International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Pramod Patil G S1 , Mr. Ravishankar Holla1*
1,2Department of ECE, R V College of Engineering, Bangalore ***
Abstract The 21st century is an era of digital revolution. There have been advancements in the technology over the two decades in various domains like the Information Technology (IT) sector, Education, Finances, Commerce and so on. There is a shift from mechanical and electronic analogue technology to digital technology. Commercesectorisnow widelypopularas E Commerce. In the first step, thorough study Golang, Microservices and docker will done to understand the concept of Design process. After the study the necessary software tools, programming languages and libraries studied along with construction methodology, algorithm will be designed. Designed Algorithm implemented in the Golang, and this algorithm is converted into Gorilla/ Mux API. API converted into independent microservices and the microservices converted into docker image. Docker imageisadoptedtotestingsoftwarebyQAteamandcheck fortestcasesandthenthisisadoptedtoSellerPortal.
In This, System achieves following inferences, Successful testing with Single SKU, Successful testing with Multiple SKU, passed all the Unit test cases in Unit testing, In SonarQube testing 12.6 percentage of duplication over 2.4k lines found, 5. 2 duplicate blocks found, 6. 10 code smells found, 7. 0 bugs, vulnerabilities and security hotspotsfound.
Key Words: Digitalrevolution,E commerce,Binpacking
E commerce packaging often refers to packaging that is used to ship the products directly to our customers. With the e commerce industry growing due to covid 19, shippingboxesarenowbecominganimportantpartofthe unboxing experience for most consumers. The main thing to consider when choosing e commerce packaging is how well it will protect the product. The organization’s seller portal displays packaging, labeling, and shipping information. So, our goal is to automate packaging selections in this portal against orders based on volumetric weights of products in order to reduce shipping costs. [1] High quality packaging is viewed asan additional investment by the majority of ecommerce businesses. What they don’t realize is that proper packagingreducesthecompany’scostssignificantly.Good packaging protects the product during shipping, reducing thelikelihoodofcustomersreturningit.[4]
The process of analysing, modifying, and processing raw data and datasets to gain insights from them is known as data analysis. Python and R are the most often used data analysis languages. However, Go is becoming increasingly popular for this reason.[3] Gota is a Go programming language dataframe and data wrangling package. Gota is similar to the Python Pandas library and is designed to interact with Gonum, a scientific computing package in Golang, akin to Pandas and Numpy. The Gota module simplifies data wrangling (transformation and manipulation) operations in Go.[5] It supports Go’s built in data types as well as a variety of file formats such as JSON,CSV,andHTML.
We utilize to filter values. Apply a filter to the dataframe object. This accepts dataframe.F, to which we provide a struct literal. The struct literal accepts a column name Colname, a comparator Comparator, and a value Comparando, which is the value for which the dataframe shouldbefiltered.
•series.Eq→Equalto.
•series.Neq→NotEqualto.
•series.Greater→Greaterthan.
•series.GreaterEq→GreaterthanorEqualto.
•series.Less→Lessthan.
•series.LessEq→LessthanorEqualto.
•series.In(http://series.In)→IscontainedIn.
The Select method assists us in selecting columns from a dataframe. [df.Select] (http://df.Select) accepts a slice of two integers that represent the number of columns that can be selected. We can choose rows by utilizing the dataframe object’s Subset function. dataFrame. Subset acceptsasliceoftwointegersrepresentingthenumberof rows that can be chosen. Gota has a variety of dataframe manipulationfeatures.[4]
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
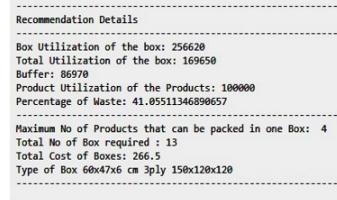
Displaypackedfunctiondisplayspackeditemsinthe bin.
