Identification of Microbe Disease Association

Abstract There are countless microbes in the human body which are closely related to human life activities and human diseases and they play various roles in the physiological process. There is growing evidence that microbes are closely associated with human diseases. Research of disease related microbes helps us understand the mechanisms of diseasesand provides new strategies for diseases diagnosis and treatment. However, traditional biological experiments are time consuming andexpensive, so it has become a research topic in bioinformatics to predict potential microbe disease associations by adopting computational methods.Thedataset used is Human Microbe Disease Association Database (HMDAD). The model is divided into data preparation, integrating the data, eigenvalue decomposition, training the model and sorting the samples. The computation model uses node similarity information, eigen decomposition, k means clustering, decisiontree classifier to score the microbe disease association. To assess the prediction ability of the model leave one out cross validation method is used. The results indicate the reliable capability for inferring the most possible microbe disease associations.Therefore,themodelachievesa superior performance compared with other approaches
Key Words: Microbe, disease, microbe-disease association, node information, link propagation, association prediction, decision tree
1. INTRODUCTION
Microorganismshavebeenwidelyfoundintheoceans,soils, human bodiesandotherplaces,and their existences have profound impacts on human life. With the rapid developmentofhigh throughsequencingtechnologiesand modern bio informatics, researches on microbiology have attractedincreasingattentionfromthescientificandmedical communities.Meanwhile,microbesparticipateindifferent levels of metabolic activities in the human body and are interdependent with the host. Therefore, the health of humanmicrobiomeinhumanbodyisanimportantfactorfor humanhealth.Onthesurface,humanlifeactivitiesdepend on microorganisms, but the hosts and their living environmentalwaysaffectthesurvivalofmicroorganisms. Forexample,theuseofantibioticsandwestern stylehigh fat dietsmayaltermicrobialcomposition.
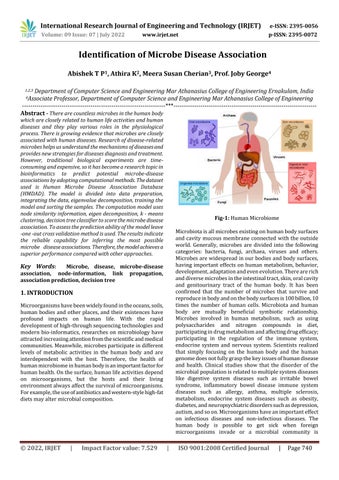
Fig 1: HumanMicrobiome
Microbiotaisallmicrobesexistingonhumanbodysurfaces andcavity mucous membrane connected withthe outside world. Generally, microbes are divided into the following categories: bacteria, fungi, archaea, viruses and others. Microbesarewidespreadinourbodiesandbodysurfaces, having important effects on human metabolism, behavior, development,adaptationandevenevolution.Therearerich anddiversemicrobesintheintestinaltract,skin,oralcavity and genitourinary tract of the human body. It has been confirmed that the number of microbes that survive and reproduceinbodyandonthebodysurfacesis100billion,10 times the number of human cells. Microbiota and human body are mutually beneficial symbiotic relationship. Microbes involved in human metabolism, such as using polysaccharides and nitrogen compounds in diet, participatingindrugmetabolismandaffectingdrugefficacy; participating in the regulation of the immune system, endocrine system and nervous system. Scientists realized that simply focusing on the human body and the human genomedoesnotfullygraspthekeyissuesofhumandisease and health. Clinical studies show that the disorder of the microbialpopulationisrelatedtomultiplesystemdiseases like digestive system diseases such as irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease immune system diseases such as allergy, asthma, multiple sclerosis, metabolism, endocrine system diseases such as obesity, diabetes,andneuropsychiatricdisorderssuchasdepression, autism,andsoon.Microorganismshaveanimportanteffect on infectious diseases and non infectious diseases. The human body is possible to get sick when foreign microorganisms invade or a microbial community is
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
imbalanced. For example, there are more abundant Fusobacterium in asthmatic patients than healthy people. Lecithinase negativeClostridiumandLactobacillusaremuch more in colorectal carcinoma patients. Increased Lactobacilluscanresultintertiarylymphoid.Alltheabove reportssuggestedthattherearecloseassociationsbetween microbes and human diseases. Therefore, finding new Microbe Disease Associations helps to provide diagnostic andtherapeuticcluesforclinicalresearches.Asmentioned, identifying potential associations between microbes and diseases has a long term theoretical and practical significance not only for better understanding of disease formation and development mechanisms but also for discoveryofnovelmedicalsolutionsfordiseaseprevention, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. However, current amountandqualityofknownmicrobediseaseassociations arefarfromsatisfyingtherequirementsofmedicalresearch. Intraditionalway,researchersattempttoobtainnewMDAs bybiologicalorclinicalexperiments,whichdemandalarge quantity of time and cost. With the rapid development of computertechnology,moreandmorecomputationalmodels have been developed to predict potential miRNA disease associations, potential lncRNA disease association and potential drug target interactions, where machine learning basedandsimilaritymeasure basedmodelshave showntheiroutstandingpredictionability.So,itisessential to logically extend these prediction methods into microbe diseaseassociationprediction field.Therefore,a deeper understanding of microbe related pathological relationshipsmayprovide new ideasforthe study of new treatmentandpreventionstrategiesfordiseases,aswellas promoteglobalhumanhealth.
