International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Haridas1 , Amey Naik2
1Deputy General Manager, Schneider Electric India Pvt Ltd 2Senior Manager, Schneider Electric India Pvt Ltd. ***
Abstract - Sheet Metal forming is a phenomenon used in various products to facilitate manufacturing of various complicated3D parts.Butenoughknowhowoftheprocessis not available. Sheet Metal extrusion also called as Pip formation being one of them, is now widely used in many Electrical products in order to simplify the entire product design.Thispaperaimsatstudyingthematerialflowof513D steel under various pre defined conditions and establishes relation and correlation between various factors. The study consisted of experimenting with various combinations of punch diameter, punch depth for various material thickness using statistical tools i.e. DOE and establishing relation between the parameters. The experimental results were analyzed and concluded which can be used as theoretical fundamental for design of sheet metal extrusion (pip formation) process.
Key Words: Coldextrusion,pipformation
The requirements of strong, high performance, and accurately finished functional 3D parts of engineering industry, make sheet bulk metal forming process widely developedcurrentlysoastofacilitatethemanufacturingof thesecomplicated3Dparts.Asoneofthetypicalsheetbulk metalformingprocesses,thesheetmetalextrusionprocess is often used as a prior forming process that is combined withstampingtoproducecomponentswithprotrudedpart or the blind cavity as the positioning element. The sheet metal extrusion process is a combined process in which punchpenetrationandextrusiontakeplaceatthesametime andalargedeformationhappensduringthewholeprocess. Therefore,thetraditionalanalyticalmethodisnotqualified toanalyzethedeformationmechanism,andthereisstillnot enoughknow howavailableaboutthisprocess.Theprocess designisoftenbasedontrialanderrortests,whichisatime consumingprocedure
Theentirepaperaimsatestablishinga relationorfinding outthefactorswhichinfluencedimensionofextrusionlike material flow behavior, rate of strain, diameter of punch, depthofpenetrationetc.
The following method or flow was followed in experimentation.
Atrialtoolwasdesignedbasedontheoreticalevaluationfor pipformation.
1) Thistoolwastriedoutin40THenselpressand resultscompared.
2) AnalysisusingDesignofExperiments(DOE)for pipformation.
3) TrialtakenaccordingtotheDOEin 5T hand press andresultscollated.
4) TrialtakenaccordingtotheDOEin 40T Hensel andresultscollated.
5) TrialtakenaccordingtotheDOEin 30T Hydraulic andresultscollated
Based on these, the metal flow behavior and influence of variousdiametersanddepthofpunchwasanalyzed.
Finallysomeconclusionsweredrawnbasedontheresults.
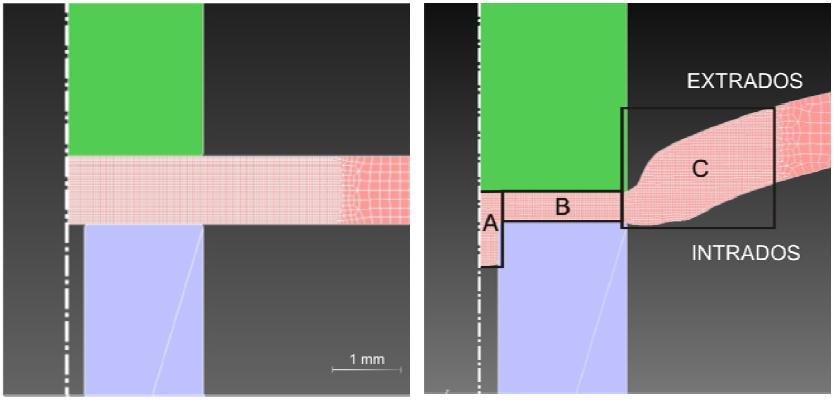
During sheet metal extrusion process, the sheet is held between the stripper and die. The punch then penetrates intothesheetmetalandextrudesittowardstheextrusion outlet of the die. The final workpiece is not the only deformed material. Three different forming areas can be distinguished: the metal filling the die cavity (A), the compressedstripbetweenupperandlowerpunch(B)and thedeformedstriparoundthepunches(C).(1).
