International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1PG Scholar, Department of Electrical Engineering, Prof Ram Meghe College of Engineering & Management, Badnera Amravati, Maharashtra,India
2 Head of Department and Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering, Prof Ram Meghe College of Engineering & Management, Badnera Amravati, Maharashtra,India ***
Abstract A rapidly developing technique for the online identificationofdevelopingproblems isconditionmonitoring of induction motors. It prevents the unanticipated failure of a crucial system. Stator defects make up between 30 and 40 percentofinductionmotorerrors.Thisstudyoffersathorough analysis of the numerous stator problems, their root causes, detectionparameters/techniques,andcurrentstate of the art condition monitoring technologies. Its purpose is to give induction motor researchers and application engineers a comprehensive overview of the state of stator fault monitoring. For rapid reference, a list of 10 research articles on the topic is included.
Key Words: Three phase induction motor, Stator faults, Fault classification
Induction motors are the main workhorse of industrial prime movers due to their extensive uses in electromechanicalenergyconversion,primarilybecauseof their low cost, fairly compact size, robustness, minimal maintenance,andoperationwithareadilyaccessiblepower source. Even though induction machines are dependable, they are occasionally put to un favorable conditions that result in flaws and failures [1], [10]. Numerous machine problems have been researched, including eccentricity, bearingfaults,brokenrotorbars,statorandrotorimbalance, andwindingfaults[7],[10].
Recentgrowthinautomationandtheresultingdecreasein direct man machine contact for system operation supervision has raised the necessity for condition monitoring.Forthegoalofidentifying,analyzing,andfixing machine issues before they lead to failure, condition monitoringisthegraphicaltrendofthemachineparameters. It is employed to improve machine performance and availability,lowerconsequentialdamage,lengthenmachine life, lower spare parts inventories, and lower breakdown maintenance[2] [6],[8].Accordingtoseveralstudies,stator winding failure accounts for 30 40% of induction motor failures[1],[10].Anverycredibleresearchwasfundedby theIEEEandtheElectricPowerResearchInstitute[1].
A thorough analysis of around 7500 motors revealed that statorproblemsweretoblame.DraftreceivedonMay20;
updatedonOctober28.TEC00126 2003,papernumber.A. Siddique and G. S. Yadava work at the Indian Institute of Technology'sIndustrial Tribology,MachineDynamicsand Maintenance Engineering Centre in New Delhi, India (110016). B. Singh works at the Indian Institute of Technology'sDepartmentofElectricalEngineeringinNew Delhi,India(e mail:bsingh@ee.iitd.ernet.in).Identityofthe Digital Object 10.1109/TEC.2004.837304 responsible for 37%ofthefailures.Asaresult,diagnostictestssensitiveto thestateofthestatorwindingareneededwhenconducting predictivemaintenanceonmotorsforstatordefects.
A thorough analysis of around 7500 motors revealed that statorproblemsweretoblame.DraftreceivedonMay20; updatedonOctober28.TEC00126 2003,papernumber.A. Siddique and G. S. Yadava work at the Indian Institute of Technology'sIndustrial Tribology,MachineDynamicsand Maintenance Engineering Centre in New Delhi, India (110016). B. Singh works at the Indian Institute of Technology'sDepartmentofElectricalEngineeringinNew Delhi,India(e mail:bsingh@ee.iitd.ernet.in).Identityofthe Digital Object 10.1109/TEC.2004.837304 responsible for 37%ofthefailures.Asaresult,diagnostictestssensitiveto thestateofthestatorwindingareneededwhenconducting predictivemaintenanceonmotorsforstatordefects.
A MATLAB based model was created and put through several fault load combination instances for motors of various sizes. Electromechanical torque created by the motor was chosen as a defect signal. The mean, variance, max,min,andF120timebasedonstatisticalandfrequency related properties were discovered to be quite unique for associatingtheacquiredelectromechanicaltorquewithits corresponding proportion of shorted turns during the constructionandtrainingoftheneuralnetwork.Fivedistinct motors referredtoasobservedmotors wereemployed throughout the neural network's training phase. On the other hand, the electromechanical torque under various fault load combination instances, previously unseen from thefirstfivemotorsandthoseoftwonewmotors(referred toasunseen),wasutilizedtoassesstheeffectivenessofthe proposed diagnostic tool. According to test findings, accuracywasbetween88and99percent.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
discussionofafeatureextractiontechniqueknownasMSAF 20 MULTIEXPANDED(MethodofSelectionofAmplitudesof Frequency Multiexpanded). The feature vectors were produced by the MSAF 20 MULTIEXPANDED. The feature vectorswereproducedbytheMSAF 20 MULTIEXPANDED. ThegeneratedvectorswerecategorizedusingtheNN,NM, and GMM classifiers, respectively (Gaussian Mixture Models). The single phase induction motors may be diagnosedusingthesuggestedapproach.Itmayalsobeused todifferentdesignsofelectricrotationalmotors.
