International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
S Dharshika 1 , Sahreen Sajad 2 , Sushmitha N 3
1 ,2 Department of Information Science and Engineering, R.V. College of Engineering, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India 3 Assistant Professor, Department of Information Science and Engineering, R.V. College of Engineering, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India ***
Abstract - Epilepsy has severe impacts on patients including disrupting their social relationships and less mobility. Prediction of the disease can help the patient prevent the onset of seizures with the help of appropriate medication. Since the traditional methods of studying EEG are prone to misdiagnosis, Machine Learning can provide a more accurate diagnosis. In this paper, we aim to survey models to better describe methodologies for a high precision model to predict epilepsy in patients.
Key Words: Seizure, EEG (Electroencephalogram), Machine Learning, KNN (K Nearest Neighbour, Logistic Regression,Decisiontree.
Epilepsyisadisordercharacterizedbythepatient’sfrequentseizureepisodes.Thesecanbebrieforevengoundetected. Inothercases,seizuresarefoundtoshowcaseconstantshaking.Epilepsyoccursbecauseofabnormalfunctioningin brain activity.WHOdefinesEpilepsyas“havingtwoormore unprovokedseizures.”The diseasecanhaveseverecomplications for the patient from breaking bones to causing accidents. In the case of epilepsy, there is no certain cause for a seizure. Seizures that are caused due to some specific causes are not considered Epilepsy. Epileptic patients usually become victimsofsocialstigmaandexperiencesocialanxietymorethanothers.
Epilepticseizuresareseenwhenthereissomesortofabnormalactivityofneuronsinthecortexofthebrain.Cortexisthe neural tissueoutsidethecerebrumofthebrainandisoftencalledgreymatter. Thisabnormal activityofneuronscanbe witnessed in the electroencephalogram (EEG) of the patient. In most cases, the underlying cause of the disease remains unknownbutcouldalsobeduetoinjuries,stroke,orcertaininfections.
People carrying the disorder experience frequent bruising or fracturing of bones due to injuries caused by the disorder. The psychological condition of the patients also seems to be affected. Epilepsy patients have higher risks of anxiety and depression due to social stigma as well as lack of self confidence. Premature deaths also occur thrice higher than the peoplewhodonotcarrythedisorder.Causesofdeathalsoincludeprolongedseizures,accidentalfalls,ordrowning.These canbepreventable.Medicationcanhelpcontroltheintensityofseizures,butmaynotalwaysbehelpful.Inabout31%of cases,themedicationsarenotmuchhelpful.Incaseswheremedicationdoesnotprovidemuchhelp,surgeryoptionsmay be considered. Epilepsy does not always remain lifelong. The symptoms can reduce to an extent that treatment may no longerbenecessary.
About 50 million people worldwide are Epilepsy patients. 5 million people are diagnosed with Epilepsy every year. CountrieswithbetterincomearelesslikelytohaveEpilepsythanthosewithlesser income.Thiscouldbebecauseofthe highertendencyinlow incomecountriestocontractbirthinjuries,malaria,andotherdiseases.
Electroencephalography(EEG)recordsbrainactivityto helpunderstandthebrainsignalscorrespondingtothestateofa human’s brain. When the EEG test is carried out, small sensors are attached to the patient’s head which helps to pick up thesignalsproducedbythebrain.Thesignalspickeduparerecordedbyamachineandadiagnosisismadebythedoctor.
TheEEGdiagnosisisalittledifficulttocarryoutandmayleadtomisdiagnosisinsomecases.Atrainedspecialistcarries outthetest.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Insomecases,anormalEEGisnotenoughtounderstandwhichtreatmentwouldbethebestforthepatient.Insuch cases, there are attempts made to record EEG when the seizure is occurring in the patient. This is referred to as the ictal recording.WhenEEGsignalsaretakenbetweenseizures,they’rereferredtoastheinter ictalrecording.Anictalrecording includesanaudioandavideowhicharesynchronized.Duringsuchtime,medicationsareusuallynotgiventothepatients incasethetestiscarriedoutinahospital.Ifit’scarriedoutoutsidethehospital,thenthemedicationsarenotwithdrawn.
