International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Adarsh A koushik1, Akash R2, Archana B H3, Likitha V4, Chandru A S5
1Adarsh A Koushik: Student, Dept. of ISE, NIE IT, Mysore, Karnataka, India
2Akash R: Student, Dept. of ISE, NIE IT, Mysore, Karnataka, India
3Archana B H: Student, Dept. of ISE, NIE IT, Mysore, Karnataka, India
4Likitha V: Student, Dept. of ISE, NIE IT, Mysore, Karnataka, India
5Chandru A S (co author): Assistant Professor, Dept. of ISE, NIE IT, Mysore, Karnataka, India ***
Robotics in engineering is fascinating that provides many opportunities for research. In addition, the development of technology in recent years has led to intelligent mobilerobots. They may be sent to hard places instead of people either because they are dangerous or because they are difficult to access. However, controlling theserobotsisadifficulttaskthat involves knowledge in various fields such as robotics, automation, programming, electronics, etc. This project aims to develop a robot that can perform operations such as automatic plowing, seed dosing, fruit picking and pesticide spraying. For manual control, the robot uses a Bluetooth pairing application as a control device and helps to navigate the robot outside the field. Farmers today spendalotofmoney on machines that help them reduce labor and increase crop yields, but the profit and efficiency are very low.
Key Words: Robotics, Farming, Bluetooth, DC motor, Servomotor, automation
Roboticsplaysasignificantroleinagriculturalproduction and management. In agriculture, time saving autonomous technology is needed to make farm management efficient. Researchers are now focusing on various operational parametersofagriculturetodesignautonomousagricultural vehicles, as conventional agricultural machinery is dependentoncropandtopology.Robotslikethesearepretty muchperfectreplacementsforhumanpowerastheydeploy unmannedsensingandmachinesystems.
Theoverallgoalofthisprojectistoprovideasynthesisof research findings on the economics of field crop robotics. The specific objectives were to: a) list and summarize publicly available research on the economics of field crop robotics,b)identifyresearchgapsandneedsrelatedtocrop robotics,andc)suggestresearchtopicsthatrequireurgent attention. This review contributes to the science by summarizing what has been accumulated about the economics of crop robots, proposing mechanisms for how thesefactsfittogether,andidentifyinggapsinthescience.
Primarily,thisstudyfocusesonprofitabilityatthefarm level,sincewithoutprofitability,croppingrobotswillnotbe widelyusedandtheexpectedenvironmental,socialandfood securitybenefitswillnotbeachieved.Whenthebenefitsof potentially profitable autonomous crop technologies were identified,environmental,socialandfoodsecuritybenefits werenoted.
Inthis,robotsareevolvedtoconcentrateeffectivelyand are also anticipated to perform operations autonomously. Theproposedideaimplementsarobottoperformfunctions similar as planting, watering, fertilizing, watching crops. Thesefunctionscanbeintegratedintoonerobotandlatterly performed. The robot is anticipated to perform functions similar as planting, watering, fertilizing, covering, autonomouslyinthefield.
The main goal of agricultural automation knowledge development is to alleviate labor energy. Advances in automation and artificial intelligence offer solutions in precisionagriculture.Workrelatedtoscattering,collection, unwantedplantcontrol.Torestoreeffectiveness.Therobots weredesignedbasedonflexibleautomaticbendingjoints. Instrumentalroboticsapplicationsthataremovingaround the world to cover other fields with robotics required, replacinghumanoperatorsareprovidingefficientresultsin myriad problems with higher competence. The advanced idea of our paper is to automate the process of planting, cultivating, pesticide spraying and tunneling to reduce humanoid effort and increase harvest. Seed cultivation is done robotically using a DC motor. The distance between twoseedsismeasuredandvariedusingamicrocontroller.It is also possible to grow different types of seeds with dissimilarspacing.Theproposedideaincludesasprayerthat wouldservetoreducefertilizerwastage,whichisdoneby sprayingtheappropriateamountoffertilizerrequiredfora particular crop. The process mode can be changed using instructionsexistingintherobotapplication.Anynonlinear relationshipbetweeninputsandoutputsiscontrolledbythis system. The next step is to develop a more advanced GPS systemthatincreasesaccuracy.Thedirectionoftherobot canbecontrolledusingrectangulargeometry
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

1.seeding 2.glass land slicing 3.cultivating 4.reaping 5.shoveling6.pesticidescattering7.monitoring
1. Theautomationdecreasestheagriculturistlabourswith fastspeedbypropagating4discordancesatatimewithline shadowing.firstly,theseedsarestoredinthevesselalsoit willbespreadacrossthefieldwithapplicabledetainmentsas mentionedinthecorrespondingprogram.
