International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
2
1 Student, Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering, University BDT College of Engineering, Karnataka, India.
2 Professor, Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering, University BDT College of Engineering, Karnataka, India. ***
Abstract - Due to the extensive use of various sensors, human activity detection has recently gained popularity in a variety of domains such as person monitoring and human robot interaction. The main goal of the proposed system is to create an activity detection model that aims to identify human actions through video using deep learning. The dataset called Kinetics is utilised to train the activity recognition model. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is one of these techniques. It is a type of neural network in deep learning that has the ability to turn on the underdone inputs immediately. These models can only currently handle inputs that are two dimensional. However, in order to detect the actions in the videos, this study uses a three dimension CNN model for classification of videos. Since 3D convolutional networks naturally apply convolutions in 3D space, they are recommended for video categorization.
Keywords: Video, Deep Learning, Kinetics dataset, inceptionV1,ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork.
Recognition of human activity is important for interpersonal interactions and human to human communication. Identification of activities is the objective of human activity recognition. Identification of activities from a range of observations of participant behaviour and the surrounding environment is the objective of human activity recognition. There are two key queries across different classification techniques: "What action?" (specifically, the issue with recognising) and "Where in the video?" (Specifically, the localization issue). The kinetic states of a person must be known when trying to recognise human activity so that the computer can do so effectively. The two activities are easily identified are walking and running because these activities occur in daily life. contrasted with, it is more challenging to distinguish between more complicated operationslike"peelinganapple."Itispossibletobreak down complex tasks into other smaller ones that are typicallysimplertoidentify.Usually,identifyingthingsin a scene can aid in a better understanding of human activitybecauseitcanrevealimportantdetailsaboutthe currentsituation.
Due to issues including backdrop clutter, partial occlusion, changes in scale, orientation, illumination, visual appeal, and image resolution, creating a completely automated human activity detection system that can accurately classify a person's actions is a difficult challenge. Furthermore, it takes time and requires knowledge of the particular event to identify behavioural roles. The challenge is complicated further by similarities within and between classes. Specifically, manypeoplemayexpressthesameclassofactionsusing varying bodily movements, and it may be challenging to distinguish between actions between distinct classes because they may be represented by identical data. The mannerinwhichhumansconductanactivitydependson theirhabits,whichmakesitchallengingtodeterminethe underlyingactivity.
A task that consists of three parts is necessary to solvetheseissues,specifically:i)whenusingbackground subtraction, the system tries to distinguish the image's background which remains static over time from any moving or shifting objects. ii) the process of tracking humanmovementsovertimethroughthesystemandiii) Thesystemcanlocateanactivityperformedbyhumanin the image using action of human and object detection. Examiningactionsinstillphotosorvideoclipsistheaim of identifying the activity performed by human. This activity recognition's objective is to properly categorise thevideotakenasinputintotheproperactivitycategory inlightofthisfact.
Over the past two decades, the categorization of humanactivitieshasremainedadifficultjobincomputer vision. Determine the two primary kinds of human activity recognition systems, namely unimodal and multimodal activity recognition methods, based on the types of sensor data used. Depending on the model of human activities, each of these two groups is then further broken down into sub categories. We thus suggest classifying human activity recognition techniques in a hierarchical manner. Unimodal approaches, which can also be characterised as space time, stochastic, rule based, and shape based methods, depict human actions from data of a single modality, such as photographs. Affective, behavioural, and social networking approaches are three categories of
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
multimodal methods that incorporate information gatheredfromseveralsources.
Another important method used for recognizing the activity is using sensors such as Wi Fi sensors, magnetometers, gyroscope and accelerometer sensors. Because accelerometer data is integrated on a mobile device, such as a smart phone or another gadget, and is easier to transport around, it is much simpler and more ubiquitous to monitor activity of humanof a more mobile individual. Mobile phones are still the most practical items we use every day, and as technology develops, they become more capable of meeting customer demands and expectations. Designers adapt the hardware of these devices by adding new devices andmodulestoincreasetheirfunctionality.Themajority ofsmartphoneshaveavarietyofinbuiltsensorsbecause sensors play a significant part in increasing their functionality and environmental awareness. This makes itpossibletogatheralotofdataaboutauser'severyday activities and life. These gadgets also have sensors including an accelerometer and a gyroscope. It is possible to record and upload someone's behaviour to a website where it can be analysed to identify activity usingtheaccelerometerdataonamobilephone.