2. RELATED WORKS
2.1 Back Propagation Neural Network Model
The Back Propagation Neural Network is one of the most popular models and is widely applied to prediction and classificationproblems.Theaimofthismethodistodesigna novel BPNN model for microbe disease association prediction. Therefore, a 3 layer BPNN with 292 nodes per layerisconstructed[4],inwhich,theinformationofknown associationsbetweeneachmicrobeandalldiseaseswouldbe usedastheinputsignalsofcorrespondingnodesintheinput layer.Next,anewactivationfunctiontoactivatethehidden layerandtheoutputlayerbasedonthehyperbolictangent functionisdesigned.Thereafter,theweightsandnodebiases oftheBPNNwouldbecontinuouslyupdatedduringtheback propagation process until the whole network reaches convergent state. The proposed model consists of three layers including the input layer, the output layer and the hiddenlayer.Thedatasetconsistsof292microbesand39 diseaseswhichareobtainedfromHMDADdatabase.Hence, theinputdatatothenetworkis292∗39dimensionalmatrix. An adjacency matrix A represents the known microbe disease association. The method for controlling a neural
value:
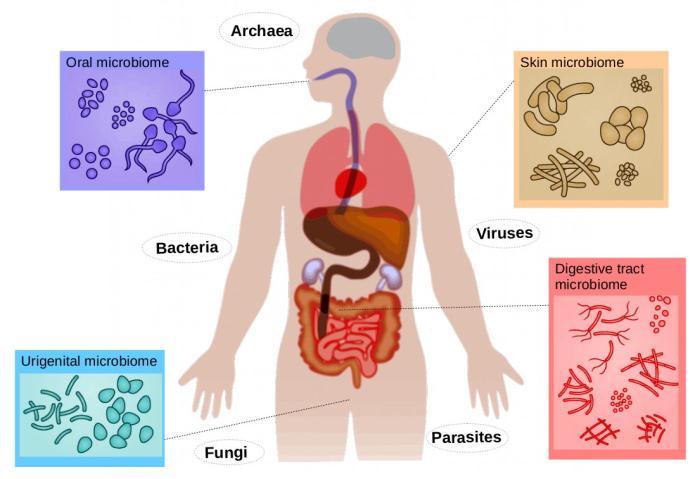
networkistosetandadjustitsconnectionweightsandnode biases.Traditionally,initialweightsaresettorandomvalues whichwillhaveadirecteffecttothetrainingefficiencyand convergence speed. Hence, Gaussian Interaction Profile kernelsimilarityisusedtooptimizetheinitialweightandto obtainsimilaritymatrixSM wheremi andmj areithandjthmicrobeinSM.IP(mi)and IP(mj)aretheithandjthrowintheadjacencymatrix.where γ ′ m is the parameter for Gaussian kernel bandwidth.
