International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Abstract - Mobile devices are the major platform for users to transfer and exchange diverse data for communication. Not just limited to communication, the rich set of diverse mobile applications have made mobile a widespread device all over the world. Market research reports from Forrester estimate the global mobile penetration to be around 50% in 2017 and is forecast to reach 66% by 2022. In India, Mobile penetration using smartphones has reached around 50% as of 2022 from 0.1% in 1998. The usability of mobile applications spreads across domains like banking, personal digital assistant, remote working, e commerce, internet access, entertainment and medical usage. Due to the increasing usage of mobile devices, numerous mobile security issues and data privacy threats are challenging both manufacturers and users. Mobile devices are an ideal target for various security issues and data privacy threats in a mobile ecosystem. Also the need for forensic extraction of data from a particular mobile device is an important aspect for the evidence. The forensic analysis helps extract, analyze the data stored on a mobile device along with its metadata, path locations, databases etc. that are not visible to the mobile user otherwise. In this paper, we have presented a detailed study on mobile hardware/software architecture, Android mobile Operating System, its vulnerabilities and security model and forensic analysis of Android mobile devices. Finally, a forensic tool is developed to extract the data from an Android mobile device, classify extracted data as safe or malicious and present it in well formatted reports.
Key Words: Android, forensics, data extraction, mobile, malicious,report
Mobilephoneshavewitnessedaremarkablegrowthinthe pastfewyearsowingtoconveniencefactorslike portability, ubiquity, highperformanceandlowpowerconsumptionof mobile processors and storage chips, high resolution touchscreen, high speed wireless networks and the convenientavailabilityofdiverseapps.Amongtheleading mobile OS platforms, Android is on the majority of smartphonesinmostcountriesintheworldwithashareof 82.8%withsignificantincreaseduringthepasttwodecades. Rich contentmobileapplicationsfurtherpenetratedailylife beyond the basic communication use, which makes usage patternsshiftfromdesktoptomobiledevicesatavigorous pace making mobile devices and applications become an indispensablepartofourdailylife.
Thus,theawarenessoftheimportanceofprivacyprotection, data usage and details about the resident data on mobile
devices has driven the demand for Mobile security and Forensics. Although each smartphone OS developer has supportedspecificsecuritymeasures,maliciouscodeshave madetheirwaytothemobiledevices.Theresidentdatahas beenthemaintargetfortheseattacksanditisimportantto knowandunderstandthedomainofdataprotectionalong with data extraction and validation for investigation purposes.
Thesciencebehindrecoveringdigitalevidencefrommobile phones is called mobile forensics[1]. Digital evidence is definedasinformationanddatathatisstoredon,received, or transmitted by an electronic device that is used for investigations.
This paper briefs about topics like mobile architecture, Android operating system, its vulnerabilities, attacks, securitymodelandforensics.Lastly,aforensictoolhasbeen implemented to extract the data from an Android mobile devicewiththehelpofadumpfile.Thetoolfurtherproceeds toclassifyextracteddataassafeormaliciousandpresentit inwell formattedreports.
2.1
Mobile Hardware Architecture:
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
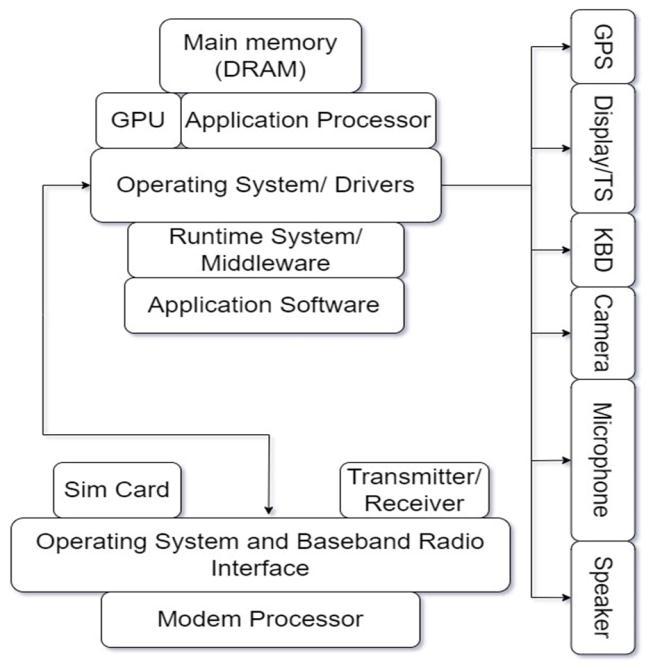
Themainusecaseofasmartphoneistoexecuteapplication software. The software gets executed with the help of an application processor often taking help from a graphics processor for rendering scenes and whenever the applicationprocessorofthegraphicsprocessorneedsdatait will access the main memory which is dynamic random accessmemory.Betweentheapplicationsoftwareandthe application processor sit two elements one is the drivers thatarenecessaryforhandlingvarioustypesofI/Ocallsand aruntimesystemorthemiddlelayerwhichtheapplication software takes help off to execute various types of application programs[2]. The I/O devices present are for example the Global Positioning System, Display and the Touchscreen,Keyboard,Camera,Microphone,Speakerand soon.Thecommunicationishandledbyamodemprocessor which receives all the signals and passes them on to the operating system and the baseband radio interface. The radio interface communicates with the transmitter and receiverandalsotheSIMcard.Thetwodifferentoperating systems residing on the application processor and the modernprocessorusuallycommunicatewitheachotherfor handlingdatacommunicationbetweenthesetwomodules.
Android architecture contains a number of componentstosupportanyandroiddeviceneeds.Android software contains an open source Linux Kernel having a collectionofC/C++librarieswhichareexposedthroughan application framework. Among all the components Linux Kernel provides main functionality of operating system functionstosmartphonesandDalvikVirtualMachine(DVM) providesaplatformforrunninganandroidapplication.
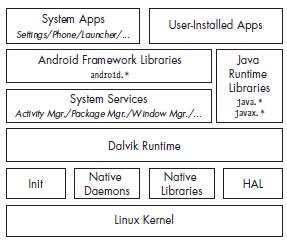
Themaincomponentsofandroidarchitectureare following:
1. Applications
2. ApplicationFramework
3. AndroidRuntime
Therearesixprimarylogicalpartitionsunderthe Androidfilesystem[3].
/boot partition consists of the Android kernel and the ramdisk.
/systempartitionaccommodatestheentireAndroidOS.This includes the Android GUI as well as the system apps that comepre installedonAndroiddevices.
/recovery partition is designed for backup and can be considered the alternative boot option or partition in an Androiddevice.
/data partition consists of all of the user’s data, including contacts,settings,appsandmessages.
/cachepartitionstoresthefrequentlyaccessedappdataand components.Clearingcachealsofreesupsomespaceinyour deviceandcanalsofixcertainissuesattimes.
/misc partition contains all the miscellaneous system settings like on/off switches, carrier or region ID, USB configuration,andcertainhardwaresettings.
The attacks at the kernel layer mainly target root privilege,sandboxing,memory,bootloader,devicedrivers etc. On the other hand, middleware layer attacks target Android architectural components like Hardware Abstraction Layer, libraries and native components. The applicationlayerattacksoccurduringruntimeofmalicious applications.
