International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
2
1 M.Tech student, Civil & Environmental Technology in the Department of Civil Engineering, Department of Technology, Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune 2 Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Department of Technology, Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune ***
Abstract The critical situation of domestic wastewater treatmentwithintheruralareasofPunecity.Theeventof on sitesystemsusinglowcostandmaintainablematerials whichwillbeappliedinsmallandremoteareas.Although thisisoftenaveryimportanttheme,fewrealscalesystems are studied. This study investigated a full scale on site domestic wastewater treatment system composed of an anaerobicfilterfullofAgavaSisalanafibers.Sisalmaybea naturalfibrouslow costbiomaterialthat'sfrequentlyfound within the surrounding environment and has no toxic effects.TheimpactofAgavaSisalanafiberondomesticwaste materialwasstudiedthroughtheanalysisoftheeventofits physical,chemicalparameters.Thevarieddetentionperiod’s proportionwasdisbursedbyindoorchecksimulation.The results clearly demonstrated that natural fibrous material may improve the removal potency of varied parameters effectively. To improve its performance and applicability, sisalwasmodifiedwithpolypyrrole/polyanilineviain situ chemicaloxidativepolymerizationtechniqueforpollutants removefromwastewater.
ModifiedSisal/polypyrrole/polyanilinewasover5.69times effectivethanrawsisalforpollutantsadsorption.Withinthe caseofsyntheticwastewater,theremovalefficiencyreached 70 %. Hence, the low cost sisal/polypyrrole/polyaniline composite was a promising alternative for domestic wastewaterremoval.
Theexperimentwasconductedinruralarealocatedwithin the city of Pune and also the system was built to serve a small community. The standard of the effluent generated allowsitsreuseinagricultureactivitiesusedfibersarerich innutrientvaluesandmightbeusedorganicfertilizer.The resultalsorevealthatfeasibilityofusingAgavasisalanain anaerobic filters providing a replacement and more maintainable landing place for this material which is currentlytreatedassolidwaste.Themixturewasshownto beafeasibletechnologyforsmallcommunities.
Key Words: Natural fibrous material, Agave Sisalana, Removalpotency,Improvement,Polypyrrole/Polyaniline, Adsorption,waterrecycle
Lackofcleanlinessisconsideredahazardtoenvironmental quality and social well being worldwide Although most regions have improved their sanitation services over the pastyears,isolatedcommunities,ruralareasanddenseness regionslocatedfarawayfromurbancentersstilllackproper sanitation facilities. Water on earth moves frequently through the water cycle of evaporation, transpiration, condensation,precipitationandrunoff,typicallyreachingthe ocean. It’s one among the foremost essential issue that's neededforeverylivingbeing.Wastematterisliquidwaste discharged by domestic residence, business properties, industries, agriculture, which regularly contains some contaminants that result from admixture of waste water fromtotallydifferentsources.Wastematterobtainedfrom numeroussourcesgottobetreatedterriblyeffectivelysoas toformasanitarysetting.Inadditiontothepresent,illness inflictingmicroorganismcanbreedupwithinthestagnant waterandalsothehealthofthegeneralpublicaregoingto beatdanger.Theprincipalaimofwastemattertreatmentis typically to allow human and industrial effluents to be disposed of while not danger to human health or unacceptableharmtonaturalsetting.sowithintheinterest ofthecommunityofthecityortownit'smostessentialto assemble, treat and eliminate all the waste matter of {the city/town}insuchsomewaythatitshouldn’t;causedamage totheordersresidingwithinthetown.Theextentandalso thetypeoftreatmentneeded,butdependsonthecharacter andqualityofeverywastematterandsourcesofdisposalon the market. The sewage after treatment could also be disposed either into a water body such as lakes, streams, rivers,estuaryandoceanorintoaland.It’sgoingtousefor several purposes like as conservation, industrial use or reclaimed sewage effluent in cooling systems, boiler feed, processwater,reuseinagriculture,horticulture,sericulture, wateringoflawns.Wastewaterreusebecomeisbecoming increasingly popular, especially in geographies where potable water in brief supply.Reduction of strength of domesticwastematterexploitationbedmaterialagavefiber asafiltermediaisonesuchkindoftreatmenttechnique adopted.Theutilizationoffastenedfilmsforwastematter treatmentmethodhasbeenmoreandmorethoughtofdue toinherentbenefitsoversuspendedgrowthsystems.This work supposed to check the applying of the comparative
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

studybetweenthefiberi.e.agaveasatoughandfastbedfor treating domestic waste matter and to understand the comparativeremovalpotencyofCOD,BOD,TDS,Chlorides withstandardgravelbedinlittlevolumereactor.Sisalfiber (Agave Sisalana) is obtained from the leaves of this plant. Thelustrousstrands,usuallycreamywhite,averagefrom80 to100and20cmlongand0.2to0.4mmindiameter.Sisal fiber is fairly coarse and inflexible. It's valued for cordage usebecauseofitsstrength, durability,ability tostretched, affinitycertaindyestuffs,andresistancetodeteriorationin water. This method of treatment adopted victimization AgaveSisalanafiberasafiltermediafollowstheprincipleof trickling bed filter inside that waste matter is formed to trickleoverafiltermediacontainingseedingagentdueto biologicalaction,theinorganiccompoundspresentinwaste matter gets rotten leading to the reduction of strength of wastematter.Uptonow,morethanthousandresearchers have introduced various kind of treatment method for removal of pollutants from wastewater like adsorption, filtration, biological processes and combination of these techniques,Generallyspeakingeachmethodhasitsintrinsic advantages and drawbacks. Adsorption is defined as the movement of the pollutant molecules from the majority solutiontoasolidsurface,mostlycalledadsorbent.Simple operation,highremovalefficiency,lesssludgeproduction, high efficiency are the important high points of the adsorptionprocess.