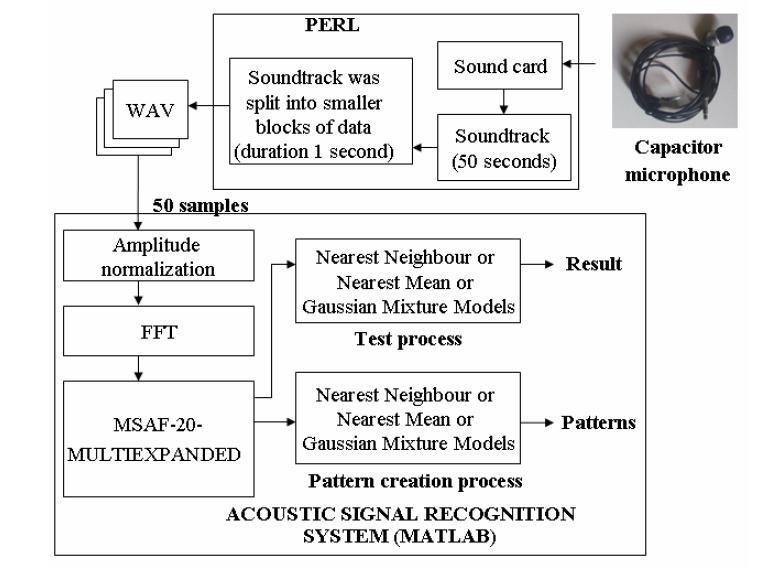
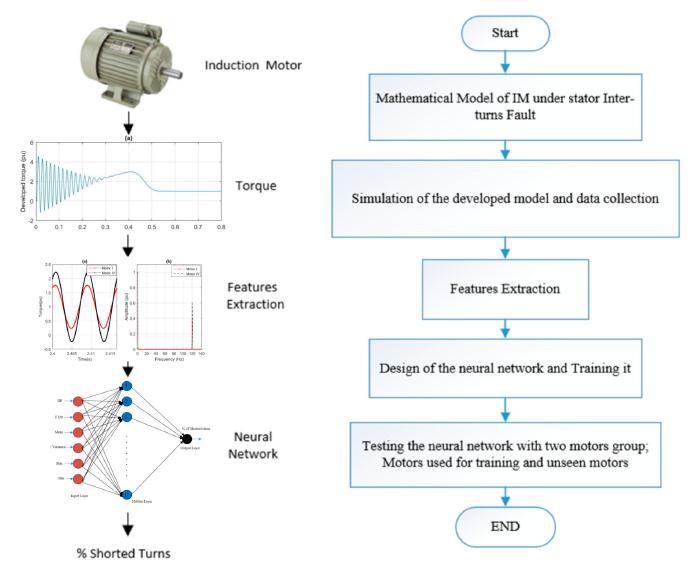
Fig 1: Threephaseinductionmotorstatorinterturnfault detectionapproach[1]
Theinventionofadiagnostictoolbasedonaneuralnetwork isdescribedinthisapproach[1]fordeterminingtheseverity andpreciseproportionofstatorinter turndefectsinthree phaseinduction motors.Thebenefitofadoptinga steady state electromechanical torque signature as a failure indicationisdemonstratedbysimulationresults.Variance, max, min, mean, and the F120 were discovered to be the most typical and distinguishable inter turn fault characteristicswhentheacquiredelectromechanicaltorque underwent time and frequency domain analysis. Because thereisjustoneinput,oneoutput,andonehiddenlayerwith 11neurons,thecreatedneuralnetworkissimple.
Additionally, 100% unseen cases of short turns/loading conditionsextractedfromseenmotorswithanaccuracyof 99%and100%unseencasesextractedfrommotorsnever seenorusedforneuralnetworktrainingwithanaccuracyof 88 96 percent were applied to the developed diagnostics tooltoexamineitseffectiveness.Contrarytoalldiagnostic equipment, which may only be used on motors utilized duringtraining,thisisthecase.Futureresearchcanadapt theproduceddiagnostictoolinthistechniquetodetectother faultkinds,suchasaconfluenceofinter turnandbrokenbar and/orinter turnandeccentricity.Asaresult,thismaybe utilized to create a thorough diagnosis tool. The current study may also be expanded upon by using the created technologyinalaboratorysetting.
