International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
M.Yogasundari [1], Dr. N.Mohanapriya[2] , K.Sivapriya[3]
PG Scholar1 , Associate Professor2 , Assistant Professor3 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Vivekanandha College of Engineering for Women ***
ABSTRACT: ThespreadofCOVID 19inthewholeworldhasputthehumanityatrisk.Theresourcesofsomeofthe largesteconomiesarestressedoutduetothelargeinfectivityandtransmissibilityofthisdisease.ThecapabilityofMLmodels to forecast the number of upcoming patients affected by COVID 19 which is presently considered as a potential threat to mankind. In particular, four standard forecasting models, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) Support vectorMachine(SVM)havebeenusedinthisstudytoforecastthethreateningfactorsofCOVID 19.Threetypesofpredictions are made by each of the models, such as the number of newly infected cases, the number of deaths, and the number of recoveries But in the cannot predict the accurate result for the patients. To overcome the issue, Proposed method using the long short termIntegrated Average (LSTIA) predict the number of COVID 19 cases in next 30days ahead and effect of preventivemeasureslikesocialisolationandlockdownonthespreadofCOVID 19.
Keywords: COVID 19, exponential smoothing method, future forecasting, Adjusted R2 score, supervised machine learning
COVID 19, the pandemic that is spreading worldwide, has revealed the vulnerability of human society to severe infectious diseases and the difficulty of solving this problem in a globally interconnected complex system. COVID 19 affected more than 100 countries in a span of weeks. As a result, the whole human race should not only collaborate to overcome the epidemic but also reasonably arrange to return to work and production according to the actual situation of each region and carry out geographical risk assessment. Many attempts have been conducted to find a suitable and fast way to detect infected patients in an early stage. After making chest CT scansof21patientsinfectedwithCOVID19inChina,Guan et al found that CT scan analysis included bilateral pulmonary parenchymal ground glass and consolidative pulmonary opacities, sometimes with a rounded morphology and a peripheral lung distribution. Consequently, COVID 19 diagnosis can be represented as an image segmentation problem to extract the main features of the disease. The disease caused by the novel coronavirus, or Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID 19) is quickly spreading globally. It has infected more than 1,436,000 people in more than 200 countries and territoriesasofApril9,2020.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID 19) is a contagious respiratory and vascular disease, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS
CoV 2). First identified in Wuhan, China, it is currently an ongoing pandemic. Common symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, breathing difficulties, and loss of smell and tasteSymptomsbeginonetofourteendaysafterexposure tothevirus.Whilemostpeoplehavemildsymptoms,some people develop acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which can be precipitated by cytokine storms, multi organ failure, septic shock, and blood clots. Longer termdamagetoorgans(inparticular,thelungsandheart) hasbeenobserved,andthereisconcernaboutasignificant number of patients who have recovered from the acute phaseofthedisease butcontinuetoexperiencearange of effects known as long COVID for months afterwards, including severe fatigue, memory loss and other cognitive issues, low grade fever, muscle weakness, and breathlessness.
Alaa A. R. Alsaeedy, A. A. R., & Chong, E [1] To introduce a new strategy to identify areas with high human density and mobility, which are at risk for spreading COVID 19. Crowded regions with actively moving people (called at risk regions) are susceptible to spreading the disease, especially if they contain asymptomatic infected people together with healthy people. Methods: Our scheme identifies at risk regions using existing cellular network functionalities handover and cell (re)selection used to maintain seamless coverageformobileend userequipment(UE).
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Sear, R. F.,Velasquez, N.,Leahy, R.,Restrepo,N. J., El Oud, S., Gabriel, N., Johnson, N. F. [2] A huge amount of potentially dangerous COVID 19 misinformation is appearing online. Here we use machine learning to quantify COVID 19 content among online opponents of establishment health guidance, in particular vaccinations (‘‘anti vax’’). We find that the anti vax community is developingalessfocuseddebatearoundCOVID 19thanits counterpart,thepro vaccination(‘‘pro vax’’)community.