AgaveSisalana,isspeciesoftrichophytenativetoSouthern North Yankee country but wide cultivated and neutral in manydifferentcountries.Ityieldsastifffiberusedinmaking variedproduct.Thetermsisalisadditionallyrefereitherto theplantscommonnameorthefiber,relyingonthecontext. It'susuallynoted as“sisal hemp”,asa results offor many years hemp was an important offer for the fiber, and differentfibersourceswerenamedonceit.Thesisalfiberis traditionallyusedforropeandtwine,andhasmanydifferent uses,atthesideofpaper,cloth,footwear,hats,bags,carpets, anddartboards.Sisalplantsxenophile,consistsofarosette of sword shaped leaves concerning one.5 2 meters (4.9 6.6ft)tall.Youngleavesmayhavefewminuteteethontheir margins, but lose them as they mature. The sisal plant optionsa7 10yearlife spanandtypicallyproduces200 250 commercially usable leaves. Each leaf contains a mean of around one thousand fibers. The fibers account for fewer than concerning multidimensional of the plant by weight. Sisalistakenintoconsiderationaplantoftropicsandzone, since production edges from temperatures more than 5 degrees stargazer and sunshine. Fiber is extracted by a technique spoken as surgical operation, where leaves are crushedandcrushedbyrotatingwheelsetwithbuntknives, thus only fibers keep. The assembly is typically on large scale,theleavestransportedtoacentralsurgicaloperation
plant,wherewaterisutilizedtowashawaythewasteparts of the leaf. The fiber is then dried, brushed and baled for export. Correct drying is important as fiber quality swear totallyonconditioncontent.Artificialdryinghasbeenfound tofinishinusuallyhighergradesoffiberthansundrying,but is not forever attainable at intervals the developing countries where sisal is formed. Fiber is later cleaned by brushing. Dry fibers are machine combed and sorted into variedgrades,totallyonthepremiseofthepremiseofthe previous in field separation of leaves into size groups. traditionally, sisal has been the leading material for agriculturetwine(bindertwineandbalertwine)thanksto itsstrength,durability,abilitytostretch,affinitysureenough dyestuffs,andresistancetodeteriorationinsaltwater.Sisal has been used as Associate in nursing environmentally friendly strengthening agent to modify mineral and fiber surroundcompositematerialsinvariedusesatthesideof theautomobilebusiness.Asextractionoffibersusesonlya tiny low share of the plant, some tries to boost economic viabilityhavetargetedonutilizingthethingsforproduction biogas, for stock feed, or the extraction of pharmaceutical materials.
Polypyrrole (ppy) andpolyaniline (PA) areoftwo widely usedconductingpolymersinenvironmentalstudiesbecause oftheirfacialsynthesis,porousstructure,regeneration,non toxicity , insolubility in water , environmental and mechanicalstabilityandlowcost.Unfortunately,conducting polymersmaysufferfromseriousdisadvantages,including aggregate formation, low process ability, low adsorption capacity,difficultiesinporositycontrol,andlowsurfacearea in which could hinder the efficiency of the process . Accordingly,variousphysicalandchemicaltechniquesare considered to solve these issues. Hence, it is of great importancetoprepareconductingpolymerscompositesto introducebettermaterialwithhigherapplicability.Sisal,or calledasAgavesisalana,couldbealow costhardfiberbio sorbentthatisoriginatedfromMexico.Brazilisthelargest producerofsisalfiberintheworld(approximately60%). Sisal fibers are utilized in the automotive industry, ropes, strings, sea cables, carpets, brooms, up holster, and handicraft and annually large amount of these fibers are discarded as waste. Apart from availability and inexpensiveness,sisalfibersowneffectivegroups(suchas cellulose,lignin,andhemi cellulose),whicharesuitablein
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1972
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
terms of adsorption processes. It was also employed for volatileorganiccompoundsandCO2adsorption.Rawsisal, like many other unmodified materials, may have some limitationsfortheadsorptionofpollutants.Modificationand composite preparation are called the simplest way of upgradingmaterial,especiallythosewhichre abundant,like sisal.Withinthepresentstudyaimatcoatinglow costsisal fiber with ppy/pA for unwanted pollutant removal from wastewater.Facilesynthesis,non toxicity,easyseparationof the spent sorbents, high performance (removal efficiency andadsorptioncapacity),inexpensiveness,andenjoyingthe advantagesofppyandpAsimultaneouslyarethesignificant pointsofsisal/ppy/pA.
14Inchx40Inch.5compartmentsofsizeisprovidedineach partsof water tank for batchoperation process..In which firsttwocompartmentsarekeptasemptyandinlastthree compartments fiber bags are to be provided. These fiber bagsareheldonstainlesssteelstandshavingdesiredheight up to 10cm & 8 cm respectively. A bison panels are to be used to make compartments in tank. Holes are made in panelsforsmoothmovementofwaterinzig zagpattern.
CentralPollutioncontrol board(CPCB)studiesdepictthat there are 920 waste treatment plants (STPs) in Asian country, of that solely 615 are operational. Thus, the {present} treatment capability is simply 21 percent of presentwastegeneration.Theremaininguntreatedwasteis that the main reason behind pollution of rivers and lakes. The large range of STPs created below Central Funding Schemes just like the Ganga Action arrange And Yamuna Action arrange Of National watercourse Action arrange aren't totally operated. There's a necessity to arrange methods and provides thrust to policies giving equal weightagetocarcerebrationofprovidedwaterlikewiseas developmentofwastemattertreatmentfacilities,recycling, recovery, recharging and absence. The future of urban facility for potable uses can rely majorly on economical wastemattertreatmentsystems,becausethetreatedwaste matterofupstreamurbancentersarethesupplyofwaterfor downstream cities. Hence provide alternative method to treat domestic wastewater, which is cost effective, more efficientanduser friendly.
For present study, Agave Sisalana fibers and Modified sisal/polypyrrole/polyanilineareusedasafiltermediafor wastewater treatment


Aplasticwatertankisusedasamodel,havingdimensionof 38Inchx28Inchx40Inch.Madeatwopartsofplasticwater tank,onepartforAgavaSisalnaandsecondpartforModified sisal/polypyrrole/polyaniline,havingdimensionof38Inchx
Sisalwasinitiallywashedseveraltimeswithwatertogetrid ofanyimpuritiesanddirtonitssurfaceandthendriedat40 °Covernight.Thesynthesisprocedurewasconductedviain situ chemical oxidative polymerization technique. In the initialstep,0.3MHCl(3mL)wasaddedto100mLdeionized water.2mLanilineand2mLpyrrolewereaddedtothe40 mLHClsolutionandagitatedforabout50min.Inanother40 mLHClsolution,1.5gsisalwasaddedandsimilarlyagitated. Inthefinal20mLofHCl,6gFeCl3wasdissolvedandmixed for30min.Iron(III)chlorideisaddedtothesolutionasthe oxidanttoconductthepolymerizationprocess.Inthesecond step, the aniline/pyrrole solution are poured into a sisal solution,andthattheyareallowedtointeractandblendone another for an hour. Finally, to finish the polymerization process, the oxidant solution was added to the aniline/pyrrole/sisalsolutionandagitatedfor24h.Toreach animprovedpolymerization,thesesolutionswerekeptinan icebathIntheend,thesynthesizedmaterialwastakenout from the solution, which had black to green color. The preparedmaterialwaswashedseveraltimeswithwaterand methanol,andthendriedattheovenfor24h.Figshowsa schematic of the synthesized procedure. The produced material was so called sisal/polypyrrole/polyaniline (sisal/ppy/Pa).
