International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
2
, Swathi Sridharan1VIII Semester, Dept. of ISE, BNMIT
2VIII Semester, Dept. of ISE, BNMIT
3
3Assistant Professor, Dept. of ISE, BNMIT, Karnataka, India ***
Abstract According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), there are 537 million people living with diabetes as of 2021. The numbers are projected to rise to 643 million by 2030 and 783 million by 2045. Almost 1 in 2 (240 million)adultslivingwith diabetesareundiagnosed.1in6live births(21million)areaffectedbydiabetesduringpregnancy.
Since people with diabetes are at risk from further complicationssuchasneuropathy,retinopathy,stroke,kidney diseases, amputation etc. implementing a system that can predict diabetes early on is necessary.
The most recent advances in machine learning and data mining technologies can be used to uncover hidden patterns, which may aid in the early detection and effective pre treatment of diabetes. Seven popular machine learning algorithms like Logistic Regression, Decision Tree, Random Forest, SVM, KNN, Adaboost and Gradient Boost were tested. The top five high performing machine learning algorithms were considered and used in Ensemble Voting Classifier.
The suggested framework works better than the individual algorithms discussedinthepaperwithanaccuracyofaround 82%. Further, the proposed system also sends recommendations in the form of diet charts and exercises for pre treatment.
Key Words: Diabetes prediction, Ensemble methods, MachineLearning,PimaIndiansDiabetesdataset,Diabetes pre treatment,Webapplication
Diabetes mellitus, also known as diabetes, is an incurable chronicdiseasecausedduetodeficiencyofahormonecalled insulin [1]. Insulin produced by the pancreas in the body, allowsglucosefromfoodtoenterthebloodstream.Diabetes occurswhenthepancreasmalfunctions,resultingincoma, pathological destruction of pancreatic beta cells, sexual dysfunction,renalandretinalfailure,weightloss,cerebral vasculardysfunction,ulcer,cardiovasculardysfunction,joint failure, pathogenic effects on immunity and peripheral vasculardiseases[2].
Diabetes is classified into two types: type 1 and type 2. Diabetestype1accountsfor5to10%ofallcasesofdiabetes.
This form of diabetes is most prevalent in childrenor adolescentsandisdistinguishedbyalimitedfunctionofthe pancreas. Since the pancreas remains partially functional, type 1 diabetes does not cause symptoms initially. The disease is not visible until 80 90% of pancreatic insulin producingcellshavebeendestroyed[3].
Diabetes type 2 accounts for 90%of the overallcases of diabetes.Chronichyperglycemiaandthebody'sinabilityto maintainbloodsugarlevelsdistinguishthistypeofdiabetes, resulting in an unusually elevated level of glucose in the blood.[4].
Recent healthcare studies have used a wide range of technologiestodiagnosepatientsandpredicttheirdisease basedonclinicaldata.MLtechniquesarenowbeingusedin thehealthcaresystemtomoreaccuratelypredictdiabetes. MLallowsacomputertolearnfromexperiencesorinputs (such as clinical data) and predict the output category (existence of disease). ML techniques are classified as supervised, unsupervised, or reinforcement learning. The features, as well as the target class, are used as input for learninginsupervisedlearning.Theinputdataisprovided without the target class in unsupervised learning. This datapoints are then clustered using a similarity metric. Reinforcement learning is a method that employs the hit and trialmethodtodeterminethebestoutcome.Awardand penaltyvaluesareusedtoachievethebestresults.
The primary goal of this research is to propose the development of an improved prognostic tool for early diabetes prediction and pre treatment. A large amount of data and datasets are available on the web or from independentbodies.ThePIMAIndiansdiabetesdatasetused inthisworkisoneofthemostcommonlyuseddatasetsin severalstudies,anditisgatheredbytheNationalInstituteof Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). DifferentMLclassifiers(LogisticRegression,DecisionTree, RandomForest, SVM, KNN, AdaboostandGradientBoost) were implemented in our proposed framework. Furthermore,weproposeanensemblingclassifier usinga numberofbasemodelsforimprovingdiabetesprediction. HardweightedvotingisusedtoensembletheMLmodels.
Theremainingpartofthepaperisorganizedasfollows.In Section 2, we discuss some relevant work that was done
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
previously. Section 3 elaborates on the proposed architecture and various algorithms tested in this study Section 4 examines the results obtained and the final implementationinanend to endwebapp.InSection5,we concludethepaperbypresentingfutureenhancements
Inrecentyears,numerousmodelshavebeenproposedand published. The authors of [5] presented a theoretical approachbasedonthreeclassificationtechniques:Support Vector Machines, Logistic Regression, andArtificial Neural Network.
