International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1M.Tech Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Ganpat University, Gujarat, India 2PG Head, Ganpat University, Gujarat India 3PG Coordinator, Ganpat University, Gujarat India ***
Abstract Construction industry have been expanding from the past decade and as a result large, medium and small scale construction companies are moving toward a well defined structured system where process optimization can be achieved through efficient database management. The Construction business gains a lot from the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) technology. Industry needs much sufficient system to manage the data volume and provide much better interdepartmental coordination. While taking a decision of investing and implementing such ERP system, there are some parameters which govern the process of decision making. These parameters help to check the viability of any ERP system for construction companies. The research identified viability parameters and ranked according to their importance. Research uses qualitative and quantitative approaches. With the help of Relative Importance Index Method and Factor Analysis importance rankings were found. RII method of analysis projected viability parameters like User friendliness of ERP Software, Acceptance of New Technology, Availability of Data, Initial Training Time, Organization's Growth Plan, Work Process Reengineering, ERP Implementation Priority, IT Infrastructure of the Organization, Customization, and Software Competency as important viability parameters whereas Factor Analysis projected, Geographic Spread of the Organization, Organization Strength, Acceptance of New Technology, Maintenance Cost, Applicability of Available ERP Software in the Market to the Organization, Development/Customization Cost, Software Competency, IT Infrastructure of the Organization, and ERP Implementation Priority as the most important viability parameters. These significant viability parameters can be used while making crucial decisions about testing the viabilityofanyERPsoftwareinconstructionorganizations.
Key Words: Enterprise Resource Planning, Viability Parameters, Decision Making, Change Management, Process Optimization, Efficient Database Management
Construction industry is booming in last decade and as a result large, medium and small scale construction companies are moving toward a well defined structured system where process optimization can be achieved
through efficient database management. Such database managementsystemsprovideimportantinformationsuch as data transparency, data clarity, data optimization, data review and analysis. Many database management tools have been present in the industry from past decade and such tools often comes with high cost, initial time investment, lengthy process, implementation & adaption challenges, and unknown risks. Most of the large scale companies have already adapted such database management tools to streamline their business process, and to optimize work efficiency. Enterprise Resource Planning software is such tool to efficiently manage data for the whole business process. ERP systems provide numerous advantages to construction industry and many construction companies know the advantages of such systems but feel resistance toward such change in the organization. The advantages of ERP systems are such as, standardized information, inter departmental coordination,improvedoperationalefficiency,dataclarity, and reduction in cost and time for completion of the project.
In current practice, only few small scale companies are using such ERP systems and factors such as lack of awareness, lack of interest, initial time and capital investment requirement, and lack of information are driving their decision making ability. Identifying viable parameters for ERP system adaption in small scale companies are the current need of the industry. These viability parameters will help the industry in the process of decision making for adapting to such ERP systems. Viability parameters will provide the necessary informationtothebusinessownersandwilleducatethem andhelpdecidetheviabilityofsuchERPsoftwarefortheir organization.
While taking a decision of investing and implementing suchERPsystem,therearesomeparameterswhichgovern the process of decision making. Currently there are not many tools for the decision makers to identify such viability parameters to make this process easier. This researchwillhelpdecisionmakerstochecktheviabilityof ERP software for their organization, with the help of identifiedviabilityparameters.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The objective of the study is to identify key viability parameters of ERP software for construction companies andtorankandprioritizeidentifiedviabilityparameters.
For this research mixed method approach was adopted wherein both the qualitative and quantitative data are collected.
To understand the basics, literatures related to “Business Process Re engineering”, “Change Management”, “Process Visualization” were referred. Along with them papers relatedto“Implementation ofERP”and“ProblemsinERP Implementation” were also referred. Further to which research work based on “Journals on tools for change management” and “Components of Work Process Change Management” were studied for better understanding of probable alternate methodologies and research gap and analyse the same. Literature review also resulted in identification of viability factors for ERP systems in other relevantstudies.
Data collection was carried out by adopting both qualitativeandquantityresearchmethodologies.Through literaturereviewsviabilityparameterswereidentifiedand were enlisted followed by one to one semi structured interviews were carried out with the relevant industry experts to find out more viability parameters. These parameters were then enlisted in a table along with the viability parameters found in the literature review. Along with viability parameters, plus and delta were also found out with the help of one to one semi structured interviews which contributed to enhanced understanding the applicability of ERP systems in the construction industry.
Identifiedviabilityparameterswerecleanedforduplicates and classified into three sections: Organization related, Software related, and Cost related. A questionnaire was formulated in such a way that importance of each identifiedviabilityparameterscanbefoundoutinorderto gain in depth knowledge about the factors and how they affectthedecision makingprocess.
The questionnaire was prepared in google survey form and distributed using WhatsApp, email, LinkedIn and throughapproachingexpertsindividually.