In paper [1], real time actions were recorded using a depth camera. RGB D sensors are the name given to the Kinect depth camera. These sensors will use a Kinect studio to record the 3D skeleton data. The RGB, depth, and tracked skeleton data from the RGBD sensor make up the SBU dataset. There are 7 participants. There are 21 sets of activities. It involves coming close, going far, pushing, kicking, shaking hands, hugging, swapping, and punching. With the aid of the Keras and Tensorflow libraries, convolution neural networks are trained. Anaconda package for Python and spyder as an IDE. In seven tasks, the suggested model provides accuracy between 80 and 100.In paper [2] the dataset consists of 30 videos from various fields, including surveillance, entertainment, and healthcare. Frames from the videos are first retrieved, and then k means clustering is performed to the extracted frames. Based on their actions,suchashandmotion,walking,running,jumping, and sitting, clusters are formed. They have a 90% accuracy rate in this paper. In paper [3], In this study, a single static video camera was employed to document typical dailyhumanactivity.Thesystemistrainedusing a multilayer perceptron feeds forward neural network. The technology as it is currently configured can distinguish between five different activities: walking, sitting,boxing,wavingone'shands,andlyingdown.This paper's primary objective is to evaluate the design system'scorrectnessbylookingathowwellitcandetect humanactivities.Inthispaper[4]thethreefundamental
Factor value:
activities used in this study are standing, sitting, and lyingdown.Thesethreefundamentalattitudescanshow ifamanisengagedinanactivityornotwhenheentersa room. The Kinect camera can detect bodily motions. SVM, MLP, and Naive Bayes are the three machine learning methods for classification that they used. SVM andMLPaccomplish99.23%and98.8%respectively,but Nave Bayes only achieves 73.43 percent. This paper [5] describes a mobile camera based vision based human activity recognition system. In this study, the rate of recognition of the five human poses standing, walking, sitting, squatting, and lying was 94.8 percent. The activities were categorised using the Support Vector Machinetechnique.
Objective of this project is to predict the activity performed by human, by taking the video as input. The main goal is to predict the activities correctly. TensorFlow model is used to classify and make prediction of daily life human activities. The model is able to recognize the human activities such as reading, writing, jogging, using computer, washing hands, yoga, hand gesture recognition and playing musical instruments.
Kinetic dataset: A repository of large scale, high quality datasets with URL connections that can contain upto650,000videoclipsthat,dependingonthedataset version, cover 400, 600, or 700 different human movementactions.Handshakes,hugs,andotherperson person and person object interactions are shown in the videos, along with musicians playing instruments. Every actionclasshasatleast400,600or700videos.Allclipis aroundtensecondslongandhasbeenmanuallylabelled with one action class. Dataset of video for human action fromDeepMindKinetics.Thereareatleast400videosin the dataset for each of the 400 human action classes. Each 10 second clip comes from a youtube video and lasts about that long. The activities are human centered and span a wide range of classifications, including interactions between people and objects like playing instruments and those between people like shaking hands.Onthisdataset,wetrainandtestneural network architectures for the classification of human action, and we present some benchmark findings. as well as a description of the dataset's characteristics and methods ofcollection.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
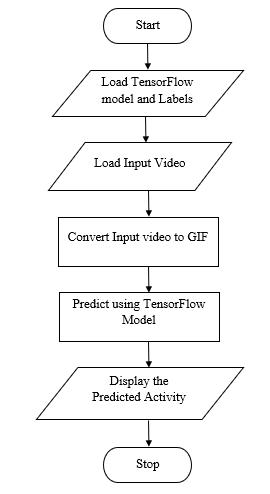
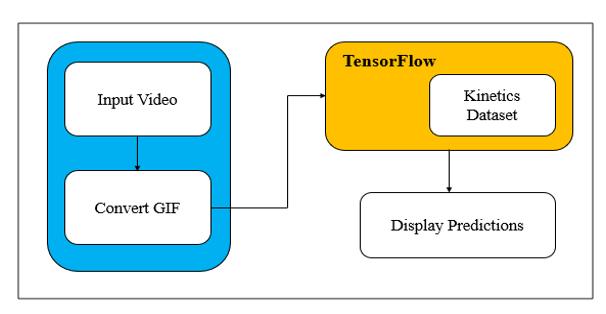
Fig 1 shows block diagram of human activity predictionsystem.thesystemcontainsvideoasaninput and video is a collection of images or frames then this video is converting to Graphics Interchange Format (GIF), GIF is soundless video. This GIF format extracts the features in video as image size of 224*224 with Frames Per Second (fps) as 25, it extracts 100 frames from original video. then this GIF Format is given to TensorFlow Model. TensorFlow is library for machine learning and deep learning methods it contains predefined model to perform task such as video classification problems, images, text and speech recognition problems. In this model contains the video classification model using a kinetic dataset model to comparetheGIFvideoformatanddisplaytheprediction on Graphical User Interface (GUI). For creating GUI, Tkinterlibraryisused.