An article describes an acoustic signal based early failure diagnosis method. A single phase induction motor was employed with the technique that was provided [2]. The followingstatesofthemotorweremeasuredandexamined by the authors: a single phase induction motor in good condition, a single phase induction motor with a faulty bearing,asingle phaseinductionmotorwithafaultybearing and shorted coils of the auxiliary winding. There was
Fig 2: Blockdiagramoftheearlyfaultdiagnostic techniquebasedonacousticsignals[2]
Theearlydefectdiagnosticmethodologybasedonauditory signals is presented in method [2]. The single phase inductionmotorwasoperatedusingthesuggestedmethod. Asingle phaseinductionmotoringoodcondition,asingle phase induction motor with a defective bearing, a single phaseinductionmotorwithabadbearingandshortedcoils oftheauxiliarywindingwereallexamined.TheMSAF 20 MULTIEXPANDEDfeatureextractionapproachwasutilised by the authors. In this article, the Nearest Mean classifier, Gaussian Mixture Models, and the Nearest Neighbor classifierwereeachexamined.
The findings of all the chosen classifiers were as follows: GaussianMixtureModels(ET=65.7 88.8%),NearestMean classifier(ET=89.7 95.3%),andNearestNeighborclassifier (ET=84.1 91.6%).Thesingle phaseinductionmotorscan be protected using the fault diagnostic approach. The proposedapproachmayalsobeusedtodiagnoseothertypes of spinning equipment. The suggested method is non intrusive and reasonably priced. However, the suggested method was susceptible to influence from outside disturbances.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The approach [3] presents a three phase asynchronous motor'sstatorshortcircuitfaultdetectiontechniquethatis basedoncurrentvectorcoordinatetransformation.Statistics showthatinter turnshortcircuits,whicharecausedbythe breakdown of turn insulation, account for 78% of stator problems. It frequently results in motor shutdown. It demonstrates the fundamentals of developing a stator windingdiagnosticsystemusingcurrentmeasurements.The simulation results supported the efficacy of the suggested methodsfordetectingstatorshortcircuitfailures.Withthe use of a lab test bench, a motor with an inter turn short circuitwasalsoevaluated.
inputdatasets.Thistechnique[4]providesadeeplearning based multi signal defect diagnostic approach that takes advantageofconvolutionalneuralnetworks'(CNNs')potent featurelearningcapabilitiesinpictures.Thesuggesteddeep model hasthecapacitytoconcurrentlylearnfromseveral typesofsensorsignals,enablingaccurateinductionmotor defectidentificationandrobustperformance.First,awavelet transformisusedtotransformtheobtainedsensorsignals into a time frequency distribution (TFD). Then, using the TFDpicturesasastartingpoint,adeepconvolutionalneural networkisusedtolearndiscriminativerepresentations.A fully linked layer in a deep architecture then provides a forecastofthestateoftheinductionmotorbasedonfeatures that have been learnt. Experiments are conducted on a machinefailuresimulatorwherebothvibrationandcurrent dataareevaluatedtodeterminetheefficacyofthedeveloped deep model. The suggested method works better than conventional fault diagnostic techniques, according to experiment data, proving its efficacy in induction motor applications. The suggested deep model is able to automaticallylearnandchooserelevantcharacteristicsthat contributetoeffectivedefectdiagnosisincontrasttoexisting approachesthatrelyondelicatefeaturesretrievedbyskilled professionals.
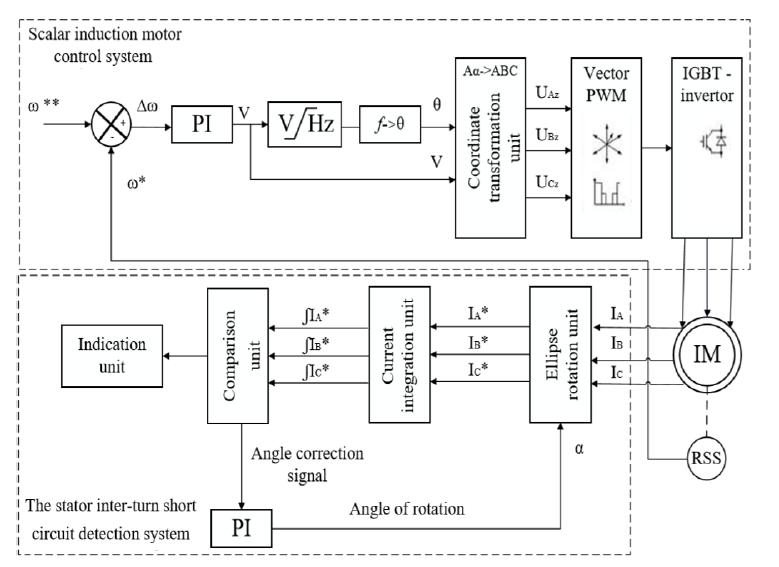
Fig 3: Threephaseinductionmotorstatorinter turnshort circuitfaultdetectionapproach[3]
Even with inexpensive current sensors, the devised diagnostic system is usable and offers a wide range of measurementaccuracy.The suggestedsystem'suseis not justrestrictedtoalabbench.Thistechniquecanbeutilised inindustrieswherethemotorisinstalledinaninaccessible location (crane electric drive, air conditioning systems, electric centrifugal pump installations, etc.), or when installationsareremotelyplaced(insuckerrodpumpand watersupplyunits).Theaforementionedtechniquesareall more computationally intensive or need for test based settings.