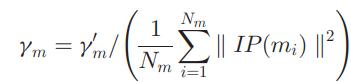
Based on similarity matrix SM, two identical initial weight matricesW[1] andW[2] canbeconstructed. Hence, W[1](i,j) is the weight between the ith node of the inputlayerandthejthnodeofthehiddenlayerandW[2](i,j)is theweightbetweentheithnodeofthehiddenlayerandthe jth node of the output layer. The bais to each node for its higher activity is set to a random value between [−ρ, ρ] initially.
Anewactivationfunctiontoactivatethehiddenlayerand theoutputlayerbasedonthehyperbolictangentfunctionis designed. Thereafter, the weights and node biases of the BPNN would be continuously updated during the backpropagation processuntil thewholenetwork reached convergent state. And then, based on the outputs of the convergent network, a microbe disease correlation score matrixcouldbeobtained.
TheGIPsimilaritywasusedtooptimizeinitial connection weights of BPNNHMDA, although it could improve the trainingprocess,butitfixedtheconvergentdirectionofthe neural network which means that some poorly optimized weightsmaynotbeconducivetoeffectivepredictionofsome potential microbe disease associations. In addition, the learningrateofBPNNwasfixedinBPNNHMDA,whichwas not conducive to the training process either. Conservative and small learning rate would reduce the training speed, whilelargelearningratemaymaketheneuralnetworkmiss theoptimalerror.Therefore,itisnecessarytoimprovethe adaptivechangeabilityoflearningratetoreducethetraining timeandimprovethepredictionperformanceofBPNNHMDA infuture.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
2.2 Bipartite Network Model
A bipartite network to predict potential microbe disease interactionsbasedonknownmicrobe diseaseassociations only.Theassumptionconsideredinthismethodistwonodes aresimilariftheyhavecommonneighborsorareconnected to similar nodes. Three datasets from the LncRNADisease database, Lnc2Cancer database and MNDR database were collected.
LetLbeasetoflncRNAsandDbeasetofdiseasesthen,the L DnetworkcanbedescribedasabipartitegraphG(L,D,E) where E is set of edges[14]. An adjacency matrix A is constructed to show the similarity between lncRNA and diseases.
Using the power law distribution, the similarity between microbesnodesareobtainediftheyhavecommonnieghbors and disease nodes as well. If they do not have common neighborsthenifthenodesareconnectedtosimilarnodes using SimRank method their similarity can be obtained. Finally, by integrating both the methods and adjacency matrixarecommendationmatrixcanbecalculatedforboth microbe and disease, then again by integrating two recommendationmatrixthemicrobe diseaseassociationcan beinferred.
2.3 Laplacian Regularized Least Squares Method
Similar diseases tend to be associated with functionally similarlncRNAs.Basedonthis,selectinglncRNAsthatarenot relatedtothegivendiseaseisdifficultorevenimpossible,so a computational model of Laplacian Regularized Least Squares for LncRNA Disease Association in the semisupervised learning framework was developed. This method prioritizes the entire lncRNAome for disease of interestbyintegratingknownphenome lncRNAomenetwork obtained from the database of LncRNADisease, disease similarity network and lncRNA similarity network. It is a global approach that can rank candidate disease lncRNA pairsforallthediseasessimultaneously.
2.4 Inductive Matrix Completion Model
Anovelmatrixcompletion basedmodelnamedIMCMDAfor miRNA disease associations prediction. This model of IMCMDA[6] was implemented based on the known miRNA disease associations, disease semantic similarity, miRNA functional similarity, Gaussian interaction profile kernelsimilarityformiRNAsanddiseases.
Thedataof knownhumanmiRNA diseaseassociationswere retrieved from the HMDD V2.0 database and a nd × nm adjacencymatrixAwasdefinedasA(d(i),m(j))=1ifdisease d(i) hasassociationwithmiRNAm(j) elseA(d(i),m(j))=0. The miRNA functional similarity was calculated based on assumptionthatfunctionallysimilarmiRNAstendtocause similardiseases.Thedatasetwastakenfromcuilabandanm
value:
*nmmatrixFStorepresentthemiRNAfunctionalsimilarity constructed in which element FS(m(i), m(j)) denotes the functionalsimilaritybetweenmiRNAm(i)andm(j).
