International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Madhuri1 , Nandini S2 , Mrs.Mona3
1,2 Student Dept. of Information Science and Engineering, BNMIT Institute of Technology, Karnataka, India 3Assistant Professor, Dept. of Information Science and Engineering, BNM Institute of Technology, Karnataka, India ***
Abstract About 10% of the adult population worldwide is affected by chronic kidney disease (CKD), one of the top 20 killers globally. CKD is a conditionthat impairs healthykidney function. Effective preventative methods for the early detection of CKD are needed due to the rise in CKD cases. This study is new inthat it has createda mechanismfordiagnosing chronic renal disorders. With the aid of machine learning techniques, this study aids specialists in investigating CKD prevention strategies through early detection. This study was concerned with analysing a dataset made up of 400 patients and 24 features. To replace the missing numerical and nominal values, the mean and mode statistical analysis methods were used. Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE) was used to select the most important features. In this study, four classification algorithms were used: support vector machine (SVM), k nearest neighbours(KNN),decisiontree,andrandom forest. Allof the classification algorithms performed well. The random forest algorithm outperformed all other applied algorithms, achieving 100 percent accuracy, precision, for all measures. CKD is a life threatening disease with high morbidity and mortality rates. As a result, artificial intelligence techniques are critical in the early detection of CKD. These techniques aidexpertsanddoctorsinmakingearly diagnoses in order to avoid kidney failure.
Key Words: Recursive Feature Elimination, Nominal values, Chronic kidney disease, Classification, K nearest neighbours,Supportvectormachice.
Intermsofthecurrentstateofsociety'shealth,chronic kidney disease (CKD) is regarded as a serious hazard. Regular laboratory testing can identify chronic kidney disease,andtherearetreatmentsavailabletostoptheillness from progressing, lessen the problems of reduced Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR), lowersthe risk of cardiovascular disease, and enhance quality of life and survival.Lackofwaterintake,smoking,apoordiet,lackof sleep,andnumerousotherfactorscanleadtoCKD.Globally, thisillnessimpacted753millionpeoplein2016,417million ofthemwerefemaleand336millionmale.Themajorityof thetime,theillnessisdiscoveredatitsadvancedform,which can occasionally result in renal failure. The current diagnosticmethodreliesontheanalysisofurinewiththeaid of serum creatinine levels. This is accomplished using a variety of medical techniques, including ultrasonography andscreening.Patientswhohavehypertension,ahistoryof cardiovascular disease, a current illness, or who have had
renaldiseaseinafamilymemberareallscreenedduringthe screening process. This method involves measuring the albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR)ina first morningurine sampleaswellasestimatingGFRfromtheserumcreatinine level.Thisresearchfocusesonmachinelearningapproaches suchasACOandSVMforimprovingpredictionaccuracyby decreasingfeaturesandpickingthebestfeatures.
Anabnormalfunctioningofthekidneysoralackofrenal functionthatprogressesovermonthsoryearsisknownas chronickidneydisease,alsopopularaschronicrenaldisease. Peoplewhoareknowntobeatriskforkidneyissues,suchas those with high blood pressure, diabetes, or who have a bloodfamilywithchronickidneydisease(CKD),aretypically screenedfor the condition. Therefore, earlydiagnosis and effectivetherapyareessentialtobattlingthedisease.Inthis work,theAntColonyOptimization(ACO)methodand the Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier are suggested as machine learning strategies for CKD. Using the fewest numberoffeaturespossible,thefinalproductcandetermine ifapersonhasCKDornot.
ChronicKidneydisease(CKD)diseasethatcanbetreated earlyonyetresultsinkidneyfailedattheveryend.Chronic renaldiseasein2016,753millionpeoplediedasaresultof itworldwide,wheretheMalefatalitiestotalof336million, whereasfemalefatalities417millionfemalesdied[1].Due toitshighmortalityrate,chronickidneydisease(CKD)has attracted a lot of interest. According to the World Health Organization(WHO),chronicdiseaseshavebecomeamajor hazardtoemergingcountries[2].Thereasonkidneyillness isreferredtoasa"chronic"conditionisbecauseitdevelops gradually over time and has an impact on how the urine systemworks.Otherhealthissuesthatarebroughtonbythe build up of waste products in the blood include diabetes, highandlowbloodpressure,boneandnervedamage,and cardiovasculardisease.Theseissuesareallaccompaniedby a variety of symptoms. Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovasculardisease(CVD)areriskfactorsforthosewith CKD [3]. Patients with CKD experience side effects, particularly in the late stages, which weaken the immunological and nervous systems. Patients may be in advanced stages in thedeveloping nations, necessitating dialysis or kidney transplants. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR), a measure of kidney function, is used by medical professionalstoidentifyrenalillness.GFRisdeterminedby factorsincludingthepatient'sage,bloodtestresults,gender,
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
and other circumstances [4]. The process of categorising legitimate, innovative, possibly helpful, and eventually intelligible patterns in data is known as data mining. In simpleterms,it'stheprocessofextractingdatafromalarge database. There are many uses for data mining, including those in business, education, government, the health care sector,andscienceandengineering.Dataminingisprimarily utilisedfordiseasepredictioninthehealthcaresector.There are a vast array of data mining techniques, including classification,clustering,associationrules,summarizations, regression,andothers,thatcanbeusedtoforecastdiseases. UsingclassificationtechniqueslikeNaiveBayesandSupport Vector Machine, the primary goal of this research is to predictkidneydisorders.Themajorgoalofthisresearchwas to identify the classification algorithm with the highest classification accuracy and execution time performance. Accordingtotheexperimentalfindings,theSVMperforms betterthantheNaiveBayes classifieralgorithm[5].Akey aspectofhealthcareinformaticsisthepredictionofchronic diseases. Early disease detection is critical for successful treatment.Inordertodiagnoseandpredictchronicdiseases, this study gives a survey on the application of feature selectionandclassificationalgorithms.Inordertoimprove the accuracy of classification systems, proper feature selectioniscrucial[6].
Accordingtothecurrentstateofstudy,theprevalenceof chronic kidney disease (CKD) rises yearly. The ability of machine learning algorithms to classify data with high accuracymakesthemmorecrucialinmedicaldiagnosisand asourceforfuturetherapyinCKDprognosis.Inthepast,the accuracyofclassificationalgorithmswasdeterminedbyhow wellfeatureselectionalgorithmswereusedtoreducedata size.OntheInternetofMedicalThings(IoMT)platform,the HeterogeneousModifiedArtificalNeuralNetwork(HMANN) has been suggested for the early detection, segmentation, anddiagnosisofchronicrenalfailure[7].GiventhatChronic KidneyDisease(CKD)isoneofthediseasesthatcanbefatal, earlydetectionandappropriatecareofCKDareencouraged to increase survivability. Age, blood pressure, specific grativity,albumin,sugar,redbloodcells,pluscells,puscell clumping, bacteria, bloodglucoserandom,and bloodurea are some of the characteristics included in the UCI's CKD datasetthatwaschosenforthisstudy.Thiswork'sprimary goalistocomputeandcomparetheeffectivenessofvarious decision tree algorithms. Decision Stump, Hoeffding Tree, J48,CTC,J48graft,LMT,NBTree,RandomForest,Random Tree,REPTree,andSimpleCartaresomeofthedecisiontree methods employed in this study. As a result, the findings demonstrate that Random Forest provides the highest accuracyinCKDidentification[8].
The system is developed using a variety of design principles;thedesignspecificationoutlinesthefeaturesof the system, its competitors or constituent parts, and how
theywillappeartoendusers.Machineswereusedtocarry outanumberofexperiments.SVM,KNN,decisiontrees,and randomforestsarethelearningalgorithmsusedtoassess the CKD dataset. The general organisation of the CKD diagnosis in this paper is shown in Figure. The missing nominal valueswerecomputedusing the modetechnique during preprocessing, and the missing numerical values werecomputedusingthemeanmethod.TheRFEalgorithm wasusedtochoosethefeaturesofrelevancelinkedtothe features of importance for CKD diagnosis. In order to diagnose diseases, these chosen traits were fed into classifiers. SVM, KNN, decision trees, and random forests werethefourclassifiersusedinthisworktodiagnoseCKD. For classifying a dataset into CKD or a normal kidney, all classifiersdemonstratedgoodresults.
