International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Shoaib S.Bedakale1, Shakeer R. Shirdhone2, Nikhil R.Mane3 , Akshata R. Kothale4
1,2,3 B.Tech Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, DBATU University, Maharashtra, India.
4 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, DBATU University, Maharashtra, India. ***
Abstract Over the last few decades rapid industrialization, rural to urban migration and high populationgrowthhaveinducedrapidurbanizationworldover and India is no exception. Consequently, the problems associatedwithurbansolidwastemanagementhaveacquired an alarming dimension. It is observed that the per capita solid waste generation rate in India has increased from 0.5 kg per day in 2011 to 0.7 kg per day in 2020.This has pressurized the existingsystemsresultinginadverseimpactsonhumanhealth andenvironment.Thoughconcertedeffortshavebeenputinby urban administration, there is vast scope for introduction of state of the artsystem tocollect,process, dispose, orreusethe solid wastes in a cost effective manner considering technical, geographic, socio cultural, industrial, infrastructural, legal, and environmental factors associated with it in an integrated manner. Ichalkaranji is one of the fastest growing cities, presently generating about 110 metric tons of solid waste per day. In this study, an attempt is made to assess the present status of Solid Waste Management System (SWMS) in Ichalkaranji city and compare it with Swachh Bharat Mission’s Municipal Solid Waste Management Rule 2016 clauses and finally suggest various improvements in view of future expansions. The work includes extensive use of Arc GIS involving overlay and proximity analysis. The study covers the aspects such as region wise generation of solid waste and infrastructure for its collection, processing and disposal, or Reuse. It is concluded that better planning, management and effective implementation of solid waste management system can be achieved using these modern tools so that clean urban environment for various cities in the country is ensured.
waste than developing countries. It is also reported that MSW generation in less developed cities is 0.3 0.7 Kg/Capita/day and for fast developing cities is 0.5 1.5 Kg/Capita/daywhilefordevelopedcitesitisgreaterthan1 Kg/Capita/dayinAsiancountrieslikeIndia.ImproperMSW disposalandmanagementcausesvarioustypesofpollution thatinair,soil,andwater.Inurbanplaces,MSWclogsdrains, creating stagnant water for insect breeding and floods duringrainyseasonsiscriticalissue.Thereisgenerationof variouspoisonousgasesfromtheopendumpingoforganic wastes in landfills and untreated leachate pollutes surroundingsoilandwaterbodies.Numeroushealthissues arearousedduetoimproperSWM.
InIchalkaranjicityprimarysourcesofsolidwasteare Household,Hotels&Restaurants,Streetsweeping&Markets / commercial area. Biomedical waste and E waste are on minor side of collection. The total quantity of waste generatedperdayisabout100 110metrictons(0.34 0.38 kg/ capita/day) CPHEEO 2000. Ichalkaranji Municipal Corporation (IMC) is responsible for solid waste management components like collection, storage, segregation, transportation anddisposal ofall solid waste generatedinthecity.Thisworkalsoinvolvesfuturewaste generation predications. This tool helps to take good decision in all aspects before any plan execution or after executionofsystem.
