International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

1
Abstract The current research focus is on the study and synthesis of the deformation characteristic of epoxy plastic syntactic foams. In the current investigation, important to achieve good reinforcement properties as we know polymer vary in their chemical structure and offer different properties there selection of polymer matrix made based on application and property requirement. thermoplastics can used to make composites The resin plastic mixture (putty like consistency) which have high viscosities beyond 4 layer stops filtering and depends on the reinforcement used in the layer it is found that if polymer matrix is filled with fibrous materials the resulting material that is process very high and excellent mechanical properties these materials can be used for load bearing and other high end application such as material are composite materials there are two component themaincomponent ofthe composite is the matrix and second is component is reinforcement which is more often called as filler. The overpriced of artificial thermoplastic fibers like glass and carbon, etc. results ineffective and products obtained from these stuff which has demanded substitute resources of stuff advancement. This is also include the usage of nearby obtainable waste thermoplastics for materials stuff advancement. In this research, the main motive is to develop, investigate and determine the mechanical properties of the reinforcement material using waste thermoplastics. The fabrication of the composite was carried out using epoxyresin as the matrix and the waste thermoplastics as reinforcement. Tests were carried out to determinethemechanicalproperties such as tensile, hardness, impact and compressive strengths. The results were studied and compared with the conventional materials and it process that the material developed can be used in structural applications with strong dependence on its mechanical properties.
Key Words: Epoxyresin,Hardener,SyntacticFoamSyntacticfoamisacompositematerial [1] Itisclosedcell composite material mixed in an epoxy and hardener matrix.[2] It has good mechanical properties, very strong andinsulationproperties,lowexpansionandlowmoisture absorptioncapacity,etc.[3] Itisdevelopedfornewmaterial andstrengthishigh.Applicationbecauseitislightweights alsoitsapplicationinshipstructureandspacecraft.Syntactic
***
foamisusedascorematerialasanynewproductstructure in composite.[4] first is matrix phase and reinforcement matrixofmaterialisbyweightiscompositeonefiberepoxy compositesareusedasstructuralmaterialsforthefuselage wings tail doors and much of the interior lightweight compositesenhanceanaircraft’sefficiency inloadcarrying capacityand hugeadvantageinfuelsavinginfactthevery firstlarge scaleseofcarbonfiberepoxycomposite isused thematrixenergysectorisalsoutilizingcompositeandthere are turbines with blades and application it is the storage tankisverylightnotasteelcylinderthisissolvedbyhaving FRPasthematerialforhydrogenstoragetankorcylinders when a polymer matrix material is mixed with a non polymermaterialsuchasametal,non metal,ametal,anoil ,aceramic,etc.toformanewmaterialthequalityofallthe othermaterialthatwegetisinthematerialalone,whichwe call polymer composite material[5][6][7]. There are two types of composite material .first is the main constitute formingthebodyofcompositematerialisthematrixphase andsecondisthematerialwhichprovidethestrengthtothe matrix material is the reinforcement matrix. Composite material are an what are constitute and what their propertiesarewhohavelearnthatcompositearelight,stiff, and strong material[8][9][10]. There are combination of two are more than two phases the very important fiber material isglass,carbon,boron,silica,andsyntheticfiber conventionalengineeringmaterialarenotabletoservethe specific need there is a requirement to develop formed material the need of material with better properties are increase thecombinationofbetter propertiescanonlybe achievedwithintroductionofnewmaterialtheprojectisan studyofnaturalfibresandparticularglassfibreandwood andfindthemechanicalstrengthandstiffnessisselectedas areinforcementbecauseofgoodproperties andalsoused 79:7.9 as the Wight ratio four epoxy and hardener and placed the one by one and applied the mixed epoxy and hardenerinbetweenthefibreslayerandusedsiliconspread and dry for 48 hours [11][18] Epoxy resin is important classesofthermosettingpolymersthatareusedinadvanced composites, because it has chemical resistance and high tensilealsohighcompressivestrength.[12][19] Ithaslow shrinkage properties during cure process, and has good adhesion,andalongwithgoodstructuralstrength[13][18].