Fig 2 shows the flowchart of human activity prediction. First step is to load or browse the video and also load the TensorFlow model. The loaded video is converting to GIF format, then that GIF format is compared to TensorFlow model and then predict and displaytheactivityonGUI.
Videoisacceptedasinputfor3DCNN.Athree dimensional kernel is convolved to the cube created by constructing many spatial and synchronous spots in a continuousstyletocreatethe3Dconvolution.Inorderto recorddataaboutmotion,theconvolutionlayer'sfeature mappings are connected to the numerous frames placed consecutively in the last layer. If the filter weights are replicated throughout the cuboid pattern. It should be notedthatthecuboid patternof3Dconvolutionlayerof filter can only select one type of feature. Convolution neural networks frequently employ a design pattern whereby the various feature maps as a result of the levelsbeingadded, whichallowsforthedevelopment of numerous different characteristics of the bottom layermaps'featuresthatarealreadyaccessible.Stacking toconfounda3Dfilterseveralconsecutiveframesjoined results in the 3D convolution, which results in the 3D cube. This technique links the feature maps to many consecutiveframes.
LeNet, AlexNet, ZFNet, GoogLeNet, Inception, VGGNet, ResNet, and MobileNets are some of the different CNN architectures.
In this project, the model is trained and tested using theInceptionV1architecture.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The categorization problem is handled by this architecture.Adeepneuralnetworktermedaninception network is made up of repeated units referred to as inception modules. Convolutional neural networks employ inception modulestoreduce thedimensionality, enabling deeper networks and more effective computing.asshowninfigure3.
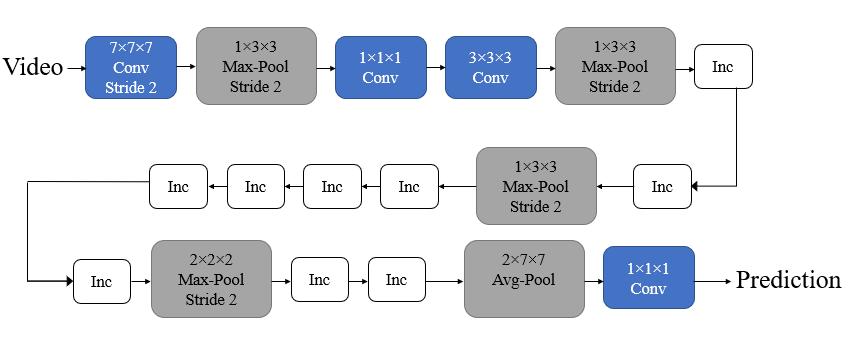
Fig 3 InceptionV1
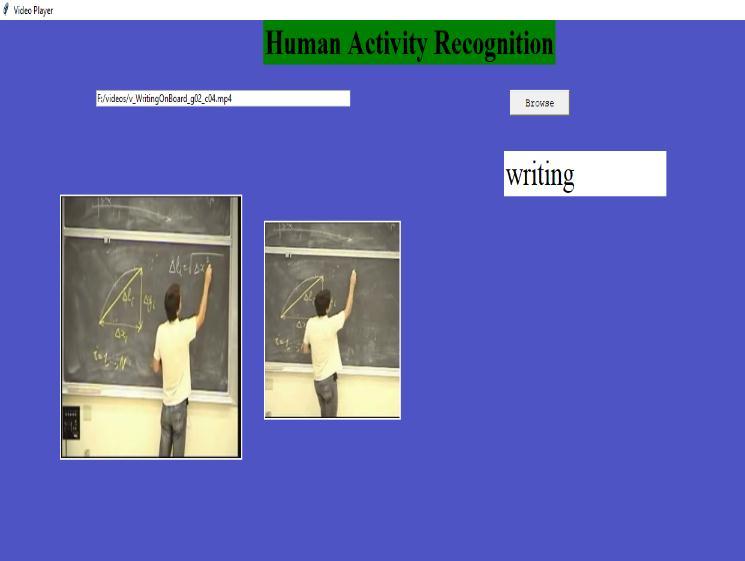
In the first step of human activity recognition, we havetobrowsevideothenitdisplaysinthefirstwindow of GUI then that video is converted into GUI that is displayed in the second window and then the predicted resultisshownasshowninthebelowfigures

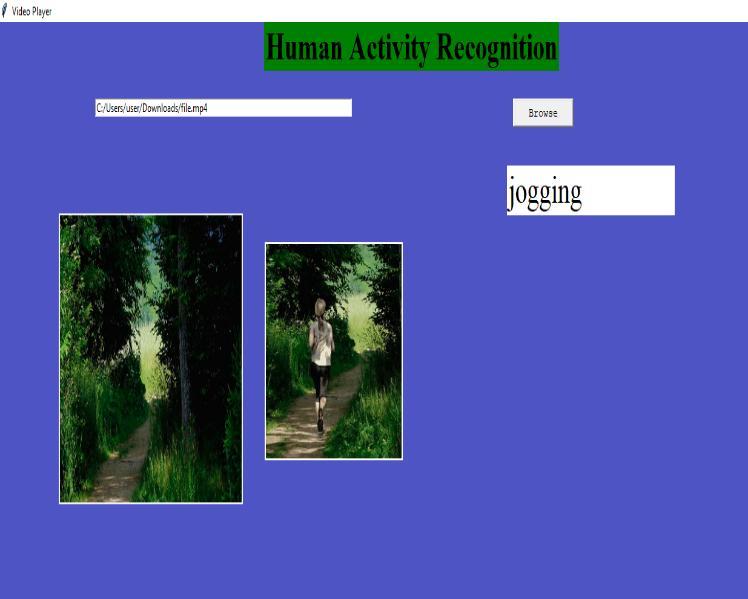

Fig 5 Activity2 Fig 6- Activity3 Fig 7 Activity4
Fig 4- Activity1
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