Malwareisthemalicioussoftwareaimedatprivate specific information which disturbs users, may cause breakdownofthedeviceandleadtoresultssuchascausing information and documents belonging to the user to be stolen or become unusable[4]. The different types of malwaresincludevirus,worm,spyware,trojanhorse,logic bomb,ransomeware,backdoor,rootkitetc.Amalwarecan steal mobile data, record calls, capture images, monitor locationorevenexfiltratedeviceinformation.
Wi Ficonnectionisoneofthesecuritythreatswhich can exploit the vulnerabilities in the Android operating system.Theattackercaneavesdropandaccessthecontent
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

ofAndroidwithouttheuserpermission.Interceptingtraffic letsattackersreadinformationthatwaspreviouslyassumed tobesafelyencrypted.
The vulnerability due to bluetooth connection allowsremoteattackerstoruntheirownmaliciouscodeon vulnerabledevicesviaBluetoothLMPpackets.Theattackers canalsousetruncated,oversized,orout of orderBluetooth LMP packets to crash devices altogether. Bluejacking and bluebuggingaretwoofthecommonexamplesofbluetooth basedattacks.
Android security model consists of the following components[5]:
Application sandbox is a security mechanism through which individual android applications run in their own “space”andcannotinteractwithotherinstalledappsorthe Android OS without proper permissions. The applications areisolated,orsandboxed,bothattheprocesslevelandat thefilelevel.Thesandboxingisdoneatthekernellevelto ensure that each application runs in an isolated environment.
Permissionsareaccessrightsthatcancontrolaccessto hardware devices, internet connectivity, data, or OS services.Thesecuritysensitiveinterfacesareprotected by AndroidpermissionsuchasPHONE_CALLS,INTERNET,and SEND_SMS. It means that the application must have the permissiontoperformtheabovetasks.Permissionssupport protection levels namely Normal, Dangerous, Signed, SystemandSigned.
Thesesecurityfeaturesareimplementedbycomparing thesigningcertificateofthe currentlyinstalledtargetapp with the certificate of the update or related application. System applications are signed by a number of platform keys.Differentsystemcomponentscanshareresourcesand runinsidethesameprocesswhentheyaresignedwiththe sameplatformkey.
Thecomponentsaredeclaredasprivateaswellaspublic. Within the same application, private components are accessible for each other. The public components are accessiblebyotherapplicationswhicharenotinthesame sandboxing, having full accessible permission, but also restrictedthroughwithcustomizedpermission.
Thecompositestructure,thetargetphysicaluser’s userIDandtheappIDaseffectiveUIDguaranteesmultiple application instances installed by multiple users get their own sandbox. Additionally, Android also guarantees dedicatedsharedstoragetoeachphysicaluser.
Security Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is a MAC implementation for the Linux kernel. Mandatory access control(MAC)ensuresthataccesstoresourcesconformsto asystem widesetofauthorizationrulescalledapolicythat canonlybechangedbyanadministratorwhileuserscannot overrideorbypassit.
Android supports verified boot using the verity targetofLinux’sDevice Mapper.Verityprovidestransparent integrity checking of block devices using a cryptographic hashtree.
Mobileforensicsisabranchofdigitalforensicsthat isevolvingintoday'sdigitaleraandisconstantlychanging as new phones are released and operating systems are updated[10]. Android forensics deals with extracting, recovering,andanalyzingdatapresentonanAndroiddevice throughvarioustechniques.Duetotheopennatureofthe Android operating system, these forensic techniques and methods can apply to more than just mobile phones: refrigerators, vehicle entertainment units, televisions, watches,andmanymoredevicesrunAndroid.It'simportant to have a clear understanding of the platform and other fundamentalsbeforewediveinandfindouthowtoextract data.
Followingarethenecessary stepsthatneedto be followedwhileperformingandroidforensicanalysis[6]:
1. Investigationpreparation 2. Seizureandisolation 3. Theacquisitionphase 4. Examinationandanalysis 5. Reporting
Fewandroidplatformtoolsusedintheprocessofforensic analysisareasfollows:
The Android software development kit is the development resource needed to develop Android applications. It includes software libraries and APIs, referencematerials,anemulator,andothertools.
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
AndroidVirtualDeviceisavirtualmobiledevice,or emulator, which runs on your computer. The emulator is especially helpful for developers for creating custom applications.Theemulatortakesconsiderableresources.
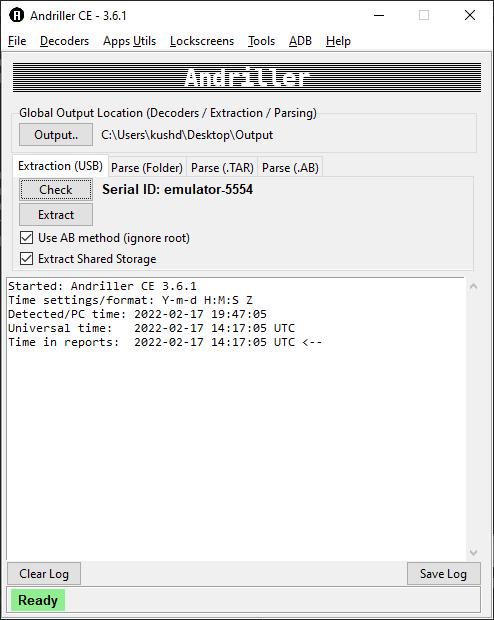
AndroidDebugBridge(adb)isaversatilecommand linetoolthatletsyoucommunicatewithadevice.[7]Theadb command facilitates a variety of device actions, such as installing and debugging apps, and it provides access to a Unixshellthatyoucanusetorunavarietyofcommandson a device. It is a client server program that includes three components:client,daemonandaserver.
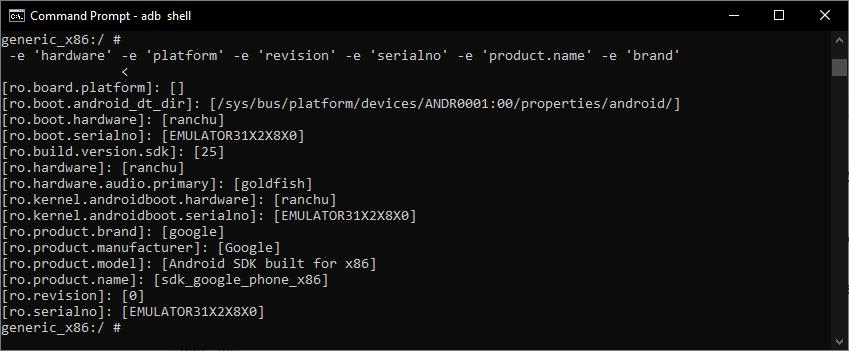
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The smartphone market is growing higher and higher.Withthedrasticchangesintechnologyandloadsof extremelyvaluabledata,dataresidentonmobiledevicesare becoming hotspots of target . The usability offered by a variety of mobile applications is adding to sensitive data. The analysis of mobile phones and data extraction could revealSMS,contacts,installedapplications,GPSdata,emails, deleteddata,etc.that canoffersignificantinsights.Android, beingtheleadingmobileoperatingsystem,thedesignofan AndroidForensicanalysistoolisthefocusofthispaperwith abrieflookontopicsdiscussedinLiteraturereview.