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056


Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Step 1 4mLanilineand4mLpyrroleareaddedtothe80 mLHClsolutionandagitatedforabout50min
Step 6 Intheend,thesynthesizedmaterialwastakenout from the solution, which had blue to green color. The preparedmaterialwaswashedseveraltimeswithwaterand methanol,andthendriedattheovenfor24h.
Step 2-Inanother80mLHClsolution,5gsisalwasadded andsimilarlyagitated


Step 3 Inthefinal40mLofHCl,12gFeCl3wasdissolvedand mixedfor30min.Iron(III)chlorideisaddedtothesolution astheoxidanttoconductthepolymerizationprocess
AsperthestandardlaiddownbytheCPHEEO(CentralPublic HealthEnvironmental&EngineeringOrganization)thefresh waterconsumptionperdayperpersonshouldbetween135 to150litersperday.Inanyruralarea,athreebedhousewith aminimumpopulationofpeopleof5peoplewouldhavea dailyestimatedwastewaterproductionof750litersperday (5 x 150) the sample was collected from a rural area. Samplingwasconductedforevery24hrsforaperiodof12 daysbetween4pmto5pm.Grabsampleswerecollectedin plasticcansrinsewithdistilledwater.


Step 4 Inthisstepaniline/pyrrolesolutionarepouredintoa sisalsolution,andtheyareallowedtointeractandblendone anotherforanhour.
Initially the model is charged with water so the sample of wastewatertobetreatedisfedintank.Aknownvolumeof sample (20L) is fed through inlet pipe at continuous rate day’sdetentionperiod.Awastewaterisfedintankatarateof 5Lpereverydayfor4totakecareofconstantlevelof20Lin eachcompartment.Boththecompartmentoffibersgetfed simultaneously.Wastewaterisfedintotankgetfiltratedor treated when it passes through the fiber bags provided in compartments.After,thistheparameterslikepH,COD,BOD, Chloride and TDS are analyzed for the sample coming the outlet by implementing the quality methods for the ExaminationofWaterandWastewater,(APHA,AWWA,20th Edition).

Step 5 To finish the polymerization process, the oxidant solutionwasaddedtotheaniline/pyrrole/sisalsolutionand agitatedfor24h.
Twodifferentfibrouspackingmaterialsusedforthepresent study, Agave sisalana and modified sial/ polypyrrole / polyaniline.Fibrousarepackageinnetplasticpacketshaving thickness 2mm. Dude to this net packing , fibers placed in straightmannerandtheygetmaximumplaceforadsorption. Samples were analyzed forthe following parameters BOD, COD,Chloride,Sulphate,andPH
5.1 Removal efficiency of using Agava Sisalana filter bed for different detention period


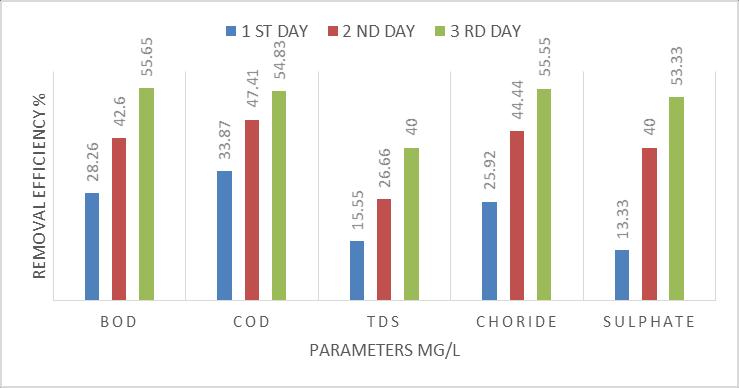
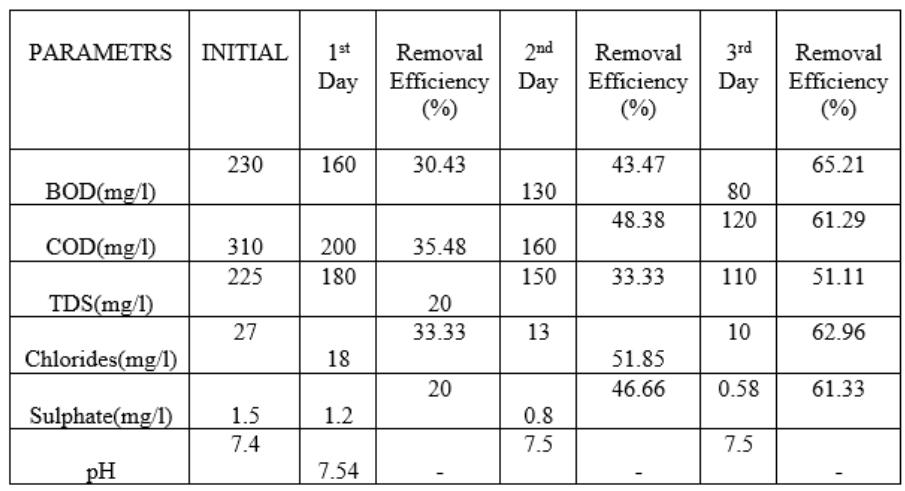
The performance of Agava Sisalana bed is checked at 36h, 72h,and96hdetentionperiod.All resultsarerepresentin Table 5.11, Table 5.1.2 & 5.1.3 respectively. It is seen that detention period increases, removal efficiency is also increases. At36h, removal of BOD IS 52.27 % and at 96h removalofBODis55.65%.At96h,thevaluesofBOD,COD, TDS, Chloride and Sulphate as 102, 140, 135, 12 & 0.56 respectively.Allvaluesatpermissiblelimit.