Fig 1: EEGSignalofanEpilepticSeizure[1]
Epilepsy Prediction and Detection have been the focus of research owing to the severe consequences of the disease and thatthepredictionofthediseasecouldleadtobettertreatments.Variousresearchpapershavebeenwrittenthatpropose newmethodstopredictEpilepsywithhigheraccuracyandhelppre processtherawEEGdatasignals.Researchpopularly involves AI and Machinelearning Techniques including Deep Learning. The following includes various related work that hashelpedusproposeamethodologyandunderstandtheadvancementinthefielduntilnow.
Authorsin[2]hadtheobjectivetopredictEpilepsyusingDeepLearningtechniques.Variousdatasetshavebeentakeninto consideration and a review of various neural networks like CNN is made. The results of the various networks are compared.
Authorsin[3]tookuseofMachineLearningclassifierstopredictEpilepsy.ThiswasdoneusingBlackBoxandNon Black Box Classifiers. In addition to this, the performance of K Nearest Neighbours, SVM, and ANN. Etc. is measured and compared.
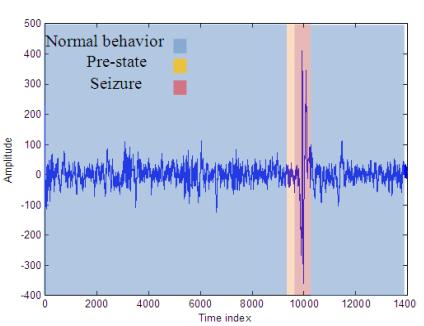
Authors in [4] had the aim to detect Epilepsy using EEG signals. The paper focuses on comparing the EEG signals of a normal patient to that of an Epileptic patient. Raw EEG waves undergo Fourier Transformation and Short Time Fourier Transformation.
Theauthorin[5]aimedtopredictEpilepsyusingEEGsignals.ThispaperfocusedontheproblemsfacedbyDeepLearning and Artificial Intelligence in regard to processing the raw EEG signals that may lead to misdiagnosis. Various evaluation metricsareusedtodisplaytheresultsandshortcomingsofthemethods.
Authors in [6] intended to make use of Artificial Intelligence in Epilepsy Detection. This comprised of application of AI including Color Coded Paradigms that could only be studied by experts as well as fully automated analyses that were lesseraccuratebutcouldbereadbyanyone.
Authors in [7] made a comparative study based on EEG and ECG (Electrocardiogram) signals and models were built. Variousevaluationparameterswereusedtocomparetheresults.
Authorsin[8]alsointendedtodetectEpilepsyusingEEGSignals.ThisinvolvedtheimplementationoftheSupportVector MachineandFeedForwardClusteringTechniquewhichwasdoneusingMATLAB.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Authorsin[9]proposedasystemthatcouldpre processEEGsignalsbasedontheirfirstandsecondderivates.Theinput featuresarereducedinthismodelwithoutdisturbingtheresultsinanyform.
ThedatasetistakenfromUCIMachineLearningRepository.11,500samplesaretakeninthedataset.Allofthesehave158 features each. Five classes are then built to categorize the taken samples referred to as 1,2,3,4,5. Class 5 corresponds to EEGsignalswhentheeyesareopen.Class4correspondstoEEGsignalswhentheeyesareclosed.Class3correspondstoif theEEGsignalidentifiesabraintumor.Class2correspondstotheareawherethebraintumorislocatedandfinally,Class 1istherecordingoftheseizureactivity.