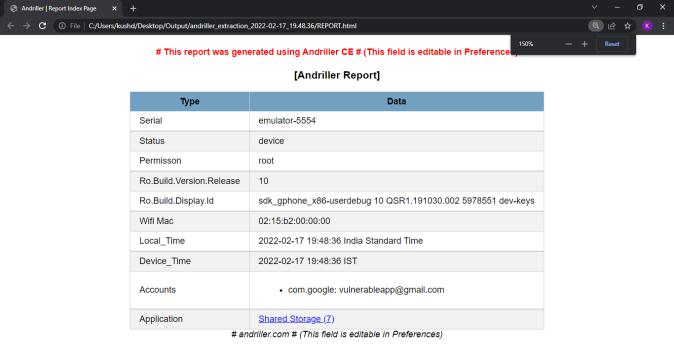
TheAndroidForensicanalysistoolshouldprovide the resident data along with the details of data like databases,tables,timestamps,relatedattributesetc.Further thetoolmustclassifydataassafeormalicious.Theresults shouldbepresentedin theformofwell formattedreports. Thetoolshouldbeeasytouseandinteractivewithausable andconvenientinterface.
mobile data and classified accordingly by the tool. The results are finally displayed in interactive, well formatted reports with a usable interface that can be viewed on any webbrowser.
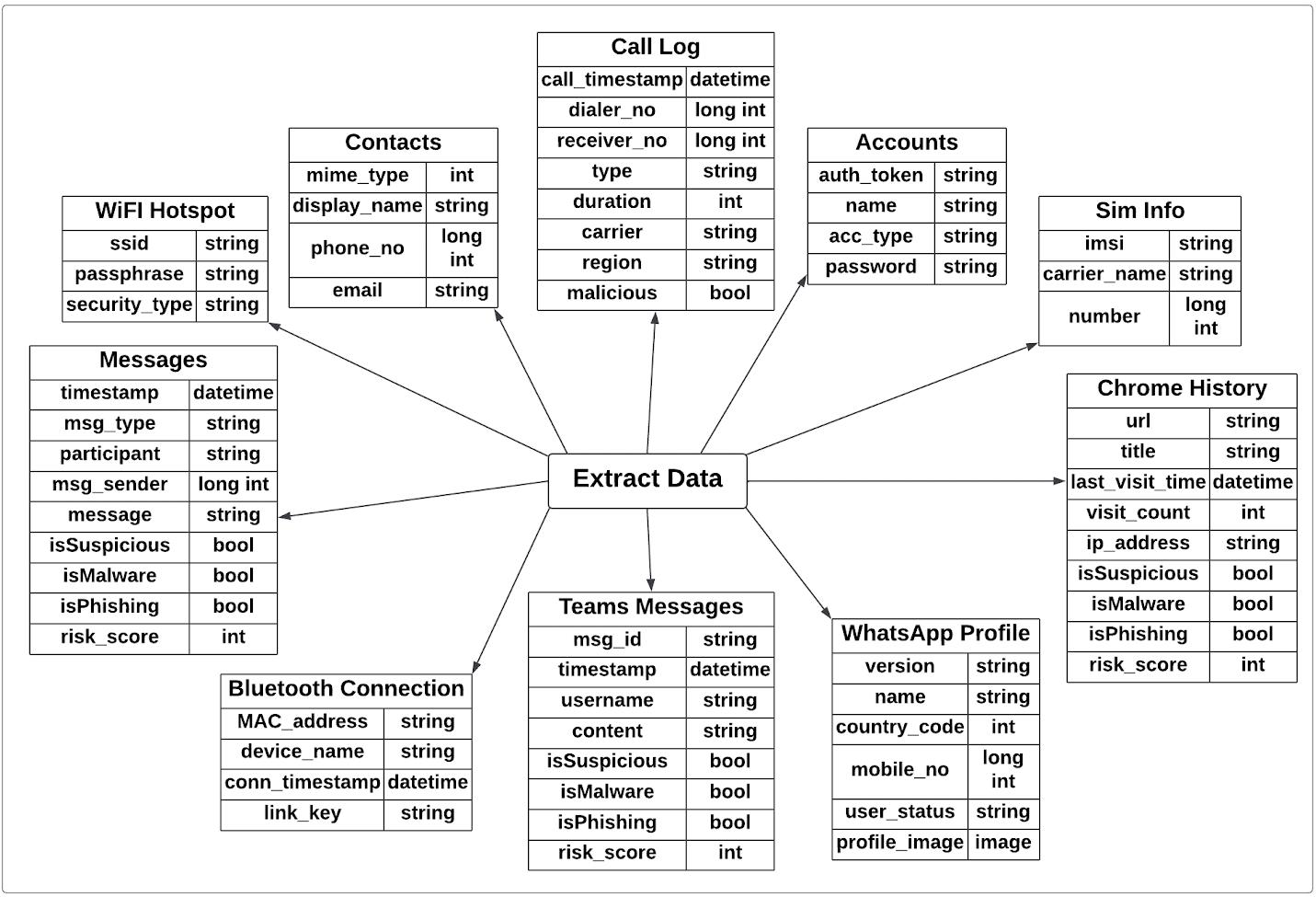
Purpose : Toextractdataaboutuseraccountdetails
Input : accountsDatabase
Output : Listofname,type,passwordforuseraccounts
Algorithm :
Step1:Searchfortheaccountstablefromdatabase fileinthedump
Step2:Ifaccountstableisnotempty: Processaccounts
Queryname,type,passwordfrom accountstable
Add data to the respective columnsofreport Else: Noaccountsdatafound Step3:Generatereport
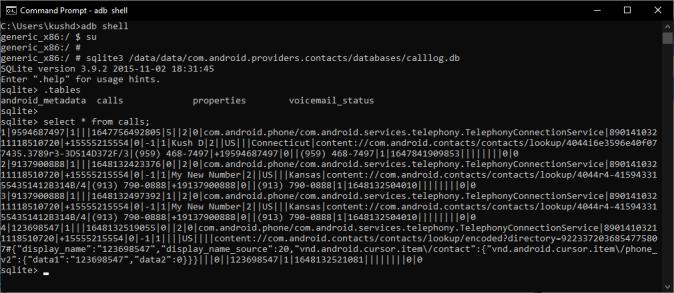
Purpose : Toextractcalldata
Input : call_logsDatabase
Output : CallerID,ReceiverID,StartandEndtimestamp,call type
Algorithm :
Step 1 : Search for calls table in the call_logs database
Step2:Initializeemptylistsforincoming,outgoing, missedcalls.
