International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology
(IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
AN EFFECTIVE APPROACH TO PREDICT COVID-19 USING DEEP LEARNING ALGORITHMS VIA X-RAY IMAGES
Sneha.C1 , Likith.S M2, Munegowda.S N3, Spoorthi.R 4 , Mr. Vijendra S N5, Dr. Dhananjaya . V6
1,2,3,4 B.E Student, Dept of Computer Science and Engineering, Impact College of Engineering and Applied Science, Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
5 Asst Professor, Dept of Computer Science and Engineering, Impact College of Engineering and Applied Science, Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
6 HOD, Dept of Computer Science and Engineering, Impact College of Engineering and Applied Science, Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India ***
Abstract ML models have long been employed in numerous application areas that required the detection and prioritization of risk variables. Several prediction approaches are widely employed to deal with forecasting challenges. Deep learning (DL) has shown beneficial in medical imaging, and in the aftermath of the recent COVID 19 epidemic, some research has begun to investigate DL based solutions for the aided detection of lung disorders. This study highlights the use of DL approaches for the interpretation of lung ultrasonography (LUS) pictures, as well as the capacity of ML models to predict the number of forthcoming patients affected by COVID 19, which is now regarded as a possible threat to humanity. In this experiment, two conventional deep learning models, RCNN and CNN, were utilized to anticipate the threatening elements of COVID 19. The project's results show that it is a promising mechanism for using these technologies in the current context of the COVID 19 pandemic. For prediction, this study employs a new combination technique. For training, manytypes of data sets areemployed, whichboosts theaccuracyofourproject.
Keywords : RCNN, CNN, Deep Learning, Machine Learning,COVID 19.
1. INTRODUCTION
Due tothefast worldwide SARS CoV 2pandemic, medical equipmentwasinshortsupply.Asidefromagloballackof mouth masks and mechanical ventilators, testing capacity has been severely constrained. As a result, suspected patients and healthcare employees received priority testing. However, thorough testing and diagnosis are critical for effectively containing the pandemic. Indeed, nations that were able to do large scale testing of potentially affected persons, paired with extensive citizen surveillance, were able to significantly control the SARSCoV 2 virus. Because most nations lack testing capability, the necessity for the search for alternate approaches to diagnose COVID 19 has increased.
Furthermore, the latest lab test, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT PCR) arrays, remains highlydependentonswabtechniqueandlocation.
COVID 19 pneumonia can quickly develop into a life threatening disease. The radiological scans of over 1,000 COVID 19 patients revealed various ARDS like symptoms, such as bilateral and multi lobar glass ground opacifications (mostly posteriorly and/or peripherally dispersed). As a result, chest computed tomography (CT) has been proposed as a feasible option for COVID 19 diagnosis. While RTPCR can take up to 24 hours and numerous tests to get clear findings, CT diagnosis can be substantially faster. However, there are substantial limitations to using chest CT: it is expensive, exposes patients to radiation, necessitates lengthy cleaning after images,andisdependentonradiologistinterpretation.
Ultrasound imaging, a more generally available, cost effective, safe, and real time imaging method, has recently gained popularity. Lung ultrasonography (LUS) is increasingly being employed in point of care settings for the identification and treatment of acute respiratory diseases.In certainsituations, it was more sensitive than a chest X ray in identifying pneumonia. Clinicians have recently detailed the use of LUS imaging in the emergency roomforCOVID 19diagnosis.Thefindingspointtodistinct LUS features and imaging biomarkers for COVID 19 patients,whichmightbeutilizedtodetecttheseindividuals as well as regulate the respiratory effectiveness of mechanical ventilation. Because of its broad range of applicability and inexpensive cost, ultrasonic imaging is a highly beneficial tool when patient inflow surpasses the usual hospital imaging infrastructure capacities. It is also accessibletolow andmiddle incomenationsbecausetoits lowprice.However,interpretingultrasoundpicturescanbe difficultanderror proneduetoahighlearningcurve.
1.1 EXISTING SYSTEM
The existing system suggests us the previous works done in a specific domain, where we can refer to and get ideas
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 3244
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
from.Manyfarmingoragricultureassistancesystemshave beenimplementedorproposedfocusedinonlyaparticular aspectorcrop
In a research paper, the scholars proposed a system to predict the amount of fertiliser needed for a specific crop banana, as well as regression methods for future plantations using Neural Networks. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are the three most important soil nutrients for crop growth. The amount of NPK in the soil varies depending on where you live. The requirements for each crop differ as well. In this paper, a model is built to recommend the amount of fertiliser neededforthebananacrop[1].
