1
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

1
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
2,3,4,5
***
Abstract - Abriefreviewofhowcancerisdetectedandcuredwiththehelpofsimulationofnanobots.Inthis,weare doing a literature survey for the detection of cancer using the nano technology concept is simulation based only. The combinationofnanotechnologyandbiologyisprobablygoingtohelpinthedetectionandtreatmentofcancer.Nanorobot is a vision in the field of healthcare in the future. Research in nanotechnology allows us to build artificial red blood cells calledRespirocytescapableofcarryingoxygenandcarbondioxidemolecules.Nanorobotscarryanddeliverlargeamounts of anti cancer drugs into cancer cells without harming healthy cells, reducing their side effects. They will detect the cancerouscellwiththehelpofsomealgorithmsandparameters.Thesenanorobotswillhavethecapacitytorepairtissues attheinfectedsite.TheworkpresentedinthispaperistheUGcreditfinalphaseprojectwork oftheundergraduatefinal yearstudentthatwasundertakenbytheUGstudent&justprovidesabriefreviewonhownanobotscouldbeusedinthe detectionandtreatmentofCancerandasjustareviewpaper,whichservesasabasisforallthestudentstocarryonthis researchworkforwardandreviewtheadvantagesofnanobotsinthehealthcareindustry.
InthefightagainstcancerdiseaseasshowninFig.1,earlydetectionisakeyfactorforsuccessfultreatment& tosave precious human life. The project work presented in this synopsis relates to such an application oriented work w.r.t. the simulation,design&developmentofnanorobotsforcancercuretherapy&diagnosticapplicationsinhumanbeingsusing AI&MLtoolswiththehelpofsoftwaretoolstudies.Nonetheless,theidentificationofmalignancyinthebeginningphase hasbeenthwarted by the natural furthest reachesofordinary diseaseanalytic techniqueslike chemotherapy whichkills notonlyhealthycancerouscellsbutalsohealthycells,hairloss,lossoforgans,etc.
Toeradicatethisproblem,theideaofthenano technologygiveshighaffectability,andexplicitnessandhasalongthese lines worked for the identification of extracellular malignancy bio markers, mutation aspects, and cancer cells in this projectabstractedsynopsiswork.Amongthemainstepstowardscancertreatment,whichwillbeusedinourworkarethe early location of malignancy cells and medication application with high particularity to reduce poison levels. Because of expanded fundamental poison levels and unmanageability with customary disease demonstrative and helpful devices, current successful strategiesliketheuseof nanorobotsin nanotechnologyare beingemployedtoimprove diagnosis and mitigatediseaseseverityhereintheprojectwork.
Theconceptsthatwearedevelopingusingnanotechnologyaregoingtobeusedforseveralcancertypestoreducethe invasiveness of cancerous cells while sparing healthy cells at the target site. This is made to use nanomaterials such as carbonnanotubes,polymericmicelles,andliposomesincancercellidentification,destruction,andremovalfromthebody. But, the current technological developments in a developing country like India hinders this growth due to the lack of infrastructural facilities. Hence, in this context, we have taken up the amalgamation of nano technology & the nano medicinetosavethemankindfromthisworld’smostinfectiousdiseasetowhichalargenumberof peoplearefallingprey anddevelopsomestrategiesinthefieldofmodeling,design,developmentofnanorobotsforthecureofcancerdisease.
The blend of nanotechnology into prescription is likely going to get some new troubles therapeutic treatment as the nanorobotsareaheavenlyvisionofmedicationinthefuture.Themostextraordinarynanomedicineincorporatestheuse of nanorobots as limited scale experts to murder the infection. An important point among the most reasonable and practicallypossibleachievementsistheremedyfordevelopmentwhichisoneoftheessentialplacesfortheexamination. Nanorobots could convey and convey a lot of hostile to malignant growth drugs into dangerous cells without hurting
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
soundcells,diminishingtheresultsidentifiedwithcurrenttreatments.Thesenanorobotswillhavetheabilitytofixtissues, cleanveinsandaeronauticscourses,andchangeourphysiologicallimits.
Anumberofauthorsacrosstheworld@theinternationallevelshaveworkedontheproposedprojectworkinsomeof thesimilarareasandhaveproducednovelcontributions. Thefollowingparagraphsthrowsalightintosuchoftheworks doneattheinternationallevelsbytheinternationalauthorswhohaveworkedonthesimilarfields.