Hu,S.,Gao,Y.,Niue,Z.,Jiang,Y.,Li,L.,Xiao,X....Yang, G. [3] An outbreak of a novel coronavirus disease (i.e., COVID 19) has been recorded in Wuhan, China since late December 2019, which subsequently became pandemic aroundtheworld.AlthoughCOVID 19isanacutelytreated disease, it can also be fatal with a risk of fatality of 4.03% inChinaandthehighestof 13.04%inAlgeria and12.67% Italy (as of 8th April 2020). The onset of serious illness may result in death as a consequence of substantial alveolardamageandprogressiverespiratoryfailure.
Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Yang, B., Zheng, X., & Chen, M. [4] A Corona Virus Disease 2019(COVID 19) cases in Wuhan were cleared, and the epidemic situation was basically controlled. Such public safety infectious disease includes influences great pressure on the national economy. At present, some countries and regions in the world are still inepidemicsituation,andthereisanurgentneedtojudge theinfectionsituationandtravelriskintheregion.
Abdel Basset, M., Mohamed, R., Elhoseny, M., Chakrabortty,R.K., &Ryan, M [5] Themanycountriesare challenged by the medical resources required for COVID 19detectionwhichnecessitatesthedevelopmentofalow cost,rapidtooltodetectanddiagnosetheviruseffectively foralargenumbersoftests.AlthoughachestX Rayscanis a useful candidate tool the images generated by the scans must be analyzed accurately and quickly if large numbers of tests are to be processed. COVID 19 causes bilateral pulmonary parenchymal ground glass and consolidative pulmonary opacities, sometimes with a rounded morphology and a peripheral lung distribution. In this work, we aim to extract rapidly from chest X Ray images the similar small regions that may contain the identifying featuresofCOVID 19
H. Liu, F. Liu, J. Li, T. Zhang, D. Wang and W. Lan [6] The ongoing outbreak of COVID 19 pneumonia is globally concerning. We aimed to investigate the clinical and CT features in the pregnant women and children with this disease, which have not been well reported. Methods: Clinical and CT data of 59 patients with COVID 19 from
January 27 to February 14, 2020 were retrospectively reviewed, including 14 laboratory confirmed non pregnant adults, 16 laboratory confirmed and 25 clinically diagnosed pregnant women, and 4 laboratory confirmedchildren.
J.Chen,L.Wu,J.Zhang,L.Zhang,D.Gong,Y.Zhao,etal., "Deep learJ. Chen, L. Wu, J. Zhang, L. Zhang, D. Gong, Y. Zhao, et al., [7] The deep learning model showed a comparable performance with expert radiologist, and greatly improved the efficiency of radiologists in clinical practice. For model development and validation, 46,096 anonymous images from 106 admitted patients, including 51patientsoflaboratory confirmedCOVID 19 pneumonia and 55 control patients of other diseases in Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University were retrospectively collected.
F.Shan,Y.Gao,J.Wang,W.Shi,N.Shi,M.Han,etal.,[8] CTimagingiscrucialfordiagnosis,assessmentandstaging COVID 19 infection. Follow up scans every 3 5 days are often recommended for disease progression. It has been reported that bilateral and peripheral ground glass opacification (GGO) with or without consolidation are predominant CT findings in COVID 19 patients. However, due to lack of computerized quantification tools, only qualitative impression and rough description of infected areas are currently used in radiological reports. In this paper,a deeplearning (DL) basedsegmentationsystem is developed to automatically quantify infection regions of interest(ROIs)andtheirvolumetricratiosw.r.t.thelung.
L. Li, L. Qin, Z. Xu, Y. Yin, X. Wang, B. Kong, et al., [9] Coronavirus disease has widely spread all over the world since the beginning of 2020. It is desirable to develop automaticandaccuratedetectionofCOVID 19usingchest CT. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID 19) has widely spreadallovertheworldsincethebeginningof2020.Itis highly contagious and may lead to acute respiratory distress or multiple organ failure in severe cases. On January 30, 2020, the outbreak was declared as a “public health emergency of international concern” (PHEIC) by WorldHealthOrganization(WHO).
T Ai, Z Yang, H Hou, C Zhan, C Chen, W Lv,Q Tao. [10] Chest CT is used in the diagnosis of coronavirus disease2019(COVID 19)andisanimportantcomplement to reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT PCR) tests. A number of cases of “unknown viral pneumonia” related to a local seafood wholesale market were reported in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China. A novel coronavirus (severe acute respiratory syndrome
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
coronavirus 2, or SARS CoV 2) was suspected to be the cause,withPhinolophusbatastheallegedorigin.