OnthePimaIndiansDiabetesDataset,SisodiaandSisodia[6] usedclassificationalgorithmssuchasdecisiontrees,Naive Bayes and support vector machine, with the Naive Bayes classifier achieving the highest accuracy in diabetes prediction.Sisodiausedatenfoldcross validationtechnique In this technique, the dataset was divided into ten equal parts, nine parts were used for training and the rest for testing.Diabeteswaspredictedusingevaluationparameters suchasrecall,accuracy,areaunderthecurveandprecision
Kumarietal.[7] implemented randomforest, Naive Bayes andlogisticregressiontothePimaIndiansDiabetesDataset andcomparedthesetotheensembleapproach.Themodel outperformed the ensemble classifier with an accuracy of 79%.
Kandhasamy and Balamurali [8] applied machine learning algorithms such as random forest, J48, support vector machineandk nearestneighbourstopredictdiabetesusing the dataset in the UCI repository. The authors used the aforementionedclassifiertwice,oncebeforeandonceafter pre processingthedata.Thetechniquesforpre processing werenotdescribed,exceptthatthedatasetcontainedsome noise that was removed later The authors assessed the predictionbasedonitsaccuracy,sensitivityandspecificity Thedecisiontreeachievedthehighestaccuracyof73.82% whenthedatawasnotpre processed.Withpre processing, randomforestobtainedanaccuracyof100%
Perveenetal.[9]useddatafromtheCanadianprimarycare sentinel surveillance network in their study. The dataset containedthefollowingattributes:gender,BMI,fastingblood sugar, triglycerides, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure. The authors implemented the bootstrap, decisiontrees,andadaptiveboostingclassifiers.
Theperformanceofvariousclassificationtechniques[10,11] suchasSupportVectorMachine,DecisionStump,Decision TreesandNaiveBayeswithoutboostingwasevaluatedand gave an accuracy of 79.68%, 74.47%, 76% and 79.68% respectively. The performance evaluation of the above algorithmswithAdaboostasthebaseclassifierimprovedthe accuracyexceptforsupportvectormachines.
This section sheds light on the materials and techniques implementedintheexperimentdiscussedinthepaper.
The ML models were trained and tested using the PIMA IndiansDiabetesdataset,whichcontainedthedetailsof768 female diabetic patients from the Pima Indian community near Phoenix, Arizona [12]. This dataset comprises of 268 diabetic(positive)and500non diabetic(negative)patients with eight distinct characteristics. The attributes are as follows:Numberofpregnancies,Glucoseinplasma,Insulin level,Diabetespedigreefunction,Skinthickness,Bodymass indexandAge.Thediabetespedigreefunctionwascomputed [12]asin(1).
Pedigree= (1)
whereiandjrepresenttherelativeswhohaddevelopedand not developed diabetes respectively. K refers to the proportion of genes sharedwith relatives (K = 0.500 fora parentorfullsibling,K=0.125forahalfaunt,half uncle,or firstcousinandK=0.250forahalf sibling,grandparent,aunt oruncle).ADMiandACLjdenotetheagesofrelativesatthe timeofdiagnosisandthemostrecentnon diabetictest.
Theconstructionofalgorithmscapableofproducinggeneral patterns and hypotheses by using supplied instances to predict the outcome of future instances is known as supervisedmachinelearning.Thegoalofsupervisedmachine learningclassificationalgorithmsistocategorisedatabased on prior knowledge. They learn the pattern from previous dataandattempttopredictnewresults.MLalgorithmssuch as rule based, instance based, function based, probability based,tree based,andsoonareusedtolocateavailabledata. ThearchitectureofourproposedmodelisshowninFig.1.
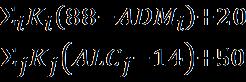
Pre
formissingvalues.Nomissingvalueswere foundinthedataset.
casethevalueoffewfieldswaszero,theywere replaced with the mean value of the respective attribute. This is necessary to obtain normal distribution.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
5. Despitethis,thereweresomeattributesthatdidnot have normal distribution. Non linear scaling was thusperformedonthem.
probability. A probability less than.5 predicts 0 and a probabilitygreaterthan0predicts1.