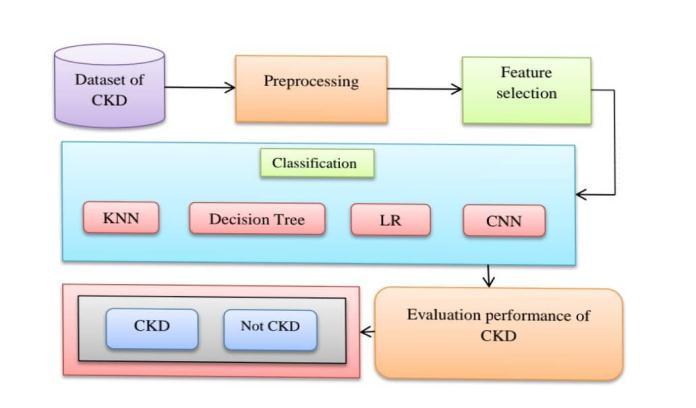
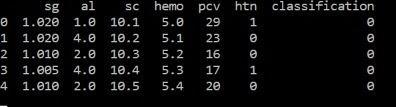
To determine whether kidney illness exists or not, the systemwillfirstdoapre process,thenitwillextractthekey informationanduseavarietyofclassificationalgorithms.In additiontotheclassfeatures,suchas"ckd"and"notckd"for classification, the dataset has 24 features total, separated into11numericalfeaturesand13categoricalfeatures.Age, bloodpressure, specificgravity,albumin,sugar, redblood cells,puscell,puscellclusters,bacteria,bloodurea,serum creatinine, sodium, potassium, haemoglobin, packed cell volume, white blood cell count, red blood cell count, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, appetite, pedal edoema, and anaemia are among the characteristics. ckd and notckd are the two values in the diagnosticclass.
Thedatasetneededtobecleanedupinapre processing stagebecauseithadoutliersandnoise.Pre processingtasks includedcheckingforunevendata,normalising,estimating missingvalues,andremovingnoiselikeoutliers.Selectionof features.Itisnecessarytofindthesignificantaspectsthat have a strong and positive connection with features of importance for disease diagnosis after computing the missing values. A robust diagnostic model cannot be built sincethevectorcharacteristicsmustbeextractedtoexclude featuresthatareirrelevantandunhelpfulforprediction.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Aftercomputingthemissingvaluesandfiguringoutthevital capabilities having a robust and fine correlation with capabilitiesofsignificancefordiseaseprognosis.Extracting the vector capabilities removes vain capabilities for predictionandfeatureswhichareirrelevantandprevents thedevelopmentofarobustdiagnosticmodel.Inthisstudy, we used the RFE technique to extract the maximum vital capabilities of a prediction. The Recursive Feature Elimination(RFE)algorithmmaybeveryfamousbecauseof its ease of use and configurations and its effectiveness in choosing capabilities in education datasets applicable to predicting goal variables and doing away with weak capabilities.
Themostwidespreadcapabilitiesconsistentwith RFE;it'sfarmentionedthatalbuminfunctionhasmaximum correction(17.99%),featuredviawayofmeansof14.34%, then the packed cell volume feature via way of means of 12.91%,andtheserumcreatininefunctionviawayofmeans of12.09%.RFECVplotstherangeofcapabilitieswithinside the dataset at the side of a cross established rating and visualizesthechosencapabilitiesispresentedinFigure2.
K nearest neighbour (KNN), which employs the supervised learning methodology, is one of the simplest machinelearningalgorithms.Dependingonhowmuchanew instance resembles existing categories, it is categorised accordingly.The KNN approachiswhatisused in this. By usingtheKNNapproach,allofyourdatacanbestored,and newdatamaybecategorisedaccordingtohowsimilaritisto theold.ThisimpliesthattheKNNapproachcancategorise newdataintopredefinedcategoriesquickly.
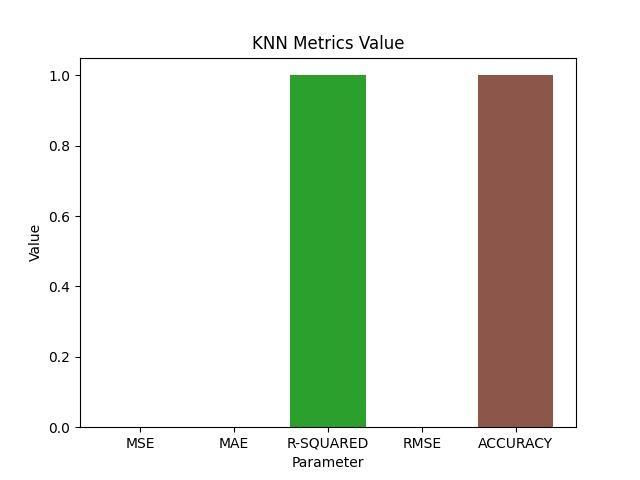
The KNN approach can be applied to regression even thoughitisfrequentlyemployedforclassificationproblems. The KNN approach, which is nonparametric and also popularly called as a "lazy learner algorithm," does not instantlylearnfromthetrainingset,butinsteadstoresand organises the data for later analysis. The KNN places new data it receives into a category that is quite similar to the newdataitsavedduringtraining.