Inthismodel,theknownmicrobe diseaseassociationsand theintegratedmicrobesimilarityanddiseasesimilarityare combinedtocalculatethepredictionscoreofeachmicrobe disease pair. IMCMDA predicts the microbe disease associations by using the low rank inductive matrix completionalgorithm.AcrucialadvantageofIMCisthatit utilizes disease similarity and microbe similarity as the feature of disease and microbe to complete the missing microbe diseaseassociation.Itmeansthatusingthefeature vectorofanewdiseasewithoutanyknownrelatedmicrobes topredicttherelevance scoresbetweenthisnewdiseaseand allmicrobes.Inaddition,searchingtheoptimalsolutionwith an alternating gradient descent algorithm made sure the reliability of the disease eigenvectors and the microbe eigenvectors.Thus,themodelisasemi supervisedmodel. The advantage of semi supervised model is that it doesn’t relyonnegativesamples.Itonlyneedspositivesamplesand unlabeled samples, which greatly reduces the difficulty of buildingmodels.
3. BACKGROUND
3.1 HMDAD Dataset
The Human Microbe Disease Association Database is a resourcewhichcollectedandcuratedthehumanmicrobe diseaseassociationdatafrommicrobiotastudies.Afterdata processing, 450 high qualityknown associations including 292 microbes and 39 diseases have been obtained. The datasetcontainsvariousparametersbutforthepurposeof determining the association, microbes and disease are encodedtonumbersandknownassociationsisreplacedwith respective numbers of microbes and disease, hence parametersarediscarded.
3.2 K means Clustering
K Means Clustering is an unsupervised learning algorithm that is used to solve the clustering problems in machine learningordatascience.Itgroupstheunlabeleddatasetinto differentclusters.tallowsustoclusterthedataintodifferent groupsanda convenientwaytodiscoverthecategories of groupsintheunlabeleddatasetonitsownwithouttheneed foranytraining.Itisacentroid basedalgorithm,whereeach cluster is associated with a centroid. The main aim of this algorithmistominimizethesumofdistancesbetweenthe datapointandtheircorrespondingclusters.Thealgorithm takestheunlabeleddatasetasinput,dividesthedatasetinto k numberofclusters,andrepeatstheprocessuntilitdoesnot findthebestclusters.Thevalueofkshouldbepredetermined inthealgorithm.
Theworkingofk meansalgorithmincludeselectionofthe numberKtodecidethenumberofclusters,selectrandomK
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
points or centroids it can be other from the input dataset. Assigneachdata pointtotheirclosestcentroid,whichwill formthepredefinedKclusters,thencalculatethevariance andplaceanewcentroidofeachcluster.Repeatthese,which meansreassigneachdatapointtothenewclosestcentroidof eachcluster.Ifanyreassignmentoccurs,thenagainreassign eachdatapointtoclosetcentroidelsefinishandthemodelis ready.
4. Implementation
Inthissection,theproposedmethodisimplementedonthe HMDAD dataset. The studies were carried out using the Google colab environment that supports python programminglanguagewithvariousmodulessuchasnumpy, math.Scikit learn library which provides a selection of efficienttoolsformachinelearningandstatisticalmodeling includingclassification,clustering.
5. DATA PREPARATION
AnadjacencymatrixAcanbeobtainedfromHMDADdataset by extracting 450 known associations. If there is a known associationbetweendiseased(i)andmicrobesm(j),thenthe value of the element A(d(i),m(j)) is 1 else 0. nd and nm representsthenumberofdiseaseandmicrobesconsidered Thisservesasinputforfurtherprocessing.