TheBayesTheoremisthebasisoftheNaveBayesalgorithm, which is used in a broad array of classification tasks. The Bayes' Theorem is amathematical equation used to determineconditionalprobabilities.Conditionalprobability isanestimateofthelikelihoodofoneeventoccurringgiven that another event has already occurred (either through assumption,presumption,assertion,orevidence).Giventhe class, Naïve Bayes works with the assumption that all the attributesareconditionallyindependent.
Adecisiontreeisagraphinwhichtheinternalnodesserveas testsontheinputdataandtheleafnodesserveasclassesof theinputdata.Thesetestsarefiltereddownthroughthetree to find the appropriate output pattern for the input. The decisiontreeisappliedindecisionanalysistoillustratethe outputasasplittingruleforeachindividualattribute.Itisa branching graph that is used to predict decision making outcomes both visually and explicitly. Each attribute is regardedasabranchingnode,andattheendofthebranch,a ruleisconstructedthatdividesvaluesbelongingtodiverse classes.Asthenameimplies,itisa tree likestructurethat endswithadecisionknownastheleaf.Therootisthemost potentially useful attribute for predicting rule formation outcomes Decisiontreesaresimpleandeasytoimplement, anditalsopredictstheresultsmoreaccurately.
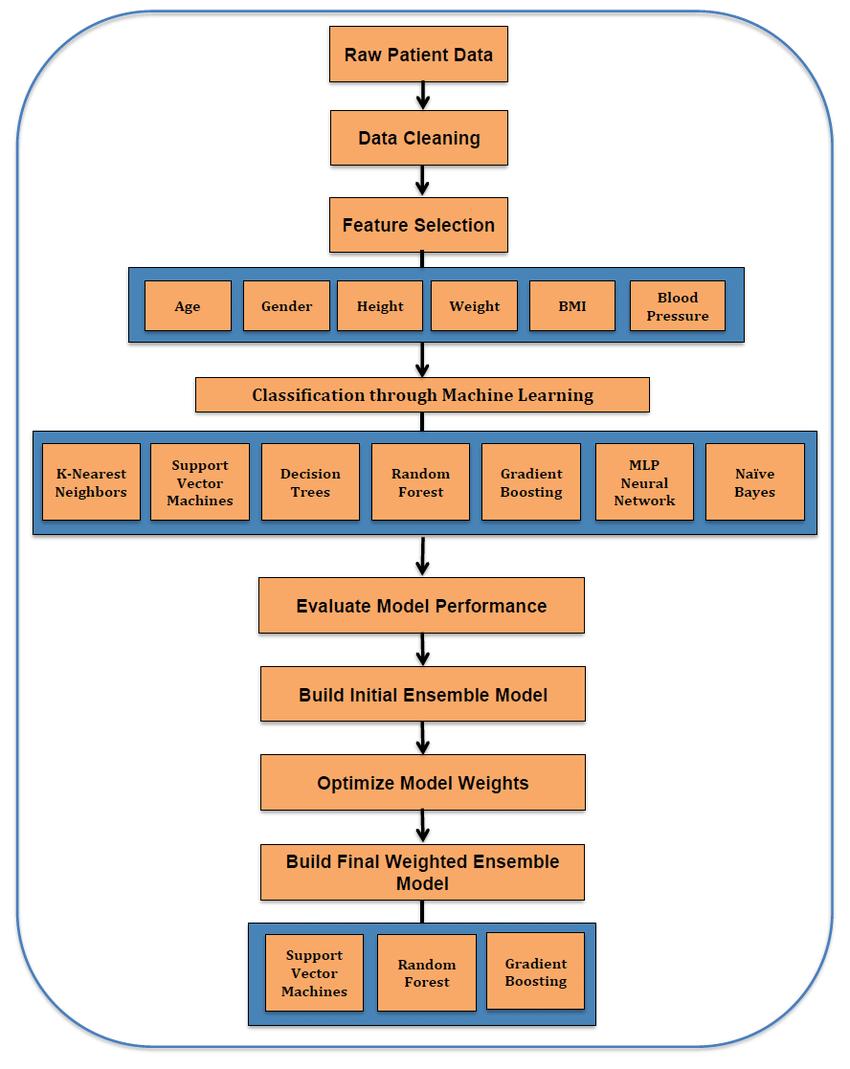
Figure 1:Theproposedarchitecturediagramfordiabetes prediction
Thefollowingsevenalgorithmswereexecutedandevaluated inthisstudy.
