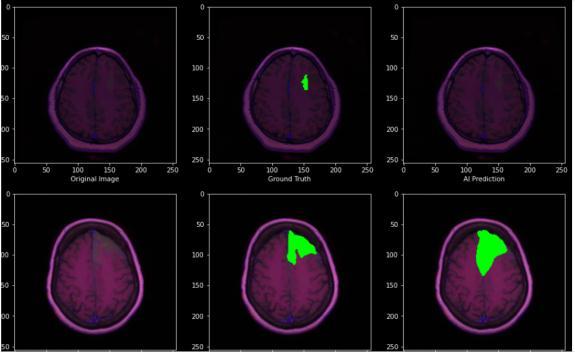
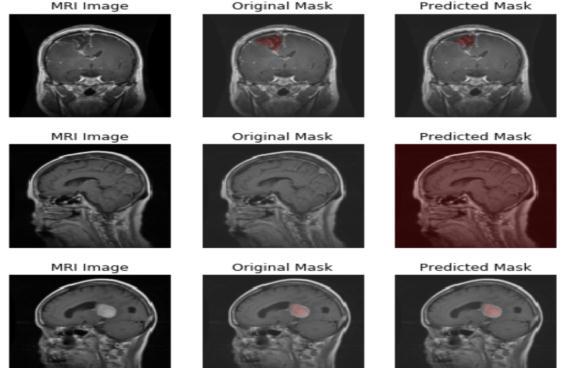
Fig.4.4.3.PredictedOutput
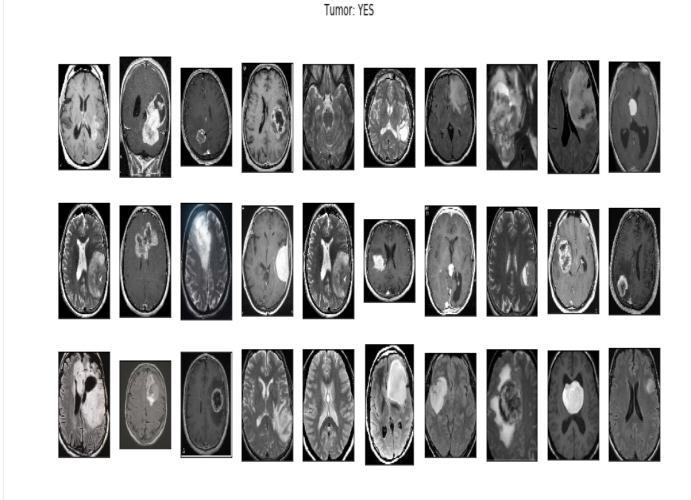
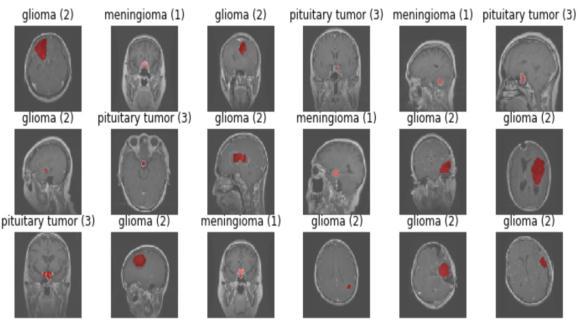
Thedatasetconsistedof708meningiomapositiveimages, 1426 glioma tumor images and 930 pituitary tumor images.
We use three separate segmentation tasks to show the u net in action. The segmentation of neural structures in recordings made using an electron microscope is the first challenge. We employed a brain tumor segment dataset for this experiment, which is accessible online. 3064 MRI scans and 3064 masks are included. A collection of 30 images serially sized 512x512 section which transmits throughelectronmicroscopyoftheventralnervecordofa Drosophila serves as the training data (VNC). To proceed with the implementation and classification, the ground truth data which is completely tagged for each image is consideredforthewhiteandbackmatteroftheimages.U netmodelhasbeenchosenfortheexperimentationasthis model does not need any further processing either before or after diagnosis which internally makes the model less pronefortheerrorsandaswellensurethatitoutperforms otherclassifierswhichmayneedtobetrainedwithstrong featuremapsaftercarefulprocessingofthedata.However theU netmodelalsosuffersawarpandrandomerror.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
train, test, and partition the data, we will use the Sklearn model.ImageDataGeneratorhasbeenimportedhere.