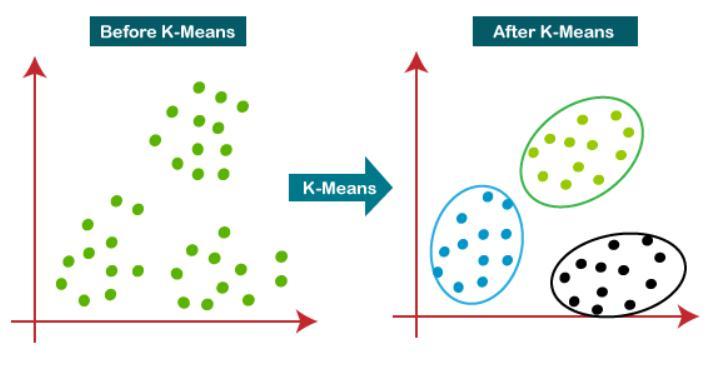
6. Node Similarity Information Measurement
3.3 Decision Tree Classifier
DecisionTreeLearningissupervisedlearningapproachused in statistics, data mining and machine learning. In this formalism,aclassificationorregressiondecisiontreeisused as a predictive model to draw conclusions about a set of observations.Treemodelswherethetargetvariablecantake adiscretesetofvaluesarecalledclassificationtrees;inthese tree structures,leaves represent classlabelsand branches represent conjunctions of features that lead to those class labels. Decision trees where the target variable can take continuous values (typically real numbers) are called regressiontrees.Decisiontreesareamongthemostpopular machine learning algorithms given their intelligibility and simplicity.
Indecisionanalysis,adecisiontreecanbeusedtovisually and explicitly represent decisions and decision making. In datamining,adecisiontreedescribesdatabuttheresulting classificationtreecanbeaninputfordecisionmaking.So,the ultimategoalistocreateamodelthatpredictsthevalueofa targetvariablebasedonseveralinputvariables.
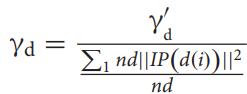
3.4 Eigenvalue Decomposition
Inlinearalgebra,eigendecompositionisthefactorizationofa matrix into a canonical form, whereby the matrix is represented in terms of its eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Onlydiagonalizablematricescanbefactorizedinthisway. When the matrix being factorized is a normal or real symmetric matrix, the decomposition is called “spectral decomposition”,derivedfromthespectraltheorem.Inother words,thistechniquedecomposesacomplexmatrixintoits eigen vectors and values, thus reduces the complexity in computation.
Consideringtheassumptionthatiftwosimilardiseaseswere associatedwithtwomicrobes,respectively,thetwomicrobes werelikelytobesimilar,andthereweresimilarinteraction andnon interactionpatternbetweendiseasesandmicrobes, GaussianinteractionprofilekernelsimilarityfordiseaseKD was constructed to indicated the similarities between diseasesbasedontheknownassociationsofdisease microbe pairs.
value:
whereγ′d=1
To effectively and scientifically predict potential microbe diseaseassociation,itisnecessarytointroduceotherdatasets with theGaussian interaction profilekernel similarity. For this, symptom based human disease dataset from HSDN takenandintegratedtheGaussianinteractionprofilekernel similarity for disease KD and the symptom based disease similarity SDM to obtain the Integrated symptom based diseasesimilaritySD.SDcanbecalculatedusing
SD=(KD+SDM)/2
ThesimilaritymatrixSm betweenmicrobesisalsofindthe sameGIPkernelsimilarityasusedfordiseasesimilarity.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
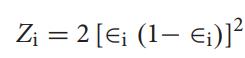
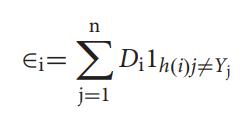
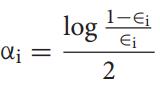
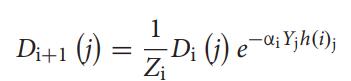
7. Eigenvalue Decomposition
Eigenvalue decomposition technique is used to reduce the largeamountofmemoryandtimeoverheadisrequiredinthe inverseoperationofthematrix.SmandSdisarealsymmetric matrix,theeigenvaluedecompositiontechniqueisusedhere toimprovethecomputationalefficiency.Sm =RmΛmRmTand Sd = RdΛdRdT are eigenvalue decomposition of Sm and Sd where Rm and Rd are eigen vectors; Λm and Λd are eigen values.
8. TRAINING THE MODEL
Themainideaofmethodistotraindifferentclassifierswhich areweakclassifiersforthesametrainingsamples,andthen groupedtheseweakclassifierswithdifferentratiostoforma strongerclassifiertoscoreandsortsamples.Decisiontreeis usedasweakclassifier.
Thesamplewithconfirmedassociationasapositivesample, else unknown sample. Since there are more unknown samplesthanpositivesamples,anditwasunreasonableto directlytrainsuchunbalanceddatasets.Anovel methodis usedtobalancethedatasetswhichusesk meansclustering to divide the unknown sample into k parts, and then randomlyextractsomesamplesfromeachpartasnegative samples,whilepositivesampleskeptunchanged.Inorderto make the dataset more balanced for effective training, the numberoftheunknownsamplesrandomlyselectedmustbe approximately equal to the positive sample. Thus, the negative and positive samples together form the training samples.Eachtrainingsamplewasweightedwithaninitial weight of 1/n, where n is the total number of training samples. The main purpose of the training process is to calculatetheproportionofeachweakclassifierinthefinal strong classifier and update the weight of each training sampleaccordingtowhetheritwasclassifiedcorrectlybythe lastclassifierandtheoverallclassificationaccuracyofthelast classifier.Afterupdating,thenewtrainingsamplesetwith modifiedweightvalues,itissenttothenextweakclassifier fortraining.
Three lists DI, h(i),Y with nelementsisbuilt.Thevalueof eachelementinDI istheweightofthecorrespondingsample whentheithweakclassifiertrainedthesample.Thevalueofi was 0, 1, 2, , , , 29. In other words,D0 was a list with all elementsbeing1/n.Theelementsinlisth(i)andYcantake thevalueeither0or1thatdependsonthepredictionofthe ithweakclassifierandthecorrespondingsampleispositive ornot.
Theerrorfunctionϵi isgivenby
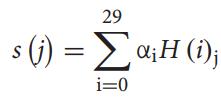
Theerrorfunctionϵiisequaltothesumoftheweightsofthe samples,whoselabelpredictedbytheweakclassifierh(i)jis differentfromtheknownlabelYji.e;ϵiisequaltothesumof theweightsofallthesamplesthatwerepredictedwrongand the prediction matrix P contains the strength between diseaseiandmicrobej.
The proportion of the ith weak classifier in the strong classifierisdefinedas Hence,itisinferredthatthesmallertheerrorfunctionis,the larger will be the proportion of the weak classifier in the strongclassifier.
ThevariateZiiscalculatedusingtheerrorfunction.
TheweightofthesampleDi+1(j)isupdatedusingtheprevious weight
Aftertheweightsofsamplesbeingupdated,thesampleswith thenewweightsweresenttothenextweakclassifiertostart thenexttraininguntilalltheweakclassifierscompletedthe training.Here30weakclassifiersareusedforreducingthe predictiontimeandtoincreasetheaccuracy.
Thescoreofthejthsample
whereH(i)jisthescoreobtainedbytheithweakclassifierfor thejthsamplei.e;thescoreofthesampleisequaltothesum oftheproductofthesample’sgoalscoredbyweakclassifier andthecorrespondingweight.
9. RESULT
The proposed model uses node information based Link Propagation for Human Microbe Disease Association prediction to prioritize the most possible disease related microbes.NodesimilarityinformationthatcontainsGaussian profile kernel similarity and characterstics of disease
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

symptom,hasbeenintegratedtopromotestrongassociations betweenthemostlikelynodesthroughlinkpropagation.The modelistrainedusingk meansclusteringandDecisiontree classifier.ThetechnologyofEigenvaluetransformationhave been adopted to simplify the solving process of the model.Leave one outcrossvalidationmethodisappliedto assess the prediction ability of the model.The model accurately calculates the score between microbe disease association which helps to determine the most potential microbethatcausesthedisease.
The accuracy of the proposed model is found to be 87.69 %.The LOOCV value of KATZHMDA and LRLSHMDA are 0.6998and0.7508respectively.Theseresultsconfirmedthe superiorpredictionperformanceoftheproposedmodel.
10. FUTURE RESEARCH
In future, the relationships between diseases and other moleculecanbediscovered,makeacomprehensiveanalysis ofthediseases.Theimprovingpredictionperformanceofthe proposed method compared to previous approaches, it is expectedthatthepredictionabilitywillbefurtherimproved if a more comprehensive similarity calculation method is takenintoconsideration.