We will analyze technique to characterizing possible packing and building optimal solutions in this research. The challenge of providing a relevant issue formulation adds to the difficulty of finding optimal solutions for the Three Dimensional Bin Packing Problem. In order to formulatetheproblem,wewillassumethateachitemIin the finite set S has three dimensions wi, hi, and di. Each identicalbinbhasW,H,andDdimensions.Theitemsand bins are rectangular boxes with three dimensions that matchtothevaluesforwidth,height,anddepth.[7]
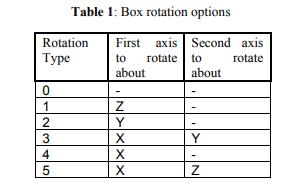
The pieces are permitted to rotate orthogonally to distinguish the answer from earlier efforts. To rotate an item,simplyswapitswidth(wi),height(hi),anddepth(di) valuesaroundinanorderedfashion.Eachitem boxhassix rectangular facets, but only three are different because "opposite"facetsareidentical.[3]
Each of the three facets can be rotated orthogonally to createanewboxform.Asaresult,eachitemcanhaveupto sixalternativerotationconfigurations.
For single dimensional problems, linear programming algorithms have been used. Evolutionary algorithms have been utilizedinsome ways insteadofheuristic algorithms [1,3]. Evolutionary algorithms could have been a good strategy for discovering a solution (in this case, the solutionspaceoftheBinpackingissue)duetotheirability tosearchenormousspaces,butevolutionarymethodshave a few shortcomings: There is little continuity between solution and problem, which means that if you modify the problem parameters little, the solution changes significantly.[6] Heuristics are more detailed, and some provideworst caseresults.
Bin packing being an NP Hard issue implies that an exhaustive search for the optimal solution is computationally intractable in general, and that there is thus no known real computationally feasible optimal solution approach for the problem. As a result, different methods of obtaining a solution must be discovered. Heuristic solution methods are the most prevalent. Items are packed one at a time, with no backtracking (once packed,anitemisnotrepacked).Formalreasoningderived from one of the following packing algorithms can be used toselectanitemtobepacked.[8]
Unassigned item is placed in the first bin that has enough space.Ifnosuchbinexists,allocatetheitemtoanewbin.
Almost identical to First Fit, except that the items are sortedindecreasingorderfirstbeforebeingpacked.
Packs unassigned item into last available bin. Searching is identical to First Fit, however the bins are ordered in reverse. If no such bin exists, move the item to a new bin.[7]
TheBestFitalgorithmplacesaniteminthebinthathasthe most space among those that fit the item. To be more specific. Items are packed one at a time in the order specified. Determine set B of containers into which the itemfitsbeforedeterminingthebin.IfBisempty,createa newbinandplacetheiteminit.Otherwise,placetheitem intheBbinwiththeleastavailablecapacity.[7]
To conduct the core of the bin packing, the developed systememploysaheuristictechnique.
The use of these heuristic approximate algorithms in the systemtosolvethebinpackingproblem:
i. guaranteesasolution,
ii. obtains a solution in a reasonable time (i.e. solutioniscomputationallyfeasibletoobtain),
iii. allowsforgeneraldatainput,and
iv. providescontinuity between the solution and the problem.
ItgoeswithoutsayingthatfailingtosatisfyIand(ii)would beunsatisfactory.Ifthesystemdoesnotmeet(iii),itloses its generality and flexibility. Condition (iii) is especially important since bins (or containers) must be packed with things(orcargo)ofvaryingsizes.
Failure to fulfill (iv) would also make it impossible for userstoretrievedataandtestalternativesolutionsduring the problem solving process. As a result, failing to satisfy (iv)indicatesthatthesystemdoesnotreadilysupportthis functionality.[6]
The system employed two basic heuristic bin packing algorithms: the First Fit Decreasing and the Best Fit. They werechosenaboveotherheuristicalgorithmsbecausethey run faster and produce solutions that are considerably closertoidealthanmostotherheuristicalgorithms.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
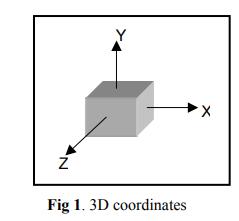
We have three packing directions: width direction, height direction, and depth way. As previously stated, each Item has six different rotation kinds. Consider the following item: Rotating about the x, y, and/or z axes yields the six rotation types. The bins are packed one at a time, and the algorithmspacktheobjectusingasequenceofpivotpoints.
We use Bin packing algorithm which means The bin packing issue is an optimization problem in which things of varying sizes must be packed into a finite number of bins or containers, eachwitha defined capacity,insucha waythatthenumberofbinsneededisminimized.