Machine learning methods proved to be effective for prediction due to automatically extracting relevant features from the training samples, feeding the activation from the previous time step as input for the current time step and networks self connections. It is a very effective prevention and treatment method to continue to increase investment in various medical resources to ensure that suspected patients can be diagnosed and treated in a timely manner. Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection operators (LASSO), and Support Vector Machine (SVM) thesetwoalgorithmsusedinmachinelearning.
• Data
•
•
•
•
•
The data information includes the cumulative confirmed cases, the cumulative numberofdeaths,newlyconfirmedcases,andthe cumulative number of cured cases provinces. We also used the data on the recent diagnoses in South Korea, Iran, and Italy, it includes the data, andhere,thedatacomesfromofficialnotifications fromvariouscountries.Alldataarefromthedaily case report and the update frequency of data is oneday.
In different control stages, the Basic reproduction number changes greatly and it affectstheintensityofcontroldirectly.Inaddition, the incubation period of the virus affects the speed of transmission directly. These two parameters need to be estimated. Current literature shows that the uncontrolled Basic reproduction. Therefore, we chose the valuation
range in the corresponding range. For the controlled Basic reproduction number, the range ofvaluationwasselectedintherangeof[0,1.5].
The data has been used (when the first caseofCOVID 19wasreportedinIndia)with80% data is used for training and rest 20% for forecastingandvalidationpurposes.Theresulting plotshowingthetotalnumberofconfirmedcases, the observed data is the data used for training purposes, official data (green line) indicates the official data available and forecasted data indicates the forecast of a total number of confirmed cases. From this graph, it is observed that the forecasted number of total confirmed positive cases closely matches with the available officialdata.
Data Preprocessing is a technique that is usedtoconverttherawdataintoacleandataset.The dataset is often incomplete, inconsistent, and/or lacking in certain behaviors or trends, and is likely to contain many errors. Data preprocessing is a proven methodofresolvingsuchissues.
This technique is suitable to use predictive neural networks or characteristic data as such infection event or non event binomial effects. The prediction accuracy of various measurements can be used for different purposes. They include the rate at which normal (non predicted prediction correctly predicts sensitivity (non infectious disease), accuracy (predicted percentage of predicted trend), positive predictive value, negative predictive value (correctly predicted infection rate is)), the ratio is Expected predictions are a measure of the likelihood that the increase in the entire process exceeds the accuracy of theindividual).
The classification technique predicts the targetclassforeachdatasetpoint.Withthehelpofthe classificationapproach,a riskfactorcan beassociated withpatientsbyanalyzingtheirpatternsofdiseases.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