Koleoso worked on the micro or the nano scale magnetic property based robots for various types of bio medical applicationsinhispaperin[1].Theyenhancedseveralbiomedicalapplicationsintheirwork,aswellassuggestionsforthe systemsthathavetheabilitytoperformmanyfunctions.Inthiscase,thefieldofsmall scalerobotworkishighlycreative, more concerted efforts are needed to improve the functionality and reliability of these machines, in these clinical applications, according to the findings of this report. Finally, further works were made in order to ensure the commercializationoftheseinstrumentsintheirarticlein[1].
Nanobots: development and future a superb article was coined by the group of authors led by Jose Roberto Vega Baudritet.al. intheirarticlein[2].Theypresentedthenextgenerationofnanodeviceshowtheyareusedtorevolutionize patient diagnosis and drug delivery technology They proposed several obstacles in developing this technology, not only from a mechanical,biological,and physicochemical standpoint, but alsoin terms ofthe dangers ofusing these nanoscale materialsandtechnologies,aswellastheircontactwiththeenvironmentandhumans.Theaimofthisreviewarticlewas todescribenanobots,theirtechnologiesanddevelopments,aswellastheirmedicalapplications,particularlyinthefieldof cancercare.
Intheirpaper[3],YamaanSaadehfocusedonNanoroboticApplicationsinMedicine LatestIdeasandPrototypes.Theaim of this paper was to provide an overview of the evolving field of nanorobotics in medicine, as well as a study of nanoroboticspossibleapplicationsinfieldsrangingfromneurosurgerytodentistry[3].
Intheirarticlein[4],Saxena et.al.focusedonthenature,architecture,andimplementationofnanoroboticsintheoncology field of study. The aim of this article was to describe the architecture of nanorobots and their role in oncotherapy in a concisemanner.Whilenanorobotworksisstillinitsearlystages,thepotentialofsuchtechnologiesislimitless.
AnapplicationofNano technologyinCancerDiagnosis&intheTherapy CancanJin et.al.havetakenaMini Reviewin theirapplication basedpaper[5].
The authors defined the most widely used nanomaterials in cancer diagnosis and treatment. They examined the problemsassociatedwithnanomaterials,whichrestrictedtheirapplicationsandhindered.[5].Theyhavehighlightedthe need of these nanomaterials for cancer treatment based on their biological properties. In summary, they targeted to demonstratethemainbenefitsofnanotechnologyaswellasthelimitationsofitsuseincancerclinicalneeds[5].
In [6], Mitra Venkatesan worked on some of the topics of the use of nanorobots for cancer treatment. A individual seekingnanoroboticcareshouldpresumetobetotallyignorantofthemoleculardevicesatworkwithinthem,saveforthe rapidchange in theirhealth.Asa result,theauthorsproposeda report on diverse approaches tocancer treatmentusing
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2910

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
nanorobotsintheirarticlein[6],buttherewasnonoveltyandnonewmethodsproposed,itjusthighlightedsomeofthe worksthatcouldbedoneinfuturewiththehelpofnanorobots.
Sarath and his colleagues focused on nanorobots as a potential diagnostic and treatment system in their paper [7]. Their paper focused on the use of nanorobots in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes,andgout.Thiswasareviewpaperthatledustorecentnanorobotstudiesinbiomedicalapplicationsandhelped ustoselecttheprojectwork[7].
Devasena Umai et.al. conducted a study on DNA nanobots a novel tool for cancer treatment in the Indian context in theirpaperin[8].
Application of Nanotechnology in Cancer was presented in a excellent article in [9] by the team of authors led by HirendraN.Banerjee&hisgroup. Thisarticleaddressedtheeffectofnanotechnologyoncancer,withafocusonbiomarker identification,imagingfordiagnosis,anditsroleintherapeuticaction,butitdidnotincludeanydetailonthemethodologies thatcouldbeusedforcancerdetection[9].
The authors of [10], led by Kumar Biswajit and his colleagues, experimented on the principles of Nanotechnology in Cancer Drug Delivery and Targeted Targeting and came up with positive findings. Their study focused on nanoparticles’ ability to recognize cells using a variety of techniques with novel distinguishing properties that set them apart from previous
anticancer treatments. It also addressed how nanoparticles carry particular drugs within cells, citing numerous promisingstudies,andhow nanoparticleseliminatethesideeffectsoftraditionalcancertreatments withtargetedcancer care[10].
Similarly, a number of authors had worked in the similar area, but only the best of them have been highlighted in this context, but many of them have lot of drawbacks or dis advantages which were posing a serious threat to the mankind. Someofthem
havebeenidentified&novelalgoswillbecreatedinordertoneutralizethesameandproposesomenovelconceptsin thedesign&developmentofnanobotstocurecancerdiseaseinhumanbeings.
From individual nanoparticles to nanomachines and nanorobots, nanomaterials are being used to cure cancer was studied bylexandreLoukanovet.al. in[11]. Asdiscussed in [11], the aim of this important analysiswas to concentrate on the latest use of clinically accepted nanoparticles for cancer theragnostic, nano vaccines, and gene therapy delivery platforms,
which included inorganic, metal, and polymer nanoparticles, nanocrystals, and various drug delivery nano systems (micelles, liposomes, microcapsules, and so on). Arizona State University (ASU) scientists, working in conjunction with authorsfrom
the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ National Center for Nanoscience and Technology (NCNST), have successfully programmednanorobotstoshrinktumorsbycuttingofftheirbloodsupply.
Shaolong Shi et.al. developed Nanorobots assisted Multifocal Cancer Detection with a Multimodal Optimization Perspectivein[13]. Whenthebiological targetfeatureisalignedwiththeblood flowvelocityprofiletriggered bytumor inducedangiogenesis,theauthorsproposedadetailednumericalillustrationtoillustratetheefficacyoftheNGA inspired MCDP. However, they did not work on enhancing the algorithm’s efficiency in order to detect all cancer areas with a sufficient number of nanorobots, it was also necessary to investigate the effect of nanorobot nonidealities such as finite lifetime,impreciseguiding,andunreliablemonitoring.
The authors of [14], led by Tianshu Chen et.al., focused on DNA Nanotechnology for Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment, showing how DNA could be used to identify and destroy cancer cells. The authors outlined recent advances in DNA nanotechnology for the fabrication of practical and intelligent nanomaterials, as well as the technology’s potential applicationsincancerdetectionandtreatment[14]
In[15],RouhallahRavanshadet.al.investigatedtheuseofRamanscattering basedmethodstodiagnosecancerusingSir C.V.Raman'sfamousscatteringphenomenon.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
Thekeyaimofthisarticlewastoincorporatesomeof themostcommon nanotechnologicalcancerdetection methods using Raman techniques. Furthermore, they have reviewed some of the more common and even more studied cancers, such as breast and colorectal cancer, as well as several interesting nanostructures, especially as SERS nano tag, special cancer biomarkers, and related approaches. Their key goal was to use Raman techniques to apply the most common nanotechnologicalapproachesincancerdetection[15].
The proposed methodology (Fig. 2&3) that may be used in our project work is presented in this section. The proposed methodology that may be adopted in the present project work is shown here in a very highly abstracted manner with variousblocksinthevertical&horizontalfashions
Automated planning Knowledge Representation &reasoning
AI Approaches
NaturalLanguage Processing Multiagent system Machine Learning
Reinforcement Learning Supervised Learning SemiSupervised Learning UnSupervised Learning
Markov Decision Processes
Classification& regression Clustering Clustering
Fig.2:UseofAI&MLapproachesforthetrainingpurposes
The concepts of AI ML DL algorithms are going to be used in the proposed project for the design of the nanorobot & its interaction with the infected cancer cell. Different training algorithms based on ANN CNN RNN are going to be used for training the nanorobotsto honeit to thecorrect target after detecting the infected cell usingon boardsensors & beams. The trainingapproachesaresimilartoateachertrainingthestudentinaparticularsubject.Oncethesystemisbeingtrained,it willbeabletodeliveritsgoodscorrectly.
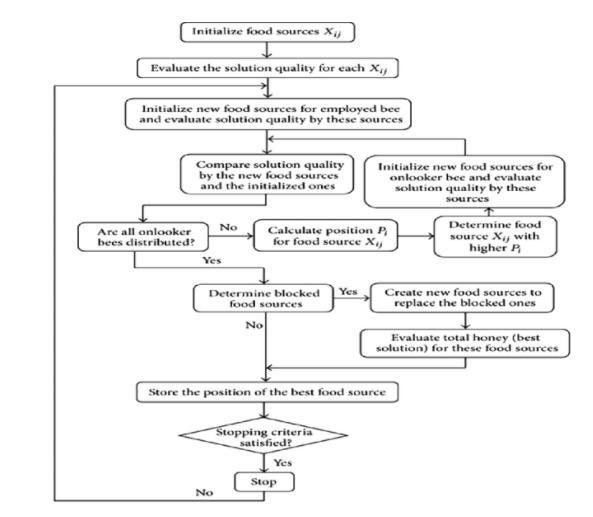
IntheArtificialBeeColonyalgorithm,thepopulationoffoodpositionsandtheartificialbeesmoveonthesefoodpositions overaperiodoftime.Thisalgorithmusedsomeagentscalledhoneybeestofindtherightsolution.
1. ThehoneybeesinABCcanbecategorizedintothreegroups:employedbees,onlookerbees,andscoutbees.
2. The employed bees exploit the food positions, while the onlooker bees are waiting for information from the employedbeesaboutnectaramountofthefoodpositions.
3. The onlooker bees select food positions using the employed bee information and they exploit the selected food positions.
4. Finally, the scout bees find new random food positions. The given solution in the search space consists of parametersthatrepresentthefoodsourceposition.
5. Thenumberofemployedbeesisequaltothenumberoffoodsources. Thetasteoffoodsourcesiscalledits“fitnessvalue”anditislinkedtotheposition.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
Fig.3:Flowchartoftheproposedalgorithmfortheimplementationofnanorobot.
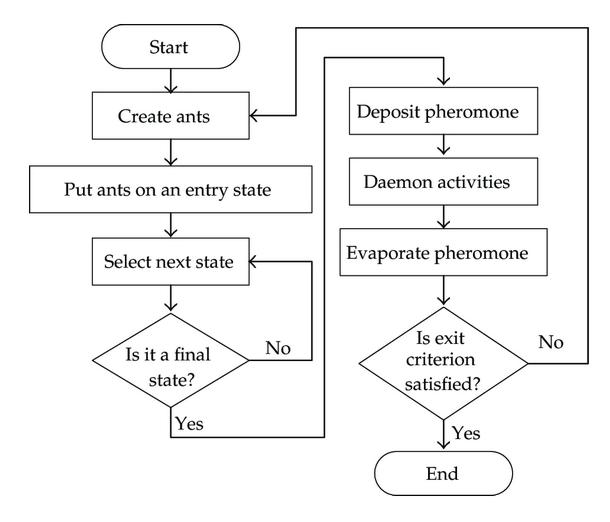
Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm is identified by the foraging behavior of ants. At this behavior, it is the indirect communicationbetweentheantswiththehelpofchemicalpheromonetrails,whichhelpsthemtofindthe shortestpaths betweentheirnestandfoodsources.
1. Createants(nanorobots)andputthemontheentrylevel.
2. Eachant(nanorobot)sensesandmonitorstheconcentrationofE cadherinmoleculesintheblood.
3. Onrecognizingit,nanorobotsmovetowardshigherconcentrationofE cadherin.
4. Each ant (nanorobot) communicates with other robots (swarm intelligence) just like ants leave a trial of pheromone behind as it reaches the target site. If trial is long the pheromone gets evaporated before any ant followsit.
5. Ifthetrialisshort,itisfollowedbeforepheromonegetsevaporated.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
Fig.4:Flowchartoftheproposedalgorithmfortheimplementationofnanorobotsinsearchofcancercells.
Thispaperaddressesthethreeimportantresearchobjectives,
i) To simulate a nano robot prototype to detect the cancerous cell using simulation tools like nano hive & cadence tools using thefollowingconceptssuchLocomotive parts,Power actuator, Sources within the body, generationofpowerfromthebloodstreaminthebody.
ii) Studying the behavior of the cancerous cells & to halt their behavioral growth by detecting that the cell is beingaffectedwiththecancerdisease.
iii) Tokillordis infectthecancerouscellbyinjectinganti cancerousnano particle&tomakeitinactive.
A brief review of the work related to the project work undertaken was depicted in the previous sections in the form of introduction, followed by literature survey. The objectives of the project work were also explored & arrived at the definitionoftheprojectproblemthathadtobetackledwith. Methodologyisproposedintheformofablockdiagramto solvetheabovedefinedproblemusingsoftware&hardwaretools,whichmaychangeinduecourseoftheprojectwork.
TheauthorswouldliketoextendtheirgratitudetothemanagementofDSItocarryoutthisresearch.
