International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)
e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022
p-ISSN: 2395-0072
www.irjet.net
Application of Digital Image Correlation: A Review Sharvari S. Patil1, Dr. P. S. Patil2 1PG
Student, Department of Civil Engineering Department of Civil Engineering, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Maharashtra, India ---------------------------------------------------------------------***--------------------------------------------------------------------2Professor,
Abstract - Digital Image Correlation (DIC) is widely used
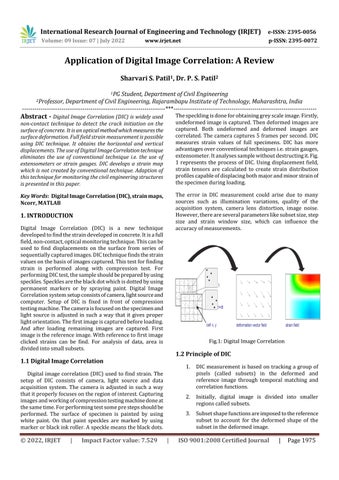
The speckling is done for obtaining grey scale image. Firstly, undeformed image is captured. Then deformed images are captured. Both undeformed and deformed images are correlated. The camera captures 5 frames per second. DIC measures strain values of full specimens. DIC has more advantages over conventional techniques i.e. strain gauges, extensometer. It analyses sample without destructing it. Fig. 1 represents the process of DIC. Using displacement field, strain tensors are calculated to create strain distribution profiles capable of displacing both major and minor strain of the specimen during loading.
non-contact technique to detect the crack initiation on the surface of concrete. It is an optical method which measures the surface deformation. Full field strain measurement is possible using DIC technique. It obtains the horizontal and vertical displacements. The use of Digital Image Correlation technique eliminates the use of conventional technique i.e. the use of extensometers or strain gauges. DIC develops a strain map which is not created by conventional technique. Adaption of this technique for monitoring the civil engineering structures is presented in this paper.
The error in DIC measurement could arise due to many sources such as illumination variations, quality of the acquisition system, camera lens distortion, image noise. However, there are several parameters like subset size, step size and strain window size, which can influence the accuracy of measurements.
Key Words: Digital Image Correlation (DIC), strain maps, Ncorr, MATLAB
1. INTRODUCTION Digital Image Correlation (DIC) is a new technique developed to find the strain developed in concrete. It is a full field, non-contact, optical monitoring technique. This can be used to find displacements on the surface from series of sequentially captured images. DIC technique finds the strain values on the basis of images captured. This test for finding strain is performed along with compression test. For performing DIC test, the sample should be prepared by using speckles. Speckles are the black dot which is dotted by using permanent markers or by spraying paint. Digital Image Correlation system setup consists of camera, light source and computer. Setup of DIC is fixed in front of compression testing machine. The camera is focused on the specimen and light source is adjusted in such a way that it gives proper light orientation. The first image is captured before loading. And after loading remaining images are captured. First image is the reference image. With reference to first image clicked strains can be find. For analysis of data, area is divided into small subsets.
Fig.1: Digital Image Correlation
1.2 Principle of DIC
1.1 Digital Image Correlation Digital image correlation (DIC) used to find strain. The setup of DIC consists of camera, light source and data acquisition system. The camera is adjusted in such a way that it properly focuses on the region of interest. Capturing images and working of compression testing machine done at the same time. For performing test some pre steps should be performed. The surface of specimen is painted by using white paint. On that paint speckles are marked by using marker or black ink roller. A speckle means the black dots.
© 2022, IRJET
|
Impact Factor value: 7.529
|
1.
DIC measurement is based on tracking a group of pixels (called subsets) in the deformed and reference image through temporal matching and correlation functions.
2.
Initially, digital image is divided into smaller regions called subsets.
3.
Subset shape functions are imposed to the reference subset to account for the deformed shape of the subset in the deformed image.
ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
|
Page 1975