As a result, it looks that Best Fit is more likely to yield a solution that is closer to the ideal solution than First Fit Decreasing, but because these values on the upper bound for the number of bins required are quite close, it is worthwhiletousebothalgorithms.[6]
Next step….,
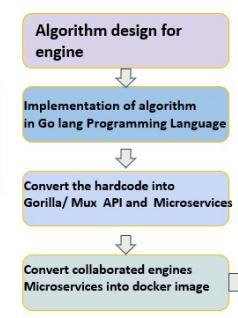
Inthefirststep,thoroughstudyGolang,Microservicesand docker will done to understand the concept of Design process. After the study the necessary software tools, programming languages and libraries studied along with construction methodology, algorithm will be designed. Designed Algorithm implemented in the Golang, and this algorithm is converted into Gorilla/ Mux API. API converted into independent microservices and the microservicesconvertedintodockerimage.Dockerimage is adopted to testing software by QA team and check for testcasesandthenthisisadoptedtoSellerportal.
The problem has numerous applications, including containerfilling,truckloadingwithweightcapacitylimits, media file backups, and technology mapping in FPGA semiconductorchipdesign.
Choose a packing direction. Each bin has three packing directions: a width (or x) direction, a height (or y)
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2032

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
direction,andadepth(orz)direction.Packeachcontainer oneatatime.[7]
First, we select a pivot point. The pivot is a (x, y, z) coordinate that represents a place in a specific 3D bin where anattempt will be made topack an item.The pivot will belocatedattheitem'sback bottomleftcorner.Ifthe objectcannotbepackedatthepivotpoint,itisrotateduntil it can or until all six potential rotation types have been tried. If the item still cannot be packed at the pivot point after rotating it, we move on to packing another item and add the unpacked item to a list of objects that will be packedwhentheotheritemsarepacked.[8]
Topackanitem,onemustfirstchooseapackingdirection. The bin'slongestsidecorresponds tothe packingstrategy Then,rotateeachitemsothatThelongestsideofthisitem is the packing side. [8] If we are packing by width, for example,wewanttheTheitem'sbreadthisdeterminedby its longest side, so for instance, if the packing direction is breadthandtheIftheitem'scurrentheightismorethanits width,thenturntheitem
If,followingtherotation(s),theitemcannotfitintothebin (i.e.oneormoreoftheitems'dimensionsexceedthebin's corresponding dimension), we rotate the item till the secondlongestsideofthisitemcorrespondstothepacking direction.Iftheitemstill doesnotfitintothebinafterthe rotation(s), we rotate it till the third longest side of the item corresponds to the packing orientation. Then, depending on the packing direction, sort the objects in decreasingorderofwidth,height,ordepth.[8]
The Bin Packing Problem and the Cutting Stock Problem aretwoNP hardcombinatorialoptimizationproblemsthat are connected. Exact solution methods can only be employed for extremely tiny cases, hence heuristic methods must be used for real world situations. Researchers have recently begun to apply evolutionary techniquestothesechallenges,suchasGeneticAlgorithms and Evolutionary Programming. We employed an ant colony optimization (ACO) strategy to tackle both the Bin Packing and Cutting Stock Problems in this paper. [7] We describebotha pureACOtechniqueandanACOapproach enhanced with a basic but highly successful local search algorithm.
It is also demonstrated that the hybrid ACO strategy requires different parameter values than the pure ACO approach and provides more robust performance across diverseissueswithasinglesetofparametervalues.When the local search algorithm is conducted with random restarts, it performs noticeably lower than when paired withACO.
Thenet/httppackageinGoprovidesawiderangeofHTTP protocol functionality. Complex request routing, such as segmenting a request url into separate parameters, is something it struggles with. Fortunately, there is a highly popular package for this, which is well known in the Go community for its high code quality. The gorilla/mux package is used in this example to define routes with named arguments, GET/POST handlers, and domain limitations. gorilla/mux is a package that modifies the default HTTP router in Go. It includes a slew of features designedtoboostproductivitywhendevelopingwebapps. It also conforms to Go’s default request handler signature function (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request), allowingthepackagetobemixedandmatchedwithother HTTPlibrariessuchasmiddlewareorexistingapps.