[1]. M.Koleoso,X.Feng,Y.Xue,Q.Li,T.Munshi,X.Chen,“Micro/nanoscalemagneticrobotsforbiomedicalapplications,” Materials Today Bio,Volume8,2020,ISSN2590 0064.
[2]. Gutierrez B, Bermudez CV, Ureña YRC, et al. Nanobots: development and future. Int J BiosenBioelectron. 2017;2(5):146 151.
[3]. Antoine Ferreira, Sylvain Martel.(2014).Guest Editorial: Special Issue on Nanorobotics, IEEE Transactions on Robotics30(1):1 3.
[4]. BhatA.S.(2015)―Nanobots:thefutureofmedicine‖,InternationalJournalofEngineeringandManagementSciences 5(1):44 49.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2914

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
[5]. Mithra Venkatesan, Bhuvaneshwari Jolad, “Nanorobots in Cancer Treatment”, January 2011, IEEE Xplore International Conference on Emerging Trends in Robotics and Communication Technologies (INTERACT),2010.
[6]. Sarath, K.S., et al. New Nanorobots a future developed Device for Diagnosis and Treatment (2018) J Pharm Pharmaceutics 5(1):44 49.
[7]. Devasena Umai R, Brindha Devi P, Thiruchelvi R, “A Review On DNA Nanobots A New Technique For Cancer Treatment”, Asian J Pharm Clin Res,Vol11,Issue6,2018,61 64
[8]. Hirendra N. Banerjee, M.D., “Mukesh Verma, “Recent Applications of Nanotechnology in Cancer Treatment”, New Technology in Cancer Research and Treatment ISSN 1533 0346 Volume 7, Number 2, April 2008 ©Adenine Press (2008)
[9]. Loukanov A, Nikolova S, Filipov C, Nakabayashi S (2019) Nanomaterials for cancer medication: from individual nanoparticlestowardnanomachinesandnanorobots. Pharmacia 66(3):147 156.
[10]. Arizona State University. "Large sized medium Cancer fighting nanorobots developed programming to take and destroy tumors: This shows first applications of DNA origami science for developed nanomedicine." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily,12February2018.
[11]. Sandeep S & Gururaj B Tennali Deepak A Yaraguppi, Sandeep S & Nitish K., “Nanobotz In Cancer Detection & Treatment”, TJPRC:Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Sciences (TJPRC:JMPS)Vol.1,Issue1,Jun2015,7 14
[12]. Chen,T.;Ren,L.;Liu,X.;Zhou,M.;Li,L.;Xu,J.;Zhu,X.DNANanotechnologyforCancerDiagnosisandTherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19,1671.
[13]. RouhallahRavanshad, Ayoob Karimi Zadeh, Ali Mohammad Amani, Seyyed Mojtaba Mousavi, Seyyed Alireza Hashemi,AmirSavarDashtaki,EsmailMirzaei&BijanZare(2018)Applicationofnanoparticlesincancerdetection bypopularresearch basedRamanscatteringtechniques, Nano Reviews & Experiments, 9:1,1373551
[14]. Vibhuti Agrahari, Vivek Agrahari, Ming Li Chou, Chew Ho Chew, James Noll, Thierry Burnouf, “Intelligent micro /nanorobots as drug and cell carrier devices for biomedical therapeutic advancement: Promising development opportunitiesandtranslationalchallenges, Biomaterials,Volume260,pp.120 163,2020.
[15]. Anchordoquy TJ, Barenholz Y, Boraschi D, Chorny M, Decuzzi P, Dobrovolskaia MA, Farhangrazi ZS, Farrell D, GabizonA,GhandehariHetal:MechanismsandBarriersinCancerNanomedicine:AddressingChallenges,Looking forSolutions. ACS Nano 2017,11(1):12 18.
[16]. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics data 2018: GLOBOCAN company estimated many incidents and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394 424
[17]. Chaturvedi VK, Singh A, Singh VK, Singh MP. Advanced Cancer Nanotechnology: A great Revolution for Cancer DiagnosisandTherapytreatment. Current drug metabolism.2019;20:416 29.
[18]. YeF,ZhaoY,El SayedR,MuhammedM,HassanMJNT. Advances in nanotechnology for cancer biomarkers.2018;18: 103 23.
[19]. Sherje AP, Jadhav M, Dravyakar BR, Kadam D. Dendrimers: The nanocarrier used for drug delivery and targeting cancercells. Int. journal of pharmaceutics.2018;548:707 20