Basedonasetofindependentvariables,logisticregression calculates the likelihood of an event occurring, such as TrueorFalse.Thedependentvariablehasarangeof0to1 becausetheoutcomeisaprobability.Alogittransformation is applied to the odds in logistic regression, which is the probabilityofsuccessdividedbytheprobabilityoffailure. Thisisalsoreferredtoaslogoddsorthenaturallogarithmof odds.Theloglikelihoodfunctionisproducedbyallofthese iterations,andlogisticregressionattemptstomaximisethis function to find the best parameter estimate. Once the optimal coefficient (or coefficients, if more than one independentvariableispresent)hasbeendetermined,the conditional probabilities for each observation can be calculated, logged, and summed to produce a predicted
Randomforestisasupervisedclassificationalgorithmthatis widelyusedinclassificationtasks.Itiscomposedofaseries ofdecisiontrees.Thesetreeshavethesamenumberofnodes but differ in their data. The outcomes of these various decisiontreeswillbeaggregatedtoproduceafinalresultthat indicatestheaverageresponseofallofthedecisiontrees.As thenumberoftreesinaforestincrease,thegeneralisation errorapproachesalimit.Thegeneralisationerrorofaforest of tree classifiers is determined by the strength of the individualtreesintheforestaswellastheircorrelation.
Support vector machines have shown to be extremely effectiveinavarietyofclassificationtasks.Itseeksthebest separating hyperplane between classes by locating the coordinates on the edges of the class descriptors. The distancebetweentheclassesisrepresentedbythemargin. SVM algorithms find a margin with the greatest possible distance.SVMsareintendedtohandlebinaryclassification datathatcanbeseparatedlinearly.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
AdaBoost (Adaptive Boosting), is a Machine Learning technique that is used as an Ensemble Method. The most commonAdaBoostalgorithmisdecisiontreeswithonelevel, whichmeansdecisiontreeswithonlyonesplit.Becausethese treesaresoshortandonlyhaveoneclassificationdecision, theyareoftenreferredtoasdecisionstumps.Itisemployed to enhance the effectiveness of any machine learning algorithm. It works best with slow learners. On a classification problem, these are the models that achieve accuracyjustaboverandomchance.Here,aseriesofweak classifiers are connected, with every weak classifier attempting to strengthen the classification of samples misclassifiedbythepreviousweakclassifier Boostingdoes thisbycombiningweakclassifiersinsuccessiontoconstruct astrongclassifier.
Gradient boosting is a type of boosting method that iterativelylearnsfromeachweaklearnertobuildastrong model.Itcanimprove:regression,classificationandranking. The word Gradient refers to the fact that multiple derivations of the same function is obtained. Gradient Boosting is a functional gradient iterative algorithm that reducesa loss functionby recursivelychoosinga function that points in the direction of the negative gradient, also calledaweakhypothesis.
ThePimaIndiansdatasetconsideredwassplitina70to30 ratio for training and testing respectively. A thorough evaluationandperformanceanalysiswasperformedonthe seven algorithms (Logistic Regression, Decision Tree, Random Forest, SVM, KNN, AdaBoost and Gradient Boost) tested.TheresultsareshowninTable1.
LogisticRegression 79.7 RandomForest 77.1
AdaptiveBoost 79.2 GradientBoost 80.2
KNearestNeighbour 76.6 DecisionTree 74.5
SupportVector 67.7
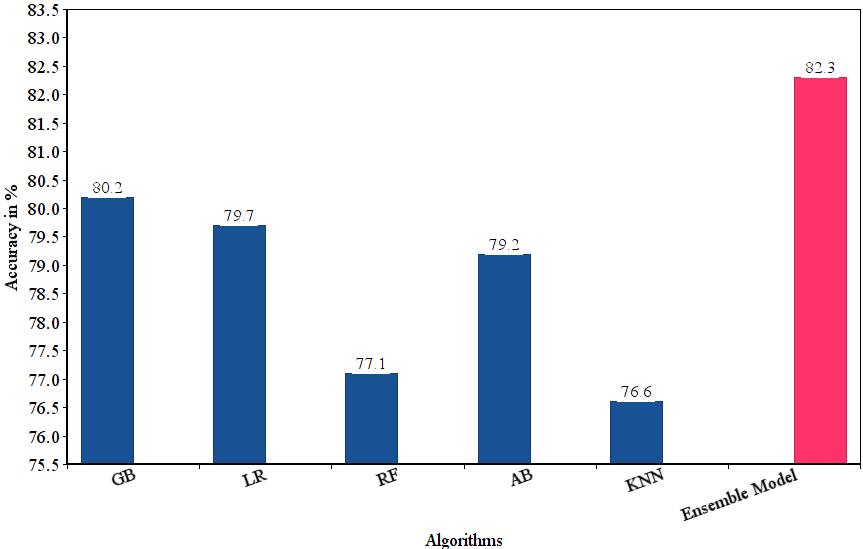
The top five highest performing algorithms i.e Logistic Regression,RandomForest,K NearestNeighbours,Adaboost andGradientBoostingwerecombinedtoformanensemble
model.Ensemblingisatypeofmachinelearningtechnique thataggregatesnumerousbasemodelstoproduceasingle robustmodel.