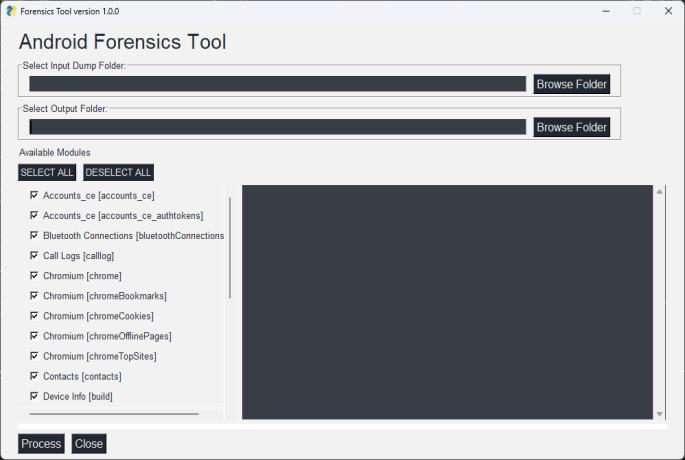
TheproposedAndroidforensictoolshouldperform nondestructiveacquisitionfromrootedAndroiddevices. It isaGUIbasedtoolbasedonpythonlanguageandlibraries.It isproposedtoproduceresultsinthewebpages.Thedump filethatcontainstheentirefilesystemoftheandroiddevice hastobecreatedpriortothedataextractionandanalysis. TheGUIofthetoolexpectsaninputpathtothedumpfolder andanoutputpathforthestorageofgenerateddatareports. Further,theuserhastoselecttheartifactsfor whichdata should be processed allowing the user to customize the reportasperneed.Sincethedataisalreadyextractedinthe dumpfolder,theexecutionofthetoolisfastandthereport should be generated without much delay. The risky or potentiallyattackdataissegregatedfromthenormallegit
Step3:Ifcall_recordsnotempty: Iterateovercallrecords. case “Incoming”: Append the call detailstoincominglist case “Outgoing”: Append the call detailstooutgoinglist case “Missed”: Append the call detailstomissedcallslist
Step 4 : Add data to the respective columns of report
Step5:Generatereport
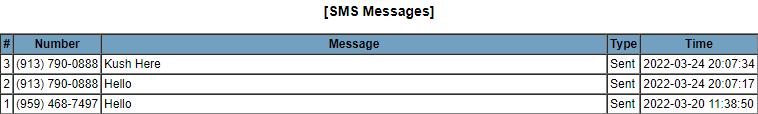
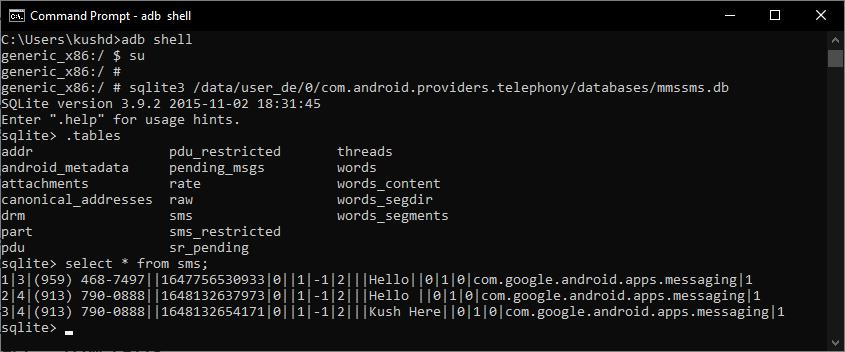
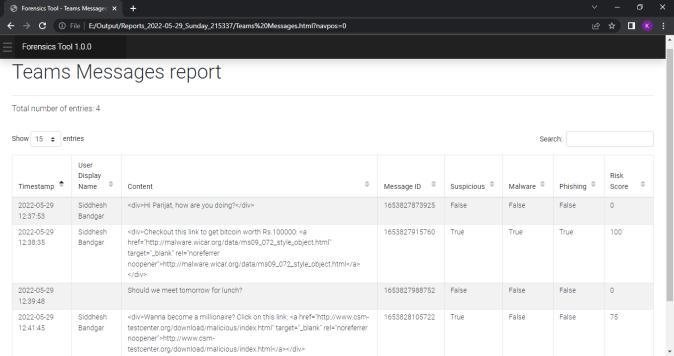
Purpose : Toextractmessagedatafromthedumpfile
Input : MMS SMS.dbDatabase
Output : Messagetimestamp,sender,receiver,content,type
Algorithm :
Step1:LookintoMMS SMSdatabase
Step 2 : Perform SQL operations(Perform Join operationtoextractdatafrommultiplerelated tablesandfilterthem)andqueriesontablesinthe abovedatabase
Step3:Generatereport
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
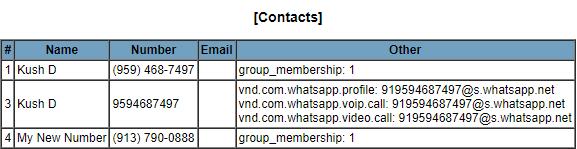
Purpose : To extract data about WhatsApp application installedonthedevice
Input : wa.db,msgstore.db
Output : WhatsAppcontactsdata WhatsAppmessagedata
Algorithm :
Step1:SearchfortheWhatsAppdatabasefromthe dump
Step2:Ifdatabaseiswa.db: Query data from a table named wa_contacts.
Ifdatanotempty: Append data to WhatsAppcontactslist
Step3:Ifdatabaseismsgstore.db: Querydatafromatablenamed messages.
Ifdatanotempty: Appenddatato WhatsApp message data list
Step4:Adddatatotherespectivecolumnsofthe report.Generatereport.
Purpose : To perform forensics to get the data on Teams Application
Input : skype_teams.db
Output : Teams_messages, Teams_user, Teams_call logs, Teams_activity feed,Teams_file info
Algorithm :
Step1:Gettherequireddatabaseskype_teams.db
Step2:Ifskype_teams.dbnotempty: RetrieveTeams_messages, RetrieveTeams_user, RetrieveTeams_call logs, RetrieveTeams_activity feed, RetrieveTeams_file info
Step3:Generatereport
Purpose : ToextractchromehistoryfromAndroiddevice
Input : ChromeMediaHistoryfolder
Output : ID, URL, title, last_updated_time, watchtime, visit_count
Algorithm :
Step1:Checkbrowserdetails,OSanditstype.
Step 2 : Open files from the input folder namely origin,playback,playback_Session.
Step3:Retrievedataandmapvalueswithdefined attributekeys.
Step4:Generatereport.
