International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

“ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF MDR-34”
Mr.Dhananjay D Pardeshi1 , Ms.Nikita D Chavan2 , Mr.Kiran D Wagh3 ,Prof.Junaid S Sayyed1,2,3Diploma Final Year Student,Department Of Civil Engineering,S.N.D Polytechnic Institute, Yeola,Maharashtra,India 4Professor,Department Of Civil Engineering,S.N.D Polytechnic Institute,Yeola,Maharashtra,India ***
Abstract The important roads with a district connecting production and markets places with each other or with the main highways are known as ‘Major District Roads’.The responsibility of construction and maintenance district authorities and state government gives grant for development.
The Major District Road 34 (MDR 34) is a Lasalgaon Patoda Yeola (423401) Road, These Road run through Yeola to Patoda, Our Project is on analysis and design of MDR 34, MDR 34 We are Analysing and designing of upto 3.740 km road from Kopargaon Yeola Road SH 10 to S.N.D polytechnic College campus.
These MDR 34 Road passing through College area so we are studying these road Keeping in view of these MDR 34 road problem, We are suggest good remedial measures to do deal with project topic “Analysis and Designs of MDR 34.All types of operation we will conduct such traffic volume count, Collection of these road data , Take survey Like photography Survey and speed study etc. To Analyze on road traffic patterns, tread and traffic operations. Visit Yeola P.W.D for collecting Information regarding its, Testing on materials of soil, Aggregate and Bitumen etc. Data analysis. To suggest to develop a methodology of MDR 34 and suggestions of future Enhancement.
Key Words: MDR 34, Testing of materials, Traffic Operations, Design of MDR-34, Remidial measures of MDR-34,Photograph Survey
1. INTRODUCTION
The important roads within a district serving areas of productionandmarketsandconnecting theseplaces with eachotherorwiththemainhighwaysareknownasMajor District Roads (MDRs).The responsibility of construction and maintenance of these roads lies with District Authorities.However,thestategovernmentgivesgrantfor development of these roads.The MDR has lower speed andgeometricdesignspecificationsthanforNHorSH
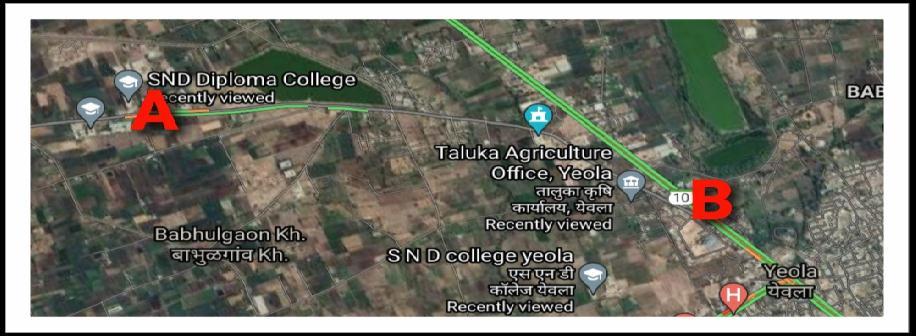
The Major District Road 34 (MDR 34) is a run through Yeola Patoda Lasalgaon Road. The length of road is 32 kilometres. Our Project is an analysis and designing of MDR 34 form S.N.D College Campus to Yeola road upto 3.740 kilometre road. These MDR 34 Road passing
4 .
through College area so we are studying these road KeepinginviewoftheseMDR 34roadproblem.Wewillbe suggest good remedial measures to do deal with project topic“Analysis andDesignsofMDR 34’’.
Fig 1:MDR 34
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Vidya V And Anju k (July 2021):In the implementation of MDR construction projects always risk arise. These risks have greater impact on the execution of the projects, the community of road users and the surrounding environment. These risks have to bestudied, managed and assessed as a risk mitigation effort. Risk identification is thus the first step in risk management process. Descriptive method used in this project identification of variable risk using considering social, technical, economical, political, legal and environmental risks.
2.2 Vasu Choube And Prof. Jitendra Chouhan (June 2021):We know that as the increment in population is directly connected to increment in vehicles. And if number of vehicles increase number of accidents is also increased.Thereasonofaccidentsareroadparametersor human error. We find out from the previews analysis of data that 66% accidents are occur due to human errors and 33% due to the parameters of road. We have 3.3 millionkmnetworkinIndiawhichconsistalltypesofroad justlikeNationalHighway(NH),StateHighway(SH),Major DistrictRoad(MDR)andotherDistrictRoad(ODR
2.3 Dhanavath Seva, Bhukya Chandrashekar And Faria Aseem (November 2017):Ina National Highway project, the engineer has to plan, design and construct either a
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2787
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
network of new roads or road link. Once a highway is constructed, development takes along the adjoining land and subsequent changes in alignment in geometric standards become very difficult. A badly aligned highway is not only a source of potential traffic hazard, but also causes a considerable increase in transportation cost and strainonthedriversandthepassengers.
2.4 Mridula G M,Ashamol Jose And Lidiya P M (November 2016) :Accidents are not natural but they are caused’ is a common cliché in the area of traffic safety. Thus if accidents are caused by some, surely the ones responsible for could be identified and appropriate remedial measures should be developed and implemented to the extend feasible. Various traffic studies such as details of road inventory, signage inventory, traffic volume, pedestrian volume count,spot speed, speed and delay, accident study etc helps in suggesting the improvement measures. Accident data collection helps to identify the cause and type of vehicles involved in the accident. This helps in suggesting measures based on design or other conditions.
2.5 Naveen.N And D.V.Manoj Kumar (May 2016):Road Transport is vital to India’s economy. India’s road networkcarriesover65percentofitsfreightandabout85 percent of passenger traffic. Flexible pavement is composed of a bituminous material surface course and underlying baseand sub basecourses. W.B.M is one type of flexible pavement. When a fast moving vehicle passes over a W.B.M road, the slurry of Murom is sucked out by thepneumaticwheeltires. Thestonepiecesgetdisturbed and finally the road su face is disintegrated. Thus the W.B.Mroadsarenotsuitableforfastmovingvehicleswith thewheelTires.
3. OBJECTIVE OF PROJECT
The main object of our project is to Analysis and DesignofMDR 34.
Todesigntheexistingpavement.
Strength, weakness, opportunity and threat of projects can be identified.
To carry out analysis of black spots using photographysurveyandvisualinspection.
Tojudgethesuitabilityofexistingroute.
To study present condition and parameters of road suchroadconditions,roadfeatures,blockspotetc.
ToAnalyseonroadtrafficpatterns,treadandtraffic operations.etc
ToconductvarioustypesoftestonMaterials.
Toensuresafetyforstudentandpedestrian.
TosuggesttodevelopamethodologyofMDR34.
4. METHODOLOGY
In these topic include the contain of analysis of MDR 34,Study area, Road measurement ,condition of existing pavement,trafficvolumecountandspotspeedstudy
4.1 ANALYSIS OF MDR 34
4.1.1 Study Area
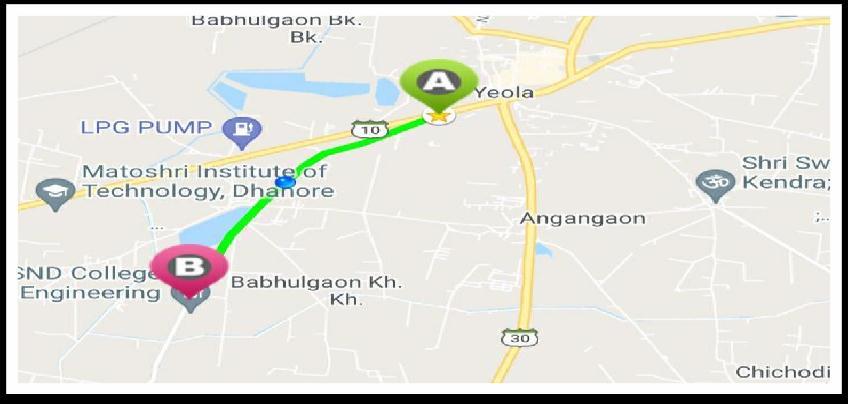
The study area lies at Yeola Taluka, District Nashik, Maharashtra. The location of study can be seen in following fig from A point (Lasalgaon Patoda Yeola Road And Kopargaon Yeola Road Connection) B Point (S.N.D polytechnic College campus),The distance between A and Bpointis3740m
Fig 2:StudyArea

4.1.2 Road Measurement
The distance between two roads point or place measures with the help of tape, Metric chain, rodometer etc it’s knowasRoadmeasurement.
Fig -3:RoadMeasurment
Pavement Width: 5.75m
Length: 3740m
Side Path: 0.9m
Thickness of Pavement:-575mm
4.1.3 Condition Of Existing Pavement
During we have been visited site for quite a number of times. The exiting road is is in Good condition but Some
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

placeswehavefound various defectinthese route. There are very few sign boards on the road and are in very bad condition.Theridingqualityonthewholestretchissome placesisbad.Therearenoroadsignsandmarkingsbeing done on the road. Drains are also improper along the existinghighway.Bothsideareaoftheseroadisless.Some arethefollowingpictureswhichItookduringmyvisitson thesitecangivetheoutlookofthehighway.
Table 1: Morningslotcounting
MORNIING SLOT COUNTING

Vehicle Category Left Turning Right Turning Bus 12 19 Car 123 192 Cycle 15 34 Two Wheelers 392 549 Three Wheelers 70 17 AnimalDriven Vehicle Other Total 612 811
ENUMERATORS RECORD AFTERNOON SLOT
Name Of Approach:-S.N.DPolytechnic. Location: Bhabulgaon Road Type: MDR 34 Date: 22October2021 District: Nashik State: Maharastra Starting Hour: 01:00pm End Hour: 02:00pm
Table -2: Afternoonslotcounting
AFTERNOON SLOT COUNTING
Fig 4:ExistingconditionofMDR
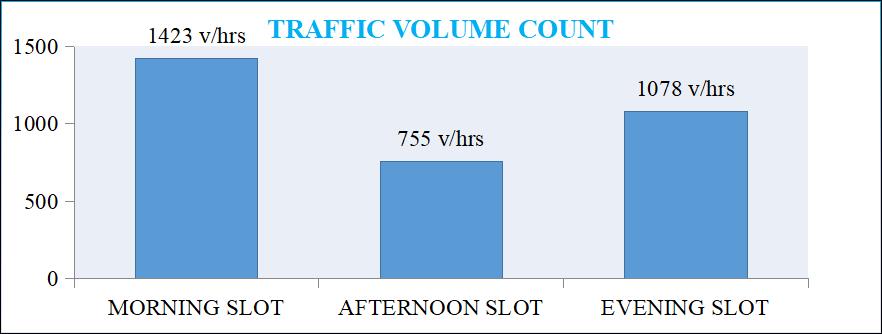
4.1.4 Traffic Volume Count


It is define as the survey of number of vehicles and Pedestrians crossing section of road per unit during any selectedperiod.
Survey Of Traffic Volume Count
ENUMERATORS RECORD MORNING SLOT

Name Of Approach: S.N.DPolytechnic. Location: Bhabulgaon Road Type: MDR 34 Date: 21October2021 District:- Nashik State:-Maharastra Starting Hour: 09:00am End Hour: 10:00am

Vehicle Category Left Turning Right Turning Bus 09 13 Car 134 136 Cycle 05 11 Two Wheelers 177 224 Three Wheelers 15 31 AnimalDriven Vehicle Other Total 340 415

ENUMERATORS RECORD EVENING SLOT
Name Of Approach: S.N.DPolytechnic. Location: Bhabulgaon Road Type: MDR 34 Date: 23October2021 District: Nashik State: Maharastra Starting Hour: 04:30pm End Hour: 05:00pm
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2789
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Table 3: Eveningslotcounting
EVENING SLOT COUNTING
Spot Speed Study
Spot speed is referred to as the instantaneous speedof a vehicle at a point or a cross section. The classification of vehicles according to speedrangeisas follows
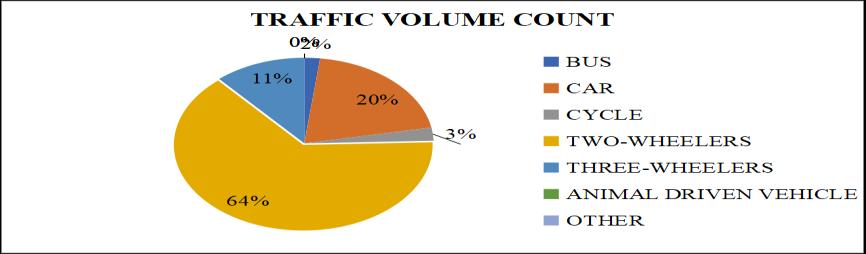
Table 4: Classificationofvehiclesbasedonspeed Speed Range(kmph) Types of Vehicle 0 10 Nil 10 20 Nil 20 30 Cycle,Tractor, Autorickshaw 30 40 Cycle,Tractor, Autorickshaw,Truck 40 50 Car,Bus,2 wheeler,Taxi 50 60 Bus,Car,
5. DETAILS OF DESIGN, WORKING AND PROCESS
5.1
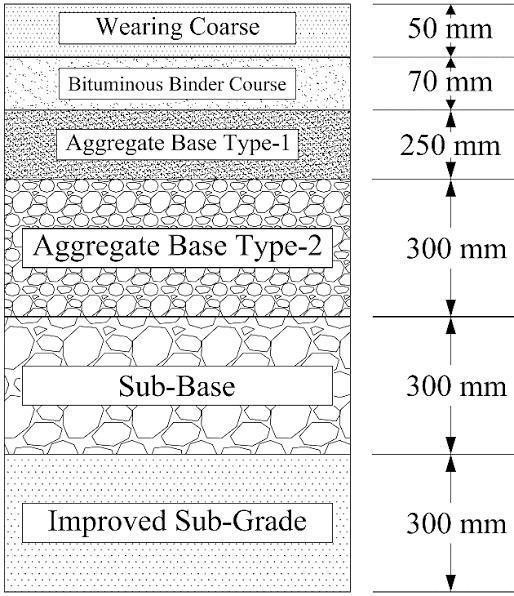
Design Of Flexible Pavement
In these we chapter include the design of flexible pavement,varioustypeoftestconductedonmaterialsuch as aggregate, soil and bituminous. And test must be crushing test on aggregate ,aggregate impact test,soil visual inspection test, casagranda test ductility,test on bituminousetc
Fig -5:DesignOfFlexiblePavement
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

5.2 Design Rate And Material
Table 5: MeasurementSheet
Sr No Particulars of Item Quantity (m3) Unit Rate Amount (Rs)
1 Sub Grade 10098 m3 916 9249768
2 HardShoulder 981.75 m3 4743 4656440.25
3 Sub Base 10098 m3 4361 44037378
4 AggregateBase Type 2 10098 m3 4732 47783736
5 AggregateBase Type 1 8415 m3 6566 55252890
6 Bituminous BinderCourse 2356.2 m3 19906 46902517.2
7 WearingCourse 701.25 m3 20118 14107747.5 TotalCost 221,990,477Rs
Table 6: AbstractSheet
Sr No Particulars of Item No Length (m) Width (m) Height (m) Quantity (m3)
1 Sub Grade 1 3740 9 0.3 10098
2 HardShoulder 2 3740 2.625 0.05 981.75
3 Sub Base 1 3740 9 0.3 10098
4 Aggregate BaseType 2 1 3740 9 0.3 10098
5 Aggregate BaseType 1 1 3740 9 0.25 8415
6 Bituminous BinderCourse 1 3740 9 0.07 2356.2
7 Wearing Course 1 3740 3.75 0.05 701.25
TotalQuantityofMaterial 42748.2m3
5.3 Testing On Material
5.3.1 Test On Aggregate Impact Test Of Aggregate:
It is the ability of aggregates that resist sudden impact or shockloadonit.Also,itcanbedefinedastheresistanceof aggregatetofailurebyimpactloadisknownastheImpact ValueofAggregate.
Procedure Of Aggregate Impact Test:
1) Sieve the material through 12.5 mm and 10.0mm IS sieves. The aggregates passing through 12.5mm
sieve and retained on 10.0mm sieve comprises the testmaterial.
2) Pourtheaggregatestofillaboutjust1/3rddepthof measuringcylinder.
3) Compactthematerialbygiving25gentleblowswith theroundedendofthetampingrod.
4) Add two more layers in similar manner, so that cylinderisfull.
5) Strikeoffthesurplusaggregates.
6) Determine the net weight of the aggregates to the nearestgram(W).
7) Bringtheimpactmachinetorestwithoutwedgingor packinguponthelevelplate,blockorfloor,sothatit isrigidandthehammerguidecolumnsarevertical.
8) Fixthecupfirmlyinpositiononthebaseofmachine andplacewholeofthetestsampleinitandcompact bygiving25gentlestrokeswithtampingrod.
9) Raise the hammer until its lower face is 380 mm abovethesurfaceofaggregatesampleinthecupand allow it to fall freely on the aggregate sample. Give 15 such blows at an interval of not less than one secondbetweensuccessivefalls.
10) Remove the crushed aggregate from the cup and sieve it through 2.36 mm IS sieves until no further significant amount passes in one minute. Weigh the fraction passing the sieve to an accuracy of 1 gm. Also,weighthefractionretainedinthesieve.
11) Compute the aggregate impact value. The mean of twoobservations,roundedtonearestwholenumber isreportedastheAggregateImpactValue..
5.3.2 Testing On Soil:
Soil testing is a very important part of building and road construction. In fact, no construction project can proceed without first making sure the soil can support the load. Thus, the purpose of soil testing for construction is to determine the suitability of the soil for the type of constructiontobedone.Thetestisalsodonetodetermine thepresenceofgroundwater.
Field Identification Of Soil:
Field identification of soil is one of the important steps in soilinvestigation.Itincludesvisualexamination,dilatancy, toughness, dry strength, organic content and shine test. Basedon thesizeof soilparticlessoilcan be gravel,sand, siltorclay.
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2791
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Table 7: FieldIdentificationOfSoil
TotalQuantityofPavementis 42748.2 m3
TotalCostofAmountis 221,990,477 Rs
7. CONCLUSION
5.3.3 Ductility Test On Bitumen:
TheDuctilityTestofBitumenisoneoftheimportanttests of bitumen which is essential before using it in road construction. The Ductility Test of Bitumen was used to measure the adhesive and elastic properties of any bitumensample.
The Procedure of Ductility Test of Bitumen:
The ductility test of bitumen is carried out in two steps Sample Preparation: In this step, the bitumen sample is filled in the briquette mould after melting it. Testing of the Specimen: In this step, the bitumen sample takeninthemouldistestedforitsductilityintheductility testingmachine.
The project deals with the “Analysis and Design Of MDR 34” of form Lasalgaon Patoda Yeola (423401) Road from Kopargaon Yeola Road to S.N.D polytechnic College campus upto 3.740 Km. Form the study following conclusioncanbedrawn: 1. After analysis MDR 34 we have conclude that its notasperIRC. 2. Improperroadsideboard. 3. Maintenanceandrepairoftherouteisrequire. 4. AfterTrafficvolumecountweconcludethatatthe time of college start then that time increase the vehicle. 5. Mostlytwo wheelerarerunthrowtheseroute. 6. Torequireincreasesafetyforstudentand pedestrian. 7. Requireplansignalsandsidewalketc.forstudent andpedestrian. 8. Itsrequiredesignshoulder. 9. Itsrequire toextendthewidthofroutebecause thepopulationofcityandcollegesdaytoday increase
8. RECOMMENDATION
1. Remove or repair potholes for the safety of road users.
Providefootpathonboththesidesoftheroadfor thesafetyofpedestrians.
Take suitable enforcement measures to reduce thespeedofvehicles. 4. Good quality materials should be used so as increasethelifeoftheroads
Provideshouldersforits
Extendthewidthofroute
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Wehaveagreatpleasureinpresentingthisprojectreport on “Analysis And Design Of MDR 34”. To express our deep regards towards those who have offered their valuabletimeandguidance inourhourofneed.Profound
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

advice and encouragement that has led to the successful completionofthisproject.
We would like to express our special thanks of gratitude to our project guide Prof.Sayyed J.S and also we would like to express our gratitude to Prof. Dhanwate D. S (H.O.D. Civil Department), and Prof.Jadhav U.B. (Principal S.N.D. Polytechnic Yeola.) For the support and the infrastructure they have provided andcontributingvaluabletimeknowledge,experienceand makingthisprojectsothatwecouldsuccessfullycomplete projectdissertationintime.
We are grateful to co ordinator Prof Chatur R.S. For ensuring thatwearedoing ourproject in professional manner, taking care of every detail and maintaining the log book. We will especially thankful to the librarian’s for making us available necessary books. We would also like to express our deepest gratitude a reverence for their encouragement and patience thought theprocessofthisproject.
Finally, before ending we would like to once again our gratitude and thanks to our family and friends for their comments, suggestions and criticism and who are involved directly and indirectly in making our projectsuccess.
REFERENCES
[1] Vidya V, Anju k (2021),“Risk Analysis and Management in MDR Construction Projects in Kerala”, International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES)Volume 9 Issue 7 ǁ 2021 ǁ PP. 52 57.
[2] Vasu Choube, Prof. Jitendra Chouhan (2021), “Identification and Improvement of Accident Black Spots on SH 1 and SH 38 Dist. Khargone (Madhya Pradesh) A Case Study”,International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology(IJRASET)Volume9IssueVIJun2021.
[3] DhanavathSeva,Bhukya Chandrashekar,Faria Aseem (2017),“Project Report on National Highways”International Journal of Engineering ScienceandComputing,Volume7IssueNo.11.
[4] MridulaG M,AshamolJose,Lidiya P M(2016),“Traffic Accident Analysis and Mitigation Measures at Kariyad (NH 544), Ernakulam, Kerala”,International Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology, 2016, Volume 4 Issue5.
[5] Naveen.N', D.V.Manoj Kumar (2016),“Analysis and Execution of WBM and Bituminous Premix Roads”, International Journal of Innovative Research in
Science, Engineering and TechnologyVol. 5, Issue 5, May2016.
[6] Nurul Hidayati, Frank Montgomery And Ronghui Liu(September 2016),“Kondisi Lalu Lintas Indonesia Dalam Konteks”, , Staf Pengajar Program Studi Teknik Sipil, Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta,Vol.10/No.2/September 2014.
[7] Liyamol Isen,Shibu.AAndSaran M.S(August2013), “Evaluation and treatment of accident black spots using Geographic InformationSystem”,International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and TechnologyVol. 2, Issue 8, August 2013.
[8] Highway Engineering, S.K.Khanna, Justo,CEG and Veeraragavan,A.
[9] “HighwayEngineering”byT.D.Ahuja
[10] “Estimation and costing in civil engineering” by B.N.Dutta
[11] “Soil mechanics and foundation engineering” by K.R.Arora
[12] “IRC 37 2001” : Guidelines for the design of flexible pavements.
[13] IRC 073: Geometric Design Standards for Rural (Non Urban) Highways 1990 [Leather Bound] By Indian RoadsCongress
[14] IRC 073 Geometric design standards for rural (Non urban)Highways.
[15] IRC : 62 1976 “Guidelines for Control of Access on Highway
BIOGRAPHIES

Mr.PardeshiDhananjayDevidas DiplomaFinalYear Student DepartmentOfCivilEngineering, S.N.D Polytechnic Institute, Yeola,Maharashtra,India.

Ms.ChavanNikitaDattatray DiplomaFinalYear Student DepartmentOfCivilEngineering, S.N.D Polytechnic Institute, Yeola,Maharashtra,India
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2793
Author PhotoInternational Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Mr.WaghKiranDeonath
DiplomaFinalYear Student DepartmentOfCivilEngineering, S.N.D Polytechnic Institute, Yeola,Maharashtra,India


Prof.Sayyed JunaidS. Professor DepartmentOfCivilEngineering S.N.D Polytechnic Institute Yeola,Maharashtra,India
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2794
