International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Akshat Ruhela1 , Aayush Srivastava2 , Akash Deepak Tyagi3,Shailendra Pratap Singh4
1,2,3 Student, ABES Engineering College, Uttar Pradesh, India 4ABES Engineering College, Uttar Pradesh, India ***
Abstract Weightdecreaseisoneofprimeproblemsforavehicle.Itwaschosentodecreaseweightofdiscbrakebymaterial AL 7075. CAD modelling software is used for designing of disc brake, brake pedal, Steering Hub etc for fulfilment of our conditions. Conditions are required to activate braking system and all wheels locking at same time. The research paper additionallyincludestheparameterfordisc,staticanalysis,andsteadystatethermalanalysisdependentondifferentparameter. Structural analysis is done because of mechanical strength of material and Thermal analysis is done on the basis of heat propertiesofmaterial.ThisresearchpaperstudiesanoptimizeddesignofthebrakingandsteeringcomponentofaGo Kart whichaimsatreducingweightandmaintainingthestrengthalongwithreducingthedeformationathighertemperaturesas comparedtotheOEMavailableinthemarket.
Abrakeisa mechanicaldevicethatutilizes retainingmovementbyactiveenergyfroma movingbodyandafterward changesoveritintoheatvitality.Thehydraulicsbrakeisakindofstoppingmechanismthatutilizesarotorisassociated withthehubofthewheelandsetof erosion material called as brake shoe is constrained generally by hydraulic poweredweightagainstthetwosidesoftherotorwhichmakesitstopwiththeassistanceofrubbing.Themostimportant parameterforanyvehicleisthebrakingsystem.Comparedtodrumbrakes,discbrakesbetter stoppingefficiency.Allthe elementsofthebrakingsystemplayanimportantroleinanyvehicle,itsfunctionsincludeslowingdownofthevehicle, maintainingthespeedduringdownwardoperation,andalsoholdingthevehicleafterithascometocompletestopthisis donebythedissipationofmechanicalenergyofthebodyintotheheatenergybythefrictionalforces.Inthehydraulic brakingsystem,thediscisbeingmountedonthewheelhubwhichmovesalongwiththewheel.Atthetimepressingbrake pedal,thepushrodconnectedtothehydraulicbrakecylinderpressurizethehydraulicfluidwiththehelpofapistontoa highextentbytakingtheadvantageofthepedalratiowhichisdefinedastheratiooftheleverageofyourclutchappliesto the hydraulic brake cylinder further thebrakefluidpassesthroughthebrakehoseswhichareconnectedtothebrake caliper.
Themechanismisofvitalapartofthedynamicstyleofanyautomobiletofacilitateaswishamendmentofdirectionsand builduseofthetiresabilitytogetlateralforcestotheverybestextent.Anathleticsdriver’ssensoryinputsprovidevisual, tactile,andmechanicalphenomenondatautilizedindevelopinga“feel”forautomotivehandlingandperformance.This feedbackiscriticalinsanctimoniesthedrivingforcetoextractmostperformancefromtheautomobile.thencethesteering isacrucialfeedbackmechanismgivingthedrivingforcedataonstabilityanddirectionalmanagement.Themanagementof associatedegreeautomobileisfinishedbymeansthatofamechanismthatprovidesdirectionalchangestothemoving automobile.TheintentionofAckermannpuremathematicsistostopthetires fromslipperyoutwardoncethewheels followaroundacurvewhereastakingaflip.theanswerforthiscanbethateveryonewheelstoowntheiraxlessettledas radiiofcircleswithastandardcenterpurpose.Sincetherearwheelssquaremeasurefastened,thiscenterpurposeshould lieonalineextendedfromtherearshaft.Thus,we'dliketocrossthefrontshafttothepresentlineatthecommoncenter purpose.whereassteering,theinnerwheelangleislargerthanouterwheelangle.Thus,forgettingtotallydifferentresults we'dliketovarytheparameterssoastogetdesiredsteeringpuremathematics.
K.SowjanyaandS.Suresh[1]havepresentedresearchpaperwhichgivesanoverviewof analysisofdiscbrakes.Brakesare mechanismsystemwhichisusedtoretardmotionofmovingbody.Discofbrakesismadeofcastironor,aluminiumcomposite.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
These areselectedbyrunningseveraltestsonsoftwarelikesPro/E(Creo Parametric)forsolidmodellingandstaticanalysis aredonebyCAD/CAEsoftwares.
Neeraj Singh at el [2] have worked on research paper which focuses around structure and test examination of braking mechanism for off road condition for BAJA 2016. Every part of braking mechanism was designed on CATIA V5 though investigatingandtemperatureanalysiswasfinishedbyANSYS16.
VivekSinghNegiatel[3]hasbeenexaminesthoughtsforutilizingdifferentparameterinthesystems,structurefactorsand rationalebehindthechoosingrightestimateofthefactors.Structureofbrakingsystemmechanismcomprisesofevaluatinghuge numberofasituationsandutilizingtoaccomplishtheideal,yetcompellingbraking.Informationidentifiedregardingtoutilized toremovenormalestimationsofdesignparameters,makinghypotheticalcountsasreasonableascouldbeexpectedunder circumstances.
KushSoniatel[4]hasbeendonethepartdeterminationofbrakingsystemmechanismistalkedabout.Differentcalculationof brakingpower,brakingtorqueandbrakeinclinationareappearing.Likewise,thesafetyofutilizingbikerotorisapprovedby calculationandthermalinvestigation.Ouressentialpointwastothinkofabrakingsystemmechanismthatisstraightforward andhasanadvancedloadalongbeingdependable.AccordingtotherulebookofSAEINDIA BAJA 2020, it was obligatory for the system to comprise of two independentoperated hydraulic circuits. Likewise, all the four wheels must be lock at the same timesimultaneously.
Sanket Nawade (5) They concluded that after the Software Computation Analysis and Numerical Analysis, & found the approximatesamedeformationinchassiswhichisnegligible.AlsoFEAanalysisissuccessfullycarriedoutonCADmodelto determineEquivalentStressesandFactorofSafety.AlsofoundtheFactorofSafetygreaterthan1,thatconcludetheirchassis designissafeandthematerialusedthatisAISI4130isbestmaterialforGoKartChassis.
MohdAnwar(6)InthisResearchPapermanualmechanicallinkagessteeringsystemisnotusedinheavyweightvehiclesdueto highaxleloads,althoughitissimpleindesignandeasytomanufacture,thereforeitiscommonlyusedinlightweightvehicles. Thevaluescalculatedinthepapermaydifferpracticallyduetosteeringlinkageserrororduetoimpropersteeringgeometry,so these values are useful to understand the interdependency of the quantities oneach other and to design a ideal manual mechanicallinkagessystemforthevehicle.
PRABHUDATTADAS(7)Thereportdiscussedaboutthedesignandfabricationofago kartvehiclegivingspecialattentionto improvementofsuspensionsystemanddynamicsoverlastmodel.Thefirsthalfofthereportdiscussesaboutthenodalanalysis ofpreviousmodelandnotingdownthepointsofreviewandlimitationsinoldmodel.Theotherhalfofthereportdiscusses aboutawholenewdesignwhichtriestoeliminatethedefectsofolddesignandalsoimplementingthepositivityofolddesignin thenewone.Italsodiscussesaboutnewdesignprocedureandthetransmission,suspensionandsteeringsystemofthenewgo kartmodel.