In a different paper proposed system's goal is to assist farmers in cultivating crops for higher yield. The crops chosen for this work are based on important crops from the chosen location. Rice, Jowar, Wheat, Soyabean, Sunflower, Cotton, Sugarcane, Tobacco, Onion, Dry Chili, and other crops have been chosen. Crop yield data is compiled from various sources over the last five years. Scholars proposed the system in 3 steps: a. Soil Classification b. Crop Yield Prediction and c. Fertilizer Recommendation[2].
A paper published at IEEE predicts the yield of nearly all types of cropsgrown inIndia.This script is novel because it uses simple parameters such as state, district, season, and area to predict crop yields in whatever year the user desires. The paper predicts yield using advanced regression techniques such as Kernel Ridge, Lasso, and ENet algorithms, as well as the concept of Stacking Regressiontoimprovethealgorithms[3].
Rainfall regimes, P application rates, soil P content, and field management practices such as field bund and open ditch construction can all influence phosphorus losses in rice wheat cropping systems. Heavy rainfalls shortly after Papplications,inparticular, causesignificant Ploss,andP lossincreaseswithincreasingPapplicationratesandsoilP content. During the rice growing season, P concentrations infieldpondingwaterregulatePconcentrationsinsurface runoff. The construction of open ditches can increase phosphorus loss during the winter wheat growing season. As a result, we propose that rice wheat cropping systems be managed to avoid heavy rain events while also balancingcrop P removal (20 30kg P ha 1inthisstudy). Furthermore,appropriatewatermanagementpracticesare recommended, such as increasing the capacity of field pondingwaterorusingcontrolledirrigationinconjunction with natural drying of the field rather than open ditches duringthewheatgrowingseason[4].
1.2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
COVID 19 is now affecting numerous nations throughout the world, including India. A few nations, like India, the United States, Germany, Italy, and others, are dealing with its spread in the community transfer phase, which means that one infected individual can infect more than 100 personswithwhomhecomesintotouch.So,theapproach is to identify sick people and place them in quarantine to preventfurthertransmission.Existingdiagnosis processes foridentifying the infectedindividual aretime consuming, whichslowsdiagnosiswhendealingwithahighnumberof cases. As a result, to address this issue, we devised a methodology that can efficiently categorize COVID 19 positive and negative situations ahead of time. The aim is to use an automated machine learning based model to categorize persons as COVID 19 positive or COVID 19 negative. As an input parameter, the model uses X ray picturesthatdepictthedisease'searlysymptoms.
2. PROPOSED SYSTEM
ML models have long been utilized in a variety of applications requiring the identification and prioritization of peril factors. To deal with forecasting issues, several prognostication methodologies are extensively utilized. Deep learning (DL) has shown utilizable in medical imaging, and during the recent COVID 19 outbreak, some research has commenced to investigate DL predicated solutions for the enhanced diagnosis of lung quandaries. ThisworkemphasizestheapplicationofDLtechniquesfor the interpretation of lung ultrasonography (LUS) images, aswellasthefacultyofMLmodelstoestimatethenumber ofupcomingCOVID 19patients. whichisnowregardedas a possible threat to humanity. In this experiment, two conventional deep learning models, RCNN and CNN, were utilized to anticipate the threatening elements of COVID 19. The project's results show that it is a promising mechanism for utilizing these technologies in the current context of the COVID 19 pandemic. For prognostication, this study employs an incipient amalgamation technique. Fortraining, many types of data sets are employed, which booststheprecisionofourproject.
3. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
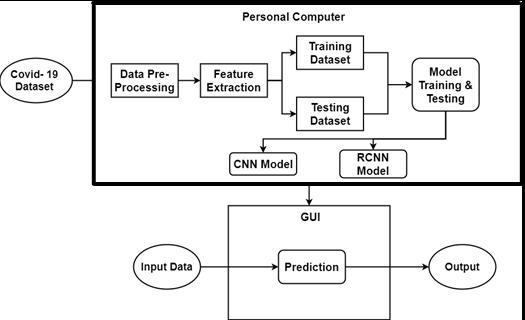
Data Preprocessing: The picture dataset received from the GitHub repository is utilized for the first phase data processing. The collection contains scanning pictures of covid and non covid patients. Each dataset is divided into training and testing datasets for further processing. Following pre processing, the dataset is sent into deep learningalgorithmsformodeltraining.
Deep learning is performed on a computer using the Python programming language. The data set can be fed into the system to be processed. The supplied image is filtered, and its features extracted. The model was trained usingtheTensorFlowartificialintelligencemodule.