Chart 5.1.1- Removal efficiency using Agava Sisalana filter bed for 36 h detention period
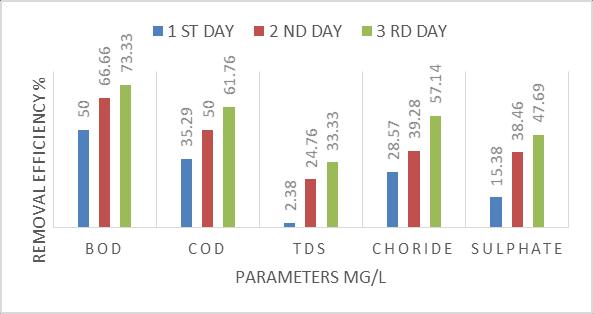
Table 5.1.1- Removal efficiency of Agava Sisalana filter bed for 36 h detention period
Table 5.1.2- Removal efficiency of Agava Sisalana filter bed for 72 h detention period
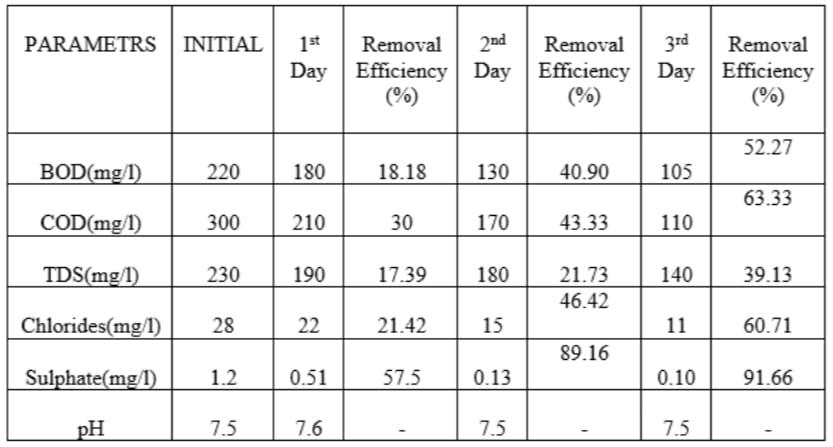
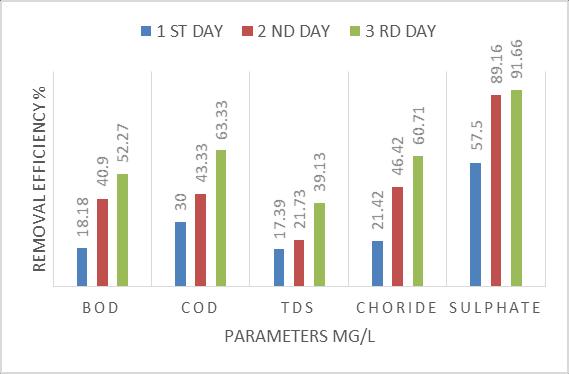
Chart 5.1.2 Removal efficiency of Agava Sisalana filter bed for 72h detention period
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
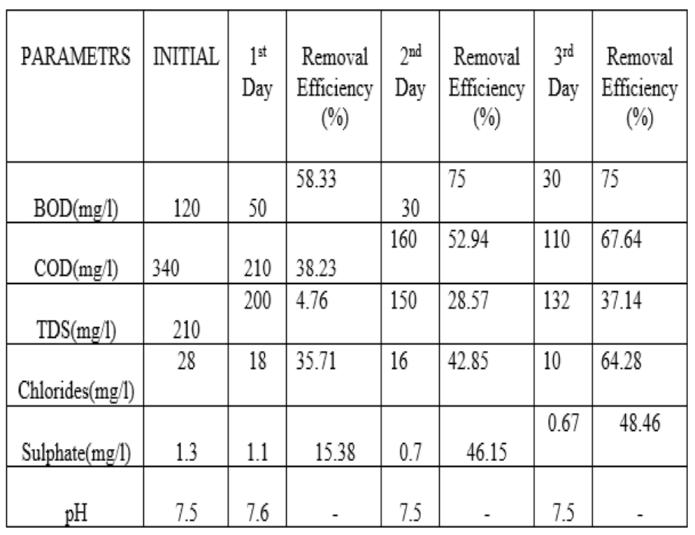
Table.5.1.3 Removal efficiency using Agava Sisalana filter bed for 96 h detention periods.
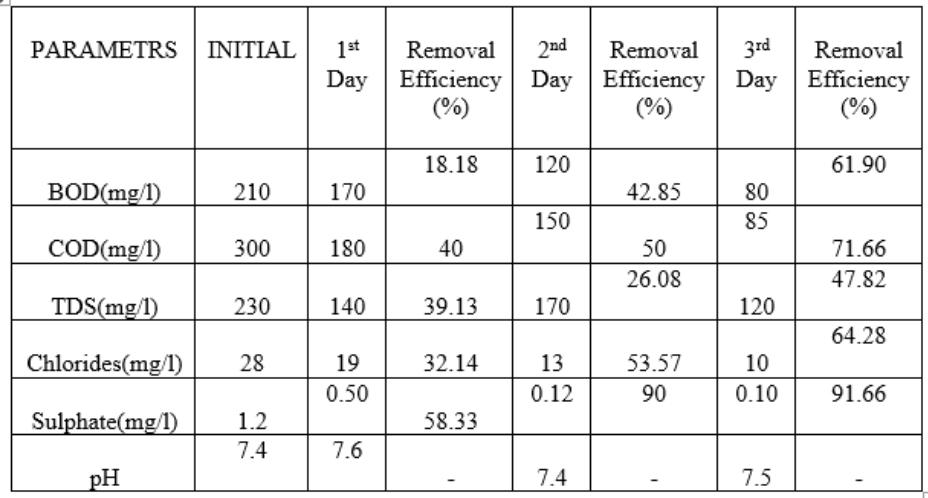
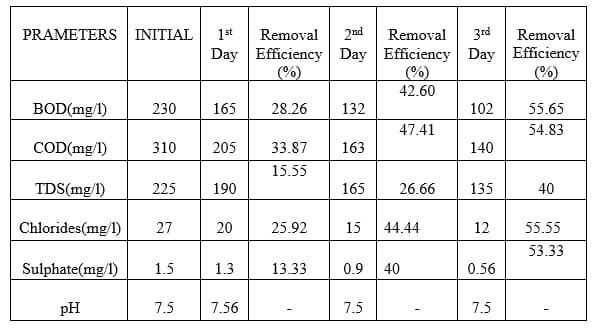
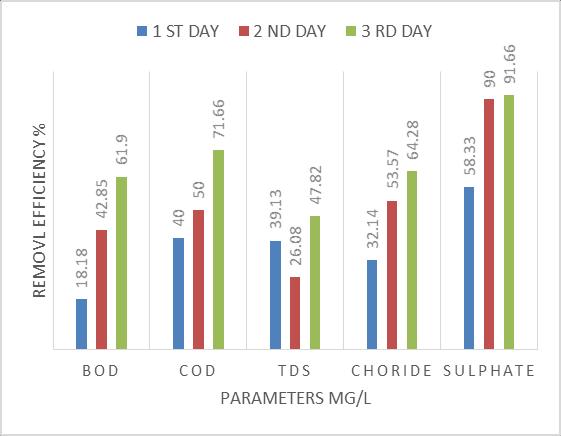
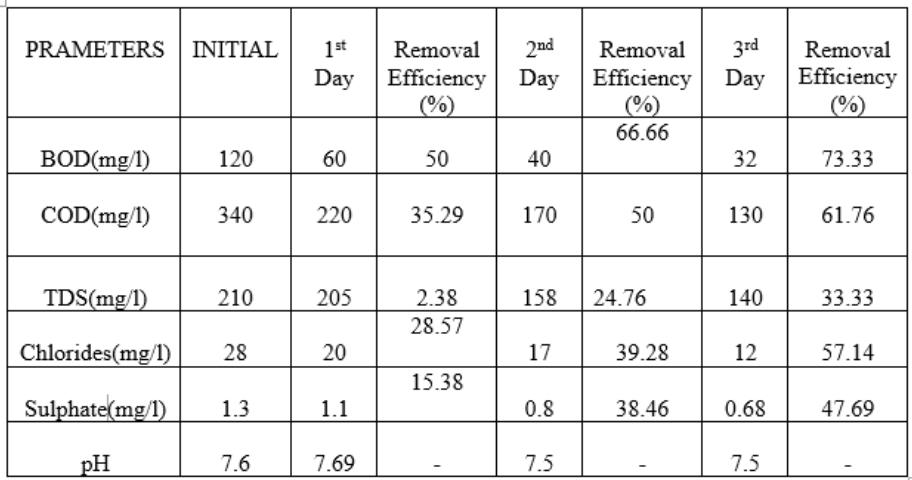
Table.4.2.1 Removal efficiency of modified sial/ polypyrrole / polyaniline filter bed for 36 h detention period
Chart.5.1.3-Removal efficiency using Agava Sisalana filter bed for 96 h detention periods
4.2 Removal efficiency of modified sial/ polypyrrole / polyaniline bed for different detention period
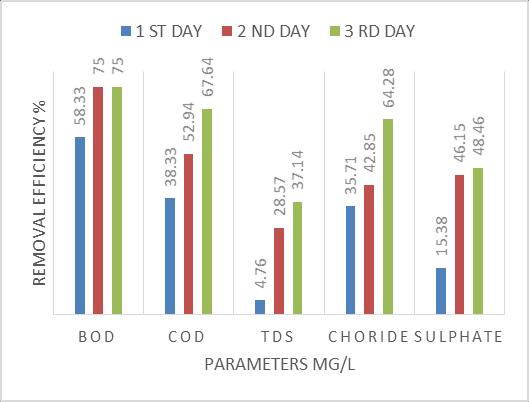
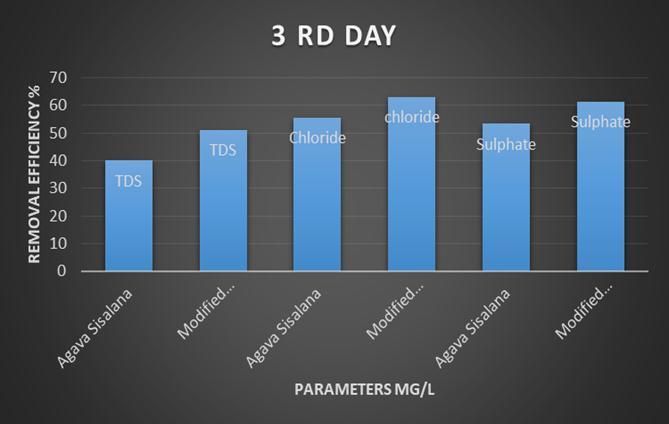