Thekeybenefitofthesuggestedapproachisthatitrequires littledataarrayprocessinginthebuiltdiagnosticsystem's algorithm. However, a comparison of the discussed and suggesteddiagnosticproceduresfordetectingstatorinter turnshortcircuitscanproducehigh qualityrelativeanalysis data that are highly helpful for verifying the method's applicability.
A potential approach for describing fault states is deep learning architecture, which uses several hidden layers to automaticallybuildhierarchicalrepresentationsfromlarge
Withitsuseoninductionmotors,thistechnique[4]presents aDCNN basedmulti signaldefectdetectionframeworkthat uses time frequency distributions of sensor signals as the inputpictures.Themulti signalmodel,whichusesCNNasits foundation,demonstratesthecapacitytoautomaticallylearn discriminative features from TFD pictures and deliver precise fault classification. In order to evaluate the effectivenessoftheproposedframework,bothvibrationand current signals are employed. Through trials, the performances of two distinct DCNN based multi signal architecturesarecompared,withthemergedmodelshowing the best results. On the basis of statistical analysis, the impactofmeasurementuncertaintyisalsoexamined.
Thedetectionofelectrical motordeteriorationisa crucial fieldofresearchnowadays.Amotor'sdiagnosticinformation istypicallycontainedinvibrationsignalsignals.Theauthors offeredamethodforevaluatingthevibrationsignalsfrom three phaseinductionmotors.Thistechniqueprovidesways fordiagnosingrotordefectsinthree phaseinductionmotors (TPIM) [5]. The methods disclosed made use of vibration signalsandsignalprocessingmethods.Theauthorslookedat thesuccessrateofidentifyingvibrationsignalreadingsfor threedifferentTPIMstates:ahealthyTPIM,aTPIMwithone brokenbar,andaTPIMwithtwodamagedbars.Theauthors proposed a method for extracting information from vibrationsignalscalledMethodofSelectionofAmplitudesof Frequencies(MSAF 12).Thefeaturevectorswereobtained using the FFT, MSAF 12, and the vector sum's mean. The three classification methods that were examined were nearestneighbour(NN),lineardiscriminantanalysis(LDA),
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
and linear support vector machines (LSVM). The performanceofthetestedclassifiersvariedfrom97.61%to 100%.
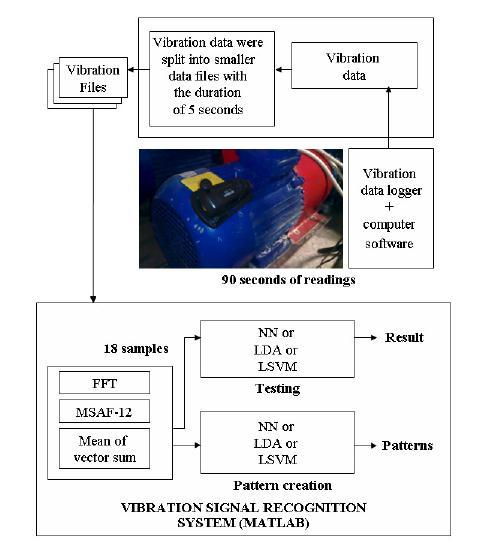
This method [5] discusses rotor of the TPIM diagnostic methods.Thesuggestedmethodsreliedonvibrationalcues. Three different TPIM states' vibration signals were examinedbytheauthors.Theresearchersexaminedthree motors:onewithoutabrokenbar,onewithonebrokenbar, andonewithtwobrokenbars(3motorsintotal).TheMSAF 12 approach was created and employed by the authors. MSAF 12,FFT,andthemeanofthevectorsumwereusedto producethefeaturevectors.
Theapproach[6]suggeststwoseparatefeatures:onebased onpeakextractionusingtheprominencemeasure,amethod takenfromthemorphologyofmountains,andanotherbased on the computation of the occupied band power ratio for particulardistinctivefaultfrequencies.Principalcomponent analysis(PCA),afeaturereductionapproachwithalinear foundation, has been used to represent all the data. The three phasecurrentsignalsonlinewerethendetectedand classified using shallow neural networks. Using signals collectedfromgrid andinverter fedinductionmotors,the efficacyofthesuggestedapproachhasbeenexperimentally verified.