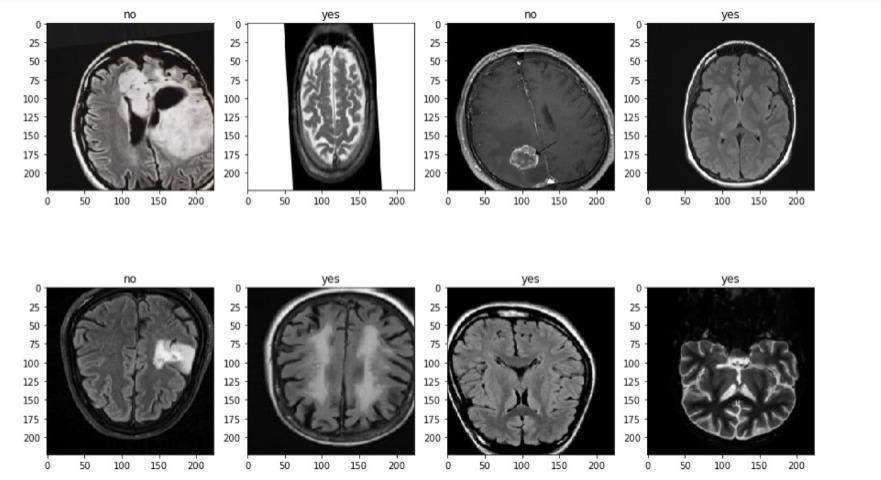
TrainandValdatasetsareseparatedinthetrainingfolder. Four groups of tumour MRIs are contained in each folder. The epoch rate was set to 50. The dataset file is then unzippedandsavedinapredeterminedpathandfolder.A dictionary is explained in relation to data visualisation. Our four classes ('glioma tumor,' "no tumor," "meningioma," and "pituitary tumor") are the dictionary keys. A directory of images is present in each row. The number of photos in each class in the training and testing sets is then counted using an initialised list. We print the total number of photos in each class for the train and test sets.

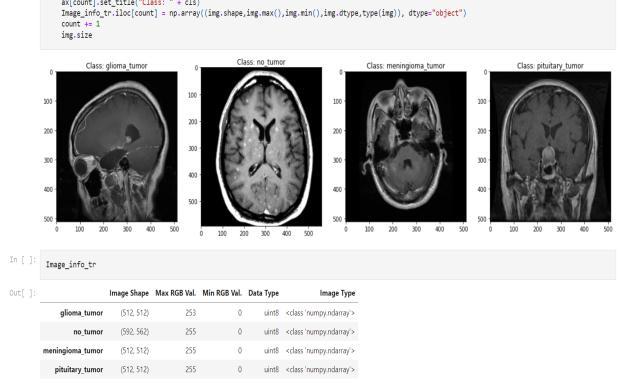
Fig.4.5.1.Accuracygraph
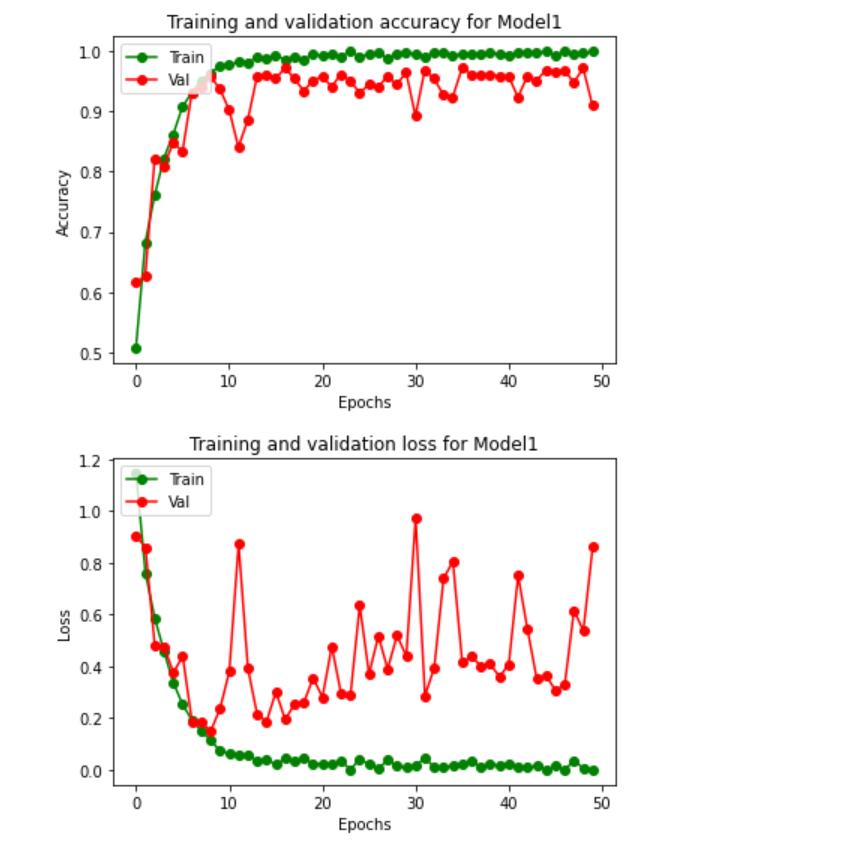
Fig.4.5.2.
ResNet is being put into practice in Keras. The dataset for the detection of brain tumours will be used for this implementation. Both the training folder and the testing folderinthisKaggleprojectcontainMRIdata.MRIimages of the corresponding tumour classes are organised into foursubfoldersineachfolder.Webeginbyimportingallof thelibrariesthatarerequiredtoimplementResNet.Given that this is a medical issue and that mistakes can be extremely expensive, we work to create an automated method for identifying and classifying brain tumours. To
VisualizeoneimagefromeachclassfortheTrainset,then save the image information in a designated dataframe. Visualize one image from each class for the Test set, then store the image information in a designated dataframe. There are two train and test folders in the Kaggle dataset. In this case, the train set was divided into train and validation sets. Next, we create a straightforward basic model and run MaxPooling. We put up data generators to processModel1'sdatainorderto:Viewtheimagesinour source folders, Feed images to our network along with their labels after converting them to float32 tensors. For thetrainingphotosandthevalidationimages,wewilleach have a separate generator. Our generators will produce batchesof150x150 pixelimagesalongwiththeirlabels.