TheperformanceofModifiedsisal/polypyrrole/polyaniline bed is checked at 36h, 72h, and 96h detention period. All results are represent in Table 4.21, Table 4.2.2 & 4.2.3 respectively. It is seen that detention period increases, removalefficiencyisalsoincreases.At36h,removalofBODIS 61.90%andat96hremovalofBODis65.21%.At96h,the valuesofBOD,COD,TDS,ChlorideandSulphateas80,120, 110, 10 & 0.58 respectively. All values are at permissible limit.(Ref3.6.2,3.6.3)
Chart.4.2.1-Removal efficiency of modified sial/ polypyrrole / polyaniline filter bed for 36 h detention period
Table-4.2.2 Removal efficiency of using modified sial/ polypyrrole / polyaniline filter bed for 72 h detention period
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
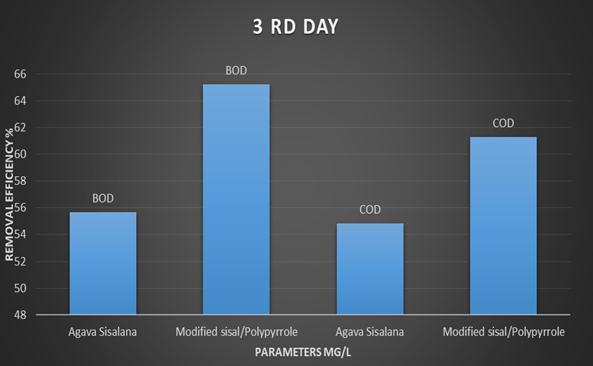
Modified sisal shows more removal efficiency than Agava sisalana. Agavasisalanahaveownnegativesurfaceandcould effectively adsorb positive compounds via electrostatic attraction. The main issue is raised once the intended compoundownanegativesurface,andnotmuchsorptionis happened due torepulsive forces. Tosolvethis obstacle,a novel composite based on sisal and modification with polypyrroleandpoly anilinewassynthesized.