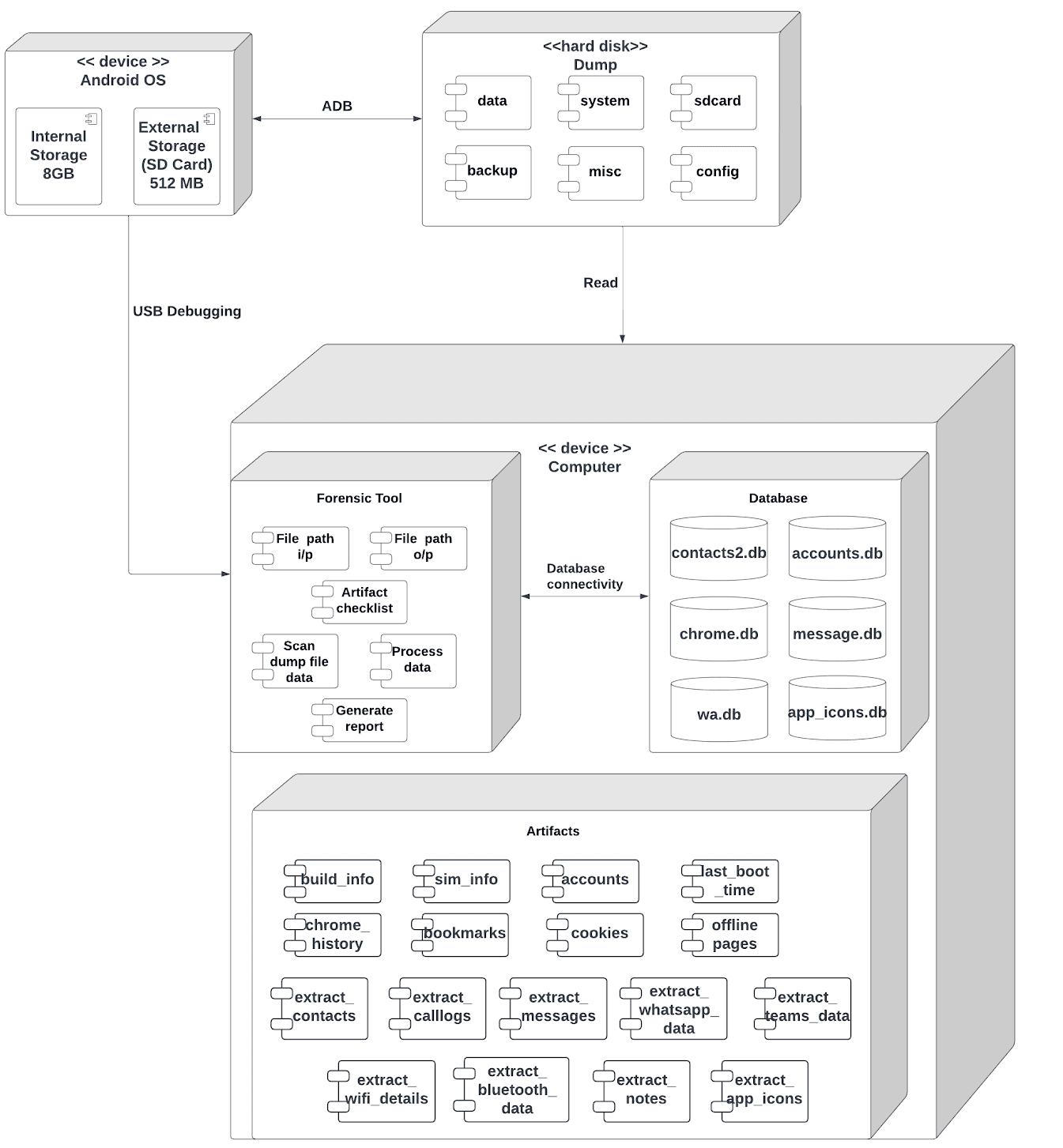
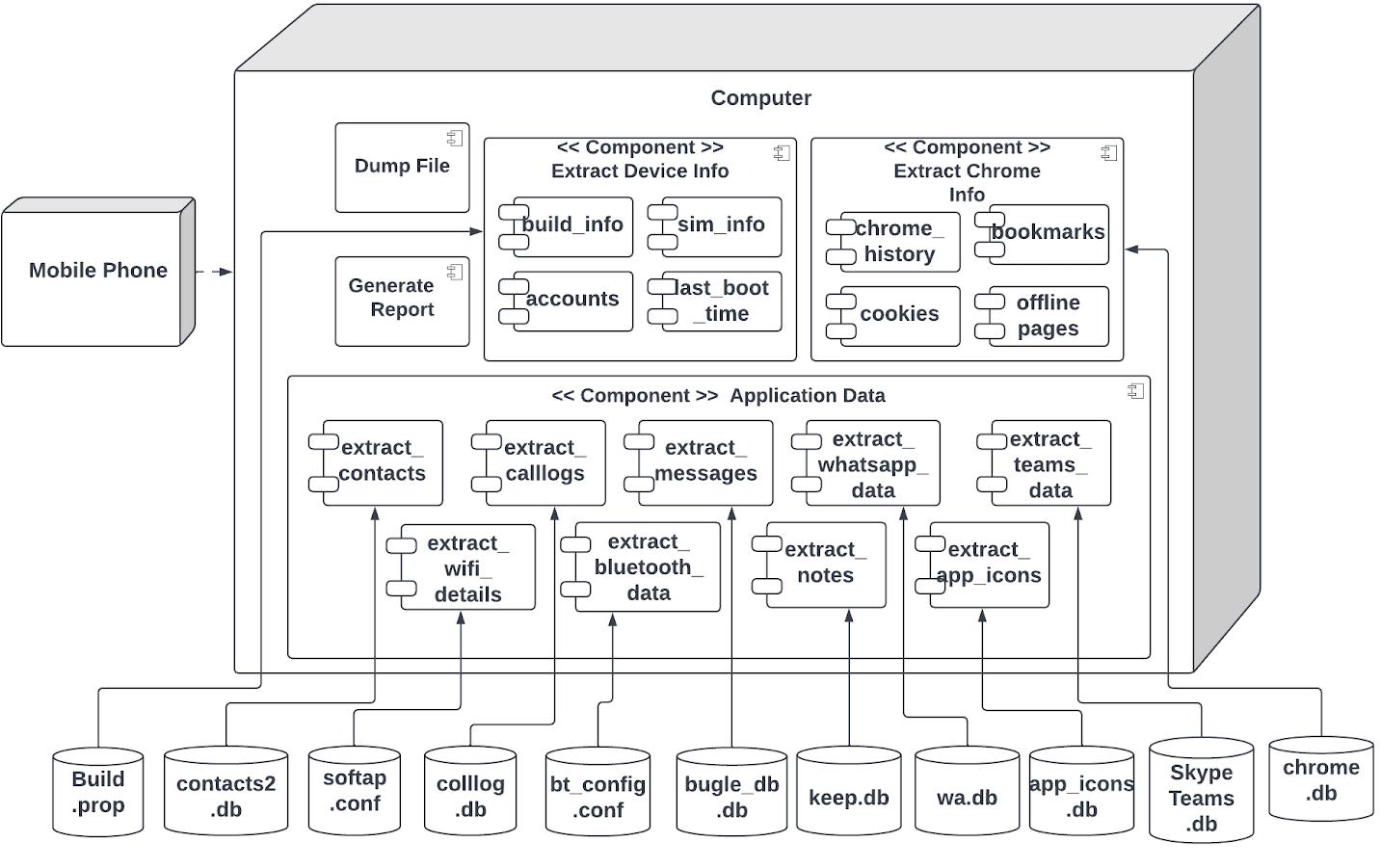
Component
Deployment Diagram
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
OS Android7.1andhigher
InternalStorage 32GB SDCard 512MB
1.
AndroidSDK AndroidStudio2020.3.1 IDE VSCode1.67.2
Language Python3.9.0
PythonLibraries PySimpleGUI4.16.0,MDB4.13
Database SQLite3.32.2
AndroidSDKPlatform tools ADB1.0.39,Emulator,DeviceFile Explorer
WeperformedtheforensicanalysisontheAndroid EmulatorofGooglePixel4.TheEmulatorandForensictool isruninacomputerhavingWindowsOS.
1. ComputerSpecifications
RAM 8GB(Min)
Processor Inteli58thgen,2.3GHz
OS Windows10,11
HardDisk 128GBSSD
USBPort USB3.0
2. MobileSpecifications
RAM 4GB(Min)
Processor Quadcoreprocessor,2.0GHz
CPU/ABI x86
Resolution 1080*2280:440dpi
CLI WindowsCommandPrompt Browser GoogleChrome,Firefox,Edge
2. MobileSoftwareSpecifications
AndroidAPILevel 25orhigher
Pre installedApplications Contacts, SMS, Calls, GooglePlay
Applications Installed Using GooglePlay Whatsapp,MSTeams
Create Android Emulator
Step1:IntheAndroidStudioMenubarnavigatetoTools > AVDManager
Step2:IntheVirtualDeviceManager,clickonCreateVirtual DeviceButton
Step3:IntheVirtualDeviceConfigurationWindow,Select theCategoryasPhoneandSelectthePixel4Phoneor any otherphonehavinggoogleplaysupportandclickNext.
Step4:SelectthesystemimageandclickNext.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Step5:GivenametotheAVD,Verifytheconfigurationsand clickonFinishbutton.