Being one of the most significant concerns, health issues require proper diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, we suggestamethodforcategorisingbraintumoursaccording

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
to their characteristics. According to a literature review, MRI pictures are the most effective tool for finding brain malignancies. The detection of brain tumours using MRI images requires the use of digital image processing techniques.Differentpreprocessingtechniquesareusedto reducenoise,cleantheimage,andchangetheimage.After that, ML algorithms are fed the clean data. Taking the suppliedimageandclassifyingitasbenignormalignantis thelaststep.
[1] Brain Tumor: Statistics, Cancer.Net Editorial Board, 11/2017(Accessedon17thJanuary2019)
[2] Brain Tumor Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network Tonmoy Hossain , Fairuz Shadmani Shishir, MohsenaAshrafMDAbdullahAlNasim,FaisalMuhammad Shah,2019
[3] Awwal Muhammad Dawud , Kamil Yurtkan, HuseyinOztoprak (2019) “Application of Deep Learning in Neuroradiology: Brain Haemorrhage Classification Using TransferLearning”,ArticleID4629859.
[4] Qiangli, Yingjian Yang, Yingwei Guo,Wei Li , Yang , Hanliu, AND Yan Kang (2021) "Performance Evaluation of DeepLearningClassificationNetworkforImageFeatures", vol.9,pp.9318 9333,2021.
[5] MortezaEsmaeili, RiyasVettukattil, Hasan Banitalebi, Nina R. Krogh and JonnTerjeGeitung (2021) “Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Human Machine Interaction in Brain Tumor Localization”Volume11.
[6] Kai Klinker, ManuelWiesche, Helmut Krcmar (2019) “DigitalTransformationinHealthCare: Augmented Reality for Hands Free Service Innovation”,Inf sys front 22,1419 1431.
[7] Jiawei Lai , Hongqing Zhu, Xiaofeng Ling (2019) “Segmentation of Brain MR Images by Using Fully Convolutional Network and Gaussian Mixture Model with SpatialConstraints”,ArticleID4625371.
[8] Asma Naseer, Tahreem Yasir,Arifah Azhar , Tanzeela Shakeel , and Kashif Zafar (2021) “Computer Aided Brain TumorDiagnosis:PerformanceEvaluationofDeepLearner CNNUsingAugmentedBrainMRI”,ArticleID5513500.
[9] Muhammad Sajjad, Salman Khan, Khan Muhammad, Wanqing Wu, Amin Ullah, Sung WookBaik (2018)”Multi
Grade Brain Tumor Classification using Deep CNN with ExtensiveDataAugmentation”,Volume30.
[10] Peter Ardhianto , Jen Yung Tsai, Chih Yang Lin 3 , Ben YiLiau4,Yih KuenJan,VeitBabakHamunAkbariand Chi WenLung(2021)“AReviewoftheChallengesinDeep Learning for Skeletal and Smooth Muscle Ultrasound Images”,volume11,Issue9.
[11] RahelehHashemzehi ,Seyyed Javad Seyyed Mahdavi, Maryam Kheirabadi, Seyed Reza Kamel (2020) “Detection of brain tumors from MRI images base on deep learning usinghybridmodelCNNandNADE”,Volume40,Issue3
[12] Mahmoud khaled Abd Ellah, Ali Ismail Awad, Ashraf A. M. Khalaf, Hesham F. A. Hamed (2018) “Two phase multi model automatic brain tumour diagnosis system from magnetic resonance images using convolutional neuralnetwork”,Jimagevideo.
[13] BijenKhagiand Goo Rak Kwon (2018) ” Pixel Label Based Segmentation of Cross Sectional Brain MRI Using Simplified Seg Net Architecture Based CNN”, Journal of healthcareengineering,volume2018,ArticleID3640705.
[14] Nudrat Nida , AunIrtaza , and Muhammad Haroon Yousaf (2021) “A Novel Region Extreme Convolutional Neural Network for Melanoma Malignancy Recognition”, ArticleID6671498.
[15] Emrah Imarak (2021) “Multi Classification of Brain Tumor MRI Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network with Fully Optimized Framework”, Iran J sci TechnalTransElectrcEng45,1015 1036.
[16] Tobias Hinz, Nicolas Navarro Guerrero, Sven Maggand Stefan Wermter (2018) “Speeding up the Hyperparameter Optimization of DeepConvolutional NeuralNetworks”,Volume17.
[17] BijenKhagiand Goo Rak Kwon (2018) “Pixel Label Based Segmentation of Cross Sectional Brain MRI Using Simplified Seg Net Architecture Based CNN”,Journal of healthcareengineering,volume2018,ArticleID3640705.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2345