Chart 4.2.2 Removal efficiency using modified sial/ polypyrrole / polyaniline filter bed for 72 h detention period
Table.4.2.3- Removal efficiency using modified sial/ polypyrrole / polyaniline filter bed for 96 h detention period
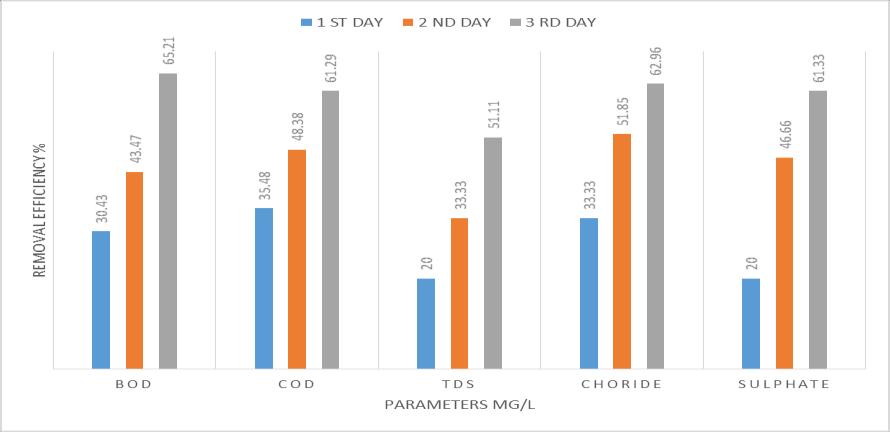
Chart.4.2.3 Removal efficiency using modified sial/ polypyrrole / polyaniline filter bed for 96 h detention period
4.4.1
Detentionperiodorcontacttimeisoneineveryofthemain parametersinadsorptionprocessforremovalcontaminants from wastewater .Fig (a) shows the pollutants removal
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
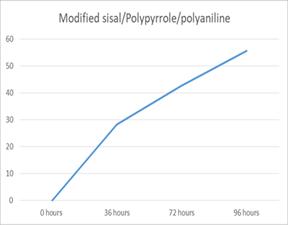
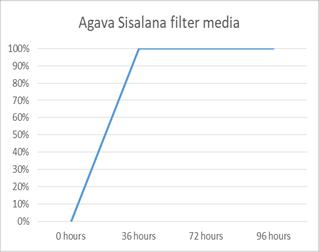
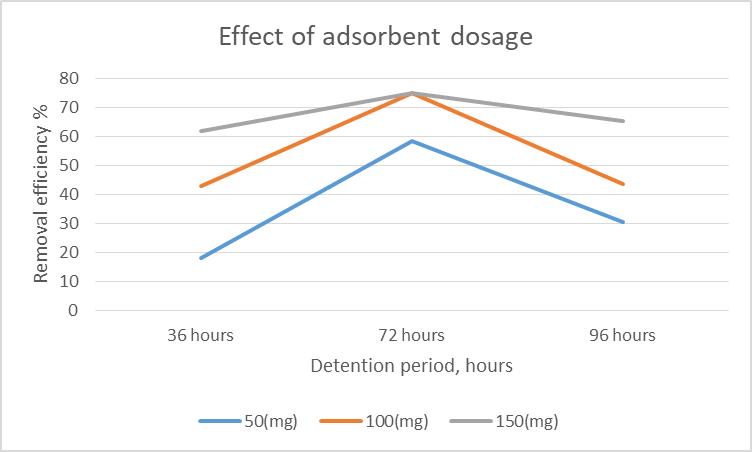
efficiencyandAgavasisalanaadsorptioncapacityatthetime rangingfrom 0to96hours.Insightofremovalefficiency,it isobservedthattheeliminationprocesscouldbedividedinto three different parts. In the starting from 0 36 hours the curve got a high slope with rapid increase in pollutant removal,until36hours,28.26%pollutantswasadsorbed.In the second stage (36 72 hours) the slope of the removal curve drastically reduced in the way that the removal efficiency slightly increase from 28.26 % to 42.60 %. Adsorptionrateinthisperiodwasnotsignificant.Withinthe conclusion (72 to 96 hours), it is substantially clear that removalefficiencyslightlyincreasefrom42.60to55.65%.It is almost constant. In similar way, by using modified sisal/polypyrrole/polyanilineremovalefficiencyshowsinfig (b).Withintheinitialstage(0 36hours)thecurvegothigh slopewithrapidincreaseinpollutantremoval,until36hours, 30.43%pollutantwasadsorbed.Withinthesecondstage(36 72hours)theslopeoftheremovalcurvedrasticallyreduced inthewaythattheremovalefficiencyslightlyincreasefrom 30.43%to43.47%.Adsorptionratewithinthisperiodwas notsignificant.Inthefinalstage(72to96hours),itisgreatly clearthatremovalefficiencyslightlyincreasefrom43.47to 65.21%. It is slightly increasing. Such behavior could be attributedtotheactualfactthatinitialstageoftheadsorption process,therearemanyvacantsitesonAgavasisalanaand modified sisal that are vulnerable to adsorb the pollutant fromwastewater.Therefore,fortheoptimumcontactperiod wassetat96hours.
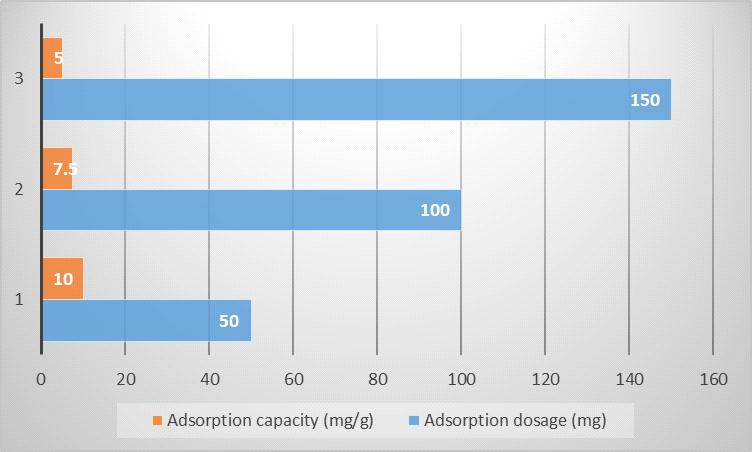
Theadsorptionrateofpollutantareinvestigatedbychanging the dosage of under optimum detention period. The importanceofadsorbentdosageisespeciallyassociatedwith the ultimate cost of treatment and removal efficient. The effectofpollutantremovalefficiencyandadsorptioncapacity undervariousadsorbentdosagesisshowninFig.(a)Itshows thatbyincreasingtheadsorbentdosagefrom50mgto150 mg,pollutantremovalefficiencyenhancedfrom43.47%to 65.21%.Higherpollutantseliminationareobservedathigher sisal/ppy/pAdosage.Logically,itisfairtosuggestthatafter the adsorbent dosage increases, more active sites become availableforpollutantremoval.Consideringtheadsorption capacity (Fig. b), different results were observed. Numerically, the adsorption capacity of 10 mg/g was achieved at an adsorbent dosage of 50 mg; however, at sisal/ppy/pAdosageof150mgtheadsorptioncapacitywas found to be 5 mg/g. Intending these figures the greater adsorptioncapacityareachievedatloweradsorbentdosage. Infact,whenthereisthelimitednumberofvacantsiteson the adsorbent (at low adsorbent dosage), competitive behaviorisoccurredbetweenpollutantsmoleculestooccupy these available sites, resulting in a greater adsorption capacityatloweradsorbentdosage.Inordertooptimizethe restofparameters,itisintendedtodecideontheadsorbent dosageof50mgdosage.