Unit testing is a software testing technique used in computer programming to check the suitability of individual pieces of source code, sets of one or more computerprogrammemodules,andtheassociatedcontrol data,usageprocesses,andoperatingprocedures.[5]
Each unit or individual component of the software application is tested as part of the unit testing process. It represents the initial stage of functional testing. The purpose of unit testing is to confirm the functionality of individual unit components. A unit is a single testable component that may be tested as part of the application software development process. Unit testing is used to ensurethatisolatedcodeiscorrect.Anspecificapplication function or piece of code is referred to as a unit component. Unit testing is typically conducted using the whiteboxtestingmethodologybydevelopers.[5]
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[Garey and Johnson, 79], on the other hand, cite simple heuristics that can be proven to be no worse (but also no better)thanarelativelytinymultiplicationfactorabovethe ideal number of bins. The concept is simple: starting with one empty bin, take the goods one by one, searching the binssofarusedforaspacelargeenoughtocontainthem.
1. Frederick Ducatelle, John Levine. Ant Colony Optimisation for Bin Packing and Cutting Stock Problems, Proceedings of the UK Workshop on ComputationalIntelligence,2001,Edinburgh.
2. Emanuel Falkenauer, A hybrid grouping genetic algorithm for bin packing, Journal of Heuristics, 1996
Bin packing is a tremendously intriguing mathematical modelissue,yetresearchonitissurprisinglynew.
In this work, we looked at how to implement the optimization of packing 3 D boxes into a finite number of bins and shown that the program will find a solution in a fair amount of time. Most alternative implementations sufferfromthemajordisadvantageoffailingtoconvergeto asolutionandhencerunning"indefinitely."Ourmeticulous designalsoincludesthevisualisationofthesolution,which meansthattheexactplacementandorientationofanitem inabinisknown.[9]
TheGGAisa geneticalgorithm thathasbeensubstantially modified to fit the structure of grouping issues. These are the problems in which the goal is to discover a good partition of a set or to group the members of the set together. The bin packing problem (BPP) is a well known NP hardgroupingprobleminwhichitemsofvaryingsizes must be put into fixed capacity bins. On the other hand, based on their dominance criterion, Martello and Toth's reduction method is one of the best OR strategies for BPP optimizationtodate.[8]
The Bin Packing Problem (BPP) is defined as follows ([Garey and Johnson, 79]): given a finite set O of numbers (itemsizes)andtwoconstantsC(thebin'scapacity)andN (the number of bins), is it possible to 'pack'all the items into N bins, i.e. does there exist a partition of O into N or lesssubsets,suchthatthesumofelementsinany ThisNP completechoiceproblemeasilyleadstotheassociatedNP hard 2 optimization problem, which is the focus of this paper: what is the best packing, i.e. what is the smallest number of subsets in the previously specified partition? Because BPP is NP hard, there is no known optimal algorithmthatrunsinpolynomialtime.[9]
3. Fekete,S.P.,J.Schepers,Anewexactalgorithmfor general orthogonal 3d dimensional knapsack problems, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1997
4. Leon Kos, Joze Duhovnik, Rod Cutting Optimization with Store Utilization, International designconference DESIGN,Dubrovnik,2000.
5. Silvano Martello, David Pisinger and Daniel Vigo, The three dimensional bin packing problem, Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS), Linthicum, Maryland,USA,2000
6. Peter Ross, Sonia Schulenburg, Hyper heuristics: learning to combine simple heuristics in bin packing problem, Discrete Applied mathematics ACM,2000.
7. Erick Dube, Leon R. Kanavathy, OPTIMIZING THREE DIMENSIONAL BIN PACKING THROUGH SIMULATION,
8. B.SampaioARRubinJ,“Improvingmicroservice based applications with runtime placement adaptation,” J Internet Serv Appl, vol. 10, no. 3, 2019,issn:1999 5403.doi:10.3391/fi1002456.
9. C. G. Rosa N Cavalcanti D, “Adaptive middleware in go a software architecturebased approach,” Appl. Sci. 2022, vol. 10, no. 2, 2018, issn: 1999 5903.doi:10.3390/fi10020014.
10. A. Kokkinaki, R. Dekker, M. de Koster, C. Pappis, and W. Verbeke, “E business models for reverse logistics: Contributions and challenges,” in Proceedings.