Step 6: We can see a new Emulator created in the AVD Manager. Run this Emulator by pressing Play Button in Actions
Install Required Packages For Forensic Tool
Step 1:NavigatetoprojectfolderintheCommandPrompt
Step 2: Install the requirements using the following command pip3 install -r requirements.txt 4.3 Android Forensics Tool Execution
Connect Android device to the computer
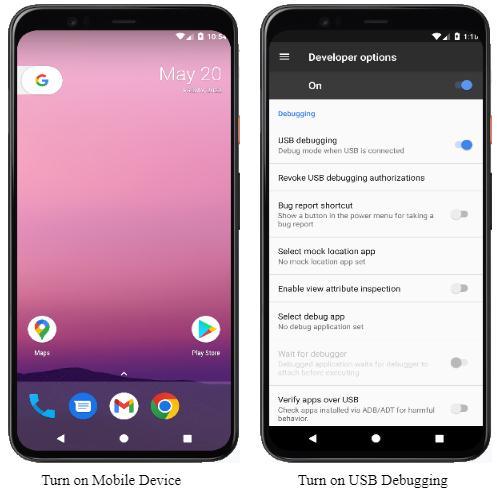
Step1:TurnontheAndroiddeviceor emulator.Connectthe mobiledevicetothecomputerusingUSBandturnonUSB debugginginthesettings.
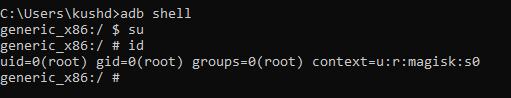
Step3:GetthesuperuseraccesstotheAndroiddevicefrom thecomputer,runtheadbshellandentercommandsuand thenenterid.
Create the dump file
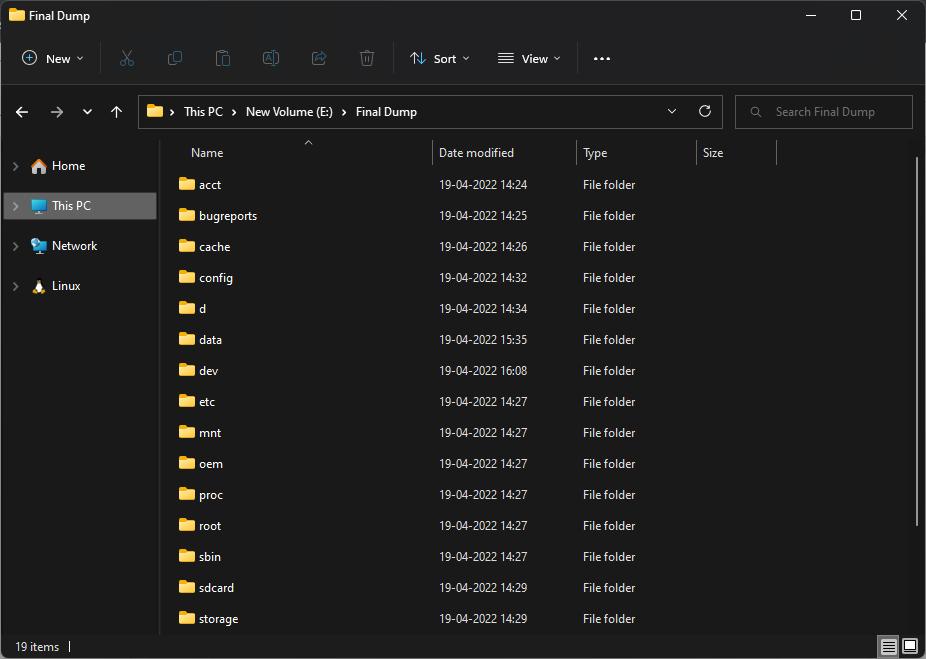
Step1:IntheAndroidStudioMenuBarnavigatetoView > ToolWindows >DeviceFileExplorer
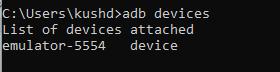
Step 2: Check the connected Android devices to the computer by running the following adb command in the commandprompt adb devices
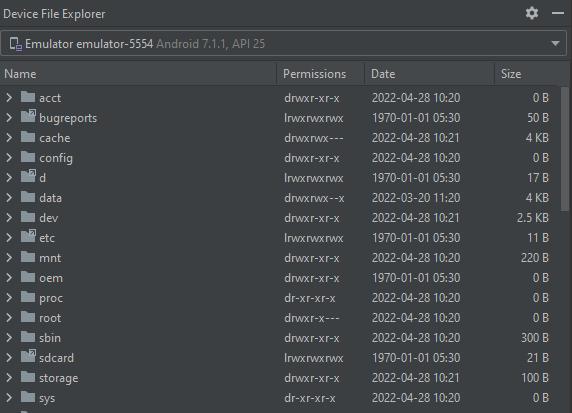
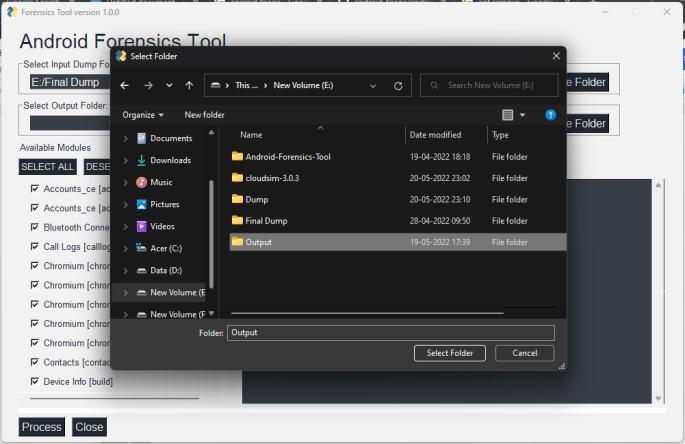
Step2:Selectthefoldersrequiredfordumpandsavethem byprovidingdumpfolderpath.Contentsofthedumpfolder areshowninnextscreenshot
Use Android Forensics Tool
Step 1: Open Command Prompt navigate to the forensic projectfolderandruntheforensictoolusingthefollowing command
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
python .\forensicsTool.py
GUIwindowofAndroidForensicsToolopens
Forensic Tool GUI has four main components:
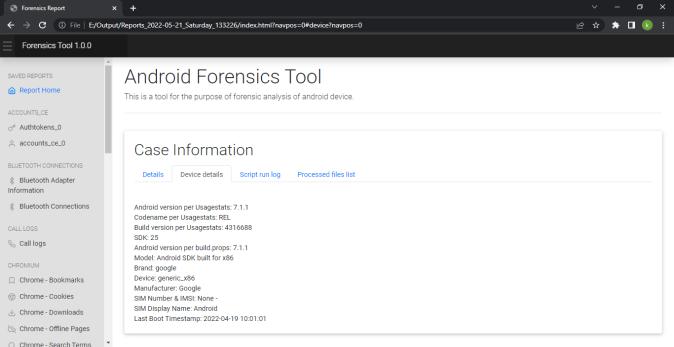
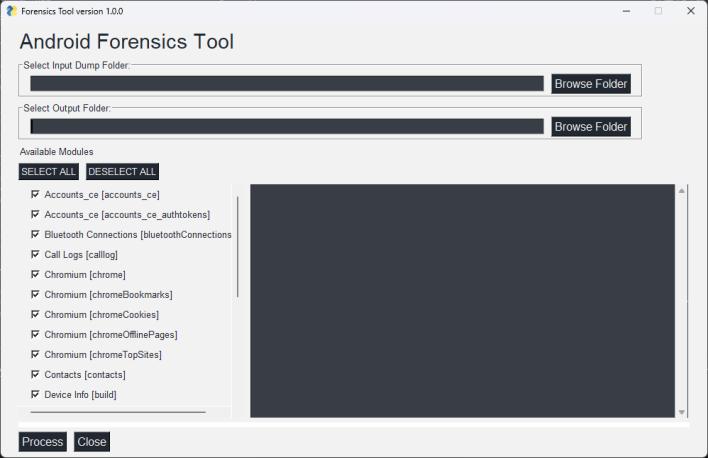
i)Inputpath:Tochooseinputdumpfolderpath
ii)Outputpath:Tochoosefoldertostoretheoutput/report oftheforensicanalysis
iii)ArtifactsList:Toselectamongtheartifactsavailablefor theforensics
iv)Executionlogdisplay:Toseethelogoftheprocessingof theforensicstool.