ArshadKhan(8)Inthispaper,ThesteeringmechanismusedwhichisAckermannsteeringgeometryisdiscussedwiththesteer casesandisexplainedinsimplequadrilateralnotationformwithtermsconsideredinmechanismandtheassumptionsmade duringthesolutionoftheAckermannsteeringgeometryproblems.Theanalysisofthesteeringsystemcomponentsthrough varioussoftware'scanbeperformedwhichdeterminesthestresses,loadsanddeformationofthesteeringsystemfromwhich thedesignengineerscanpredictthesafetyofthesystemandcanalsobemodifiedandminimizationoftheerrorsinthesystems canbedone.
Mr.GirishMekalke(9)Thispaperdiscussedaboutthedesignandfabricationofago kartvehiclegivingspecialattentionto improvementofchassissystem.Thusthekartwasdesignedusingbasicautomobileprinciples.Itisanalyzedusingfiniteelement techniquestoproveitseffectiveness.Finally,aneffectivedesignforthekartisdevelopedwhichcanoutperformtheexistingkarts andalsointheupcomingeraofautomobilevehicles.
RamagiriSaiKiran(10)Inthispapermodelofchassisisstructuredin3DCADModelingsoftwarewhichgivesextraordinary adaptabilitytothecreatoranditisveryeasytoimportforanalysisinANSYSorsomeothersimulationsoftware.Inthisstudy,it isclearlyseenthatthenaturalfrequenciesofAISI4130andAL 2014 T6arehigherincomparisonwithdifferentmaterial.AL 2014 T6wasselectedonaccountoflessdensityandhighyieldstrengthwhencomparedtoAISI4130alongtheselines,todesign ago kart,itisbasictothinkaboutthebodytoweightproportion.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Assumed and Experiment Values
PARAMETER VALUES Reference
Coefficientoffriction(RoadandTyre)µr 0.8 Experiment
Coefficientofstaticoffriction (brakepadanddisc)µbp 0.5 Experiment
Frontrotordiameter(RDF) 685.8 mm 170 mm Assumed
Rearrotordiameter(RDR) 170 mm Assumed
Massofvehicle 1371.6 mm Assumed
Effectivebrakepadsarea(ABP) 0.0018338 m2 Calculated
Maxvelocity(v) 12.5 m/s Transmission department
Areaofpistonofmastercylinder(AMC) 2.85 × 10-4 m2 Calculated
Wheelbase(L) 1371.6 mm As per therulebook Wheeldiameter(Front) 533.4 mm Transmission Department
Wheeldiameter(Rear) 558.8 mm Transmission Department
DistanceofCGfromrearaxle(a) 685.8 mm Roll Cage Department
Wheel
Fromequation (i), we get RF = 1943.98N
RF =W×(a+coefficientoffriction×h)×cos(b h ) (i)
Sliding force required to lock the wheel SF =µr×RF =1555.18N
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Braking Torque acting on front wheel - TF=SF×Radiusofwheel=
414.76NmThesametorquewillactonrotor
TF =TROTOR =414.76Nm (ii)
Fromequation(ii),weget
Radial Force acting on rotor
FRF =(TROTOR×2)/RDF =4879.529N
Force acting on brake pads
Fbp =µbp ×FRF ×2 =4879.529N
Pressure required for pulling caliper piston out
Pp =Fbp /AP1 =5.374MPa
Same Pressure will act on piston of master cylinder. Therefore, force required
FMC1 =PP ×AMC =1531.7N (iii)
Rear Wheel
RR=W×(L a µrh)cosβ/L (iv)
Fromequation(iv),weget =655.67N
Sliding Force
SR =µr×RR =524.536N
Braking Torque acting on rear wheel
TR =SR×Radiusofwheel =146.55Nm
TR=TROTOR= 146.55NmFRR= (TROTOR×2)/ RDR =1724.18N
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Force acting on brake pads Fbp = µbp ×FRR ×2 =1724.18N
Pressure required for pulling caliper piston out Pp =Fbp /AP2 = 2.14MPaFMC2 =PP ×AMC (v) =611N
Force required to pull piston of master cylinder
From equation (iii) and (v),wegetFMC =FMC1+F MC2 =2142.69N Mass Required =218.42Kg
Pedal Ratio =10:1
Mass required to press pedal = 21.84Kg
TakingAckermannprincipalofsteeringAckermannprincipleofsteeringisusedtoclarifytheequationofwheelsontheinside andoutsideofaturnrequiredtofindoutcirclesofvariousradius.
100%Ackermannsteeringgeometry.
Maximumroadbankangleis20°.
Optimumkingpininclinationanglerangeis4°to8°.
Fronttorearweightratiois40:60.
Takingaccelerationduetogravityas10m/s^2.
Goals:
Toenablesmoothandstablemanoeuvringofthevehicle.
Tooptimizethesteeringeffort.
Provideadjustabilityforparameterssuchascasterangleandtoe.
Toselectandimplementthebestmechanismthatsuitsthepurpose.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Camber:Thecamberangleissettozerodegreebecausewedonotusesuspensionsystemtoprovidedynamic camberduringcornering.
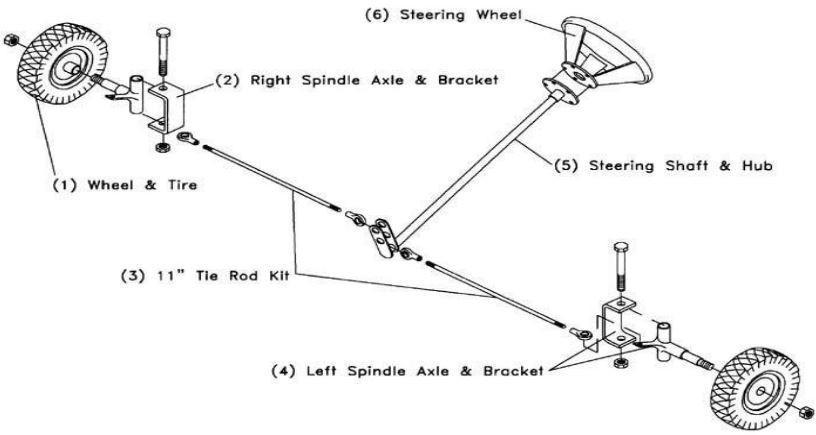
Caster: It is the angle formed by the axis of the bolt that is kingpin inclination whichconnectsthestub axlestotheknuckle.
KingpinInclination:DuetothegeometryofthestubaxletheKingpinoffsetishigh,whichdemandslarge kingpininclinationtominimizescrubradiuswhichisnotfeasible.Henceitissetto0(zero)degree.