Fig 4: Vibrationbasedthreephaseinductionmotorfault diagnostictechnique[5]
Thefollowingthreeclassificationtechniqueswereused:NN, LDA, and LSVM. The calculated outcomes of the aforementioned classifiers were equivalent to outcomes attainedbyfurtherdiagnostictechniques(TEVSRwasequal to100percentfortheMSAF 12).Thedescribeddiagnostic methods cost little money. Costs for acceleration and vibrationdatarecordersarearound$100.ThepriceofaPC isbetween$250and$300.Thegivenstrategiesareeffective indetectingdegradation,asshownintheresultssection.The studydemonstratedthatvibrationsignalsincludediagnostic data. The suggested methods can also be used to identify bearingproblems,brokengears,andbrokensprocketteeth inspinningelectricalmotors.
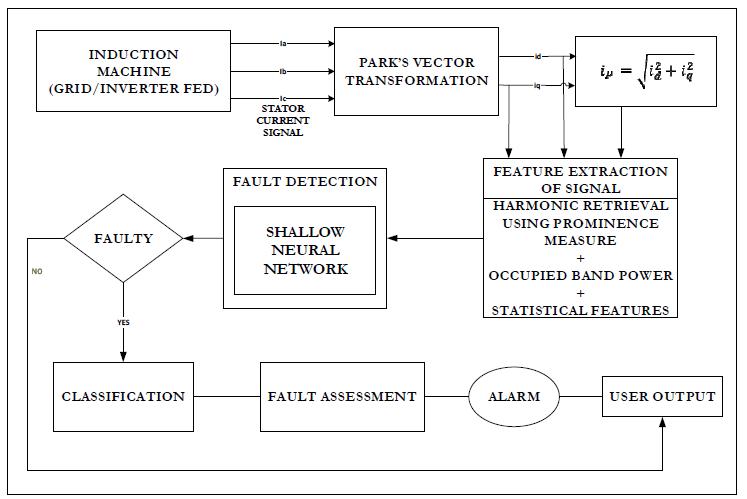
A two stage fault detection and classification strategy particularly created for spinning electrical devices is presented by this method [6]. The strategy makes use of brand new,frequency domain specificconditionindicators.
Fig 5: FDandclassificationschemeusingNon Parametric, Statistical FrequencyFeaturesandShallowNeural Networks[6]
Using two stage NNs, a defect detection and classification technique has been developed with accuracy levels exceeding 95%. The selection of characteristics that generalizethedatainmanydifferentwaysandareableto differentiateclassesintheeventofanomaliesisakeyfactor in improving the system accuracy. Thus, the following featuresarethekeyfocusofthismethod's[6]contribution:
First, the usage and improvement of the prominence measure basedpeakextractionapproach,whichhasnotyet been suggested or used in the field of FD and CM. The frequencyspectrumelaborationinthesuggestedtechnique allows for fault analysis customization. Although it is not required, previous knowledge of the model order is necessarytoproperlyextractsignificantpeaks.Themethod of prominence is more time efficient than classical and parametric basedstrategiesforharmonicretrieval,performs aswellforshorttimeintervals,anddoesn'trequireanypre processing.
ThesecondistheusageoftheoccupiedBPRratioinrelation to the frequency spectrum's CFFs. In order to combat external noise produced by the inverter, these characteristicsalsoincorporatestatisticalfrequencyaspects.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Creatingthistechnique[7]aimstoofferanovelmethodfor identifying and diagnosing electrical problems in three phaseinductionmotors, especiallythosethat occurinthe stator winding. The stator winding usually breaks down when an induction motor fails. To better comprehend internalwindingfaultininductionmotor,fourcasestudies of distinct three phase induction motors (TPIM) were analyzedundertwoconditions:normalwindingcondition andwindingsshortedbetweentwophases.Thisstrategyis outlined in the frequency response analysis (FRA) measurement on the stator winding with the inter phase short [7]. It is also advised to classify and quantify the problem using the Frequency Response Analysis (FRA) interpretivetechnique.TocomprehendtheFRA,astatistical indicatorknownastheNCEPRItechniqueisusedtocompare themeasuredresponses.
can result in awful things like operational accidents, manufacturing disruptions, and raw material losses. Identification of defect has therefore become increasingly crucial inInduction motor maintenance.Bearingfailureis oneofthemanyproblemsthatmaydevelopinamotorand, ifignoredatanearlystage,cancausecatastrophicdamageto themachine.Therefore,itisnecessarytocontinuallycheck the condition of the bearings in induction machines. A unique method [8] is put forward that makes use of the discretecosinetransform(DCT)toanalysesspeedandthe probabilistic neural network (PNN) to pinpoint bearing errors. When the motor is used under various loading situations with both good and bad bearings, the stator currents of the induction motor are examined and categorized.Theexperimentalresultsvalidatethevalueof thecreatedtechnique,andthesuggestedPNNclassifierhas thecapacitytoclassifythevariousformsofdefectinbearing. When compared to traditional SVM and ANN classifiers, PNN basedmotorbearingdefectidentificationanddiagnosis performsbetter.

Fig 6: EquipmentconnectiontomeasuredFRAformotor windings[7]
Thisapproachhadaphasetophaseturns(PPT)errorinthe TPIM winding [7]. The PPT defect in the TPIM winding causessomefluctuationintheFRAresponse,accordingto thecomparisonoffrequencyresponses(FR).Inpart4,the changes in FRA signatures for windings were understood andexamined.Accordingtoadiscoveryofthisapproach[7], it has been demonstrated that the fluctuation in the FRA responseinphaseswhilemeasuringthefrequencyresponse may be used to diagnose and identify a defect that was caused by a PPT problem. Additionally, this technique [7] offeredtheFRAvalidationatthePPTfaultsituationutilizing one of the NCEPRI algorithm's recognized statistical indicators. Where, according to the assessment factor's computation(E12),thefrequencyregionswiththehighest levels of distortion are those with low and medium frequencyranges.Additionally,thedistortionlevel will be minimal in the high frequency region. The suggested techniquehadanadvantageousoutcome;itmayberegarded as a novel technique for locating and diagnosing the PPT defect in a three phase induction motor. Additionally, the established method's applications may be utilized to diagnoseandfinddifferentkindsofTPIMdefects.
Asynchronousmotorsarewidelyusedinavarietyofsectors. Inductionmotorsarestronganddependable,buttheycan developavarietyofproblems.Inductionmotormalfunctions
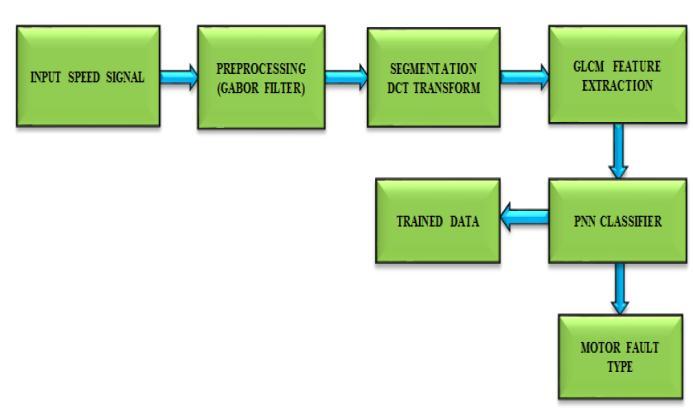
SVM and ANN based classifiers are compared to the PNN classifier'seffectiveness.PNNisnotonlyusefulforanalysing thesituationinwhichadefectoccurred,butitalsospeedsup calculationandproducesaperceptiveconclusionregarding thereasonforspeedexaggeration.Theperformanceindices taken into account for evaluating the performance of the suggested PNN classifier are accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity.TheresultsshowthatPNNclassifiersoutperform ANN and SVM based classifiers in terms of accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity, regardless of the number of pictures.asQ learningisusedtotrainPNN.Itisregardedas one of the key models in the categorization issue. PNN classifier can therefore be utilised to solve future bearing defect detection issues. This suggested approach is highly useful and keeps the speed in a stable condition. It is also crucialforthepowersystem.
It is crucial to predict an induction motor's unknown probleminordertoavoidanunplannedshutdown.Usinga multiclass support vector machine (SVM) and a decision directedacyclicgraph,anunknowninductionmotordefect has been identified and authenticated from other types of
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
failuresinthiscase(DDAG).Inductionmotorswithvarious typesofknownfaultstatesandoneinductionmotorwithan unknowntypeoffaultconditionareusedtoacquirethree phasecurrentdatasamples.Inordertodistinguishthekind of unidentified fault from the mixture of several types of faults, an experiment using motor fault current signature analysis(MFCSA)hasbeenconducted.
Twoeigenvaluesofstatorcurrents,referredtoasprincipal components,areusefulfaultfeaturesofthemotorsthatare captured with the aid of PCA transformation. Principal component analysis (PCA) is a feature extraction and dimensions reduction process that is used to extract information from fault current signature of each faulty motor. One versus. one (OVO) SVM technique is used to nonlinearly separate each pair of classes out of the six classesbyallocatingtheunknowntestsampletotheclass usinganRBFtypekernel.Eachdefectiveinductionmotor's numerous PC values for each phase are grouped together intooneclass.Foreachphase'sn classissue,theOVO SVM buildsn(n 1)/2classifiers,andtheDDAGapproachisused tobuilda directedacyclicgraphutilizing theclassifiers to makeanaccuratedeterminationregardingtheclassification of the unknown defect. According to the maximum membership count produced by classifiers, the unknown faultiscategorizedforeach phaseamongseveral typesof faults,andthefaultisalsovalidatedusingtheDDAGfindings fromthethreestages.
types of malfunctioning induction motors' current signal characteristicsaregroupedintosixdifferenttypesofclasses, andoneunknownkindiscategorizedamongthesixtypes phase wise.