Thehardvotingclassifierwasimplemented.Hardvotingisan ensembling method that selects the class with the highest number of votes. The votes refer to each individual base modeloralgorithmintheensemble.Chart1comparesthe performance of the five algorithms considered against the finalensemblemodel.
Ensemble models have a number of advantages. They outperform individual models in terms of predictive accuracy. They are very useful when the dataset contains bothlinearandnon lineardatasincedifferentmodelscanbe combined to handle this type of data. With ensemble methods,biasorvariancecanbereduced,andthemodelis usuallyneitherunderfittednoroverfitted.Mostimportantly, ensemblemodelsarealwayslessnoisyandmorestable.
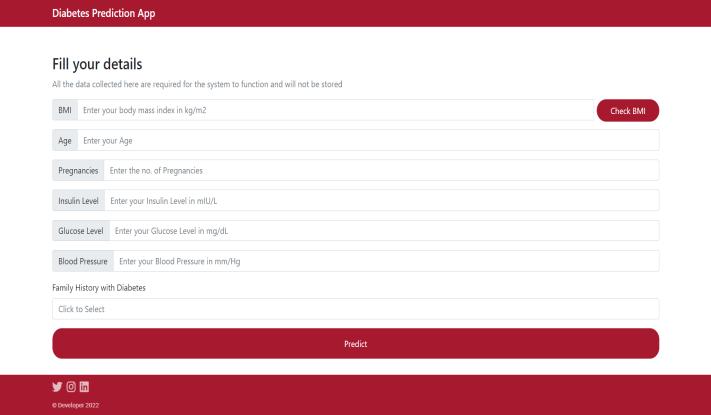
Thefinalensemblemodelbuiltformedthecruxoftheend to end application that was created. A webapp using HTML,CSSandJavaScriptwasdeveloped.Thewebsitewould collect user details through a form in the input page as showninFigure2.
Figure -2:Inputpageofthefinalapplication
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Themodelwouldrunonthebiologicaldetailsprovidedand predictwhethertheindividualisatariskofgettingdiabetes. Incaseanindividualisprone,anewpagewithrecommended dietcharts,exercisesetc.areprovidedinordertopre treatit effectively.ThisisshowninFigures3and4.
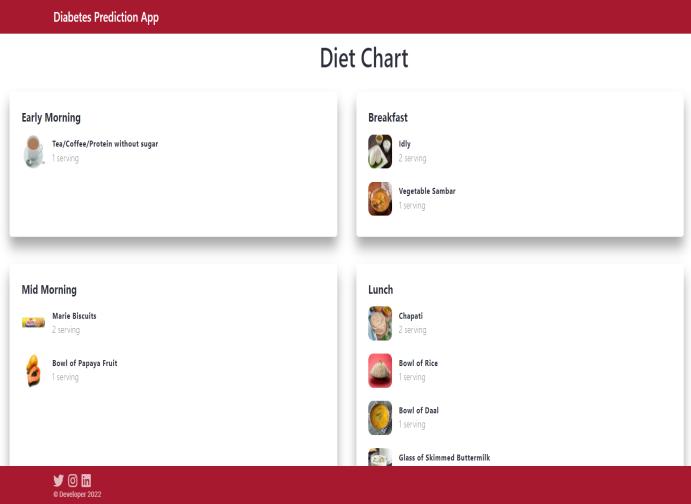
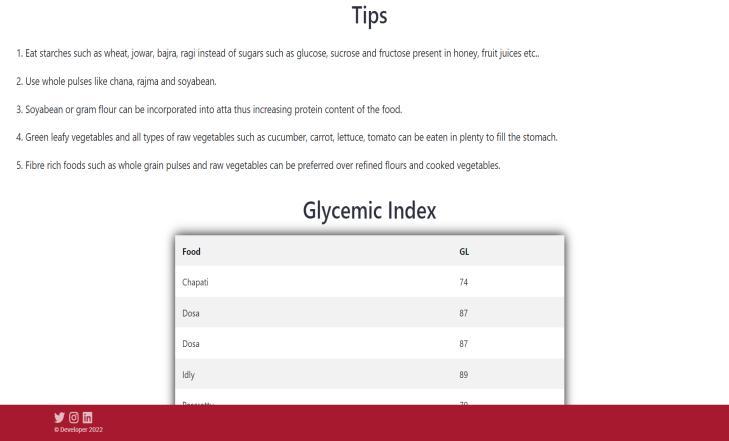
Inadditiontotheaboverecommendations,glycemicindex (whichisafigurebetween0 100thatdenotestheabilityof carbohydratesinfoodtoincreasethebloodsugarlevel)of some common foods is mentioned for users to make informeddecisions.Further,othergeneraltipsarepresented tocreatemoreawarenessasshowninFigure5.