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page520
Puneet Kumar Bhatia1 , Aditya Mall 2 , Anand Gopal Yadav3 ,Akash Singh4 ,Dhirendra Pratap Singh5 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Buddha Institute of Technology, Gorakhpur, Uttar Pradesh, India 2,3,4,5 Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Buddha Institute of Technology, Uttar Pradesh, IndiaInternational Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
•J.R.M ALMEDA et.al (2012)[14]Work on the effect of diameter of glass, wood on the mechanical behaviour of microspherecompositehefindthatmechanical behaviour of glass microsphere is achieve by varying diameter of microsphere.Wallthicknessofmicrosphereisindependent ofmeansize,soitisimportanttoachieveoptimumdiameter towallthicknessratioanditismostimportantprocessing parameter.
•AARE ARUNIIT et.al (2014)[15] Researchonthetopicof effect of wood microsphere on a mechanical and physical characteristicthefocusedstudyistofindminimumcostwith of composition of composite which is light in weight but havingdesirablemechanicalproperty.
•K.C. YUNG et.al (2014)[16] Researchondifferentproperty of hollow glass microsphere, they filled hollow glass microsphere in the epoxy matrix with varying volume% from0 50ofhollowglassmicrosphere.Inthisprocessthey gotimprovedpropertylikecoefficientofexpansionandglass transitiontemperature.
Raw material choose for this experimental work are as follows


I EpoxyResinLY556 II Hardener HY951 III SiliconeSpray IV Plywood V. Polythene VI. CelloTape
There are three types of sample has been prepared using Epoxyresin(LY556),hardener(HY951)[17], polytheneand Plywood.
I. By using only epoxy and Hardener
Fig 1 EpoxyResin(LY556)andHardener(HY951) [17]

Fig 2 Thisimageshowingthesampleofepoxyandhardener
II. By adding a layer of Polythene in the above sample(Reinforcement of polythene)
Fig 3 Thisimageshowingthereinforcementofpolythene.





International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net
ISSN: 2395 0072
•Thestrengthofimpactandcompositematerialisdepends accordingtodifferentlayerofthermoplasticinimpacttest. Impact strength of different sample is grew with growing layer of Reinforcement up to 3 layer and then begin reducing.
AfterperformingcompressiveTest,Thefollowingresultsare obtains
FractureLoad=46.2kN
Cross sectionAreaofrectangularSpecimen
A=30*15=450mm2
So, Compressivestress=Fractureload/Area Compressivestress=(46.2×103)/450=102.66MPa
FractureLoad=56kN
Cross sectionAreaofrectangularSpecimen
A=30*15=450mm2
So, Compressivestress=Fractureload/Area Compressivestress=(56×103)/450=124.44MPa
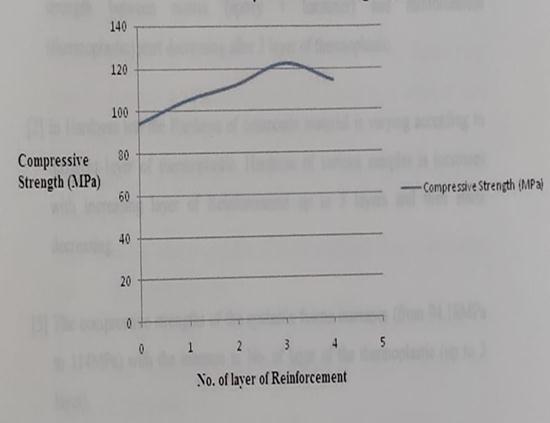
Compressive Strength curve with different layer of reinforcementareshownbelow
•The Hardness of composite material is differing in accordance with different layer of thermoplastic in the hardnesstest.Hardnessofdifferentsampleisincreasedwith increasing layer of Reinforcement up to 3 layer and then startreducing.
•InTensiletrialthetensilestrengthofcompositematerialis differinginaccordancewithdifferentlayerofthermoplastic. Tensilestrengthof1layersampleisincreasedthenfurther decreaseat2and3layersofreinforcement&at4layerof reinforcementthetensilestrengthisincreased.Itmeansthat thecharacteristicsoftensilestrengthofcompositesmaterial arenotpoor.