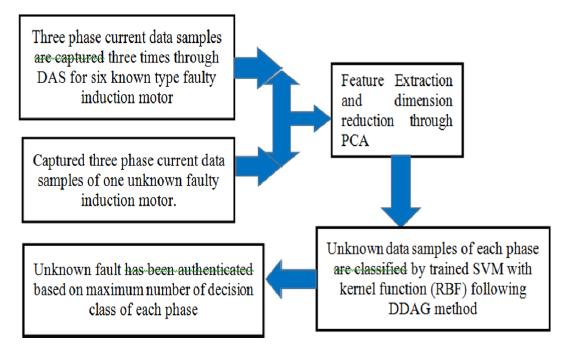
Depending on the (n 1)number ofmembership classesof the DDAG for each of the three phases independently, the unknowntypefaultiscategorizedforeachphaseifthereare nclasses,andtheunknownfaultisauthenticated.TheDDAG approach speeds up pairwise categorization while maintainingtrainingaccuracy.Thisideahasneverbeenused beforetoidentifyaninductionmotordefectofanunknown nature.Anysortofdefect,notjustonespecifickind,canbe categorizedamongtheclassificationsthatarealreadywell established. This study uses six different types of malfunctioninginductionmotors,althoughanyissuemaybe identifiedandvalidatediftherearemorerecognizedclasses than six. There are several restrictions on how faults are classifiedusinglinearseparatinghyperplanes.Theclasses areseparatedusingakernelfunctionthatisRBF basedto getridofthis.Sinceofthedisperseddata,linearseparation ischallengingbecauseitpresentsasignificantclassification challenge. The SVM kernel function converts data from a highdimensionalspaceintotheoriginalfeaturespace.
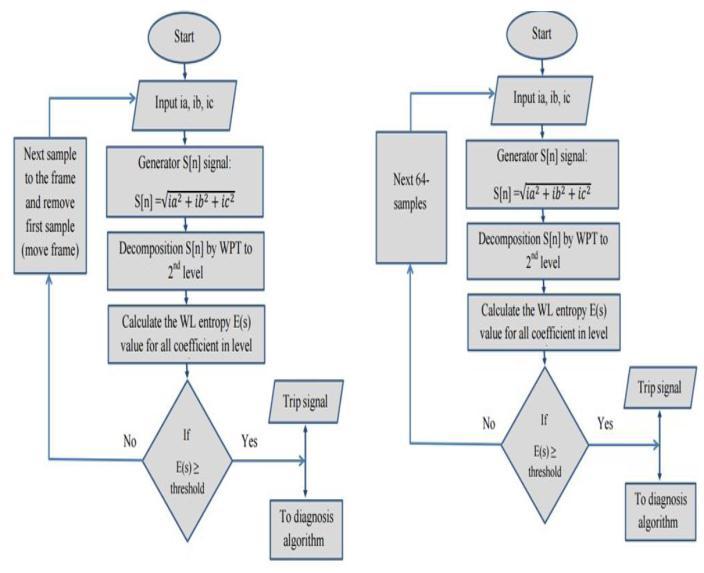
Thisapproach[10]describesaWaveletPacketTransform based fault detection method for three phase induction motors (WPT). The suggested approach uses a frame of samples from an induction motor's three phase supply current.BycalculatingtheRootMeanSquare(RMS)valueof the three phase current samples at each time stamp, the threephasecurrentsamplesarethenmergedtoproducea single current signal. The final step is to partition the obtainedcurrentsamplesintowindowsof64samples.The samples in the resultant window are then processed independently. Non overlapping window samples and moving/overlappingwindowsamplesarethetwostrategies used by the suggested algorithm to construct window samples.Non overlappingwindowsamplesareproducedby simplysplittingthecurrentdatainto64 samplewindows, whereas moving window samples are produced by taking thefirst64currentsamplesandthenrepeatedlymovingthe windowonesampleatatimeacrossthecurrentsamples.