Fig (a)
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Intermsofadsorptionapplicabilityinarealenvironment,it
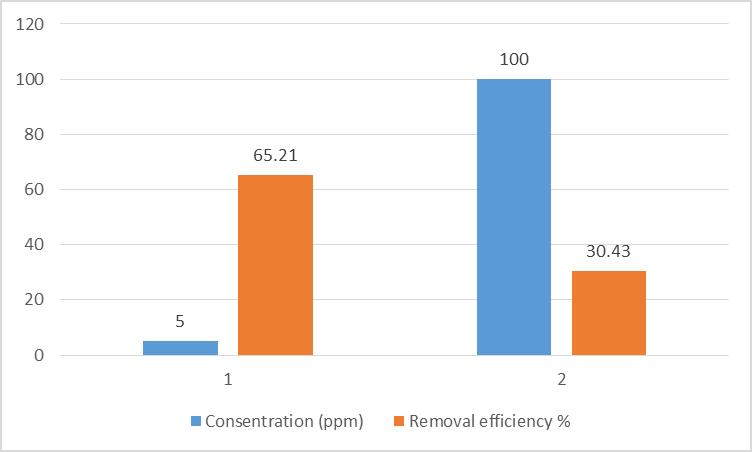
is important to determine the effectofdifferent pollutants concentrations.Accordingly,chart 4.4.3representstheeffect ofcontaminantsconcentrationontheremovalefficiency.The experiments are conducted at contact time 96 hours and adsorbentdosage150mg.Basedontheobtainedresults,the highest removal efficiency of 65.21 % are observed at contaminantsconcentrationof5ppm.However,thelowest removalof30.43%,areseenatacontaminantsconcentration of 100 ppm. It can be explained that the quantity of obtainableactivesitesonsisal/ppy/pAareconstantandonce contaminantsconcentrationincreases(dudetoseason wise variationseenincontaminantconcentration)thenumberof pollutantmoleculesincrease.However,theserequiredsites do not seem to be available, leading to lower removal efficiencyathighercontaminantsconcentration.Incontrast, at pollutants 5 ppm, the contaminants molecules could simplyoccupythesitesandberemoved.Approximately,all pollutantsareremoved.
4.4.5
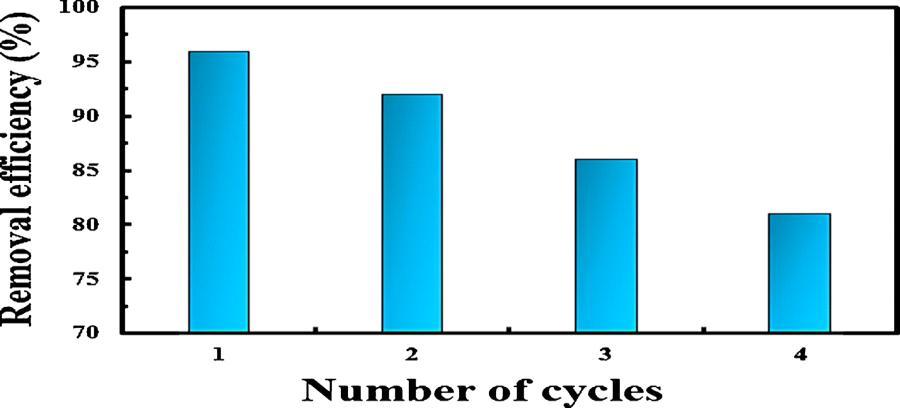
In view of total treatment cost in adsorption processes, adsorbentplaysanimportantroleandscientistsattemptto employbiomaterialsfoundintheenvironment.Inthepresent study,thereusabilityofbio sorbentsisal/ppy/pAwastested underoptimumconditions,andalsotheresultsarepresented inFig.4.4.5Thespentadsorbentisfirstlywashedwithdis tilled water, and then dried at ambient temperature. After that, it had been washed several times with 0.1 M NaOH solution(100mL).Next,itabsolutelywasagainwashedwith ethanolanddistilledwater,andthendriedat60°C.Itwas found that one the adsorbent was used for four times; the removal efficiency was still more than 80 % for pollutant adsorption.Thus,theresultsrevealedthatsisal/ppy/pAmay be successfully utilized for the removal of pollutant from wastewater.
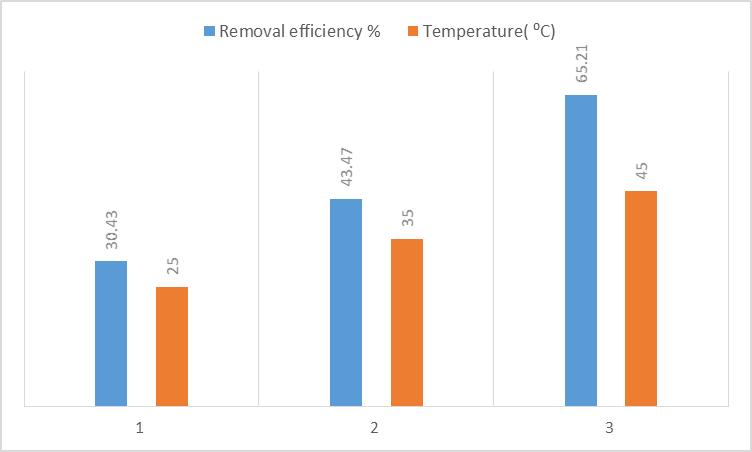
Based on numerous investigations, the temperatureof the workingsolutiondirectlyeffectsontheinteractionbetween adsorbateandadsorbent.Withinthepresentstudy,theeffect oftemperaturerangingfrom25to45°Cwasstudied.These resultsareshowninChart 4.4.4accordingly,byincreasing the temperaturestarting from 25 °C to 45 °C, the removal efficiencyincreasedfrom30.43%to65.21%,revealingan endothermicnatureofsisal/ppy/pAforRO5adsorption.This behavior is mainly because of the interaction between adsorbateand adsorbent, which could be said thatat high temperaturesisal/ppy/pAsitesexhibitgreateraffinityand adsorptionenergytowardpollutantmolecules.Sincedonot seemtobemanydifferenceswithintheremovalefficiencies andthecostoftemperatureadjustingwithintheindustrial scale.
Chart
4.4.6
The fluctuation of PH during absorption process in Agava sisalana bed media is constant throughout all detention period.Butinthemodifiedbedmediaisgetalterthesurface chargeofthematerial.ByincreasingthePHfrom2to8,the
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
removalefficiencydecreasesfrom99%to30.43%.Identical trendsareobservedforadsorptioncapacity.
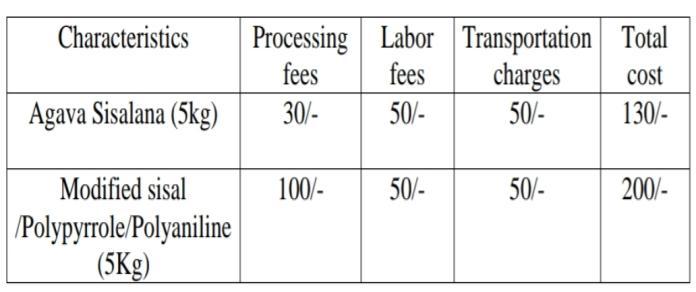
Extraction process of Agava Sisalana fibers is simple to implement. Fiber is extracted by a technique spoken as surgicaloperation,whereleavesarecrushedandcrushedby rotating wheel set with buntknives, thus onlyfiberskeep. The assembly is typically on large scale, the leaves transported to a central surgical operation plant, where waterisutilizedtowashawaythewastepartsoftheleaf.The fiber is then dried, brushed and baled for export. For 5kg fiber extraction process required 30 rupees per kg, labor chargesare50/ ,transportationchargesare50/ andtotal costforcompleteprocedureis130/ ,formodifiedsisalfibers required some experimental procedure. The experimental procedure was conducted via in place chemical oxidative polymerizationtechnique.Forthisprocedure100rupeesper kgchargesrequired.Laborchargesis50rupeesperkgand transportationchargesisalso50rupeesperkg.Totalcostis requiredforthiscompleteprocedureis200rupeesperkg.