Fig: Steeringsystem CALCULATIONS Required
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
C. Outer angle (ϕ): Tanϕ=L/(R*sinδ+T/2)=1143/(2000+1016/2) Tanϕ=0.45574ϕ=24.50°
D. Actual turning radius: R”=√(B2+X2)R”=√[(457.2)2+(2000.28)2]R”=2051.86m E. Ackermann angle (��):
Adetailedstudywasdonetopickthemostcompatiblematerialforfabricationofthebrakingsystem.Variousfactorswere consideredwhileselectingthematerialsuchasavailabilityofmaterialwithmechanicalstrength,elongationatbreak,Hardness weldability,costetc.ThematerialwhichweselectedwasAl 7075T6becauseofitsbetteryieldstrengthandultimatetensile strengthascomparedtoothermaterial. Mechanical properties of AL 7075 T6 Properties Values Density 2.81g/cc Ultimate Tensile Strength 572MPa Tensile Yield Strength 503MPa
Adetailedstudywascarriedouttoselectthemostsuitablematerialdependingonthefactorssuchasavailabilityofmaterial, Yieldstrength,weight,cost,weldability.AISI4340wasselectedoverAISI1018onthebasisofavailability,cost,Yieldstrengthand fatiguestrength.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
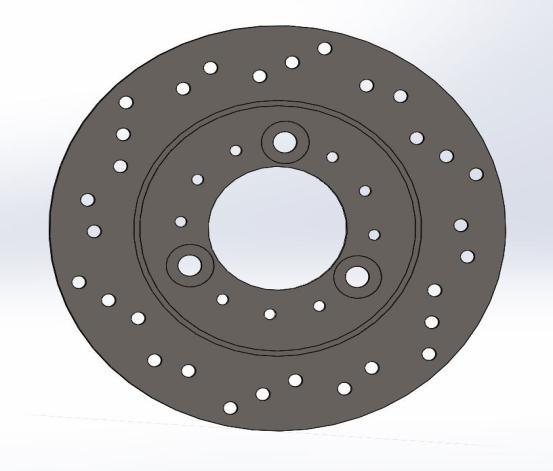
Figure: Model of rotor
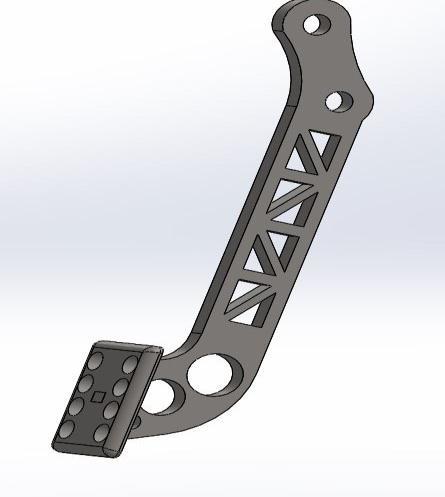
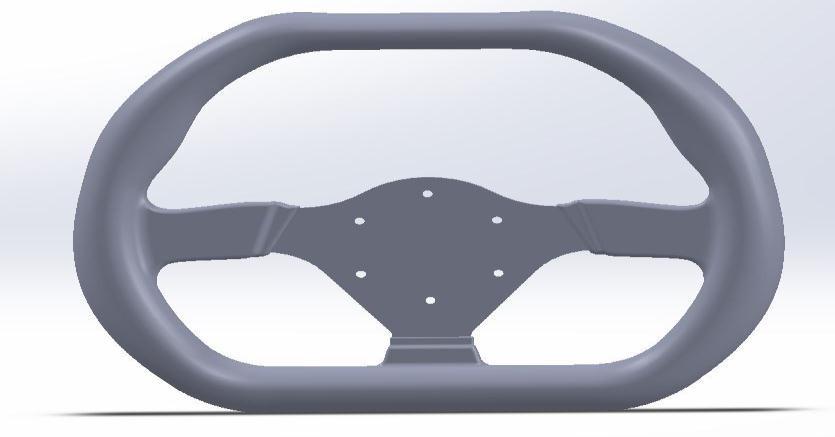


Figure: Model of brake pedal DESIGN: STEERING COMPONENTS
Figure: - Model of Steering wheel
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

ISSN:
0072
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
BRAKE PEDAL
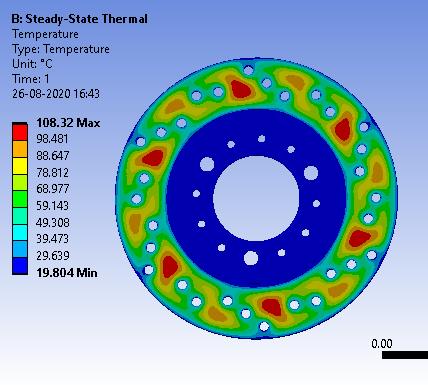
Figure: SteadyStateThermal
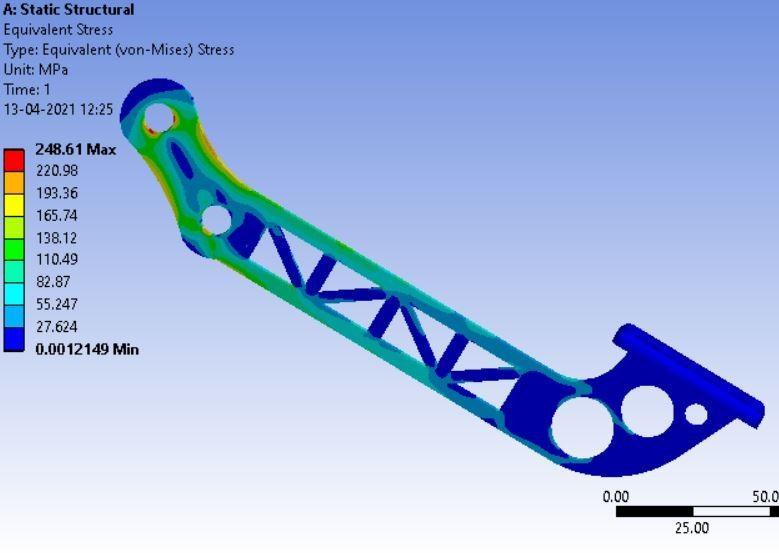
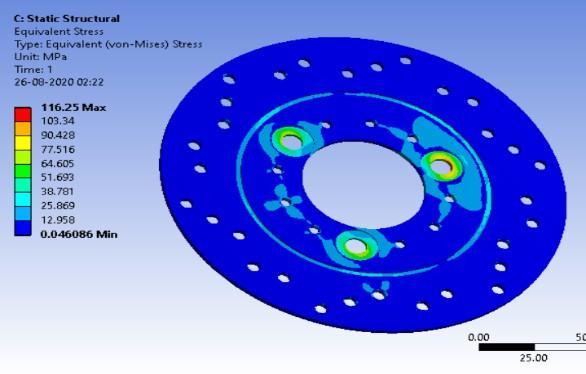
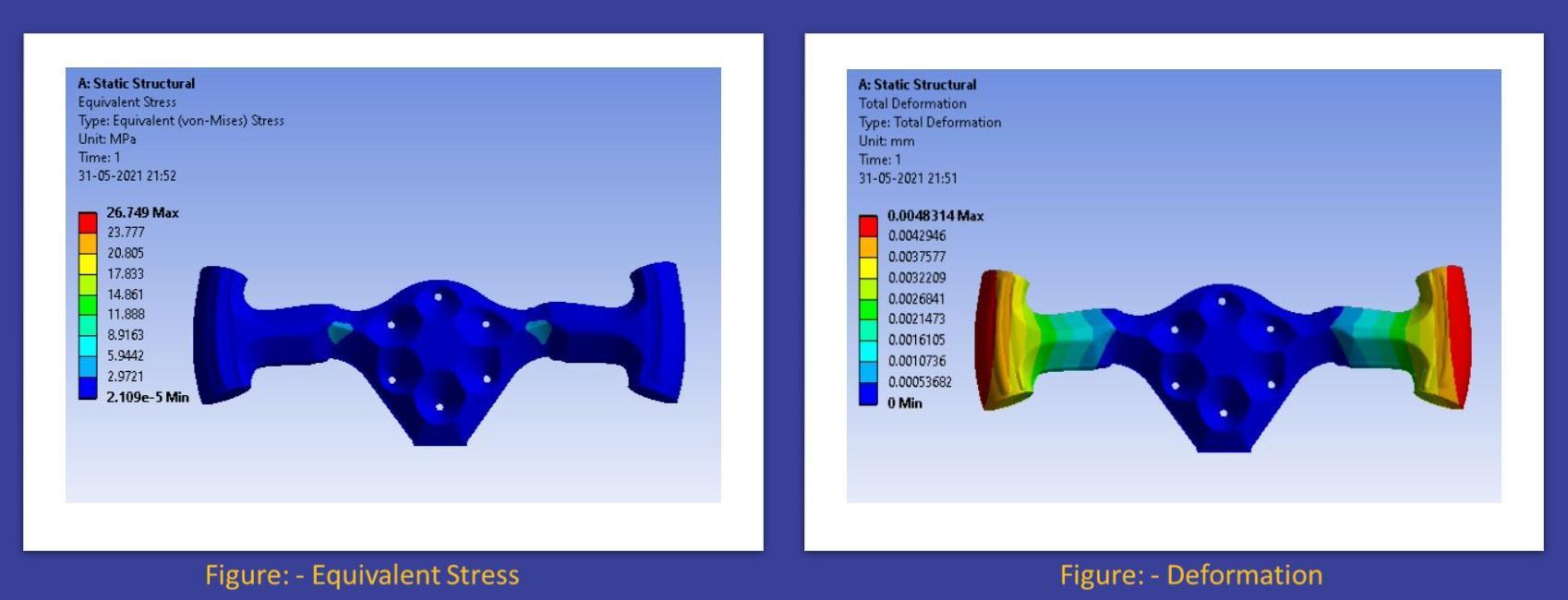
Figure: EquivalentStress
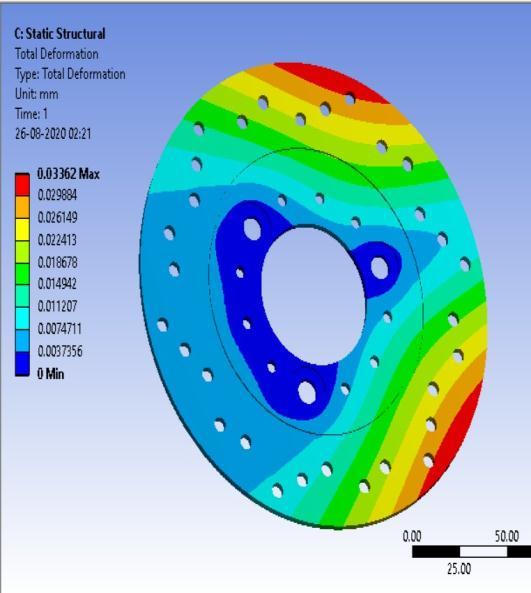
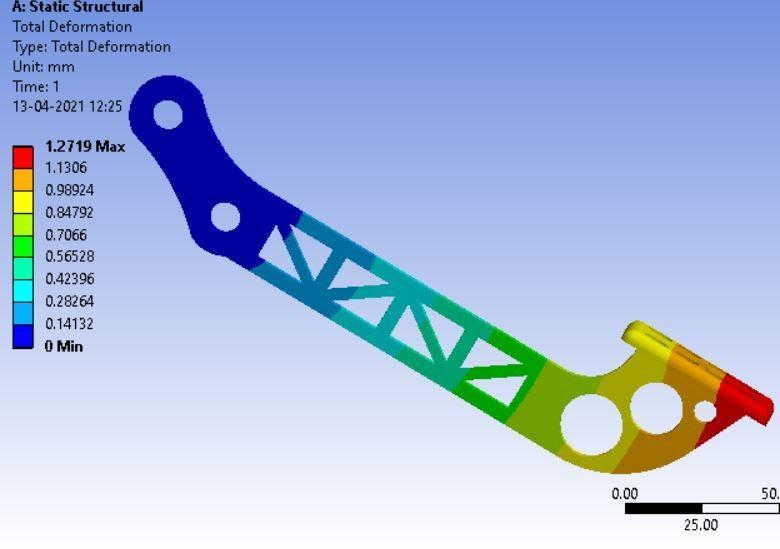
Figure: TotalDeformation
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