Incontemporaryindustry,determiningthetypeofunknown fault is a difficult process. The purpose of this job is to categoriesandvalidatethekindofunidentifieddefectthat happenedinthemachine,togetherwiththelocationofthe issue. The defect is categorized as a combination of many faulttypes,includingbothelectricalandmechanicalfailures. Six separate defective induction motors' current signals were selected for the investigation because current signature analysis may be used to quickly and cheaply identifybothmechanicalandelectricaldefects.Sixdistinct
The final 63 samples from the previous window plus one additionalsamplemakeupthecurrentwindowofsamples. The defect detection time is decreased to a single sample accuracy by using the overlapping approach. However, it usesmuchmorecomputermemoryandiscomputationally more expensive than the non overlapping technique. The subsequent window samples are handled individually as follows:Eachsamplefromtheresultantwindowissubjected toa two level WPT operationby the suggested technique, whichdividesitscoefficientsintofourwaveletsub bands. The trip signal is then activated to disconnect the motor fromthepowersourceusinginformationfromwavelethigh
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
frequencysub bandsforfaultdetection.TheEntropypower Energy (EE) of the high frequency WPT sub bands' coefficientswasutilizedtoassessthemotor'sconditionafter the suggested technique was initially implemented in the MATLAB environment. The programmed then determines what kind of defect there is if the induction motor has a problem. The suggested algorithm condition was then evaluatedinareal worldsettingwherevariousfailureswere artificially created in the induction motor. The proposed systemwasthenputintoanempiricalconfiguration.
Thesuggestedsystemmayidentifyamalfunction,cutoffthe inductionmotorfromthepowersource,andthenactivatea tripsignaltosafeguardthemotorfrommoreelectricalharm. It was also demonstrated that, while having a larger computational cost and memory utilization than the nonoverlapping technique, a one sample moving window coulddetecttheerrorsignificantlymorequickly.
simulationtechniquesofstatorfaultsareurgentlyrequired. These techniques must take into account nonlinear ties, saturation effects, etc. of magnetic substances and supply anomalies in order to clearly distinguish the relevant frequency components from other components caused by time harmonics, machine saturation, etc. The newest AI approaches for stator fault monitoring and modeling/simulation of defective motors have their own sections. Future developments in the diagnosis of stator faultshavealsobeenexplored.
[1] Maraaba, L., Al Hamouz, Z., & Abido, M. (2018). An efficientstatorinter turnfaultdiagnosistoolforinduction motors. Energies, 11(3),653.
[2]Glowacz,A.,Glowacz,W.,Glowacz,Z.,&Kozik,J.(2018). Early fault diagnosis of bearing and stator faults of the single phase induction motor using acoustic signals. Measurement, 113,1 9.
[3] Solodkiy, E., Dadenkov, D., & Salnikov, S. (2019). Detection of stator inter turn short circuit in three phase induction motor using current coordinate transformation. In 2019 26th International Workshop on Electric Drives: ImprovementinEfficiencyofElectricDrives(IWED) (pp.1 4). IEEE.
[4] Shao, S., Yan, R., Lu, Y., Wang, P., & Gao, R. X. (2019). DCNN based multi signal induction motor fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 69(6),2658 2669.
Fig 9: Threephaseinductionmotorfaultdetectionusing movingframealgorithmandnon overlappingwindow framemethod
The suggested procedure was first tested using an actual motorandtestingapparatus,thenitwasimplemented.The computerresultsandtheexperimentalfindingsonavariety of motors were in agreement. To the authors' knowledge, transmissionlinefaultdetectionhasmadeextensiveuseof theStockwellandHilberttransformstogether.However,asa future improvement to the suggested technique, their applications for defect detection and classification in inductionmotorscanberesearched.
Here is a quick overview of the most common electrical issues that affect induction motors, particularly stator failures,alongwiththemostrecentdevelopmentsintheir detection and diagnosis. To keep up with the most recent developments, more precise and effective modelling and
[5]Glowacz,A.,Glowacz,W.,Kozik,J.,Piech,K.,Gutten,M., Caesarendra, W., ... & Khan, Z. F. (2019). Detection of deteriorationofthree phaseinductionmotorusingvibration signals. Measurement Science Review, 19(6),241 249.
[6]Kumar,R.R.,Cirrincione,G.,Cirrincione,M.,Tortella,A.,& Andriollo,M.(2020).InductionMachineFaultDetectionand Classification Using Non Parametric, Statistical Frequency FeaturesandShallowNeuralNetworks. IEEEtransactionson Energy Conversion, 36(2),1070 1080.
[7] Alawady, A. A., Yousof, M. F. M., Azis, N., & Talib, M. A. (2020).Phasetophasefaultdetectionof3 phaseinduction motorusingFRAtechnique. International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive Systems, 11(3),1241.
[8]HadiSalih,I.,&BabuLoganathan,G.(2020).Induction motor fault monitoring and fault classification using deep learning probablistic neural network. Solid State Technology, 63(6),2196 2213.
[9]HadiSalih,I.,&BabuLoganathan,G.(2020).Induction motor fault monitoring and fault classification using deep
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

learning probabilistic neural network. Solid State Technology, 63(6),2196 2213.
[10] Hussein, A. M., Obed, A. A., Zubo, R. H., Al Yasir, Y. I., Saleh, A. L., Fadhel, H., ... & Abd Alhameed, R. A. (2022). DetectionandDiagnosisofStatorandRotorElectricalFaults for Three Phase Induction Motor via Wavelet Energy Approach. Electronics, 11(8),1253.