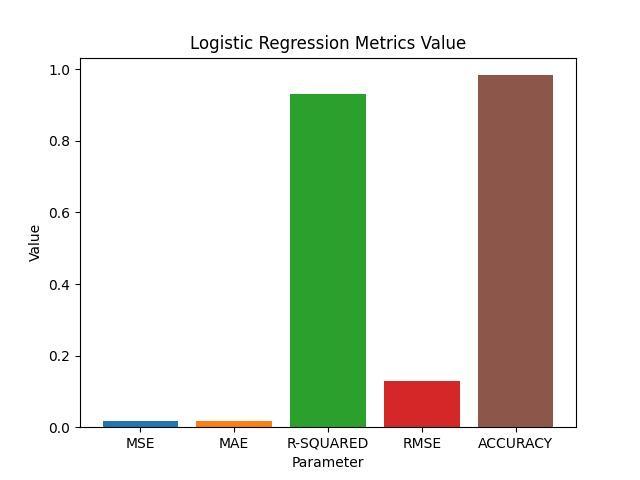
Thewidelyusedstatisticaltechniqueoflogisticregression is used to model binary outcomes. In statistical research, logistic regression is carried out using various learning techniques. The LR algorithm was developed using a differentneuralnetworktechnique.Althoughthisapproach iseasiertosetupandutilise,itsharesmanysimilaritieswith neuralnetworks.
Fig.4.LogisticRegressionMetricsValue.
C. CNN:
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
We are constructing the CNN algorithm to forecast the kidney disease CNN model comprises following layers . A feed forward neural network known as a convolutional network analyses data by processing it in a grid like architecture. It is also referred to as a ConvNet. Data detectionandclassificationaredoneusingaconvolutional neuralnetwork.
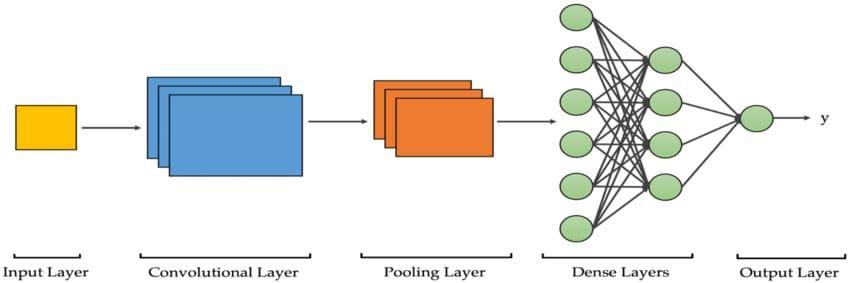
Several prior related studies were used to evaluate the performanceoftheproposedsystems.Theaccuracyranges ofthepreviousresearcharebetween96.8percentand66.3 percent,itshouldbeemphasised,butthesuggestedsystem has achieved accuracy of 100 percent using the Convolutionalneuralnetworkmethod.Whencomparedto current systems, it is seen that the proposed has the best outcomes.Thedatasetisrandomlysplitinto25%fortesting andvalidationand75%fortraining.Tochoosetheirrelevant subset characteristics, the Recursive Feature Elimination approach was presented. Then, classifiers were used to process the chosen features in order to diagnose CKD. It should be highlighted that the suggested system has producedencouragingoutcomes.Inordertoprioritisethe featuresandassigna percentageto eachfeaturebased on thecorrelationwiththetargetfeature,weutilisedtheRFE algorithmtodeterminethebestassociationsbetweeneach featureandthetargetfeatures.