2. GrasssliceandunwantedplantjunkingUndesirableplant intheestatedamagesthemaincropandperformanceasa barricade for development of the crop also decreases the yieldofthefield.
3. The main perception of cultivating is to turn over the advanced bed of the slush, transferring superior nutrient contentstothefaceofthesoilandmakingthenutritivesoil forthepurposeofhusbandry.
4. Picking is the act of taking away crop from field it was growing and moving ittoa defended point for processing, nursingorpacking.
5. Diggingisactuallythecombinationoftwoprocesses,the firstbeingthebreakingorcuttingthefaceofthesoilandthe alternatethedumpingandredirectionofthematerialsetup there.
6. In order to give safety to the farmers from fungicide infectionsanditssidegoods,robotswillbereplacingworkers fortheestateexertion.
7. Thisbotalsoincludestimetotimemonitoringofestateand givesecurityalerttoownerincaseofbuttinskypresencein farmland.
Thesefunctionscanbeintegratedintoasinglevehicleand alsobeperformed,whichismoreeffectiveandcosteffective.
• Weedcutter
• Planningplate
• Rotatoryblade
• Flexiblepipe
• IR(8051)SensorandSSTcontroller
• GSM(GlobalSystemforMobileCommunication)
• ControlUnit
• ServoMotors
• Powersupplycircuit
• Perforatedplough
• Watertank
• Submersibleminiwaterpump
• IOTtransmitter&receiver
• OperatingSystem:Windows10
• KeilMicrovision4
• EmbeddedC
• SSTBootstrapLoader
• AndroidSdk
• Eclipse
• EmbeddedJava