Ideally the process should collect as much material as possibleandfavorthefillingofthediecavity,butwhenthe volume between the punches is reduced the material also flowsoutwards.Theamountofmaterialoutsidethepunches should be reduced as much as possible, because it is detracted from the workpiece and furthermore the deformationofthestripadjacenttothetooledgesishigher. (1).Analyzingvariouscomponents,whichwerecontained Pipfeatured,wehaveconcludedthatapproximately50 60% materialisflowintocavityi.e.regionA;whereasremaining material flow into region C. Based on this understanding, followingformulaisformulated.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
wasdecidedtogoaheadwith DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS BY TAGUCHI METHOD.
Design of Experiments (DOE) is a powerful statistical techniqueintroducedbyR.A.FisherinEnglandinthe1920's tostudytheeffectofmultiplevariablessimultaneously.
Taguchi has envisaged a new method of conducting the design of experiments which are based on well defined guidelines. This method uses a special set of arrays called orthogonalarrays.Thesestandardarraysstipulatetheway of conducting the minimal number of experiments which couldgivethefullinformationofallthefactorsthataffectthe performanceparameter.Thecruxoftheorthogonalarrays methodliesinchoosingthelevelcombinationsoftheinput designvariablesforeachexperiment.
Basedontheabovephenomenonatrialtoolwasdesigned and released for manufacturing. Then tool trial was conductedonthe40THenselMachine.Theintentionofthis trialwastoestablishrelationbetweenthetheoreticalvalues andpracticalvaluesofpipwithvariedpunchdiameterand penetration.
Whiletherearemanystandardorthogonalarraysavailable, each of the arrays is meant for a specific number of independentdesignvariablesandlevels.Forexample,ifone wantstoconductanexperimenttounderstandtheinfluence of 4 different independent variables with each variable having 3 set values ( level values), then an L9 orthogonal arraymightbetherightchoice.TheL9orthogonalarrayis meantforunderstandingtheeffectof4independentfactors each having 3 factor level values. This array assumes that there is no interaction between any two factor. While in manycases,nointeractionmodelassumptionisvalid,there aresomecaseswherethereisaclearevidenceofinteraction. InourcasewehaveconsideredL9orthogonalarraywith3 influentialfactorsand3levels
It was decided to develop experiments with controlled externalenvironmentandfollowingaparticularpattern.It
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
For513Dmaterial
Taguchi Analysis: Res 1, res 2, res 3 versus A, B, C
ResponseTableforMeans
Level A B C
1 2.584 2.922 2.834
2 2.836 2.726 3.300
3 3.261 3.033 2.547
Delta 0.677 0.308 0.753 Rank 2 3 1
ResponseTableforSignaltoNoiseRatios Largerisbetter
Factorsconsidered:
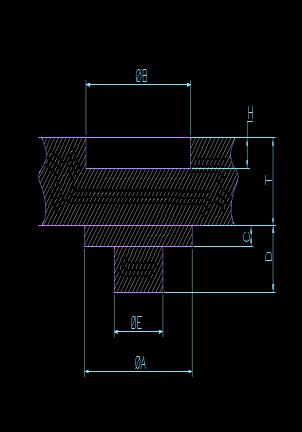
A Punchdiameter(Ø5.05,Ø5.64,andØ6.00
B PunchDepth(0.80,0.90and1.00)
C MaterialThickness(1.2,1.5and1.6)
Experimental Conditions:
1) FirsttrialwithDOEwasconductedin5THand Pressandtheresultsareshown.
2) Secondtrialwasconductedin40THensel MechanicalPress
3) Thirdtrialwasconductedin30THydraulicPress
ANALYSIS REPORT FOR 513D MATERIAL (5T Hand Press)
Level A B C
1 7.690 9.046 8.700
2 8.611 8.039 9.726
10.060 9.275 7.934
2.370 1.236 1.792
1 3 2
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Experimental Conditions of T1, T2 and T3 with DOE: T1