11. CONCLUSION
The prediction of microbe disease association serves as a biomarker detection and drug discovery for disease diagnosis,treatment,prognosisandprevention.Thedatasets used by the model were relatively reliable. The potential similarities for diseases and microbes through Gaussian interaction profile kernel similarity were extracted, eigen decomposition reduces the computational complexity and multipleweakclassifierscombinedintoonestrongclassifier accordingtodifferentweightstoscorethesamples.Thehigh precision weak classifiersaccounted fora high proportion whichimprovetheaccuracyofthestrongclassifier.
REFERENCES
[1] Prioritizing Human Microbe Disease Associations Utilizing a Node Information Based Link Propagation Method LI PENG 1 , DONGZHOU 1 , WEI LIU2 , LIQIAN ZHOU3,LEIWANG4,BIHAIZHAO4,ANDJIALIANGYANG 5,IEEEAccess,Volume8,2020.
[2]HumanMicrobe DiseaseAssociationPredictionBasedon AdaptiveBoostingLi HongPeng1†,JunYin2†,LiqianZhou1 ,Ming XiLiu3*andYanZhao2*.
[3] A Novel Method for LncRNA Disease Association PredictionBasedonanlncRNA DiseaseAssociationNetwork Pengyao Ping, Lei Wang , Linai Kuang , Songtao Ye , MuhammadFaisalBulandIqbal,andTingruiPei,IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY AND BIOINFORMATICS,VOL.16,NO.2,MARCH/APRIL2019.
[4] Identifying Microbe Disease Association Based on a NovelBackPropagationNeuralNetworkModel,HaoLi,Yuqi Wang , Zhen Zhang , Yihong Tan , Zhiping Chen , Xiangyi Wang,TingruiPei,andLeiWang,IEEE/ACMTRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTATIONAL BIOLOGY AND BIOINFORMATICS, VOL.18,NO.6,NOVEMBER/DECEMBER2021.
[5] Novel human lncRNA disease association inference basedonlncRNAexpressionprofilesXingChen1,2,*andGui YingYan1,2.
[6]PredictingmiRNA diseaseassociationbasedoninductive matrixcompletionXingChen1,*,LeiWang1,JiaQu1,Na Na Guan2,Jian QiangLi2.
[7] Link Propagation: A Fast Semi supervised Learning Algorithm for Link Prediction Hisashi Kashima Tsuyoshi Kato† Yoshihiro Yamanishi‡ Masashi Sugiyama• Koji Tsuda¶.
[8] A New Link Prediction Algorithm: Node Link Strength Algorithm Yin Guisheng1 , Yin Wansi2 , Dong Yuxin3 Department of Computer Science and Technology Harbin EngineeringUniversityHarbin,China
[9]Aneigenvaluetransformationtechniqueforpredicting drugtarget interaction Qifan Kuang1 , Xin Xu3 , Rong Li2 , Yongcheng Dong3 , Yan Li1 , Ziyan Huang1 , Yizhou Li1 MenglongLi1.
[10]FastandScalableAlgorithmsforSemi supervisedLink PredictiononStaticandDynamicGraphsRudyRaymond1 andHisashiKashima2.
[11] RNMFMDA: A Microbe Disease Association Identification Method Based on Reliable Negative Sample Selection and Logistic Matrix Factorization With Neighborhood Regularization Lihong Peng, Ling Shen, LongjieLiao,GuangyiLiuandLiqianZhou*.
[12] Integrating random walk and binary regression to identify novel miRNA disease association Ya Wei Niu1 , Guang HuiWang1*,GuiYingYan2andXingChen3*.
[13]ARobustAlgorithmBasedonLinkLabelPropagation for Identifying Functional Modules from Protein protein Interaction Networks Hao Jiang, Fei Zhan, Congtao Wang, Jianfeng Qiu, Yansen Su, Chunhou Zheng, Xingyi Zhang, SeniorMember,IEEE,andXiangxiangZeng.
[14]BPLLDA:PredictinglncRNA DiseaseAssociationsBased onSimplePathsWithLimitedLengthsinaHeterogeneous NetworkXiaofangXiao1†,WenZhu2†,BoLiao1,2*,Junlin Xu1,ChanglongGu1,BinbinJi2,YuhuaYao2,LihongPeng3 andJialiangYang2,4
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page745