Fig 1 :BlockdiagramofProposedSystem
4. PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
This project may be divided into three major steps: data processing,modeltraining,andprediction.Theprimary
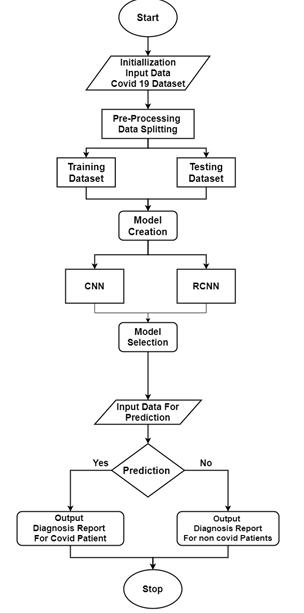
prediction technique based on input data is based on an imagedataset.
Model Training: The second stage is model training. For training purposes, two types of model generation algorithmsareused:CNNandRCNN.Afterbuildingmodels using dataset supporting characteristics, they are all comparedforcorrectness.
Model Selection: The model that was built is stored for prediction. Prediction is the third phase. A graphical user interface(GUI)isdesignedtofacilitateuserinteraction.
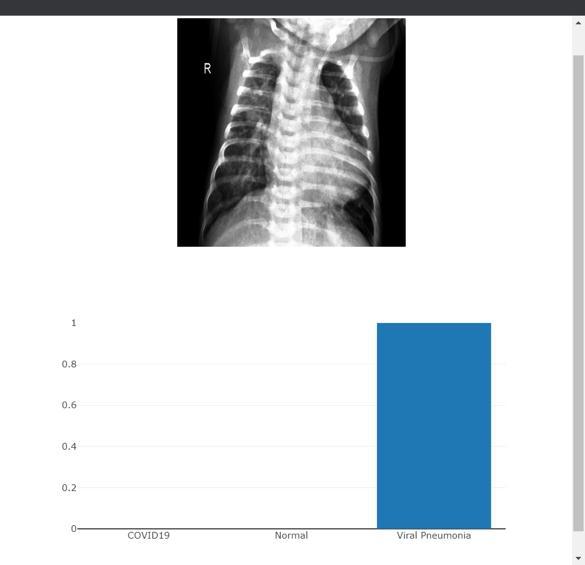
Input data for Prediction: This GUI includes choices for addingapictureasinput,selectingapredictionmodel,and seeing the expected result. The user can provide scanned image data of a patient, and our technology will forecast whetherthepatientisaffectedbycovid.
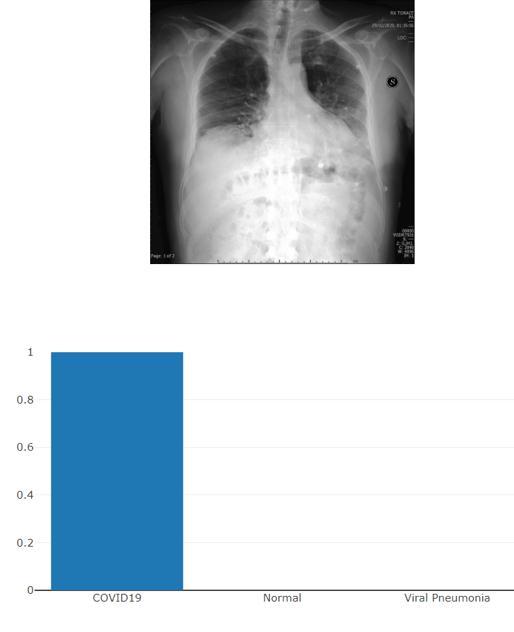
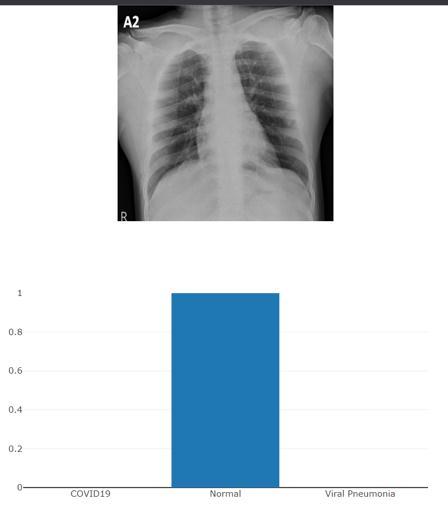
5. OUTCOMES
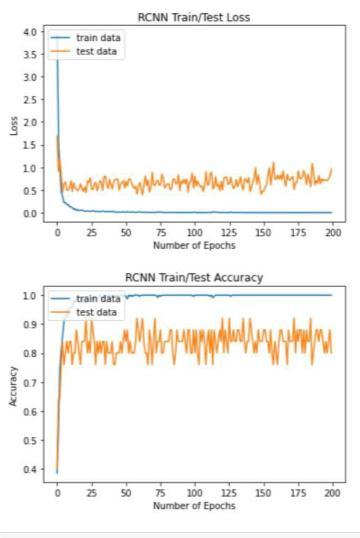
Graph 1 : GraphicalRepresentationofLossduring training&Accuracyofresult
Fig 2 : SystemDesign
6. CONCLUSION
Inthispaper,wepresentanensemblebasedDeQueezeNet model comprisedofDenseNet121and SqueezeNet1.0.The model's performance is evaluated by applying it to X ray images to predict COVID 19 positive and negative instances. The performance measures of accuracy, precision,andrecallareusedtoevaluateperformance.The confusion matrix demonstrates that the suggested approach can accurately detect COVID 19 positive and negative situations. The model's relevance is indicated by itsappropriate accuracyandhigh precision. Acomparison study is also conducted using current work on the performance criteria. In which it is noted that the performance of the suggested model is much superior, indicating the model's relevance. Furthermore, it demonstrates that the suggested model is best suited for identifyingCOVID 19positiveandnegativesituations.
REFERENCES
[1] R.Niehus,P.M.D.Salazar,A.Taylor,andM.Lipsitch, “Quantifying bias of COVID 19 prevalence and severity estimates in Wuhan, China that depend on reported cases in international travelers,” medRxiv, p.2020.02.13.20022707,feb2020.
[2] Y. Yang et al., “Evaluating the accuracy of different respiratory specimens in the laboratory diagnosis and monitoring the viral shedding of 2019 nCoV infections,” medRxiv, p. 2020.02.11.20021493, feb 2020.
[3] S. Salehi, A. Abedi, S. Balakrishnan, and A. Gholamrezanezhad, “Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID 19): A Systematic Review of Imaging Findingsin919Patients,”AmJRoentgenol,pp.1 7, mar2020.
[4] A. Bernheim et al., “Chest CT Findings in CoronavirusDisease 19(COVID 19):Relationshipto Duration of Infection,” Radiology, p. 200463, feb 2020. [Online]. Available: http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiol.20202004 63
[5] F. Mojoli, B. Bouhemad, S. Mongodi, and D. Lichtenstein, “Lung ultrasound for critically ill patients,”pp.701 714,mar2019.
[6] R. Raheja, M. Brahmavar, D. Joshi, and D. Raman, “Application of Lung Ultrasound in Critical Care Setting:AReview,”Cureus,vol.11,no.7,jul2019.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[7] Y. Amatya, J. Rupp, F. M. Russell, J. Saunders, B. Bales, and D. R. House, “Diagnostic use of lung ultrasound compared to chest radiograph for suspectedpneumoniainaresource limitedsetting,” International Journal of Emergency Medicine, vol. 11,no.1,dec2018.
[8]
E. Poggiali et al., “Can Lung US Help Critical Care Clinicians in the Early Diagnosis of Novel Coronavirus (COVID 19) Pneumonia?” Radiology, p. 200847,mar2020.
[9] Q.Y.Pengetal.,“Findingsoflungultrasonographyof novel corona virus pneumonia during the 2019 2020epidemic,”IntensiveCareMedicine,no.87,pp. 6 7,mar2020.
G. Soldati et al., “Is there a role for lung ultrasound during the covid 19 pandemic?” J Ultrasound Med, 2020.
“Proposal for international standardization of the use of lung ultrasound for COVID 19 patients; a simple, quantitative, reproducible method,” J. UltrasoundMed.,2020.
K. Stefanidis et al., “Lung sonography and recruitmentinpatientswith earlyacuterespiratory distress syndrome: A pilot study,” Critical Care, vol. 15,no.4,p.R185,aug2011.
K. A. Stewart et al., “Trends in Ultrasound Use in Low and Middle Income Countries: A Systematic Review.”InternationaljournalofMCHandAIDS,vol. 9,no.1,pp.103 120,2020.
S. Makridakis, E. Spiliotis, and V. Assimakopoulos, “Statistical and machine learning forecasting methods: Concerns and ways forward,” PloS one, vol.13,no.3,2018.
G. Bontempi, S. B. Taieb, and Y. A. Le Borgne, “Machine learning strategies for time series forecasting,” in European business intelligence summerschool.Springer,2012,pp.62 77.