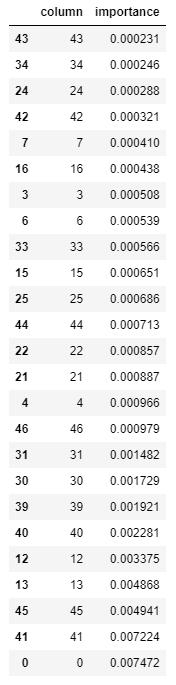
Anewdatasetisobtainedfromtheoldonebytransformingusingdiscretewavelettransform.Byadjustingthesizeofthe componentbasisfunctions,itissimpletoestimateaspikeintheEEGsignalsincewaveletshaveafinitesupport.Anytime varyingsignal,forinstance,willbedividedintosmalleruniformfunctions,referredtoasthefundamentalfunctions,using discrete wavelets. A total of 25 features are taken from the dataset that has the highest importance using feature extractiontechniques.Randomforestfeaturesselectiontechniqueisusedforthispurpose.Followingarethecolumnsand theirimportance: Fig 2: FeatureImportance
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Followingaresomeofthemodelsthatareusedalongwithperformancemetricsandtheircomparison:
2.3.2
This classifier helps to measure the Euclidian distance between the test data and the training data. Here, we do not calculate for the closest image. We look for multiple k closest images in the training set which is used to predict which classthetestimagebelongsto.
Training:AUC:0.992,Accuracy:0.640,Recall:0.281,Precision:0.998,Specificity:0.999,Prevalence:0.500 Validation:AUC:0.975,Accuracy:0.840,Recall:0.241,Precision:0.958,Specificity:0.997,Prevalence:0.208
Logistic Regressionwill helptogivea linearrelationshipbetweentwoimages.This will inturnhelptocalculatethetrue andthefalsevalues.Ifthemodelisseparatedbasedonpositiveandnegativeelements,themodelworksbetter.
Byimposingalinearfunctionontheinputfeaturesbyprojectingthesamplepointsontoaline,logisticregressionanalyses theinputcharacteristics.Thelogisticregressionlineisproducedbymaximizingthelogoflikelihood,whichisthesameas maximizing the likelihood, by the linear function, which is achieved by adding the log of the likelihood of each sample point. In a binary classification model, the best fitting function would indicate that the probability of the positive class wouldbeverynearto1(100percent),andtheprobabilityofthenegativeclasswouldbeverycloseto0.
Training:AUC:0.628,Accuracy:0.666,Recall::0.538,Precision:0.722,Specificity:0.793,Prevalence:0.500 Validation:AUC:0.975,Accuracy:0.840,Recall:0.241,Precision:0.958,Specificity:0.997,Prevalence:0.208
They select the decision boundary that optimizes the distance from the nearest data points of all the classes, and SVMs varyfromotherclassificationtechniques.Themaximummarginclassifierormaximummarginhyperplaneisthenameof thedecisionboundaryproducedbySVMs.Theaccuracyachievedis96%.
ThenumberofparametersrequiredfornaiveBayesclassifiersislinearinthenumberofvariables(features/predictors)in alearningtask,makingthemextremelyscalable.Insteadofusingacostlyiterativeapproximation,asisthecasewithmany othertypesofclassifiers, maximumlikelihood training maybe performedsimplybyevaluatinga closed form expression thattakeslineartime.
Training:AUC:0.982Accuracy:0.930,Recall:0.890,Precision:0.967,Specificity:0.970,Prevalence:0.500 Validation:AUC:0.985,Accuracy:0.960,Recall:0.916,Precision:0.893,Specificity:0.971,Prevalence:0.208
Recurrent neural networks are a type of long short term memory. The output from the previous phase is sent into the currentstepofa5RNNasinput.Itaddressedtheissueoflong termRNNdependency,inwhichtheRNNcanpredictwords fromcurrentdatabutcannotpredictwordsheldinlong termmemory.
RNN'sperformancebecomeslesseffectiveasthegaplengthrises.Bydefault,LSTM maysavethedataforaverylongtime. Itisutilizedfortime seriesdataprocessing,forecasting,andclassification.
Atotalof50epochswasgiventoachieveanaccuracyofover95%.
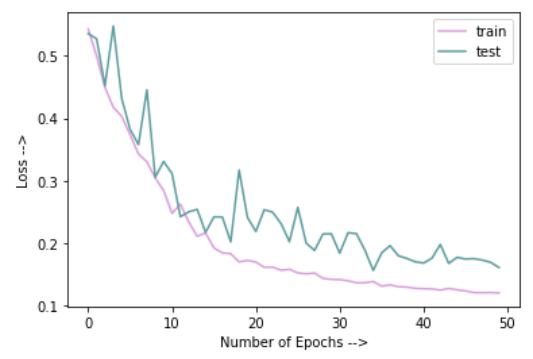
Graphsforlossandaccuracyareplottedtorecordhowthesekeptchangingwiththenumberofepochs.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Fig 3: Trainingv/sValidationLoss
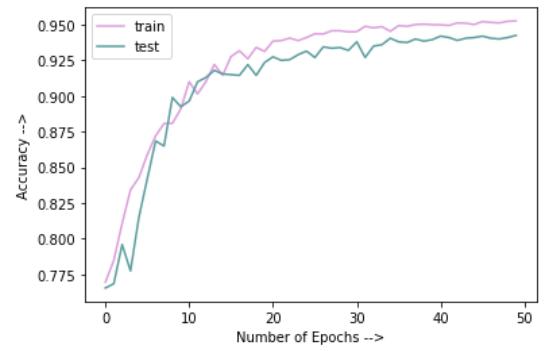
Fig 4: Trainingv/sValidationAccuracy
A decision tree often poses a question, then categorizes the sample based on the response. Category or numerical classificationsarebothacceptable.Thetreefinishesafterthealgorithmhavesplitallsamplesintoclassesorbysatisfying specificcriteriaoftheclassifiercharacteristics.
Theclassifyingmethodoperatesbyrepeatedlydividingdataintosub regionsofthesameclass.Arootnode,oftenknown as the root, is the top of the tree. There are arrows leading both to and away from internal nodes, sometimes known as simply nodes, which branch out farther. Last but not least, arrows point to Leaf Nodes or just Leaves but not away from them.
Training:AUC:0.985,Accuracy:0.982,Recall:0.964,Precision:0.999,Specificity:0.998,Prevalence:0.500 Validation:AUC:0.865,Accuracy:0.909,Recall:0.853,Precision:0.744,Specificity:0.922,Prevalence:0.208
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Thiswillbeusedifarandomruleisusedtoclassifythedataset.Tosimulatethedecisiontree,errorpruningisusedsothat thedatagetsrandomized.Thebatchsizeistakentobe100.
Random Forest in itself is a collection of tree classifiers that give an average output of the multiple tree classifiers. Randomnesscouldeitherbethenumberofrowsintheoriginaldatasetorthenumberofcolumnsorbranchesofeachtree inthedataset.TosimulateRandomForest,theseedistakenas1.Theserepresentthenumberofthreadsthatwillbeused toconstructtheforest.
Batchsizeistakenas100andthenumberofiterationsisalsotakentobe100.Thesearethenumberoftreesintheforest. By bootstrapping the set of samples or utilizing an arbitrary number of characteristics at each split, a random forest is created by grouping decision trees that are not connected with one another. As Random Forest blends flexibility with decisiontreesimplicity,itimprovesaccuracy,whichisoneofthedecisiontrees'limitationsasaclassifier.
Training:AUC:0.997,Accuracy:0.964,Recall:0.943,Precision:0.985,Specificity:0.985,Prevalence:0.5006 Validation:AUC:0.990,Accuracy:0.958,Recall:0.937,Precision:0.869,Specificity:0.963,Prevalence:0.208
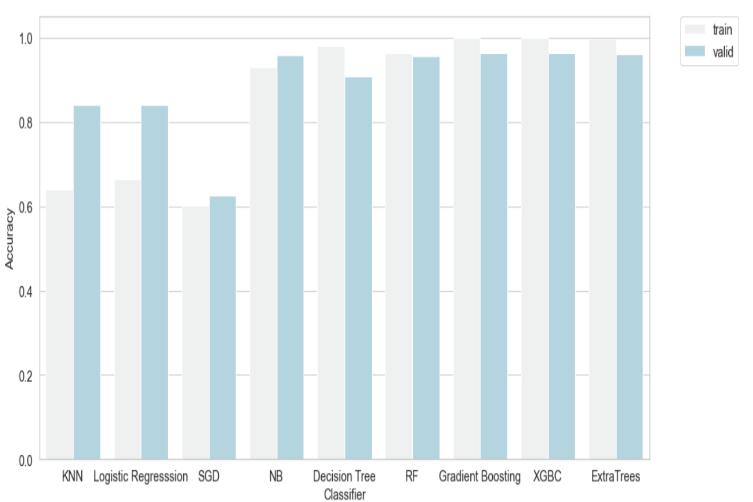
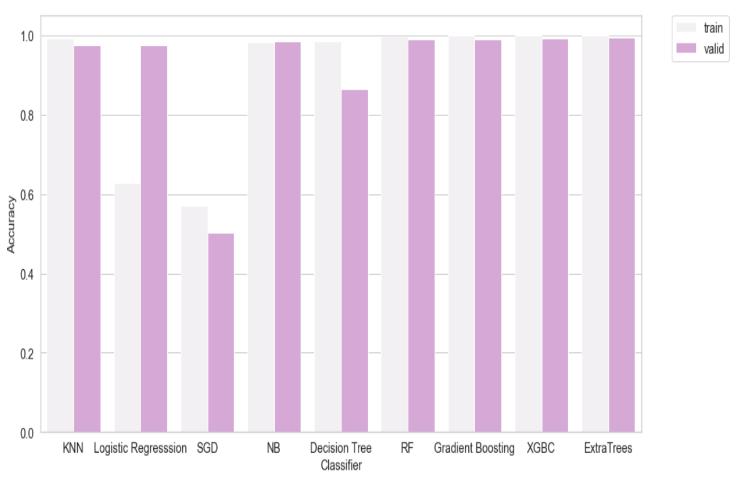
Variousperformancemetricsaretakenintoconsiderationtofindoutwhichmodelperformsthebest.Athresholdvalueis setto0.5.Inordertocompare,twooftheperformancemetricsaretakenforvisualizingi.e,AUCandaccuracy.Followingis theoutputobtained:
Fig 5: Accuracyofeachmodel
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Fig 6: AUCofeachmodel
The prediction of Epilepsyisstill undergoing research andnosuchsystemhas been builtyet thatis100% reliableto be used by experts in the medical field. Besides, these systems require some sort of technical expertise as well as medical expertisewhichmayormaynotbealwayspresent.
TheusageofEEGsignalsispreferredoverECGsignalsbuttheserequireabetterformofpreprocessing.Therawdataform needsbetterhandling.Epilepsycasesaremoreprevalentincountriesthatdon’thaveagreat economicsetup,assuch,the needistodeploysuchsystemsinthesecountrieswhere Epilepsyisgrowingeveryyearandmedical treatmentisalmost negligible.
ThispaperproposesmodelstobetterpredictEpilepsyinpatients.Asmorecasesareemergingeveryyear,thispaperaims tohelpresearchersbetterchooseamodelthatcanhelppatientswhoarepronetobecomeEpilepticsoastoprovidebetter treatmentandhealthfacilities.
The patient’s EEG signals would help the system to predict if they have Epilepsy or not. The model is expected to train usingthedatasetofvariousepilepticandnon epilepticpatientssoastohelppredictconsecutiveseizuresinepilepsy. The goal of this work is to help patients with the disorder as they usually become prone to various physical injuries like accidents or falls. Since the social stigma around such patients who suffer severe episodes of seizure is high, the self confidenceofsuchpatientsseemstobelackingandbecomingthecauseofotherproblemslikedepressionandanxiety.We aim to help predict the neurological disorder in susceptible patients so that the right course of treatment is given at the righttimesothatithelpstoreduceormaybe,evenpreventthedisorder.