Based on the responses received on the questionnaire survey data analysis was carried out with the help of Factor Analysis method that assigned weightage to
parameters. According to the weightage each viability parameters were ranked where viability parameters with the highest weightage was ranked first and remaining wererankedaccordingly.Toprankedviabilityparameters werethenvalidatedbytheindustryexperts.
Sharma, Sharma and Shekhavat explains the implementation of ERP system (SAP) in phased manner where in depth study of critical success factors, implementationstrategiesandenvironmentoftheprojects were carried out through focused group method. Paper discussed about factors that lead to failure of implementation of ERP system. Paper also includes the business process reengineering in different phases of the implementationofERPsystem.[1]AnotherstudyinGreece discussed about development of conceptual framework whichinvestigatesthefactorsaffectingtheimplementation of ERP. [2] Shi and Halphin discussed about ERP technology and its current development in construction industry. Paper also provides brief study on the direct implementation of ERP in construction industry. [3] Syed M. and Ahmed et al. investigated the competency and implementation status of ERP in a contracting firm where they explored various barriers faced by contracting firms while implementing ERP. The major takeaway from the research was lack of knowledge and training lead to poor implementation of ERP in contracting firms. Paper also discussed about the customization needed for the best suitability for contracting firms. [4] Singh and Arora research is based on the reduction of failure in implementing ERP where they discussed about the implementationoflifecycleofERPwhichincludesselection of ERP, Project Planning, Gap analysis, Work Process Reengineering, Training, Testing, Implementation and Maintenanceandfailurefactorswereidentifiedlike,lackof customization,insufficienttrainingandinsufficienttesting. [5] Yu Rong ZENG, Lin WANG and Xian Hao XU discussed about its vital investment and its significance of future competitiveness and performance of small and medium scaleenterprises.Theydiscussedimportanceofqualitative and quantitative factors on selection of best ERP system based on Multiple Criteria Decision Making (MCDM). Brief ofeachliteraturereviewisprovidedintotabularform. [6]
The data collected for the thesis is both quantitative and qualitative. This also classifies the data into primary and secondarydata.Theprimarydataincludesinterviewsand literature review. The secondary data has been collected by questionnaire surveys of stakeholders of ERP users to helpvalidatethehypothesisfortheprimarydata.
Following the literature review, a series of personal interviews are conducted as a part of primary data collectionwhichwasfollowedbyanonline questionnaire.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
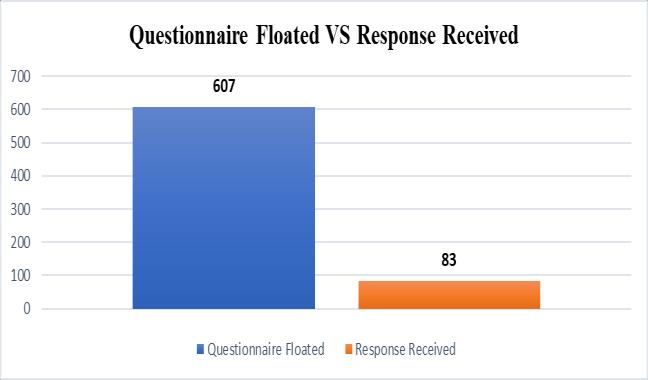
The survey form is divided into Five sections, "A Introduction”, section “B Personal information " and "C Factors related to Organization”, “D Factors related to ERP Software, and “F Factors related to Cost” Section A “Introduction" consists of brief information about the undertaken study. Section B “Respondents Details” consists of personal information of the participants including fields like name of the respondent, title/designation, organization, years of experience and e mail address. Section C, D and E consist of the identified factorsbasedonOrganization,softwareandcostinwhich the respondents were asked to provide a rating to them based on its importance. The online questionnaire was floated,atotalof83acceptableresponseswerereceived.
Based on the literature review and personal interviews, a total of 25 viability parameters were identified. Among all the viability parameters some were related to organization,some wererelatedtoERP softwareandrest were related to cost hence, viability parameters were categorizedin3sections.
Fig 1: TypeofDataCollection
For collecting the data, a through literature review was conductedandviabilityparameterswereidentified which govern the decision making while investing and implementingERPsystem.Basedontheliteraturelimited numbersofviabilityparameterswereidentifiedthuscame the need of identifying more viability parameters for which open ended interviews were conducted. Based on the requirement of the research, industry experts having averageexperienceof22+years,havinggoodexpertisein working with ERP system were identified. Interviewee’s roles in the organizations varied from Senior Manager to Top Management. An Interview form was developed where personal details of interviewees were fetched like, Name, Years of Experience, Role and Designation in the Organization, their Highest Qualification and Type of Organization. Along with that, questions related to research were drafted to get needed output (Viability Parameters).Interviewcontainedfollowingquestions.
1.DurationforwhichtheorganizationisusingERP?
Quantitative data is obtained through opinion survey. A questionnaire was prepared first which was pilot tested andaftercorrectionsitwasadministeredonline.