Diabetesisacriticalandchronicdiseasethatcausesspikein blood sugar. Diabetic nephropathy, stroke, and failure of variousorgans,especiallythekidneys,veins,andeyescanall becausedbyundiagnoseddiabetes.Asaresult,oneofthe most pressing medical issues in the world is the early detectionofdiabetes.Theaimofthepaperwastoimplement anend to endapplicationthatwoulddetectdiabetesearly onandensurepre treatmentthroughdietcharts,exercises etc.Initially,thestudyperformedcomparativeanalysison seven algorithms (Logistic Regression, Decision Tree, RandomForest, SVM, KNN, AdaboostandGradientBoost) whose accuracy lied within the range of 67 80%. Thus, accuracy was improved to 82% by building an ensemble modelofthefivehighestperformingalgorithms.Infuture: selecting a dataset bigger than the Pima Indians dataset, testing deep learning algorithms and improving feature extraction methods are various criterions to consider to obtainabetterfittingmodeltoimproveaccuracy.
[1] Z. Punthakee, R. Goldenberg, and P. Katz, “Definition, ClassificationandDiagnosisofDiabetes,Prediabetesand MetabolicSyndrome,”Can.J.Diabetes,vol.42,pp.S10 S15,2018.
[2] R.Vaishali,R.Sasikala,S.Ramasubbareddy,S.Remya, andS.Nalluri,“Geneticalgorithmbasedfeatureselection andMOEFuzzyclassificationalgorithmonPimaIndians Diabetesdataset,”inProc.InternationalConferenceon ComputingNetworkingandInformatics,Oct.2017,pp. 1 5.M. Young, The Technical Writer’s Handbook. Mill Valley,CA:UniversityScience,1989.
[3] L. Lucaccioni and L. Iughetti, “Issues in Diagnosis and TreatmentofType1DiabetesMellitusinChildhood,”J. DiabetesMellit.,vol.06,no.02,pp.175 183,2016.
[4] “Type2Diabetes:aReviewofCurrentTrends ,”Int.J. Curr.Res.Rev.,vol.7,no.18,pp.61 66,2015
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[5] T. N. Joshi and P. P. M. Chawan, “Diabetes Prediction UsingMachineLearningTechniques,”Ijera,vol.8,no.1, pp.9 13,2018.
[6] D.SisodiaandD.S.Sisodia,“Predictionofdiabetesusing classificationalgorithms,”ProcediaComputer Science, vol.132,pp.1578 1585,2018.
[7] S. Kumari, D. Kumar, and M. Mittal, “An ensemble approach for classification and prediction of diabetes mellitus using soft voting classifier,”International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering, vol. 2, pp.40 46,2021.
[8] J. P. Kandhasamy and S. Balamurali, “Performance analysis of classifier models to predict diabetes mellitus,”ProcediaComputerScience,vol.47,pp.45 51, 2015.
[9] S.Perveen,M.Shahbaz,A.Guergachi,andK.Keshavjee, “Performance analysis of data mining classification techniques to predict diabetes,”Procedia Computer Science,vol.82,pp.115 121,2016.
[10] Vijayan V, Ravi K (2015) Prediction and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus a machine learning approach, December,pp122 127
[11] Polat K, Güneş S, Arslan A (2008) A cascade learning systemforclassificationofdiabetesdisease:generalized discriminantanalysisandleastsquare support vector machine.ExpertSystAppl34(1):482 487
[12] J.W.Smith,J.E.Everhart,W.C.Dickson,W.C.Knowler, andR.S.Johannes,“UsingtheADAPlearningalgorithm to forecast the onset of diabetes mellitus,” in Proc. AnnualSymposiumonComputerApplicationinMedical Care,Nov.1988,pp.261 265.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