Thepotentialofsisal/ppy/pAasacost effectiveadsorbentto adsorbpollutantisevaluatedinthepresentstudy.Itisfirst time that sisal/ppy/pA is synthesized and used for such removal of wastewater pollutants. Electrostatic attraction and physical adsorption were introduced as the chief mechanisms for pollutants removal from wastewater. Inthisstudy,ithasbeenshowedthattreatmentthetreatedof sisalfiberswithAniline/pyrroleshowsabettercapacityin the removal of pollutants from domestic wastewater than naturalsisalfibers,withmaximumadsorptioncapacityupto 65.21mg/g.Ithasalsobeenshownthatthebestresultsfor bio sorptionofcontaminantsonnaturalandmodifiedsisal fibers were obtained usingan adsorbent dose of5g/l and after a detention period 96h. The adsorbed quantities of pollutants decreases with increasing temperature. Pollutants removal from wastewater is increased with increasingcontactperiodlike36h,72h,&96handahigher dosageofsisal/ppy/pAprovidedmoreplaceforpollutants removal, which was favorable in terms of performance. ConsiderablereductioninBOD,COD,TDS,nutrientssuchas chloride,sulphateareachievedbyusingAgavasisalanafilter bed and Modified sisal/ppy/pA filter bed. The removal
efficiencyofBOD,COD,TDSandChloride,Sulphatebyusing Modified sisal/ppy/pA filter bed are found to be 65.21%, 61.29%, 51.11% & 62.96%,61.33% respectively which is higherthanthatofAgavaSisalanafiltermediaisfoundtobe 55.65%, 55.48%, 42.22%,& 55.55%, 53.33% respectively .Highremovalefficiency,nontoxicity,availability, andcost effectivenessarethemainprosofsisal/ppy/pA.Thismodelis used in any season, pollutants concentration is inversely proportional to removal efficiency. When pollutants concentrationis5ppmthenremovalefficiencyis65.21%and when pollutants concentration is 100 ppm then removal efficiencyis30.43%relativelyless.Hencehereconcludethat pollutants increases, removal efficiency decreases. ThecostofAgavasisalanafibersusedfortreatmentof150 litersofwastewaterisaboutRs 133,whichiseconomicalthan compared to modified sisal/poypyrrole/polyaniline fibers cost about Rs 200.However the treatment efficiency of modifiedisfoundtobehigherthanthatofAgavaSisalana. The fluctuation of PH during absorption process in Agava sisalana bed media is constant throughout all detention period.Butinthemodifiedbedmediaisgetalterthesurface chargeofthematerial.ByincreasingthePHfrom2to8,the removalefficiencydecreasesfrom99%to30.43%.Identical trends are observed for adsorption capacity. The treated wastewatercanbeusedforcarwashing,irrigation,watering lawns,and,rechargeofaquifers.Thismethodisuser friendly and can be used as pre treatment process for wastewater treatment.Thetreatmentmethodiseasilyimplementinany developedruralarea.Insteadofconventionalmediasuchas sandetc.Useofnaturalandmodifiedfibrousmaterialsasa fixedbedinwastewatertreatmentequallyshowspromising efficiencyoforganicsandnutrients.Theusedfibersarerich in nutrient values and can be used organic fertilizer. The resultalsodemonstratethatviabilityofusingAgavasisalana inanaerobicfiltersforthetreatmentofsewagefromsmall communities. The quality of the final effluent generated allows its recycle in agriculture activates. This system requiredmaintenanceevery6months.Thisprovidesanew andmoremaintainablelandingplaceforthismaterialwhich iscurrentlytreatedassolidwaste.
Modified sisal/ppy/pA could also be utilized for variety kinds of pollutants, including pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
Agavasisalisoneofthegreatestbiomaterialswhichis highly capable of being used in many composites. Furtherstudyonagavasisalana’sremedialpropertiesand attention will be paid to the sustainable management of these plants in the country in a sustainable manner Infutureperspectivethebiomassofsisalmaybeused for removalofcadmiumandleadionsincontaminatedwater
Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1. Ali Khadira “Low cost sisal fibers/polypyrrole/polyaniline bio sorbent for sequestration of reactive orange 5 from aqueous solutions
2. M. Dizbay Onat, E. Floyd, U.K. Vaidya, C.T. Lungu, Applicabilityofindustrialsisalfiberwastederived activated carbon for the adsorption of volatile organic com pounds (VOCs), Fibers Polym. 19 (2018)805 811,https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221 018 7866 z
3. Dr.Harinath“Studiesonnaturalfiberousmaterial as fixed aerated beds for domestic wastewater treatment”
4. BendjeffalH“Effectofthechelatingagentsonbio sorption of hexavalent chromium using Agave sisalana fibers” Chin. J. Chem. Eng. (2017), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2017.10.016
5. Walter“N.L.dosBiosorptionofPb(II)andCd(II)ions by Agave sisalana (sisal fiber) Microchemical Journal 97 (2011) 269 273 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2010.09.014
6. Munigala Srikavyal “Experimental studies on fiberous materials as aerated beds for domestic wastewatertreatment”
7. LuanaMattosdeOliveiraCru“Usingcoconuthusks inafull scaledecentralizedwastewatertreatment system: The influence of an anaerobic filter on maintenanceandoperationalconditionsofasand filter”EcologicalEngineering127(2019)454 459 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2018.12.021
8. Ana S. Mestre “Chemically activated high grade nonporous carbons from low density renewable biomass (Agave Sisalana) for the removal of pharmaceuticals” https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.10.081
9. S.Vigneswaran “Fiitration Technologies In WastewaterTreatment”
10. Chris Sheba M “Evaluation of bio based fibers for treatment of wastewater from textile industry” https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334083 839
11. A. Ashiq, N.M. Adassooriya, B. Sarkar, A.U. Rajapaksha,Y.S.Ok,M.Vithanage, Municipalsolid wastebiochar bentonitecompositefortheremoval of antibiotic ciprofloxacin from aqueous media, J.
Environ. Manage. 236 (2019) 428 435, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.006.
12. Sneha G “ Natural fiberous material as fixed aeratedbedsfordomesticwastewatertreatment”
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1981