[1] Mostafa I. El Sayeid, Entessar Gemeay, Salah Khames, Turkey Alotaiby, Saleh A. Alshebeili, Fathi E. Abd El Samie, “Statistical Analysis of EEG Signals in 7 Wavelet Domain for Efficient Seizure Prediction.” American Journal of BiomedicalEngineering.usingsentiment”,March2016
[2] Shoeibi,A.; Khodatars,M.;Ghassemi,N.;Jafari,M.;Moridian,P.;Alizadehsani,R.;Panahiazar,M.;Khozeimeh,F.;Zare, A.;Hosseini Nejad,H.; Khosravi,A.;Atiya,A.F.;Aminshahidi,D.;Hussain, S.;Rouhani,M.;Nahavandi,S.;Acharya,U.R. Epileptic Seizures Detection Using Deep Learning Techniques: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5780.
[3] Siddiqui, M.K., Morales Menendez, R., Huang, X. et al. A review of epileptic seizure detection using machine learning classifiers.BrainInf.7,5(2020).
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[4] S. Gupta, S. Bagga, V. Maheshkar and M. P. S. Bhatia, "Detection of Epileptic Seizures using EEG Signals," 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Signal Processing (AISP), 2020, pp. 1 5, doi: 10.1109/AISP48273.2020.9073157.
[5] K.Rasheedetal.,“MachineLearningforPredictingEpilepticSeizuresUsingEEGSignals:AReview,”inIEEEReviewsin BiomedicalEngineering,vol.14,pp.139 155,2021,doi:10.1109/RBME.2020.3008792.
[6] Kaur,Taranjit &Diwakar,Anirudra & Kirandeep, &Mirpuri, Pranav& Tripathi,Manjari& Chandra, PSarat& Gandhi, TapanK.(2021).ArtificialIntelligenceinEpilepsy.NeurologyIndia.69.10.4103/0028 3886.317233.
[7] Yang,Yikai&Truong,Nhan&Maher,Christina&Nikpour,Armin& Kavehei,Omid.(2021).AcomparativestudyofAI systems for epileptic seizure recognition based on EEG or ECG. 2021. 2191 2196. 10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9630994.
[8] Bhatia, Prabhpreet & Sharma, Anurag. (2016). Epilepsy Seizure Detection Using Wavelet Support Vector Machine Classifier.InternationalJournalofBioScienceandBio Technology.8.11 22.10.14257/ijbsbt.2016.8.2.02.
[9] Brari,Zayneb&Belghith,Safya.(2021).Anovel MachineLearningapproachforepilepsydiagnosis usingEEGsignals basedonCorrelationDimension.IFACPapersOnLine.54.7 11.10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.11.018.
[10] R.G.Andrzejak,K.Lehnertz,C.Rieke,F.Mormann,P.David,C.E.ElgerIndicationsofnonlineardeterministicandfinite dimensional and finite dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: dependence on recording regionandbrainstate.
[11] Samiee, K., Kovacs, P., and Gabbouj, M. “Epileptic seizure classification of EEG time series using rational discrete shorttimefouriertransform,”2019IEEE
[12] SSyedMuhammadUsman,ShehzadKhalid,andMuhammadHaseebAslam.“Epilepticseizurespredictionusing deep learningtechniques,”2020IEEE
[13] Nhan Duy Truong, Levin Kuhlmann, Mohammad Reza Bonyadi, Damien Querlioz, Luping Zhou, and Omid Kavehei. “Epilepticseizureforecastingwithgenerativeadversarialnetworks,”2019IEEE
[14] Levin Kuhlmann, David B Grayden, Fabrice Wendling, and Steven J Schiff. “The role of multiple scale modelling of epilepsyinseizureforecasting,”2015AmericanElectroencephalographicSociety
[15] Djoufack,Laurent&Tchiotsop,Daniel&Atangana,Romain&Louis Dorr,Valérie&Wolf,Didier.(2021).Classification ofEEGsignalsforepileptic seizuresdetectionandeyestatesidentificationusingJacobipolynomialtransforms based measures of complexity and least square support vector machine. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked. 23. 10.1016/j.imu.2021.100536.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