Words: Urban Solid Waste Management System, Geospatial tools
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) consist of various types of waste like, Residential and Commercial establishment unwantedanddiscardedmaterials,streetsweepingwaste, construction and demolition debris, sanitation residues, trade and non hazardous industrial waste, treated biomedicalsolidwaste.Daybydayaroundtheglobe,waste generation rates are rising. In 2020, the total waste generated by world cities was 2.24 billion tonnes of solid waste,amountingtoafootprintof0.79kilogramsperperson per day. With the rapid growth of population and urbanization,thegenerationofwasteisexpectedtogenerate ranging3.5 6milliontonperdayofsolidwasteby2025.It observedthat in developed countriesgenerate more solid
IchalkaranjiCity,thesecondlargestcityinKolhapur district after Kolhapur city in Maharashtra. Although Ichalkaranji city has population of 292062; its urban / metropolitan population is 325,709 of which 169,870 are males and 155,839 are females The city's population as shown above is excludes newly growing industrial and residential areas, villages that are partly included by Ichalkaranji(knownaspartofthecity)buthavingKabnur, Yadrav andKorochietc as a gram panchayat. VillageShahapur Village, Ichalkaranjiwas included in IchalkaranjiMunicipalCorporationin1985. Itsliteracyrate is85.98%whichishigherthanthenationalaveragewhichis 59.5%.Thecityisknownas“ManchesterofMaharashtra”as it has maximum number of power looms & spinning mill contributingtodailyturnoverof100CroresRupees.Thecity under IMC jurisdiction covers a geographic area of 29.84 sq.km. Ichalkaranji Municipal Corporation lies between latitudes 16°42'32.4072''N and longitudes between 74°27'21.8808''E.Ichalkaranjicitysituatedatanaltitudeof
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2424

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
538meters(1768ft.)abovemeansealevel(MSL).Theentire jurisdiction of IMC is divided in to 31 electoral wards, 26 administrativewards.
In this research work an attempt is made to assess adminwardwisewastegenerationitscollection,segregation, transportation, treatment and disposal land fill site using geospatialtoolsi.e.GeographicalInformationSystem(GIS) and critically study technical, Socio economic, health and environmentaleffectsofrespectiveadminward,withmulti criteriaanalysismethodhavebeenstudiedtofindbestwaste managementstrategyforthecitybasedonvariouscriteria.
Theresearchworkisdividedintothreecomponents:
1. Studyofexistingsolidwastemanagementsystem usingofGeospatialtools
2. Comparison of existing solid waste management systemwithSolidWasteManagementRule2016.
3. Suggestingsomefuturemajorsthatcanbecarried outFutureGenerationofMSW.
The most important parameter to be considered is populationofstudyarea.Thepopulationofeachadminward isconsideredforthisresearchwork.Adminwardwisewaste generationiscalculated.Thecomponentsofexistingwaste management waste generation, collection, transportation, processinganddisposal.Thedetailprocessisexplainedin flowchartFigure(2).
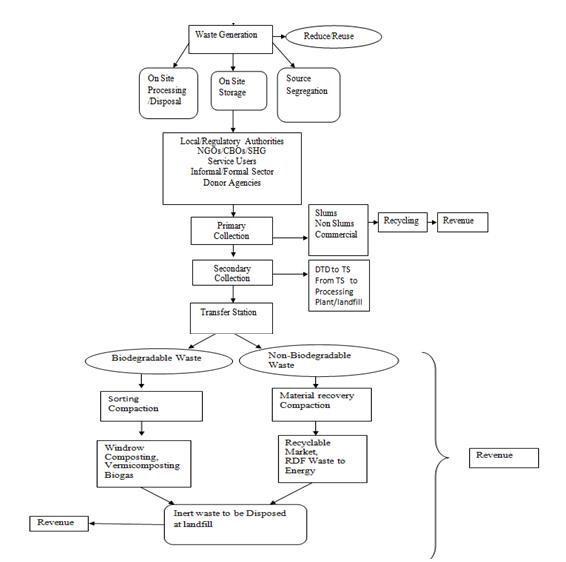
Figure2:SolidWasteManagementFlowChart.