Tooltriedin5T HandPress
Allthe9 experiments conductedand resultsrecorded.
Fromtheabovetwographsitcanbeconcluded thatfollowingconditionisoptimum:
A3 B3 C2 since larger is better.
AlsowhenwecalculatethePercentcontributionofeachof thesefactorswegetthefollowingtable:
Factor Percent Contribution on result (Pip height)

PunchDiameter 32.83% PunchDepth 4.54% Materialthickness 35.29% Error 27.33%
Toolspeedwasless sincetrialconducted inHandpress
Somesampleswith multiplestrokesalso takenfor experimentation
Results of T1 trial recorded and analyzed as per DOE above.
Thisresultshowsthat Punch diameter playsavitalrolein determiningthedepthofpipthananyotherfactor 1 0
Interactiongraph
This interaction graph shows relation between Punch diameterandPunchdepth.
The optimum condition found was with 6Ø punch, 1mm penetrationin1.5mmthick513Dmaterial.Alsothepercent contribution ofpunchdiameterfound more thandepth of punch.Thesameneedstobevalidatedinourexistingtools. But the greatest factor contributing towards larger pip heightisMachinespeedorSPM.Thisexperimentationwas doneinHandpresswhoseSPMisverylow. AstheSPMis low,theflowofmaterialwasmoreuniformandlongerpip height could be achieved. This clearly states that the height of pip depends on the rate of strain applied to the material. Slower the process, better the material flow.
So it can be concluded that if component requirement is higherthancomponentthickness,itisbettertorunthetool inHydraulicpressorslowerpresstogettheresults.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Tooltriedin40T HenselMechanical Press
Allthe9samples takenandresults recorded
Toolspeedwas high Somesamples withmultiple strokesalsotaken for experimentation

Component Photo
T3 trial conditions Component Photo
Tooltriedin 30THydraulic Press
Results of T2 trial as shown below:
Trial No Punch Diameter (ØB) Punch Depth (H) Result (D)
1 6.00 0.75 2.1 2 6.00 0.75 2.2 3 6.00 0.75 2.4 4 6.00 0.75 2.3 5 6.00 0.75 2.3 6 6.00 0.75 2.5 7 6.00 0.85 2.62 8 6.00 0.85 2.70 9 6.00 0.85 2.72
FromT2trialresultsitisclearthatwith6Øpunchand0.85 mmpenetrationin1.2mmthickmaterial,wecangetapip heightof2.5 2.7mmmaximumincludingdomeheightof around0.5.ThisexperimentagainprovesthefacttheType of Machine (Mechanical or Hydraulic) plays a vital role in determiningtheheightofpip.IncaseofHandpress,since theSPMislow,thematerial couldpossiblyflowindeeper space and around 3 times the material thickness height could be achieved. But same tool with similar conditions when tried in Mechanical press could not provide height morethan1.5timesmaterialthickness.Theintentionofthis trialwastoestablishthesignificanceofMachineselection forthisprocess

12samples takenand results recorded Toolspeed waslow Trial No Punch Diameter (ØB) Punch Depth (H) Result (D) 1 6.00 0.85 3.15 2 6.00 0.85 3.20 3 6.00 0.85 3.38 4 6.00 0.85 3.00 5 6.00 0.85 3.10 6 6.00 0.85 3.20 7 6.00 0.85 3.40 8 6.00 0.85 2.60 9 6.00 0.85 3.10 10 6.00 0.85 3.10 11 6.00 0.85 3.30 12 6.00 0.85 3.30
This trial was conducted in Hydraulic press to establish correlationbetweentheresultsofHandpressandHydraulic press.Itcanbeseenfromtheabovetablethattheresultsare matchingandtheobservationsaresimilartothatofHand press.
Inthispaper,thesheetmetalextrusion(Pipformation)was simulated with various values of Punch diameter, Punch Penetration, Machine selection, Tool construction. The StatisticaltoolusedtoreplicatethisscenariowasTAGUCHI Design of Experiment. Based on the experiments and the analysis,somefactorsinfluencingbettermaterialflowcanbe summarizedasbelow:
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3040
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1) As per our percent contribution matrix in DOE it wasfound Diameter of punch playsavitalrolein determiningthepipheight.Thepunchdepthplays onlyminimalroleinincreasingtheheight.
2) Thenextimportantfactorthataffectsthematerial flow is rate of strain that is applied on the material.Theslowertheratebetteristhematerial flow.Hencehydraulicmachinearealwayspreferred aboveMechanicalPresses.
3) Thematerialflowalsodependsonthe polishing of the die and the die radius.Sooptimumdieradius isrequiredformaterialtoflow.Thusincreasingthe dieradiusimprovesmaterialflowwhileincreasing thepunchradiusrestrictstheflow.
4) Tool construction plays a very vital role in determiningtheextrusionheight.Thepunchshould be directly connected to Punch holder for better materialflow.
(1) Simulation of a Full Forward Extrusion Process fromMetalStrip,MarionMerklein,TommasoStellin andUlfEngel,ChairofManufacturingTechnology, University of Erlangen Nuremberg, D 91058 Erlangen,Germany,Pg..494.

Ms.HarshaHaridas DeputyGeneralManager,SEIPL.
 Mr.AmeyNaik SeniorManager,
Mr.AmeyNaik SeniorManager,
SEIPL