•Thecompressivestrengthofcompositematerialisdiffering in accordance with different layer of thermoplastic in compressivetest.ofcompositescompressivestrengthofthe increasesandstrong withincreasinglayerofReinforcement up to 3 layer and then start decreasing. It means the propertiesofcompressivestrengthmaterialareverygoodas comparetotensilestrength.
I would like to thank PhD Scholar and Former Assistant professorMr.DirendraKumar,whohavehelpedmeinthe understandingtheconceptof compositeandreinforcement.
[1] JohnBibin,ReghunadhanNairCP,AmbikaDeviK,Ninan KN.Effectoflow densityfilleronpropertiesofsyntactic foamsofcyanateester.MaterSei2007:42:5398405.
[2] Wouterson Erwin M, Boey Freddy YC, Hu Xiao, Wong Shing Chung.Specificpropertiesandfracturetoughness of syntactic foam: effect of foam microstructures. ComposSciTechnol2005;65:1840 50.
[3] NikhilGupta,RaymondYe,MaurizioPorfiri.Comparison of tensile and compressive characteristics of vinyl ester/glassmicroballoonsyntacticfoams.Composites: PartB41(2010)236 245.
[4] C. Swetha, Ravi Kumar. Quasi static uni axial compression behavior of hollow glass Microspheres/epoxy based syntactic foams. Materials andDesign32(2011)4152 4163.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[5] GuptaN,Kishore,WoldesenbetE,SankaranS.Studieson compressivefailurefeaturesinsyntacticfoammaterial.J MaterSci2001;36:4485 91.
[6] WenfengXie, Hao Yan, Qilin Mei, Ming Du, Zhixiong Huang.Compressiveandfracturepropertiesofsyntactic foam filled with hollow plastic bead (HPC). J Wuhan UnivTechnol MaterSciEd2007:22:499 501.
[7] ViotPh,ShankarK,BernardD.Effectofstrainrateand densityondynamicbehaviouroffoam.ComposStruct 2008,86:314 27.
[8] GuptaNikhil,MaharsiaRahul.Enhancementofenergy absorption in syntactic foams by nano clay incorporation for sandwich core applications Appl ComposMate2005;12:247 61.
[9] YilmazerUlku.Tensile,flexuralandimpactpropertiesof a thermoplastic matrix reinforced by glass fiber and glassbeadhybrids.ScienceandTechnology44(1992) 119 12
[10] KimHoSung,KhamisMohammadAzhar.Fractureand impactbehavioursofhollow
[11] micro sphere/epoxyresincomposites.ComposPartA: ApplSciManuf2001;32:1311 7.
[12] BrostowWitold, Lobland Haley E. Hagg, Brittleness of materials:implicationsforcompositesandarelationto impactstrength.
[13] Xiao Feng Li, Kin Tak Lau, Yan Sheng Yin. Mechanical properties of epoxy based composites using coiled carbonnanotubes.
[14] Composites Science and Technology 68 (2008) 2876 2881.
[15] Chun KiLam,Hoi yanCheung.Kin takLau,Li minZhou. Man waiHo,DavidHui.clustersizeeffectinhardnessof nanoclay/epoxy composite. Composites. Part B 36 (2005)263 269.
[16] Tang Qi, Jianghong Gong. Effect of porosity on the microhardnesstestingofbrittleceramics:Acasestudy onthesystemofNIO ZrO2.CeramicsInternational 39(2013)8751 8759.
[17] G.Raghavendra,ShakuntalaOjha,S.K.Acharya,S.K.Pal. A Comparative Woven Jute/Glass Hybrid Polymer Composite With and Without Reinforcing of Fly Ash Particles.
[18] GujjalaRaghavendra, Shakuntala Ojha, Samir Kumar Acharya,ChittaRanjanDeo.StudyingtheParametersof theSolidParticleErosionandTestProcedureM.Young, The Technical Writer’s Handbook. Mill Valley, CA: UniversityScience,1989.
[19] R. Nicole, “Title of paper with only first word capitalized,” J. Name Stand. Abbrev.in press. K. Elissa, “Titleofpaperifknown,”unpublished.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page524