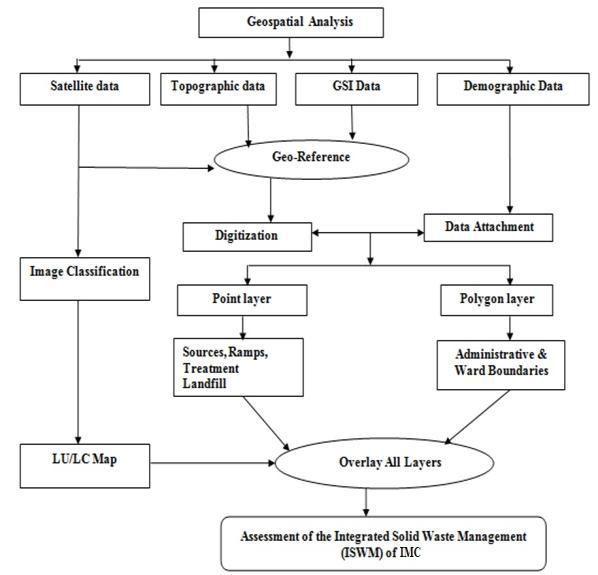
Themainobjectiveofthisresearchworkistostudythe current solid waste system of Ichalkaranji city using Geospatial tools.Thedata collectioninvolvedcollection of topographical maps, ward maps, satellite data and demographicdetails.Thecollectionofthesedataandtheir sourceareshown
Ichalkaranji city wardmap Ichalkaranji Municipal CorporationDocuments
GoogleImage Googleearthpro
SatelliteImagery bhuvan.nrsc.gov.in Carsat 1,CartoDEMallversions
Demographicdetails Ichalkaranji Municipal Corporation,Censusdata
All Secondary data related Solid Waste Management
Solid waste department, Ichalkaranji Municipal corporation
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The brief information about steps involved in implementationmethodologyforthepresentresearchwork.
1. DataCollection:ProcurementofSatellitedataand relatedattributedata.
2. Data Processing: Geo correction of topographical mapsandimageprocessing
3. Application of standard image processing techniques to identify the existing solid waste systemofstudyarea.
4. Creation of GIS layers: digitization of ward map, locating smaller ramps, treatment plant and administrative boundary of study area from the topographical maps and Google images using GIS software’s.
5. Preparationofthematicmaps:Generationofresult basedthematicmaps.
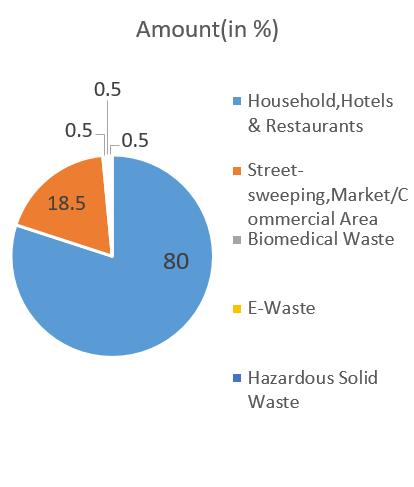
systemstudyisconductedusinggeospatialtools.Thematic mapshavebeengeneratedusingArc GIS10.2.Tostudythe spatialvariationsoftheMSWMSItisseenthat,Ichalkaranji generates 100 125 metric tons of waste every day from different sources in adminwards. Ichalkaranji waste compositionconsists45%oforganicwaste55%otherwaste (fig5). About 80 percent of the waste is generated from households(domesticwaste),hotels,restaurantsandStreet sweeping & Markets / commercial area establishments whichtogetheraccountforover18.5percentofthewaste generated and biomedical waste, E waste & Hazardous waste account 0.5% generation each. (table2). Waste generation based on population. The generation rate per capita per day was considered as 0.4kg/capita/day accordingtoWorldBank.Awarenessofwastereductionat sourceneedimprovement.Toachievezerogarbagemodelit important to focus on waste segregation. Ichalkaranji city generates Dry Waste and Wet Waste almost in equal proportion(40% 40%)and20%mixedwaste.SolidWaste CollectionsystemofIMCisprojected.(Intable2)
Scientificlandfillsiteisessential.Decentralizedtreatment method needs to be adopted. Other waste like C and D is processed in one plant under IMC. Special waste like hazardous waste, biomedical waste, plastic waste and E wastespecialtreatmentplantshavebeenestablishedbased on generation capacity. However special waste treatment awareness is needed to avoid harmful effects on environment and public health. The research work suggestionsneedtobeimplementedinSWMsystemofIMC forurbansustainabledevelopment.