• In traditional farming separate machinery need to be usedforeachcultivationalactivitylikerotarytillerfor ploughing,manualseeding,rollersforlevellingthesoil, pumpingwater,weedcuttingmachinerywhichincludes morelabourwork.
• However, in recent years this has been overcome by robotsthatcanperformonlysingleordualtasksbutare notcosteffective.
• Asbetteryieldingforcropsisearnedbyfarmers,there starts the risk of burglar activity which needs to be consideredtosaveone'slivelihood.
• Theproposedideaimplementsthevehicletoperform the functions such as ploughing, seed sowing, mud leveling, creating heap, digging holes, water pumping, pesticide spraying and weed cutting
• Thesefunctionscanbe integrated into a single vehicle andthenbe performed,whichismoreefficientand cost effective.
Thisbotalsoincludestimetotimemonitoringoffarmand provide security alert to owner in case of intruder presenceinfarmland.
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
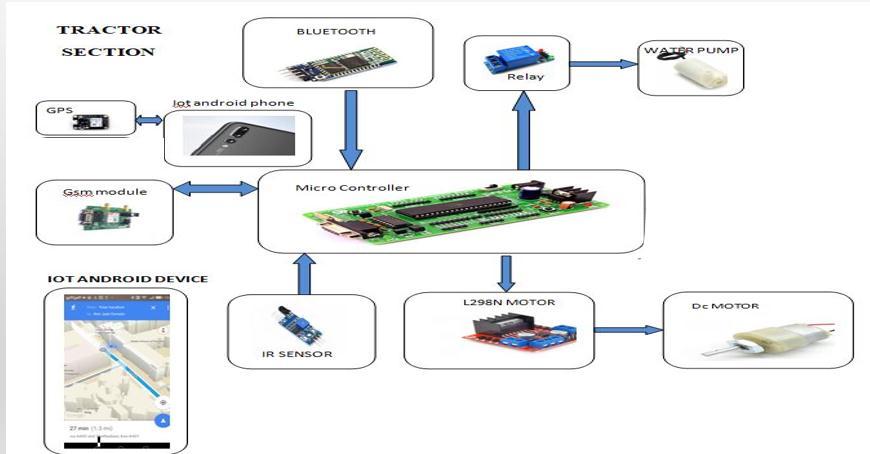
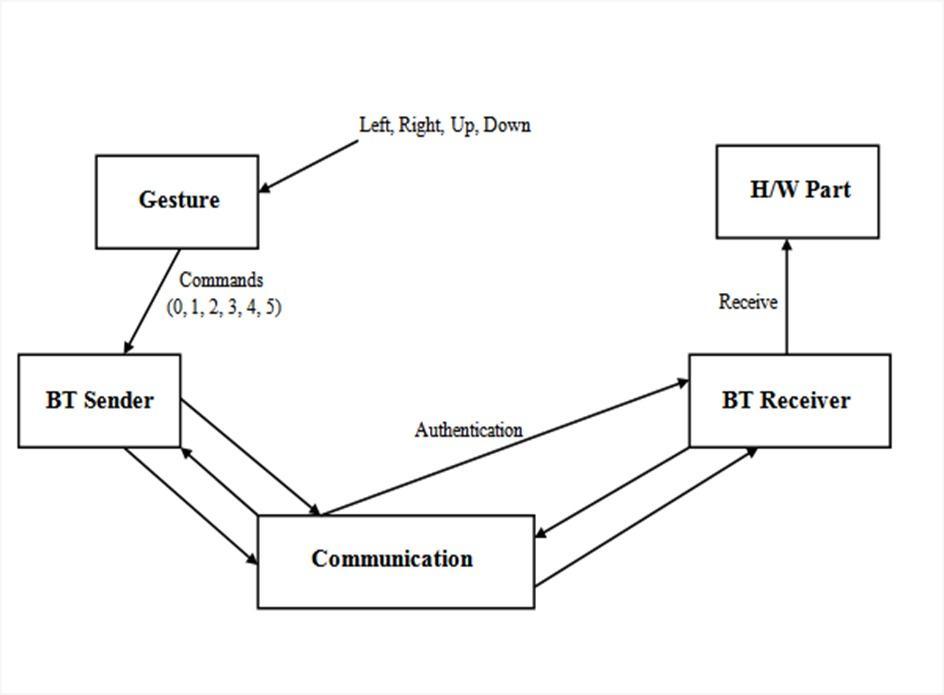
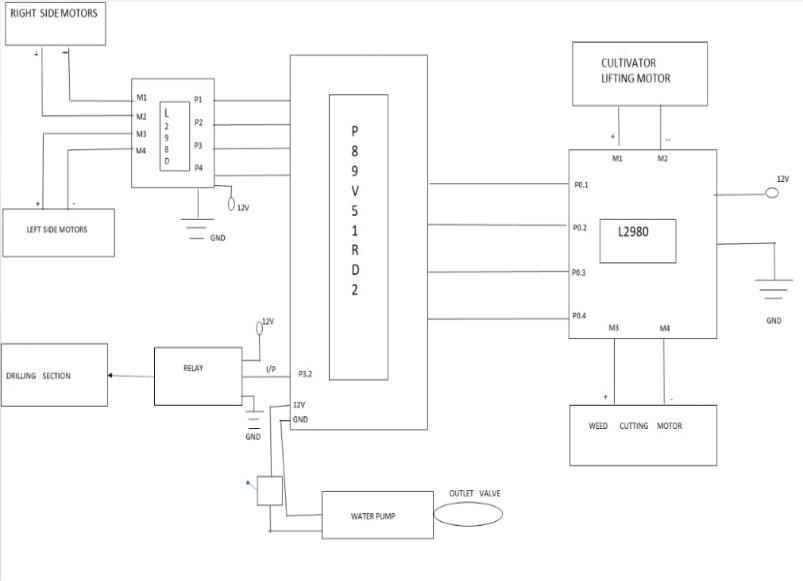
The microcontroller controls the four wheels agribot according to the input from the IR sensor. Android the application takes a command from the user, such as a selection mode (automatic and manual) or what the operationshouldbeperformedandisfurthersenttotheWi Fimodule.Thethecontrollerinturnreceivesthecommand from the Wi Fi module (Esp32866). The microcontroller motordriverisalsousedtoissuecommandstherespective engines that will perform the operations including ploughing,sowing,levelling,wateringandfertilizingcrops.
x Agribot will connect to Wi Fi x Commands will be sent fromthemobileapplicationxAccordingly,thegivenspecific taskwillbeperformed
At the user end, when a person opens the application the Bluetooth will be enabled and the connection will be established.Theusercanselectthepreferredactivityfrom thelistandperformsit.Attheendoftheactivity,theagribot MSP430F5529IPNwillperformactivatetheappropriateDC motorDRV10983QPWPRQ1(30W,20Vautomotive3 phase sensorwithoutBLDCmotordriverwithloadtippingsupport 24 HTSSOP 40 to 125) a the selected operation is performed by the train driver. When MSP430F5529IPN receivestopsignal,activitywillbestopped.
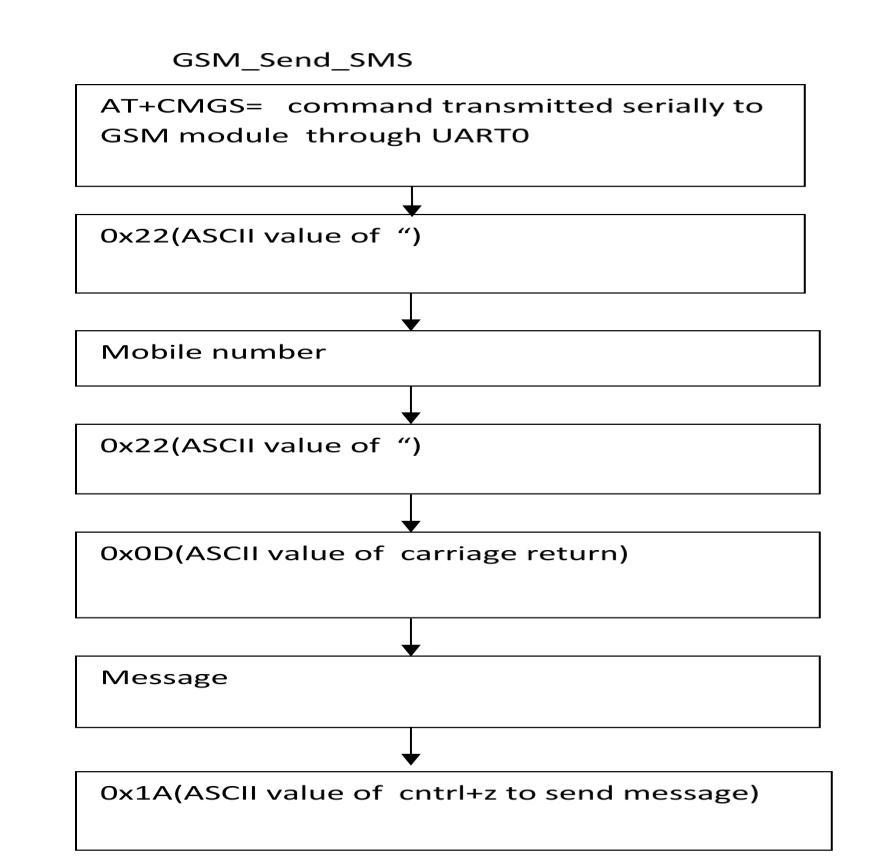
Fig. 4: GSMFlowChart
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
GSM,adigitalmobilecommunicationstandarddevelopedby theEuropeanTelecommunicationsStandardInstitute(ETSI), hasbeenespousedbyfurtherthan100countriesworldwide. GSMstandardoutfit occupiesmorethan80ofthecurrent global cellular mobile communication outfit request. It's presentlythemostextensivelyusedmobilephonestandard. ChinahasestablishedaGSMmobilecommunicationnetwork coveringtheentirecountry.Shortcommunicationservice( SMS)isavalue addedserviceoftheGSMsystem.Itusesthe signaling channel to transmit information, and its transchargemodeistobestoredandencouragedfirst,that is,aftertheshortcommunicationistransferredout,it'llbe stored in the short communication center( SMC) first and also for shielded by SMC to the receiver. SMS are transmittedthroughawirelesscontrolchannel,whichcan be stored and encouraged through SMC. The system of getting SMS about the vehicle position on the mobile outstation is to set up a short communication broadcast monitor on the Android outstation. When a new communicationisreceived,themonitoringsystemcancover the content of the SMS latitude/ longitude that has been formattedonthetackle,parsedit,anduprootedthelatitude andlongitudeinthecontentbyusingthewordhousekeeper acterprisoner.Afterthat,it'spassedtotheexertioninthe displaychart.
ThecommunicationbetweentheGSMmoduleandthemain chip is realized through a periodical harborage, and the programprosecutioninflowisshowninFig.4.
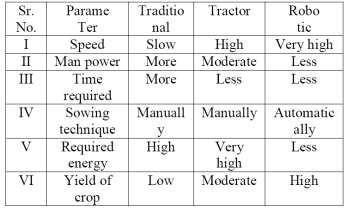

This project is primarily based on minimizing manpower andequipmentcosts.Anattempthasbeenmadetodevelopa Bluetooth controlled agricultural robot that performs ploughing, sowing seeds and levelling mud. The proposed system is powered by a battery and controlled by a Bluetoothdevice.Withthehelpofthisrobot,thefarmercan do other side work in addition to operating the robot. By doing multiple activities simultaneously, a farmer can increase his income, resulting in the development of the Indianeconomy.
Theadvantageofthissystemisthereductionof labourcosts and time. In this work, a robot is built and established to perform automatic and manual sowing, irrigation and fertilizationinthefieldofagriculture.Therobotisexpected tosupportfarmersinmakingtheirfarmsmoreefficient.
Itcanhelpfarmersintheinitialstageoffarming.
[1] Siddharth gupta, pooja a Kulkarni “IoT Based MultipurposeAgribotwithFieldMonitoringSystem”inIEEE on2020
[2]ShwetaMadiwalar,SunitaMeti,NikhilaDomanal,Kaveri ugare "A Survey on Solar Powered Autonomous Multipurpose Agricultural Robot" in IEEE conference on 2020
[3]Dr.ChandaVReddy,AnudheepR,HMVishal,HarshithaS, Sai Spoorthi N "Agro bot" in on International Advanced Research Journal in Science, Engineering and Technology Vol.8,Issue8,August2021
[4] Chandana R, Nisha M, Pavitra B "A Multipurpose Agricultural Robot for Automatic Ploughing , Seeding and Plant Health Monitoring" on IETE 2020 Conference Proceedings
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[5] Arpit Sharma,Reetesh Verma,Saurabh Gupta and Sukhdeep Kaur Bhatia "Android Phone Controlled Robot UsingBluetooth"onInternationalJournalofElectronicand ElectricalEngineering.
[6] Md. Didarul Islam Sujon, Rumman Nasir, Mahbube Mozammel Ibne Habib, Majedul Islam Nomaan, Jayasree Baidya, Md. Rezaul Islam "Agribot: Arduino Controlled AutonomousMulti PurposeFarmMachineryRobotforSmall to Medium Scale Cultivation " on 2018 International ConferenceonIntelligentAutonomousSystems
[7] Akshay Y. Kachor,Ketaki Ghodinde "Design of microcontrollerbasedagribotforfertigationandplantation" oneInternationalConferenceonIntelligentComputingand ControlSystems(ICICCS2019)
[8]GowthamkumarSN,AnandGWarrier,ChiragBShetty, Gerard Elston Shawn D’souza "Multipurpose Agricultural Robot"onInternationalResearchJournalofEngineeringand Technology(IRJET)Volume:06Issue:04|Apr2019
[9] Vishnu Prakash K, Sathish Kumar V, Venkatesh P, Chandran A, “Design and fabrication of multipurpose agricultural robot”, International Journal of Advanced ScienceandEngineering Research,Volume:1,Issue:1,June 2016,ISSN:24559288.
[10]NithinPV,ShivaprakashS,“Multipurposeagricultural robot”,InternationalJournalofEngineeringResearch,ISSN: 2319 6890)(online),2347 5013(print) Volume No.5 Issue: Special6,pp:1129 1254.
[11] Mahesh.R.Pundkar, a seed sowing machinea review, IJESSVolume3,Issue3ISSN:2249.
[12] Mr.Sagar R. Chavan, Prof. Rahul D. Shelke, Prof. ShrinivasR.Zanwar,“Enhancedagricultureroboticsystem”, International journal of engineering sciences & research technology,ISSN:2277 9655.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1155