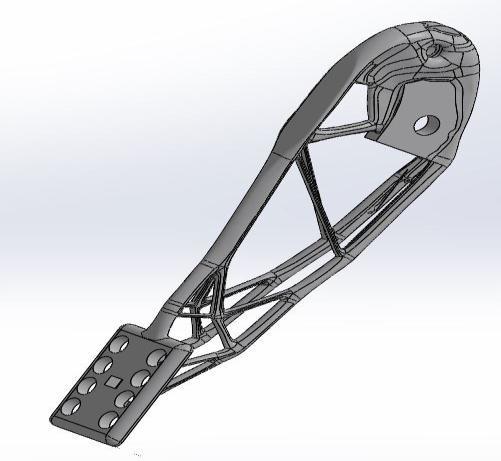
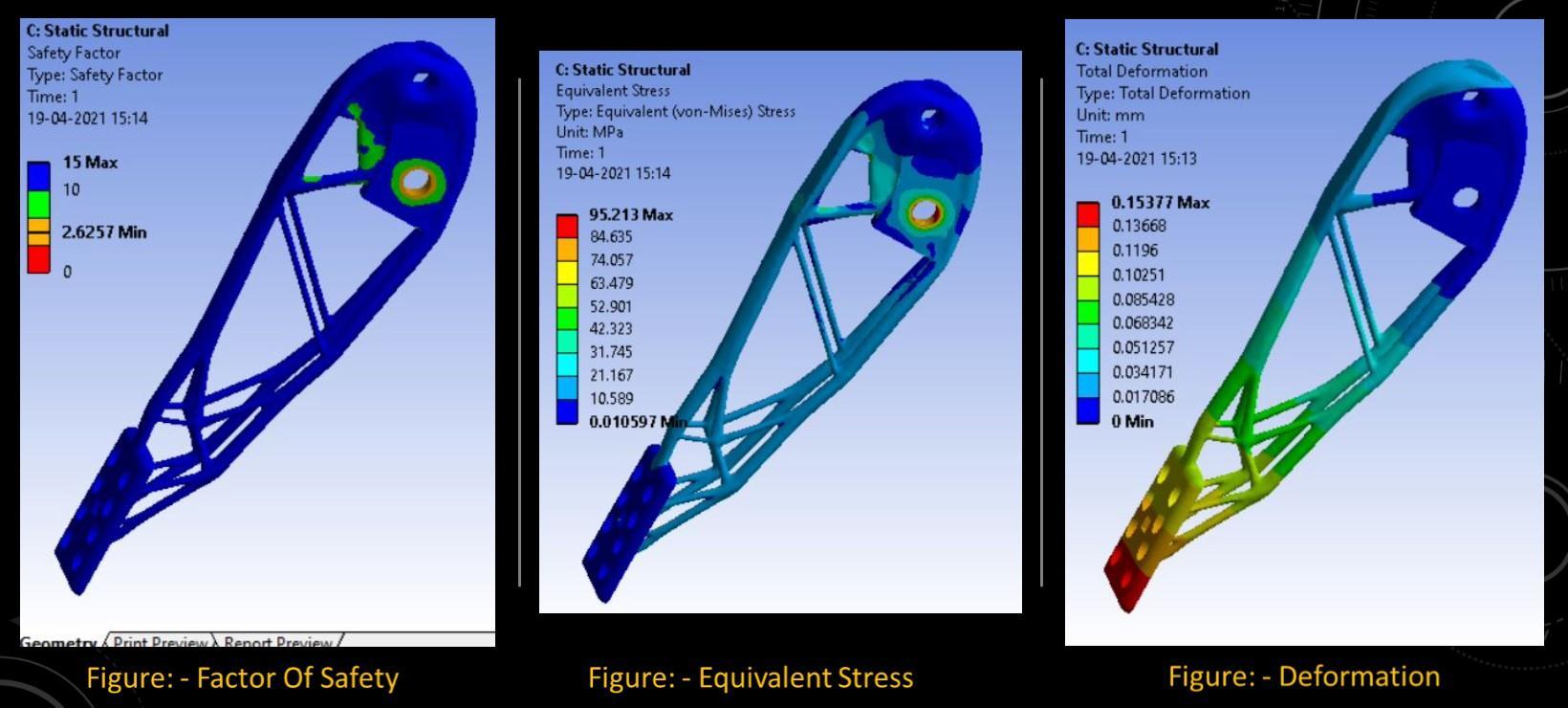


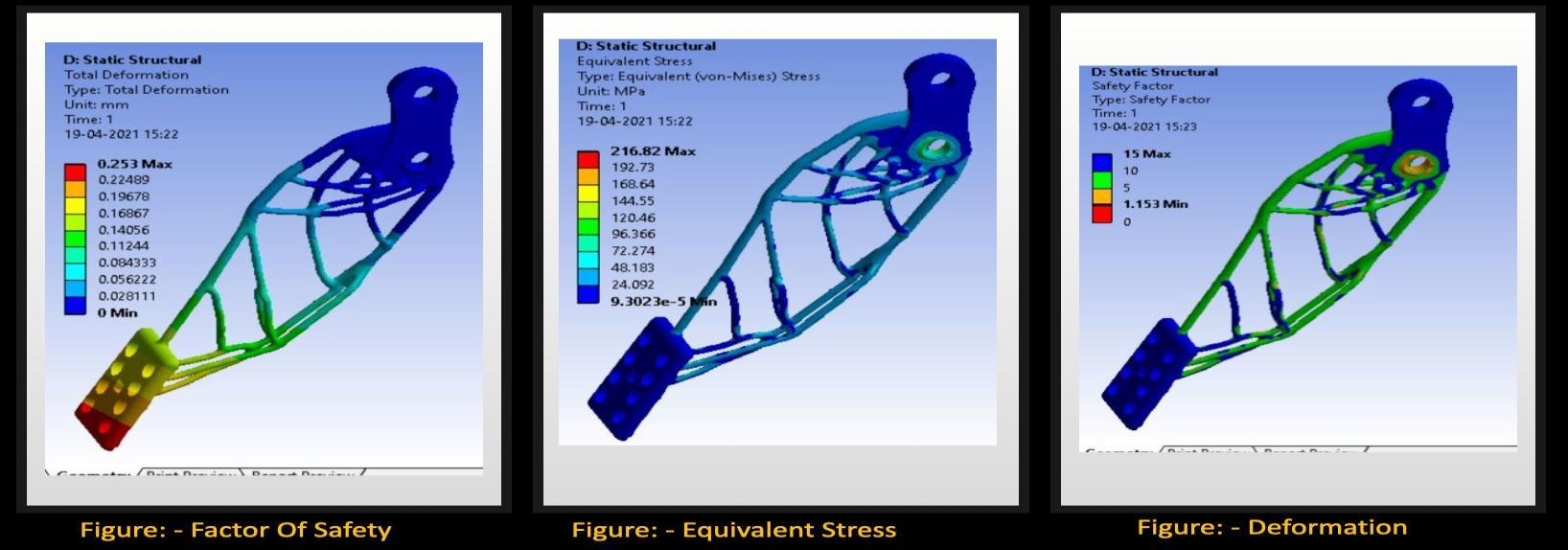
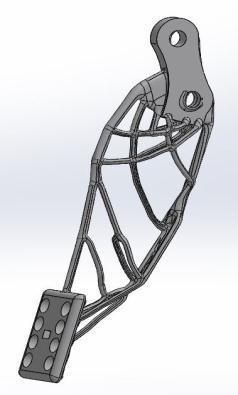
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Specifications: Volume = 30164.73mm3 Mass=81grams Analysis of Brake Pedal 2. Steering Wheel
Specification: Volume = 326637.46 mm3 Mass=872grams

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Specification: Volume=109316.98mm3 Mass=808grams
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
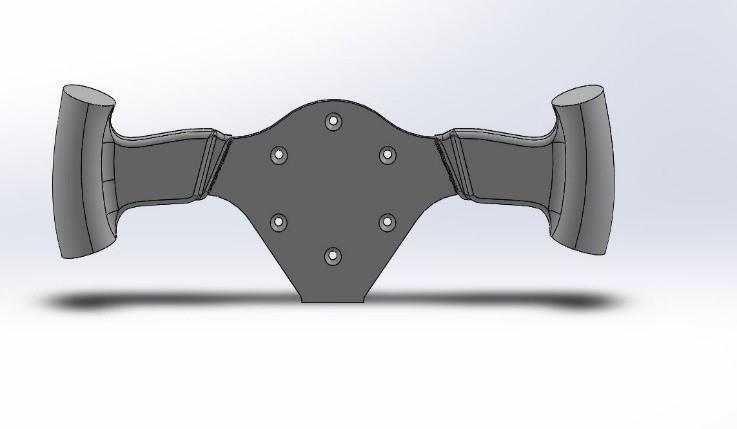
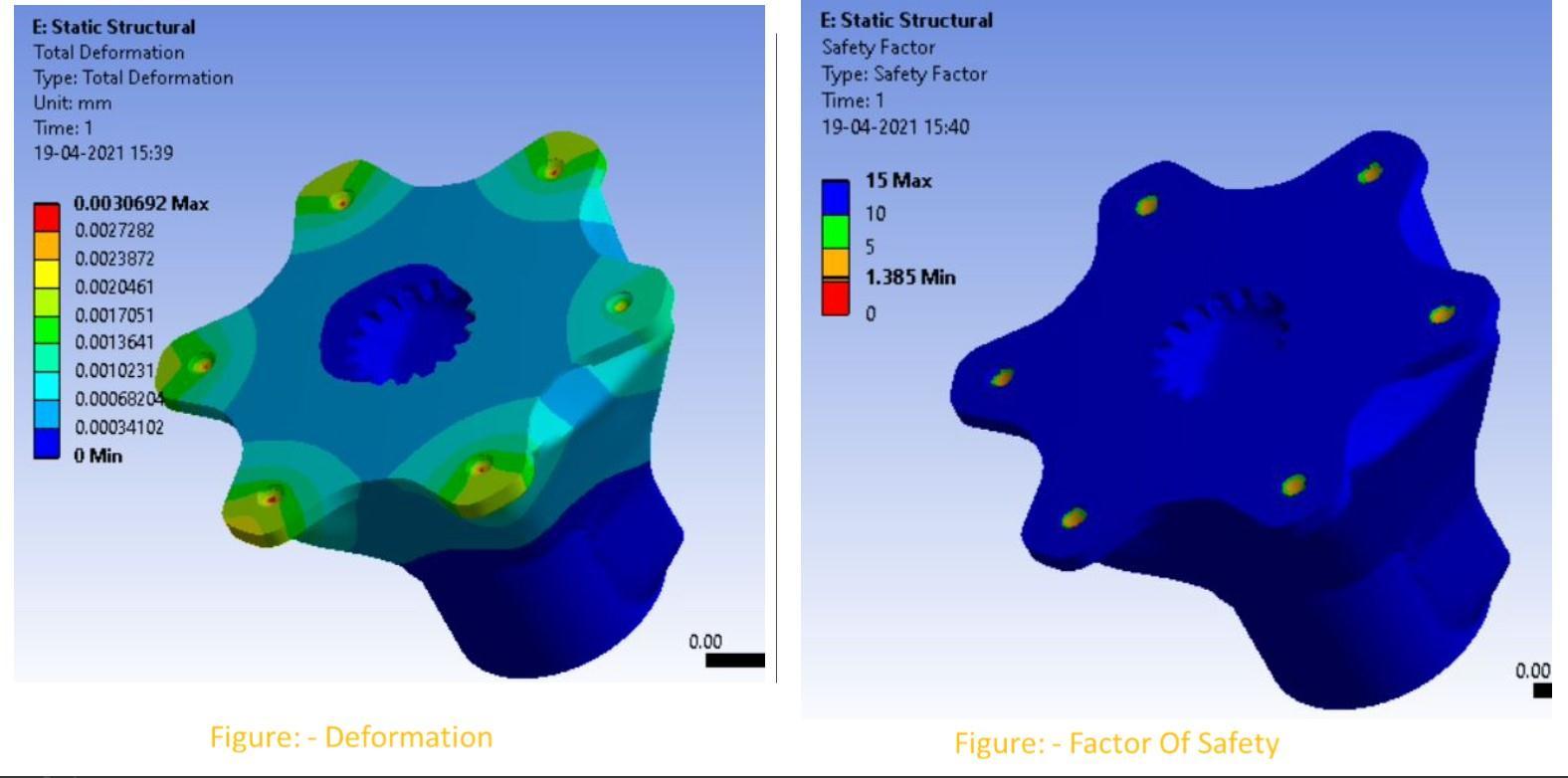
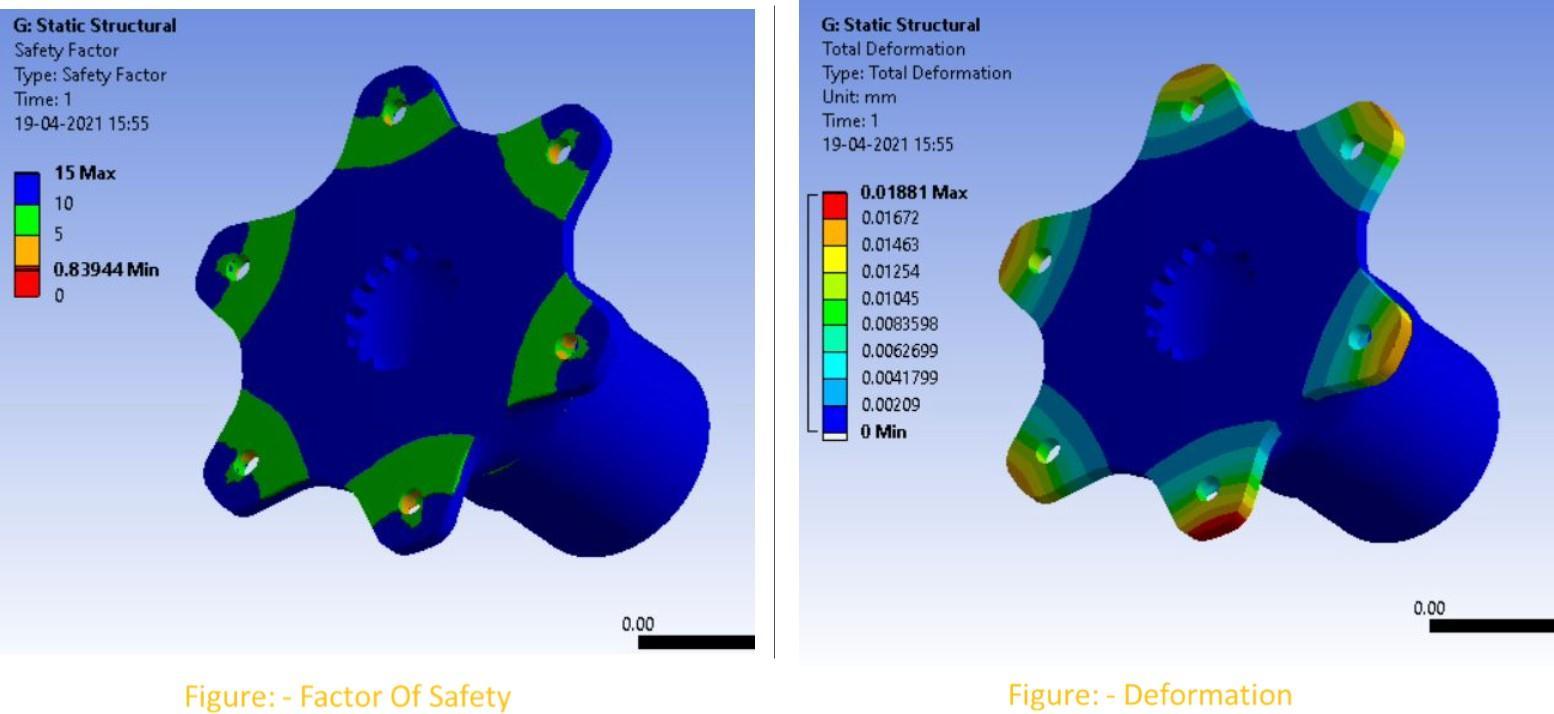
Specification: Volume = 71877.17 mm3 Mass=532grams
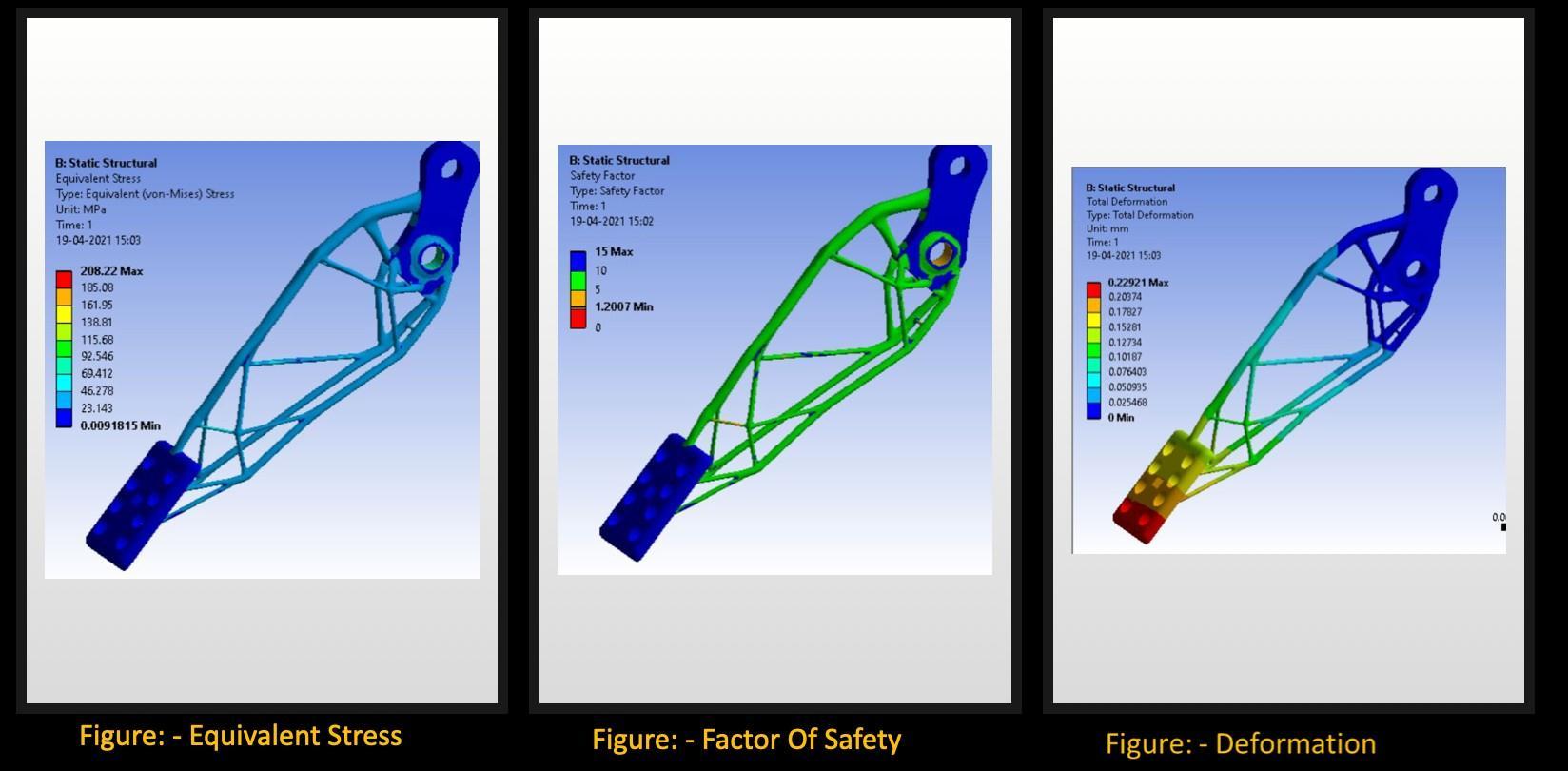
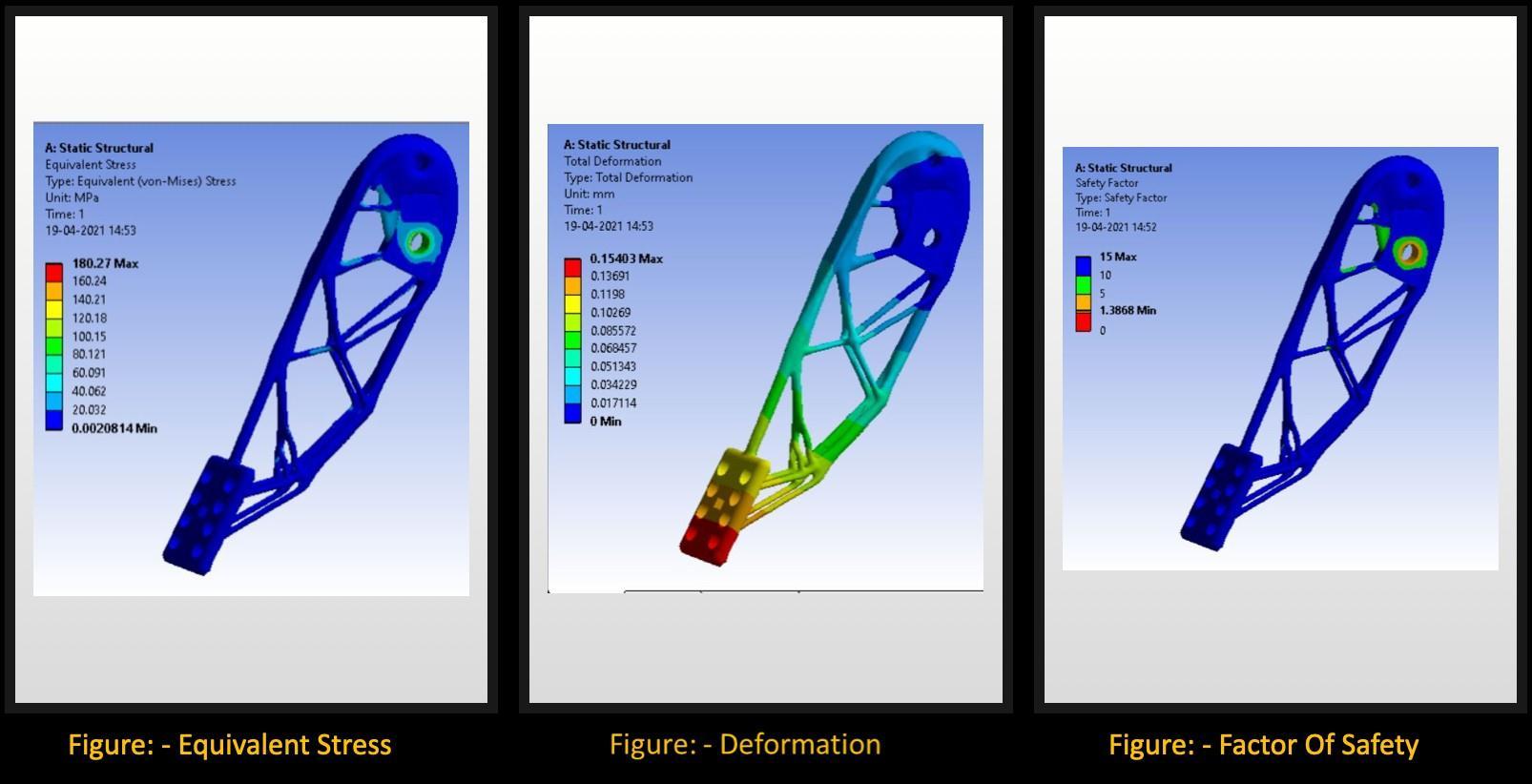
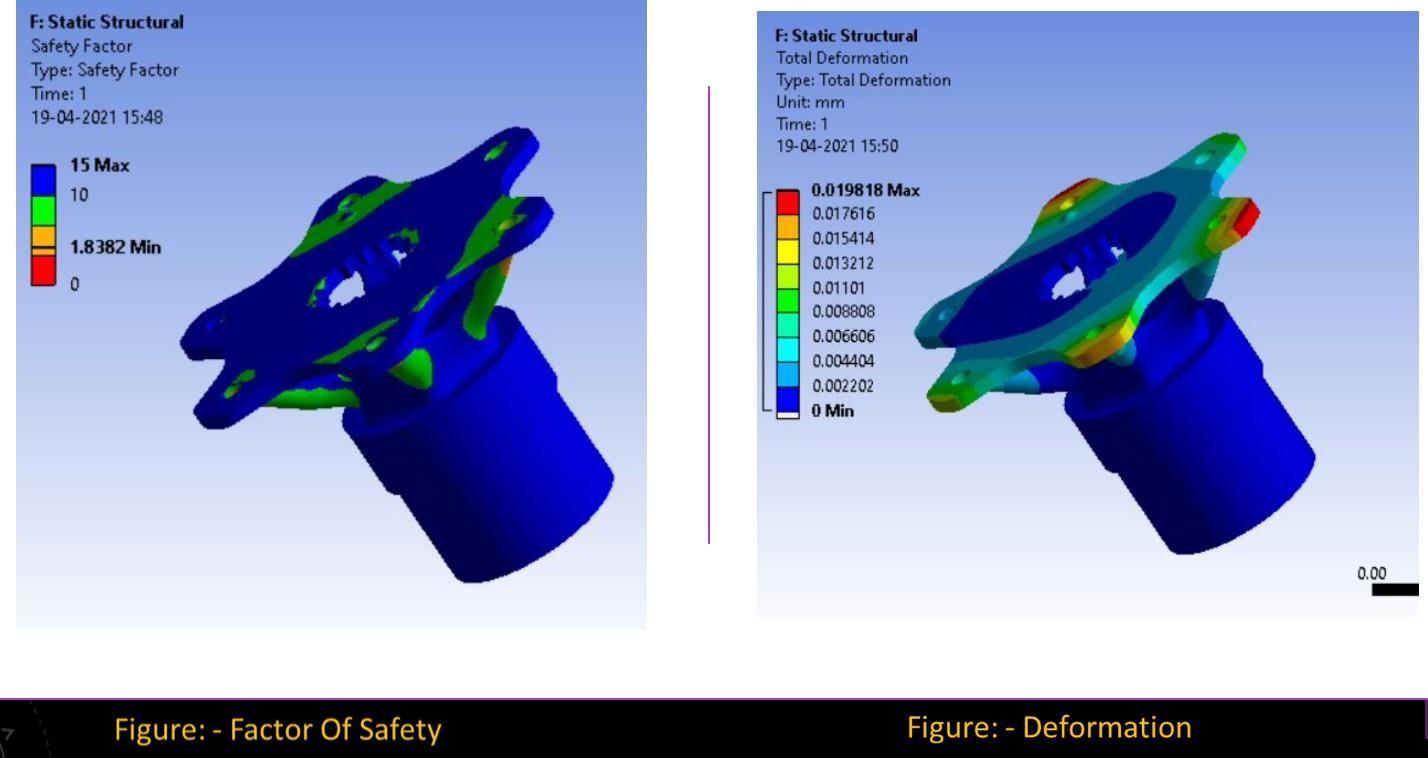
Analysis Of Steering Hub