Figure3:FlowchartofGeospatialAnalysis.
Themunicipal solidwaste managementsystem(MSWMS) includesreduce/reuse,recycle,composting,wastetoenergy and finally landfill. The detail solid waste management
Figure4:
(SolidWasteManagementDept,IMC)
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Year Projected Population(at rate1.54%/yr.)
GenerationRate (Kg/capita/day) Waste Generation (TPD)
2011 290560 0.3 109
2021 295035 0.4 118
2031 299579 0.5 150
2041 304192 0.6 182
Table4:Futuregenerationofsolidwaste (WorldBankreport)
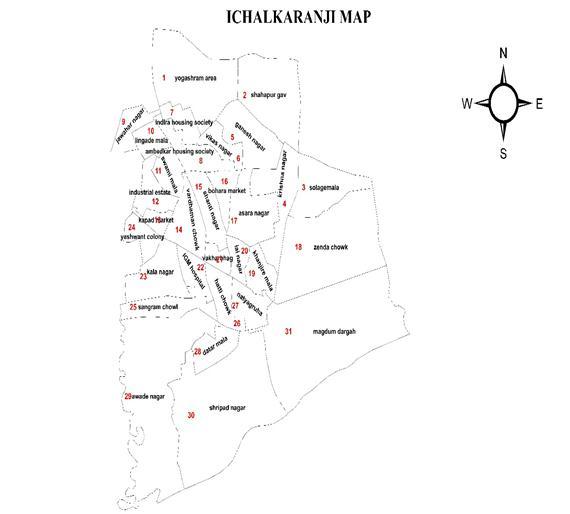
Table3:solidwastecollectionsystem IMCsecondary system.
PresentlyIMCgenerated100to125tonsofwasteper day.Percapitaperdaywastegenerationis380 450gram. SinceIndiaisunderlowermediumincomecategorybyword bank the waste generation rate varies from 0.7 1.5kg/capita/day. Future solid waste generation for Ichalkaranji city is projected on the basis of 0.4 0.6kg per capitageneration.Decadewisegenerationofmunicipalsolid waste under IMC is as per Table 5 which indicates about threefoldincreaseinquantityofSWwhencomparedto2011 level. Thus meticulous planning and effective implementationofMSWMSbyIMCisessential.
Currently, the present SWM of Ichalkaranji satisfies with SolidWasteManagementRule2016.Butasthepopulationis increasingtherewillbeincreasesolidwastegeneration.So, in future there will be need to implement transfer station betweencollectionareaandlandfillstation.
Fig:5-LocationMapofStudyArea.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

1. HinganeHemalata,ManeT.T,(2014)AnalyticalStudyof SolidWasteManagementinIchalkaranji,India”,Journal ofEnvironmentalResearchandDevelopment.
2. Nitin Mundhe, Ravindra Jaybhaye, Ravindra Jaybhaye (2014) Assessment of Municipal Solid Waste ManagementofIchalkaranjiCityUsingGeospatialTools. InternationalJournalofComputerApplications(0975 8887)Volume100 No.10,August2014.
3. Chang,K.T.,2010IntroductiontoGeographicInformation System,5thEd.McGraw HillInternationalEdition.
4. IchalkaranjiCitySanitationPlan,IchalkaranjiMunicipal Corporation,2011
Fig:6 PopulationDistributionofIMC.
5. Solid Waste Management Rules, By Union Ministry Of Environment,ForestsAndClimateChange,GOI,2016
6. JoelSotamenou,(2019)SelectionoftheBestSolidwaste Management Yaounde using an Analytical Hierarchy Process.AdvanceinEnvironmentalWasteManagement& Recycling.