In this work, activity Recognition is done through video,takenasinputandapplyingTensorFlowmodel to predict the activities of human being in their daily life. The system's design allows it to function indoors with just a single static camera. Through a series of picture processing operations, the fundamental characteristics of human movement are retrieved. The outcome demonstrated an acceptable rate of precision in all training,testing,andvalidationphases.Itassomeofthe applications, advantages and disadvantages. HAR has become an integral part of analysing and interpreting human activities in different applications of computer vision, robotics, and many more. The results have provided the baseline output performance and the challenging dataset will be helpful for researchers to classifyactivitiesin computer vision having verysimilar intraclassproperties.
[1]A. Bagate and M. Shah, "Human Activity Recognition usingRGB DSensors,"2019InternationalConference onIntelligentComputingandControlSystems(ICCS), 2019,pp.902 905, doi:10.1109/ICCS45141.2019.9065460.
[2]R. Bhardwaj, S. Kumar and S. C. Gupta, "Human activity recognition in real world," 2017 2nd International Conference on Telecommunication and Networks (TEL NET), 2017, pp. 1 6, doi: 10.1109/TEL NET.2017.8343569.
[3]M.Babiker,O.O.Khalifa,K.K.Htike,A.HassanandM. Zaharadeen, "Automated daily human activity recognition for video surveillance using neural network,"2017IEEE4thInternationalConferenceon Smart Instrumentation, Measurement and Application (ICSIMA), 2017, pp. 1 5, doi: 10.1109/ICSIMA.2017.8312024.
[4]R.AlfuadiandK.Mutijarsa,"Classificationmethodfor prediction of human activity using stereo camera," 2016 International Seminar on Application for Technology of Information and Communication (ISemantic), 2016, pp.51 57, doi:10.1109/ISEMANTIC.2016.7873809.
[5]Kai Tai Song and Wei Jyun Chen, "Human activity recognition using a mobile camera," 2011 8th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI), 2011, pp. 3 8, doi: 10.1109/URAI.2011.6145923.
[6]N. Archana and K. Hareesh, "Real time Human Activity Recognition Using ResNet and 3D Convolutional Neural Networks," 2021 2nd
International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication, Embedded and Secure Systems (ACCESS), 2021, pp. 173 177, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS51619.2021.9563316.
[7]N. Junagade and S. Kulkarni, "Human Activity Identification using CNN," 2020 Fourth International Conference on I SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I SMAC), 2020, pp. 1058 1062, doi:10.1109/I SMAC49090.2020.9243477.
[8]C. Shiranthika, N. Premakumara, H. L. Chiu, H. Samani, C. Shyalika and C. Y. Yang, "Human Activity Recognition Using CNN & LSTM," 2020 5th International Conference on Information Technology Research (ICITR), 2020, pp. 1 6, doi: 10.1109/ICITR51448.2020.9310792.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