A data driven forecasting/estimation method has been used to estimate the possible number of positive cases of COVID 19 in India for the next 30 days. The number of recovered cases, long short termIntegrated Average (LSTIA) daily positive cases, and deceased cases has also been estimated by using and curve fitting. The effect of preventing measures as social isolation and lockdown has also been observed which shows that by these preventive measures, the spread of the virus can be reducedsignificantly.Althoughthismethodoftenrequires sufficientdatatosupportit,intheearlystagesofepidemic transmission, this method can still be used to more accuratelypredicttheindicatorsofepidemictransmission in the short term, so as to provide intervention control at
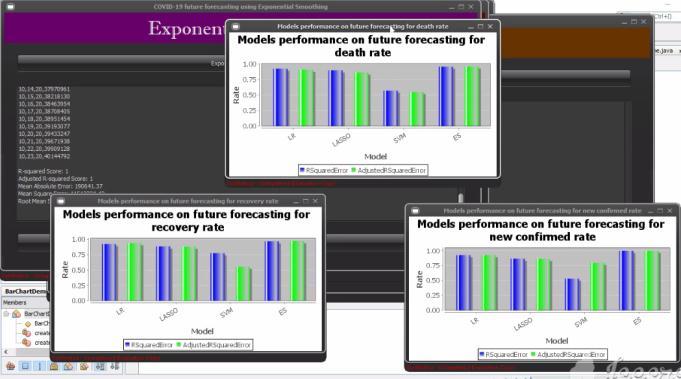
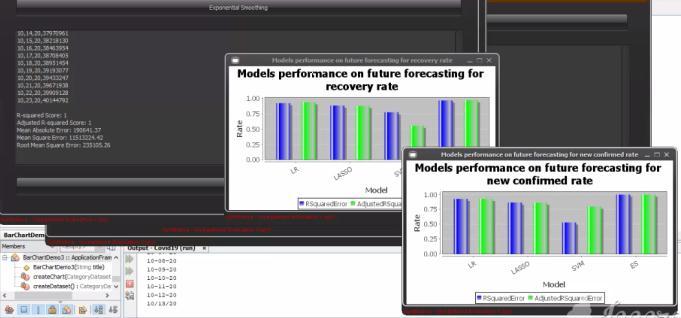
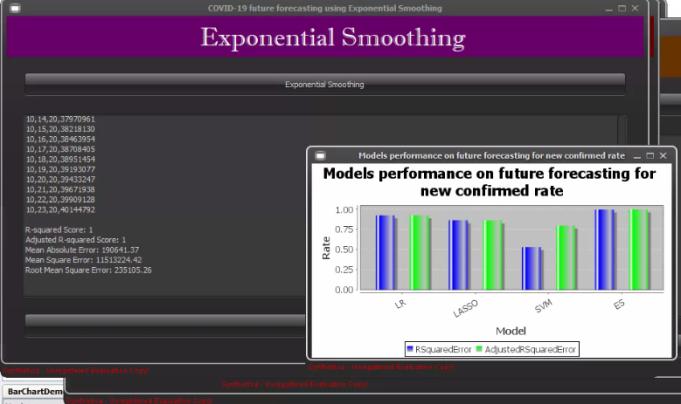
all levels of the departments and policy implementation providesshort termemergency prevention programs. The prediction results of three different mathematical models are different for different parameters and in different regions.Ingeneral,thefittingeffectofLogistic modelmay bethebestamongthethreemodels.
1. Alsaeedy, A. A. R., & Chong, E. (2020).Detecting Regions at Risk for Spreading COVID 19 Using Existing Cellular Wireless Network Functionalities. IEEE Open Journal of Engineering inMedicineandBiology,1 1.
2. Sear, R.F., Velasquez,N.,Leahy,R.,Restrepo,N. J., El Oud, S., Gabriel, N., … Johnson, N. F. (2020).Quantifying COVID 19 content in the onlinehealthopinionwarusingmachinelearning. IEEEAccess,1 1.
3. Hu, S., Gao, Y., Niu, Z., Jiang, Y., Li, L., Xiao, X. … Yang, G. (2020).Weakly Supervised Deep Learning for COVID 19 Infection Detection and ClassificationfromCTImages.IEEEAccess,1 1.
4. Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Yang, B., Zheng, X., & Chen, M. (2020).Risk Assessment of COVID 19 Based On Multisource Data from a Geographical View. IEEE Access,1 1.
5. Abdel Basset, M., Mohamed, R., Elhoseny, M., Chakrabortty, R. K., & Ryan, M. (2020).A hybrid COVID 19 detection model using an improved marine predator’s algorithm and a ranking based diversityreductionstrategy.IEEEAccess,1 1.
6. F.PetropoulosandS.Makridakis,“Forecastingthe novel coronavirus covid 19,”Plos one, vol. 15, no. 3,p.e0231236,2020.
7. G. Grasselli, A. Pesenti, and M. Cecconi, “Critical care utilization for the covid 19 outbreak in lombardy, italy: early experience and forecast duringanemergencyresponse,”Jama,2020.
8. C. P. E. R. E. Novel et al., “The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (covid 19) in china,” Zhonghua liu xing bing xue za zhi= Zhonghua liuxingbingxuezazhi,vol.41,no.2,p.145,2020.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

9. Y.Grushka CockayneandV.R.R.Jose,“Combining prediction intervals in the m4 competition,” InternationalJournalofForecasting,vol.36,no.1, pp.178 185,2020.
10. N.C.Mediaite.Harvardprofessorsoundsalarmon ‘likely’ coronavirus pandemic: 40% to 70% of world could be infected this year. Accessed on 2020.02.18. [Online]. Available: https://www.mediaite.com/news/harvardprofess or sounds alarm on likely coronavirus pandemic 40 to 70 ofworld could be infected this year/.