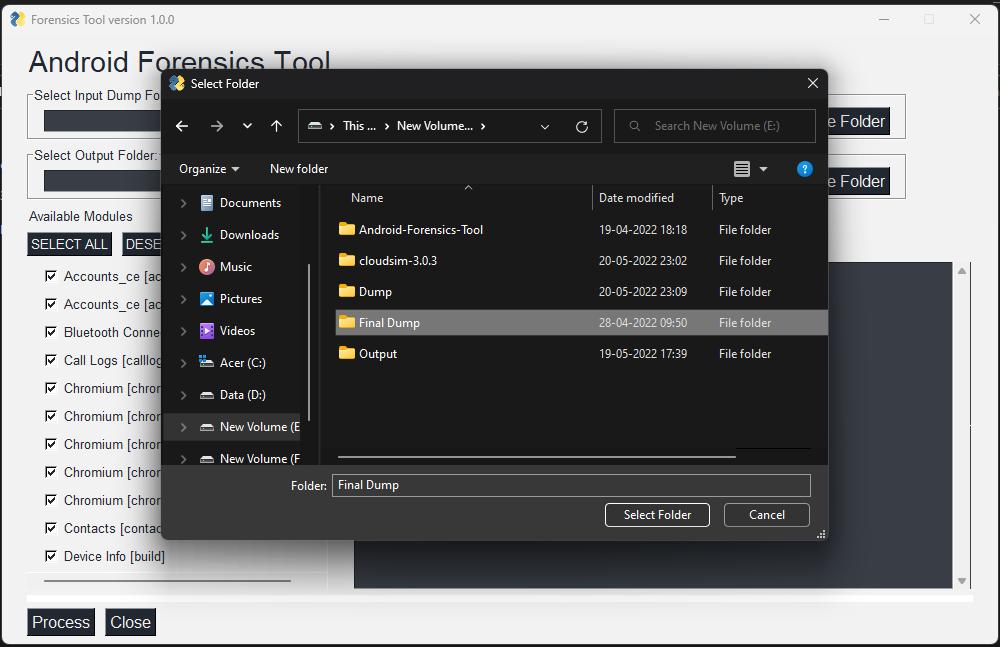
Step 2: Click on the Browse Folder button in Input Dump FolderandchoosetheDumpFolder.
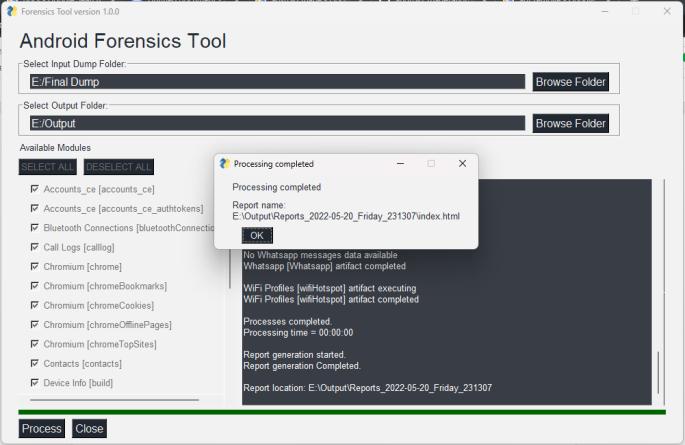
Step4:Afterforensicanalysisprocessingiscompletedwe get the pop up window indicating processing complete messageandreportfilenameandpath.ClicktheOKbutton wecanseethereportinthebrowser.
Step 3: Select output folder to save the forensic analysis output:
We can view the report generated in any web browser window. Following screenshot shows the index pageofthereport.Reportisdividedindifferenttabsbased onartifactsandwecannavigatetoeachartifactreport by clickingontheartifactname.

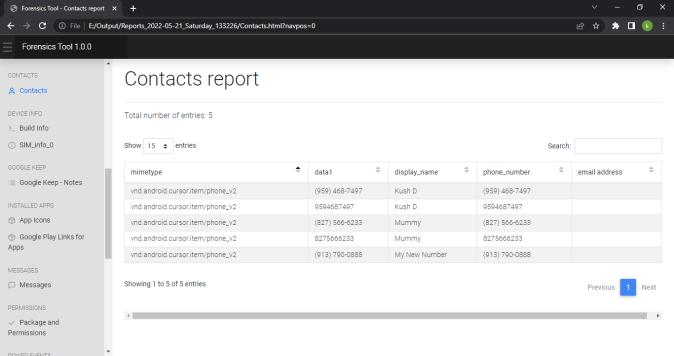
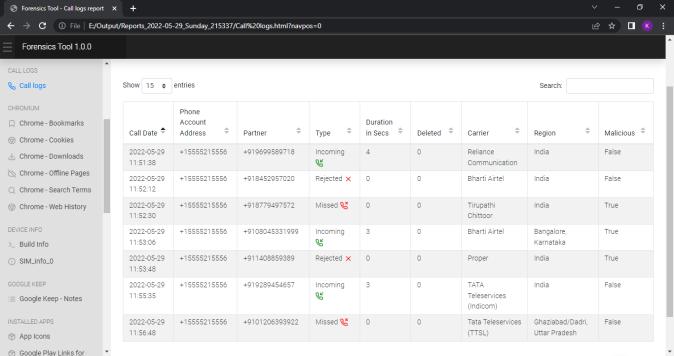
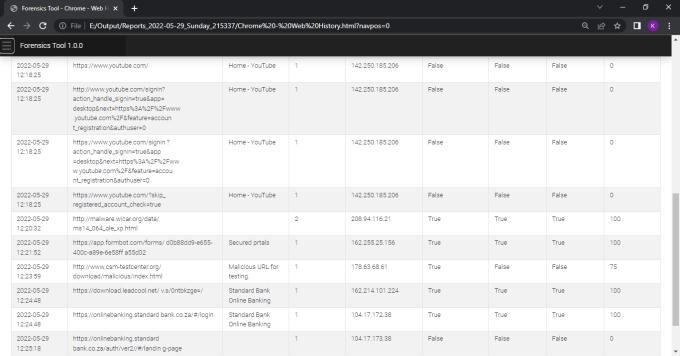
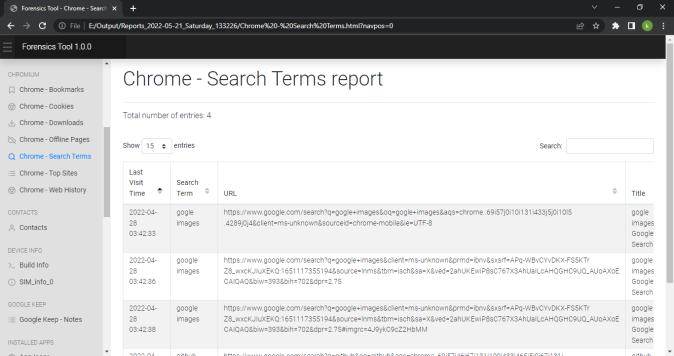
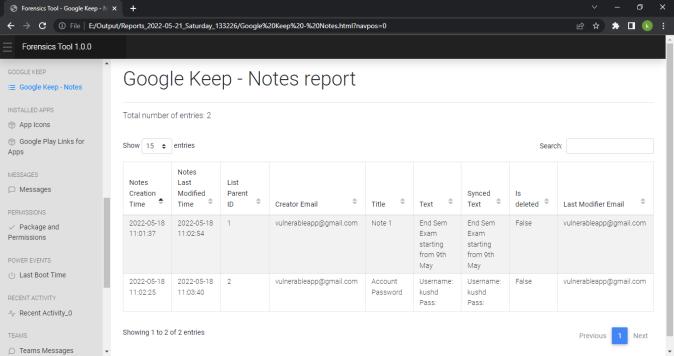
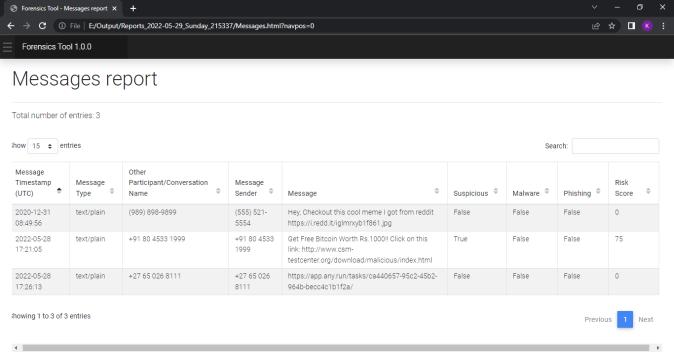
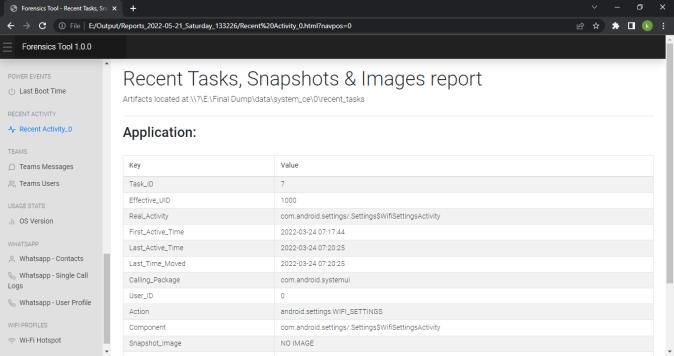
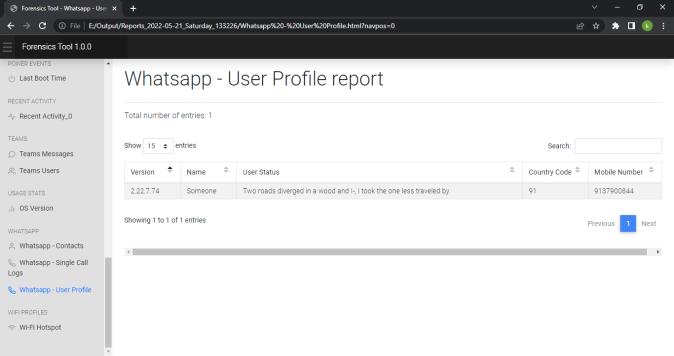
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The paper initially addresses the complete architecture of the mobile phones, with Android OS architecturebeingthelimelight.Thevulnerabilities,threats owingtohardwareandsoftwarearchitectureswerelooked upon. The Android security model was briefly discussed followed by mobile security w.r.t threats and attacks. The fewprominentmobileattackslikeimproperplatformusage, information gathering attack etc were also presented. Finally, a detailed discussion about the android forensics wasprovided.
Thefieldofmobileforensicsisboundtoattaingreat value as the ever precious data on smartphones are becomingatargetforcyberattacks.Thestudyincludesuse ofopensourceforensicsandanalysistools,frameworkssuch asAndroidDebugBridge,AndrillerTool,MobSF Tool, etc. Theirresultsaredocumentedasaguideforfurtherstudying andresearchpurposes.
Finally,anAndroidforensictoolforthepurposeof non destructive data acquisition software tool for rooted android devices was implemented and results were displayed. The tool was implemented with a user friendly GUI, that takes input an android dump file and an artifact checklistaspertheuserpreference.The extracteddata is furthercheckedforanymaliciousorpotentialattackdata. Thetoolgeneratestheresultasinteractive,wellformatted HTML based reports with classification of data as safe or risky, malicious. The reports can be viewed on any web browser.