7. HwangCL,YoonK,Multipleattributesdecisionmaking methods and applications. In: a state of the art survey. SpringerVerlag181
8. EnvironmentalStatusReport,IMC2018 2019
9. SWMStrategicPlan,IMC,2017 2025
10. WorldBankGlobalReview,Sept 2019
11. InternationalSolidWasteAssociation,2017
12. ARC GIShelpmanual
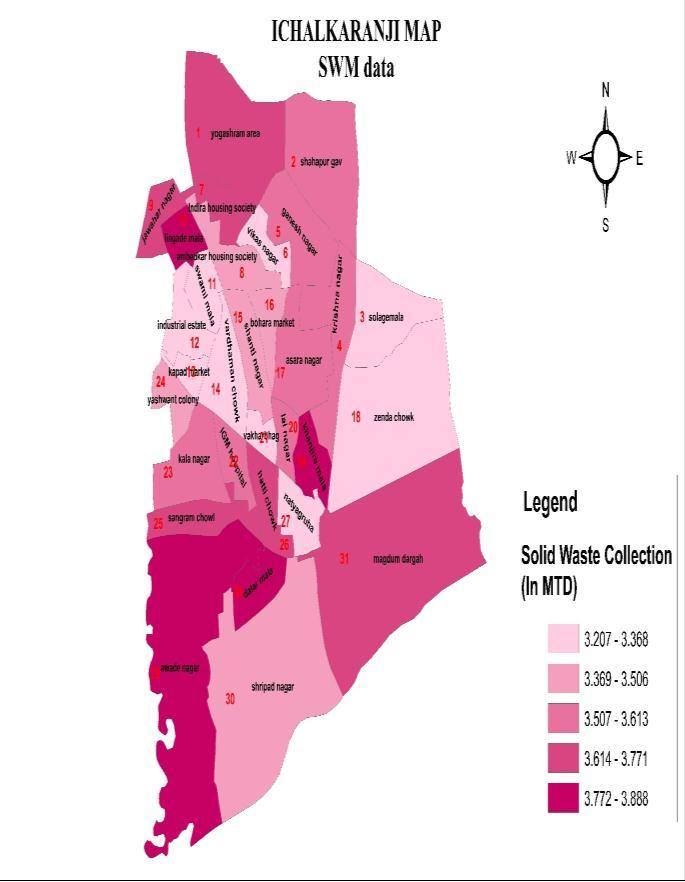
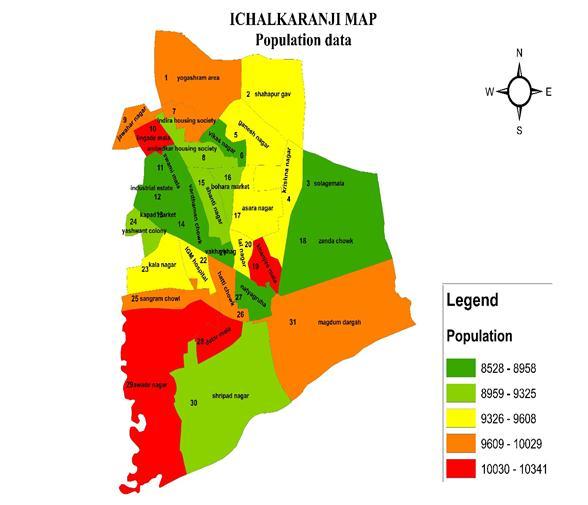
The study demonstrated that in view of the rapid urbanization, a well planned MSWMS with its effective implementationisneedofthehourforIchalkaranjicity.The detail planningandspatial status ofimplantationstudy of MSWMSconsideringitsvariouscomponentscanbepossible using geospatial tools for better results, minimizing the environmental impact on urban health. Various results obtainedinthisthestudyareusefulinplanningMSWMSfor thecityemphasizingtheimportanceoftherequirementof Solid Waste Management System (SWMS) for all urban establishmentsinthecountry.
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |