International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Satyam Kumar1 , Shubham Kumar2 , Laxmi V3
1Student, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, BNM Institute of Technology, Karnataka, India
2 Student, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, BNM Institute of Technology, Karnataka, India
3 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Information Science and Engineering, BNM Institute of Technology, Karnataka, India ***
Abstract The goals of video analysis tasks have changed significantly over time, shifting from inferring the current state to forecasting the future state. Recent advancements in the fields of computer vision and machine learning have made it possible. Different human activities are inferred in tasks based on vision based action recognition based on the full motions of those acts. By extrapolating from that person's current actions, it also aids in the prognosis of that person's future action. Since it directly addresses issues in the real world, such as visual surveillance, autonomous cars, entertainment, etc., it has beenaprominent topicinrecent years. Tocreateaneffective human action recognizer, a lot of study has been done in this area. Additionally, it is anticipated that more work will need to be done. In this sense, human action recognition has a wide range of uses, including patient monitoring, video surveillance, and many more. Two CNN and LRCN models are put out in this article. The findings show that the recommended approach performs at least 8% more accuratelythanthetraditionaltwo streamCNNmethod.The recommended method also offers better temporal and spatialstreamidentificationaccuracy.
Key Words: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Long term Recurrent Convolutional Network (LRCN), HumanActivityRecognition(HAR),DeepLearning(DL).
Human Human interactions, such embracing and shaking hands,aswellasHuman Objectinteractions,likeplayinga guitar or tossing a ball, are the two categories in which human action can be broadly classified. This categorization is based on human behavior, and human behavior is defined by gestures, positions, etc. Due to differencesinspeed,lighting,partial occlusionofpersons, perspective,andanthropometryofthosetakingpartinthe different interactions, it might be difficult to recognize humanactivity.Othersaremorestronglyconnectedtothe process of recognizing the activity, while certain identification issues are more closely related to the difficulty of identifying and monitoring people in videos. Action classes are vulnerable to substantial intra class variance because of the camera's perspective. When a personraisesanarmwhilebeingobservedfromthefront or the side, it is not the same gesture as when the same arm is raised. Additionally, lifting the left, right, or both arms in different ways all denote the same motion of
raising the hands. Then there is the issue of a person's particularwayofperformingagesture,includinghowlong itlastsandhowitisperformed.Anotherthingtoconsider is human anthropometric variations, such as those broughtonbyage,size,andbodycomponentratios.
Over the last few decades, researchers have presented a number of handmade and deep nets based action detection algorithms. In the early effort, which was based onhand craftedfeaturesforunrealisticactivities,anactor wouldcarryoutvariousactionsinascenariowithasimple background. These systems extract low level characteristicsfromthevideodataandtransmitthemtoa classifier like a support vector machine (SVM), decision tree,orKNNinordertodetectactivities.
Abdellaoui, M., Douik, A. et al,[1] proposed a brand new DBN based HAR technique, attempts to increase the accuracy of human activity categorization. Segment the videoclipsfromthehumanactivitydatasetintoframesas a firststep. Theresultisthenconverted to binaryframes, and the resulting frames are subjected to a series of morphological filtering techniques in order to improve their quality. Then, generate an input matrix containing the training data, the testing data, and their labels by convertingthenewframesintoa binaryvector.Theinput data for our DBN architecture are represented by this matrix. The DBN classifier will be trained using the trainingdatamatrixinthelastphase,andtheclassification outcomewillbeextracted.
Yu Wei Chao et al,[2] proposed a better method for locating temporal activity in video, called TAL Net, and was modelled around the Faster RCNN object identification framework. By using a multi scale architecture that can accommodate extreme variation in action durations, TAL Net can improve receptive field alignment, extend receptive fields to more effectively exploit the temporal context of actions for proposal generation and action classification, and explicitly take into account multi stream feature fusion while highlighting the significance of fusing motion late. On the THUMOS'14 detection benchmark, the model achieves state of the art performance for both action suggestion and localization, as well as competitive performance on theActivityNetchallenge.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3081
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
For video recognition, Feichtenhofer, Christoph & Fan, et al,[3] introduce SlowFast networks. The suggested model includes two pathways: (i) a Slow pathway that operates at a low frame rate to record spatial semantics, and (ii) a Fast pathway that operates at a high frame rate to record motion with precise temporal precision. It is feasible to maketheFastrouteexceedinglylightwhilestillenablingit to acquire important temporal information for video identification by reducing the channel capacity. The SlowFast technique is acknowledged with generating considerable improvements, as the proposed models successfully classify and detect actions in films. On the crucial video recognition tests Kinetics, Charades, and AVA,providecutting edgeaccuracy.
The automatic detection of human behaviors in surveillancefootageisexploredbyDing,Chunhui&Fan,et al,[4]. The majority of currently used methods rely their classifiers on very complex characteristics that are computed from the raw inputs. CNN is a deep model that can respond immediately to the raw inputs. However, as this time, these models can only accept 2D inputs. In this study,abrand new3DCNNmodelforactionrecognitionis developed. This model utilizes 3D convolutions to extract features from the spatial and temporal dimensions, effectivelycapturingthemotioninformationrecordedina large number of nearby frames. The developed model generatesmultiplechannelsofinformationfromtheinput frames, and the final feature representation combines informationfromchannels.further,boosttheperformance and propose regularizing the outputs with high level features and combining the predictions of a variety of differentmodels
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs),a strong group of models for image recognition issues, have been proposed byAndrejKarpathyetal,[5].Encouragedbythesefindings, present a thorough empirical analysis of CNNs' performance on large scale video classification using a new dataset consisting of 1 million YouTube videos divided into 487 classes. Investigate several ways to strengthena CNN'sconnectioninthetimedomainsothat itcantakeuseof local spatiotemporal data,andsuggest a multiresolution, foveated architecture as a potential fast tracking option. By retraining the top layers on the Kinetics 400 Action Recognition dataset and seeing notable performance increases compared to the Kinetics 400 baseline model, further research the generalization performanceofourbestmodel(63.3percentupfrom43.9 percent).
A variety of applications, including video surveillance, identification verification, the development of intelligent systems for human machine interaction, and many more, benefitfromtheusageofhumanactionrecognition(HAR). Intherealmofcomputervisionandmachinelearning,itis
adifficultproblem.Recognizinghumanactionrequiresan effective feature representation. For HAR, identifying characteristics and focusing only on the geographical region is insufficient; it also has to consider how features have changed over time. Recent years have seen the development of a wide range of action representation techniques, including local and global features based on temporalandspatialchanges,trajectoryfeaturesbasedon key point tracking, motion changes based on depth information, and action features based on changes in human pose. Due to its effectiveness in object identification and picture categorization, deep learning has been widely employed by researchers to identify humanaction.
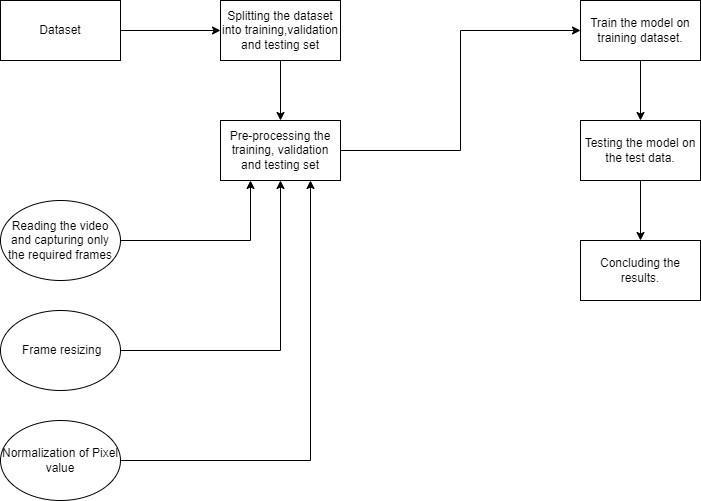
The proposed methodology considers two different deep learning models to predict action in the video. After applying the models for prediction, determination of which model performs better and select an appropriate modeltoobtainbetterefficacy.Inthispaper,theproposed models are CNN and LRCN, which are two of the most recent and effective methods for action prediction in videos, as deep learning mechanisms. The process design ofthesuggestedapproachisshowninFigure1.
Dataset: The Kinetics dataset is a sizable, top notch datasetforidentifyinghumanactivityinvideo.Depending on the dataset version, the Kinetics 400[1] collection of large scale, high quality datasets of URL links to up to 650,000 video clips covers 400/600/700 human activity classes. Handshakes, embraces, and other human human and human object interactions are shown in the films, along with musicians playing instruments. Each action classhasatleast400/600/700videos.Theaveragelength of each clip is 10 seconds, and each has been manually assignedasingleactiontype.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Dataset Preprocessing: The Kinetic 400 dataset will be imported first then, dataset has been divided into three sets: training set, test set, and validation set in ratios of 0.8, 0.1, and 0.1 respectively. In a pre processing step, first, extract a frame from video, then the frame will be resized into 64 x 64 and at last normalization of pixel valueoccurs.Afterpreprocessingofthedataset,themodel CNNandLRCNwillbecreatedandthetrainingsetwillbe fedintothemodel,afterthatthemodelwilltestthemodel on test data. At last, the result will be concluded which modelisbetterbycomparingaccuracy.
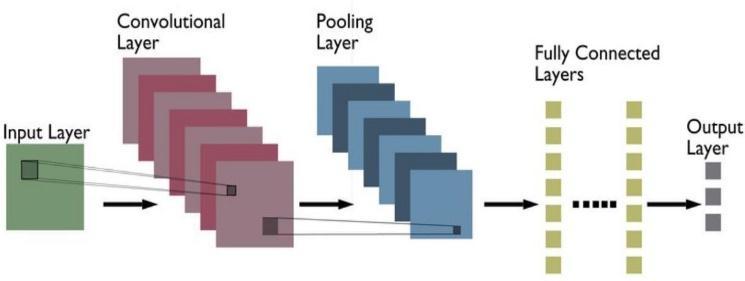
A kind of deep neural networks called convolutional neuralnetworks(CNN/ConvNet)aremostfrequentlyused to assess visual images. When people think about neural networks, matrix multiplications typically spring to mind, but with ConvNet, that is not the case. It makes use of a unique method called convolution. In mathematics, convolutionshowshowtheformofonefunctionisaltered bytheotherbytakingtwofunctionsandproducingathird function.Thepictureisdividedintoregions,andeacharea isthenassigneda different hidden node.Onlyone area of the image is where a pattern is discovered by each concealed node. This region is under the authority of a kernel, often known as a filter or window. A kernel technique allows us to apply linear classifiers to non linear problems by projecting non linear data into a higher dimensional space without physically visiting or comprehendingthathigher dimensionalregion.
Convoluted across the x and y axes is a filter. Several filtersareusedtoextractdifferentpatternsfromtheimage. A variety of filters are utilized at various tiers when buildingthemodel.Inourmodel,4,8,16differentfiltersare applied at various levels. When the output of one filter is convolvedacrossthewholepicture,a2 dlayerofneurons known as a feature map is created. Each filter manages a single feature map. Each filter manages a single feature map.Thesefeaturemapsmaybelayeredtocreateathree dimensional array, which may then be utilized asan input to other layers. The Convolutional layer of a CNN is responsible for doing this. Following these layers are the poolinglayers,asdepictedinFigure2,whichminimizethe output's spatial dimensions (obtained from the convolutional layers). Simply said, a window is shifted in bothdirections,andthefilterorwindow'smaximumvalue is applied (Max Pooling layer). The sole distinction between the two is that, on occasion, the average value during the timeframe is utilized in place of the highest number. As a consequence, the convolutional layers increase the depth of the input picture while the pooling layersdiminishthespatial dimensions(heightandwidth). A image that can be flattened into a 1 dimensional array has information that is encoded using a significant architecture.
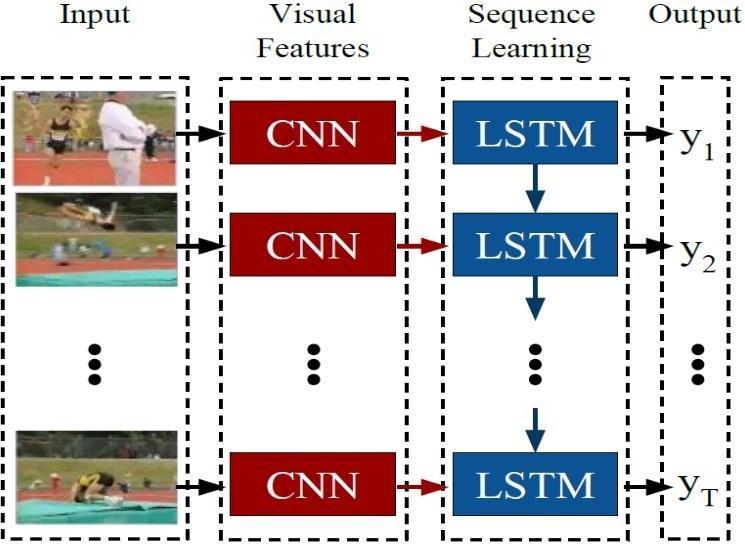
The end to end trainable LRCN is a CNN and LSTM combination that is appropriate for complex visual comprehension tasks including activity detection, video description, and picture captioning. When compared to earlier models, which either assumed a fixed visual representation or carried out simple temporal averaging for sequential processing, recurrent convolutional models are deeper because they learn compositional representationsinspaceandtime.Additionally,becauseit isdirectlycoupledtotheconvolutionalnetwork,itmaybe taughtintemporaldynamicsandconvolutionalperceptual representations.
As seen in figure 3, LRCN uses a CNN to handle the variable length visual input. Additionally, the LSTM, a stack of recurrent sequence models, receives input from their outputs. The final result of the sequence models is a variable length prediction. With time varying inputs and outputs,suchasactivitydetection,picturecaptioning,and video description, the LRCN is a suitable model for handlingthesetasks.
Results from CNN and LRCN Models: The implementation was completed using the Python
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
programming language in the Google Collaboratory's Jupyternotebookenvironment.Modelwhenrunonvideo, is able to recognize Human action well. The frames are extracted from video. It is processed and passed through the model. Then the model predicts the human action. Generalization hence can be taken as another metrics for validation and evaluation of the performance. It is not something that can be plotted, but the evaluation can be done in terms of human action recognition. The several factors affecting this can be the background clutter, changes in scale, lighting and appearance and so on. As discussed, the models are trained with more than 300 videos classes. Thus, it can easily predict human action accurately.Thetotallosstogetherwithvalidationlossand training accuracy along with validation accuracy varied over iterations of performance evaluation for the two models as shown in below figure 4 7. In epoch versus accuracygraph,epochisplotted onx axisandaccuracy is plotted on y axis, when epoch is increased the accuracy also gets increased, while in epoch versus loss graph, epoch is plotted on x axis and loss is plotted on y axis, whenepochisincreasedthelossgetsdecreased.
Fig-6: WiththeLRCNmodel,overallandvalidation accuracy.
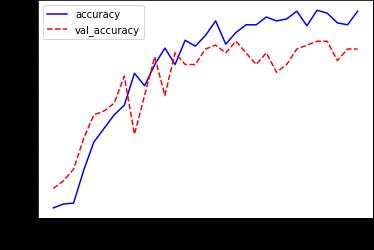
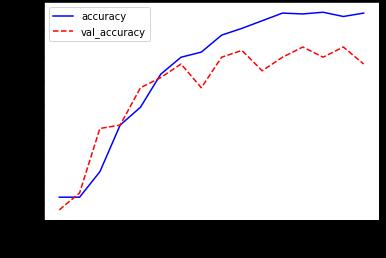
Fig -4: WiththeCNNmodel,overallandvalidation accuracy
Fig 7: WiththeLRCNmodel,overallandvalidationloss.
Table1,showstheresultsofactionrecognitionindifferent videos.Whenvideoisprovidedasinput,theframewillbe extracted from the video and fed into the model. Model extract different features from frame and label action to frameandlabeledframewillbedisplayedasoutput.
Table 1: DifferentvideoHumanactionRecognition Results.
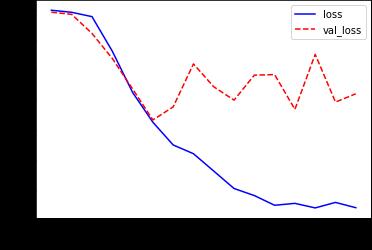
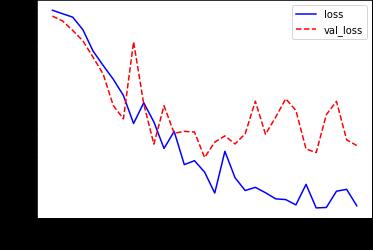
File Name Input Image Result
Fig 5: WiththeCNNmodel,overallandvalidationloss.
Playing_Piano. mp4


Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasplaying piano. Archery.mp4
Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasArchery.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

Making_pizza. mp4
Performing_yo ga.mp4
Playing_flute.m p4

Javelin_throw. mp4
Man_running_o n_treadmill.mp 4
Person_strecthi ng_leg.mp4
Child_climbing_ on_tree.mp4
Person_jogging _on_street.mp4
Air_drumming. mp4

Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasMaking Pizza.

Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionas PerformingYoga.
Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasPlaying Flute.
Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasArchery.

Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasMan runningon treadmill.
Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasPerson stretchingleg.

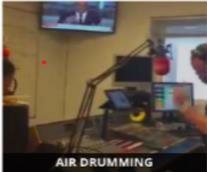

Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasChild climbingontree.


Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasPerson Jogging.
Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasAir
Abseiling.mp4


Person_perfor ming_triple_ju mp.mp4
Person_making _tea.mp4
Drumming.
Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionabseiling.
Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasPerson Performingtriple jumping.
Thisvideois providedasan inputandmodel identifiedthe actionasPerson makingtea.
Comparison of CNN and LRCN Model Results: Create a classification report first, which includes the results obtained for the two models. After comparing the results obtained in paper Action Recognition in Video Sequences using Deep Bi directional LSTM with CNN Features [12], ourmodeloutperformsbyatleast 8%accuracy.Finally,it has been determined that the relative to the CNN model, the LRCN model displays much higher accuracy. ComparisonofResultsfromCNNandLRCNModelsshown inTable2. Table
A
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3085
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
accomplished by using an LSTM based model in place of the conventional convolutional neural network in its spatial stream. The CNN model has been made fast and robust in terms of speed and accuracy with the use of Conv2D layers, dropout regularization, and ideal model hyperparameters. The model proposed in this paper obtained, 84.68% accuracy and 89.71% accuracy in CNN andLRCNmodelrespectivelywiththeKinetic 400dataset. In this article adopting this Human Activity Recognition framework as a future effort to develop an IoT based smart monitoring system for eldercare or childcare. Additionally, if one can create our own dataset using a camera for a certain set of common activities individuals engageinonadailybasis,thatwouldbeidealforthetask. Deep Learning applications seem to have a wide range of enhanced uses in the near future for this study field. The useofthereinforcementlearningparadigmontheareaof activity recognition and classification is also suggested in thepaperasapotentialdirectionforfuturedevelopment
[1] Abdellaoui, M., Douik, A. (2020). Human action recognition in video sequences using deep belief networks.TraitementduSignal,Vol.37,No.1,pp.37 44.https://doi.org/10.18280/ts.370105
[2] Yu Wei Chao, Sudheendra Vijayanarasimhan, Bryan Seybold, David A. Ross, Jia Deng, Rahul Sukthankar; Rethinking the Faster R CNN Architecture for TemporalActionLocalization.ProceedingsoftheIEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR),2018,pp.1130 1139
[3] Feichtenhofer, Christoph & Fan, Haoqi & Malik, Jitendra&He,Kaiming.(2018).SlowFastNetworksfor VideoRecognition.
[4] Ding, Chunhui & Fan, Shouke & Zhu, Ming & Weiguo, Feng&Jia,Baozhi.(2014).ViolenceDetectioninVideo by Using 3D Convolutional Neural Networks. 8888. 551 558.10.1007/978 3 319 14364 4_53.
[5] Karpathy,Andrej&Toderici,George&Shetty,Sanketh & Leung, Thomas & Sukthankar, Rahul & Fei Fei, Li. (2014). Large Scale Video Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 1725 1732. 10.1109/CVPR.2014.223.
[6] S. Z. Gurbuz and M. G. Amin, ‘‘Radar based human motion recognition with deep learning: Promising applications for indoor monitoring,’’ IEEE Signal Process.Mag.,vol.36,no.4,pp.16 28,Jul.2019.
[7] Y. Kim and H. Ling, ‘‘Human activity classification based on microDoppler signatures using an artificial
neural network,’’ in Proc. IEEE Antennas Propag. Soc. Int.Symp.,Jul.2008.
[8] Jalal A, Kamal S, Kim D. A Depth Video Sensor Based Life Logging Human Activity Recognition System for Elderly Care in Smart Indoor Environments. Sensors 2014;14(7):11735 11759.https://doi.org/10.3390/s140711735.
[9] J. Li, S. L. Phung, F. H. C. Tivive, and A. Bouzerdoum, ‘‘Automatic classification of human motions using Doppler radar,’’ in Proc. Int. Joint Conf. Neural Netw.(IJCNN),Jun.2012,pp.1 6.
[10] MW. Li, B. Xiong, and G. Kuang, ‘‘Target classification and recognition based on micro Doppler radar signatures,’’ in Proc. Progr. Electromagn. Res. Symp. FALL(PIERS FALL),Nov.2017,pp.1679 1684
[11] https://www.deepmind.com/open source/kinetics
[12] A. Ullah, J. Ahmad, K. Muhammad, M. Sajjad and S. W. Baik, "Action Recognition in Video Sequences using Deep Bi Directional LSTM With CNN Features," in IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 1155 1166, 2018, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2778011.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