1. Sathe, Sneha C., and Nilima M. Dongre. "Data acquisition techniques in mobile forensics." 2018 2nd international conference on inventive systems and control (icisc).IEEE,2018.
2. Boueiz, Marie Rose. "Importance of rooting in an Android data acquisition." 2020 8th international
symposium on digital forensics and security (ISDFS).IEEE, 2020.
3. Almehmadi, Tahani, and Omar Batarfi. "Impact of androidphonerootingonuserdataintegrityinmobile forensics." 2019 2nd International Conference on Computer Applications & Information Security (ICCAIS). IEEE,2019.
4. Pan , Y., Ge, X., Fang, C., & Fan, Y. (2020) “A systematic literature review of android malware detectionusingstaticanalysis.” IEEE Access, 8,116363 116379.
5. Dar,MuneerAhmad."Anovelapproachtoenhance thesecurity
6. ofandroidbasedsmartphones." 2017 International Conference on Innovations in Information, Embedded and Communication Systems (ICIIECS). IEEE,2017.
7. Riadi, Imam. "Forensic Analysis of Android based InstantMessagingApplication." 2018 12th International Conference on Telecommunication Systems, Services, and Applications (TSSA).IEEE,2018.
8. Htun,NaingLinn,MieMieSuThwin,andChoCho San."EvidencedatacollectionwithANDROSICStoolfor androidforensics." 2018 10th International Conference on Information Technology and Electrical Engineering (ICITEE). IEEE,2018.
9. Hoog, Andrew. Android forensics: investigation, analysis and mobile security for Google Android. Elsevier, 2011.
10. Elenkov,Nikolay. Android security internals: An in depth guide to Android's security architecture. NoStarch Press,2014.
11. Dwivedi,Himanshu. Mobile application security. Tata McGraw Hill Education,2010.
Kush Dabade, B.Tech Student, Dept. Of Computer Engineering and IT, VJTI College, Mumbai, Maharashtra

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Parijat Dhalkar, B.Tech Student, Dept. Of Computer Engineering and IT, VJTI College, Mumbai, Maharashtra


Siddhesh Bandgar, B.Tech Student, Dept. Of Computer Engineering and IT, VJTI College, Mumba,Maharashtra

Anshul Shende, B.Tech Student, Dept. Of Computer Engineering and IT, VJTI College, Mumbai, Maharashtra
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