• Inthispaperwehavediscussedthecalculationofsomebrakingparameterswhicheffecttheperformanceof ourvehicle,andweuseAL-7075T6fordiscbrake.Wegowithresults obtaininoursimulationonANSYS Workbench.Fromthesetofvariables,thebestresultsare found at deformation is 0.014503 mm, factor of safety is 1.89 and temperature at152.21Con4AL-7075T6with3.5mmthickness.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
• Inthecaseofthebrakepedal,theinitialweightofthecomponentwas296grams,thebestiterationtoobtain thehighestfactorofsafetywasiteration1withafactorofsafetyof 2.62.Theweightreductionwas58.78%fromitsoriginalweightage.
• Incaseofthesteeringwheel,theinitialweightofthecomponentwas2139.31grams,thebestiterationhasa factorofsafetyof7.62.Theweightreductionwas59.24%fromitsoriginalweightage
• IncaseoftheSteeringhub,theinitialweightofthecomponentwas1432grams,thebestiterationhasafactor ofsafetyof1.838(1stiteration).Theweightreductionwas89.8%fromitsoriginalweightage.
1. K.Sowjanya,S.Suresh,“StructuralAnalysisofDiscBrakeRotor”,InternationalJournalofComputerTrends andTechnology(IJCTT),Vol.4Issue7 July2013
2. NeerajSingh,R.S.Bharj,KamalKumar,“OptimumDesignandExperimentalAnalysisof BrakeSystemfor BAJAATV”,InternationalJournalofResearchinManagement,Science&Technology(E ISSN:2321 3264)Vol. 5,No.3,December17”.
3. VivekSinghNegi,NayanDeshmukh,AmitDeshpande,“DesignandAnalysisofBrakesystem”,International JournalofAdvanceEngineeringandResearchDevelopmentVol 4(11),November 2017”.
4. KushSoni,GaurangVara,IshitSheth,HarshilPatel,“DesignandAnalysisofBrakingSystemforISIEESVC”, InternationalJournalofAppliedEngineeringResearchISSN0973 4562Vol 13,Number10(2018)pp.8572 8576”.
5. NeerajSingh,R.S.Bharj,KamalKumar,“OptimumDesignandExperimentalAnalysisof BrakeSystemfor BAJAATV”,InternationalJournalofResearchinManagement,Science&Technology(E ISSN:2321 3264)Vol. 5,No.3,December17”.
6. VivekSinghNegi,NayanDeshmukh,AmitDeshpande,“DesignandAnalysisofBrakesystem”,International JournalofAdvanceEngineeringandResearchDevelopmentVol 4(11),November 2017”.
7. KushSoni,GaurangVara,IshitSheth,HarshilPatel,“DesignandAnalysisofBrakingSystemforISIEESVC”, InternationalJournalofAppliedEngineeringResearchISSN0973 4562Vol 13,Number10(2018)pp.8572 8576”.
8. VallamkonduArunKumar,SettyKalyan “ActiveSafetyBrakingSystem” InternationalJournalofScientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 12, December 20131 ISSN2250 3153
9. ISHWARGUPTA1&GAURAVSAXENA,“STRUCTURALANALYSISOFROTORDISCOFDISCBRAKEOFBAJA SAE2013CARTHROUGHFINITEELEMENTANALYSIS”,InternationalJournal ofAutomobileEngineering ResearchandDevelopment.
10. AkshatSharma,AmitKumarMarwah,“BrakingSystems:Past,Present&Future”,Vol.2,Issue 3,pp.29 31, March 2013ISSN 2250 1991