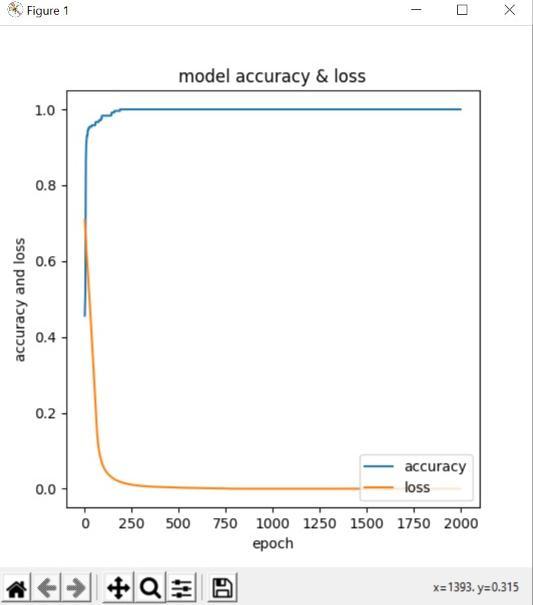
Fig.6.ModelAccuracyandLoss
Accuracy=(TN+TP/TN+TP+FN+FP)∗100% whereTNstandsforTrueNegative, TPstandsforTruePositive, FNstandsforFalseNegative,and FPstandsforFalsePositive.
ThisstudyshedlightonthediagnosisofCKDpatientsto address their condition and obtain therapy in the early stages of the disease. The data was gathered from 24 characteristics were found in 400 patients. 25% of the dataset was used for testing and validation, and the remaining 75% was used for training. In order to replace missingnumericalandnominalvaluesandremoveoutliers fromthedataset,meanandmodestatisticalmeasureswere used, respectively. The most strongly representative CKD characteristics were chosen using the RFE method. The classification algorithms SVM, KNN, decision tree, and randomforestwerefedwithspecificfeatures.Allclassifiers' parameters were adjusted for the best classification performance,andtheresultsfromallmethodswerepositive.
[1] GunarathneW.H.S.D,PereraK.D.M,Kahandawaarachchi K.A.D.C.P, “Performance Evaluation on Machine Learning Classification Techniques for Disease ClassificationandForecastingthroughDataAnalytics for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)”,2017 IEEE 17th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[2] S.Ramya, Dr. N.Radha, "Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease Using Machine Learning Algorithms," Proc. International Journal of Innovative Research in ComputerandCommunicationEngineering,Vol.4,Issue 1,January2016.
[3] S.Dilli Arasu and Dr. R.Thirumalaiselvi, “Review of Chronic Kidney Disease based on Data Mining Techniques”,International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 0973 4562 Volume 12, Number23(2017)pp.13498 13505
[4] L. Rubini, “Early stage of chronic kidney disease UCI machinelearning repository,”2015. R. E. Sorace, V. S. Reinhardt,andS.A.Vaughn,“High speeddigital to RF converter,”U.S.Patent5668842,Sept.16,1997.
[5] S.A.ShindeandP.R.Rajeswari,“Intelligenthealthrisk predictionsystemsusingmachinelearning :areview,” IJET, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 1019 1023, 2018. M. Shell. (2002) IEEEtran homepage on CTAN. [Online]. Available:http://www.ctan.org/texarchive/macros/lat ex/contrib/supported/IEEEtran/
[6] Himanshu Sharma,M A Rizvi,”Prediction of Heart Disease using Machine Learning Algorithms: A Survey”,InternationalJournalonRecentandInnovation TrendsinComputingandCommunicationISSN:2321 8169,Volume:5Issue:8
[7] Asif Salekin, John Stankovic, "Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease and Selecting Important Predictive Attributes," Proc. IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), IEEE, Oct. 2016, doi:10.1109/ICHI.2016.36.A.Karnik,“Performanceof TCPcongestioncontrolwithratefeedback: TCP/ABR and rate adaptive TCP/IP,” M. Eng. thesis, Indian InstituteofScience,Bangalore,India,Jan.1999.
[8] PinarYildirim,"ChronicKidneyDiseasePredictionon Imbalanced Data by Multilayer Perceptron: Chronic Kidney Disease Prediction," Proc. 41st IEEE International Conference on Computer Software and Applications (COMPSAC), IEEE, Jul. 2017, doi: 10.1109/COMPSAC.2017.84 Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specification,IEEEStd.802.11,1997.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