The parameters are measured on a scale suggesting criticality of that factor. A score of 5 indicates the parameter has a high degree of importance, while the score of 1 indicates the least degree of importance. The respondentsratethesefactorsinanonlinesurveythrough Google form. The mediums of contacts were, Email, LinkedIn,WhatsApp(Personal&Groups)andIn person.
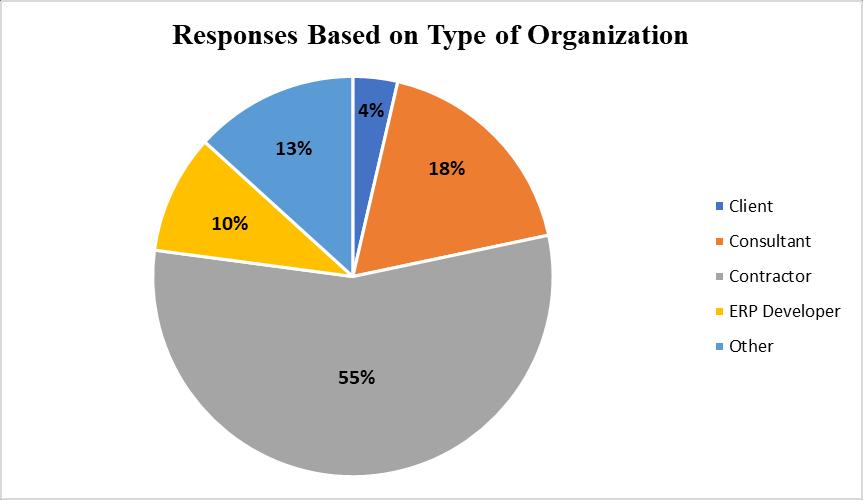
Two of the very standard methods were used to analyze the data which was collected from the questionnaire survey. The analysis is divided into two major parts, basic analysis and advance analysis. Basic analysis consists of analysis based on the rating and its relevance with the indirect variables like, Type of Organization, Experience andQualification.Theadvanceanalysisconsistsofanalysis through RII method and Factor Analysis with Principal Component. Chart -2:
system. Acceptance of new technology is commonly faced hurdle in any organization because it comes with challenges and behavioral changes in each individual, it also depends on the age of the individual. Followed by availability of the data; in any ERP system availability of the data is the major concern and authenticity of the data analsoadrivingfactor.4thrankedfactorisOrganization’s growth plan, where future plan of the organization to growandexpand.
Initial Training Time: ERP software requires training to each user and while implementing the ERP software it is really time consuming to train the users of the organizationanditusuallytakesalotoftimewhichmakes it a very important viability parameter. Organization structure and its complexity has good impact on the decision making. If the organization’s structure is lengthy and complex and individuals of the organization has multiple roles it will be really hard to implement the ERP systemintheorganization.
Table -5: RankingBasedonMeanValue

Amongall threecategories meanvalueofERPSoftware is the highest hence, importance of ERP software, its user friendliness, its initial training time, its suitability, flexibility in terms of customization are all important parametersbeforeinvestingandimplementinginanyERP System.
Based on the response “Very Important” each viability parameters are rated and ranked. Below table show ranking of viability parameters based on the response “VeryImportant”.
Table 6: RankingBasedontheImportanceRating(Very Important)
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
User friendlinessofanERPSoftwareisranked1as54out of 83 respondents found it very important as a viability parameter. Availability of the data is again a driving viability parameter as authentic and timely data availabilityisreallyimportantin anyERPsystemtocarry out the required information. 49 out of 83 also found Acceptance of New Technology is a very important viability parameter as new technology introduces new changes and challenges and to some extent it also increases the efforts of each individual in terms of data entry. To operate and maintain the ERP system good IT Infrastructure is required. 43 out of 83 respondents find IT Infrastructure of the Organization a Very Important viability parameter. 42 out of 83 respondents also found Initial Training Time is also a Very Important viability Parameter.
Data Analysis was carried out with two methods where initial method of data analysis was done through RII Method.Thismethodisusedtodefinerelativeimportance ofvarious factors,caused anddelayeffect. This methodis onlyusedwhenthesamplesarecollectedonaLikertscale. Answers provided by the responder is then transformed into relative importance indices which is carried out with thehelpoftheequationshownbelow.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
A statistical method is factor analysis. It's a term used to characterize the variation between observable and associated variables. Factors are a type of unobservable variable that has a lesser number of possibilities. It's a data compression technique.It'sa methodforcondensing abignumberofvariablesintoasmallnumberofvariables based on their importance. Factors are small sets of variables that have been minimized. The goal is to keep theoriginalvariables'natureandcharacterwhilereducing theirnumbertomakemultivariateanalysiseasier.Afactor is a set of variables that are connected in a linear way. Thesearethevariablesthataccountforthemajorityofthe variations in the original data set. The variables are statistically unrelated. This aids in the resolution of the multi collinearity issue. Here KMO & Bartlett’s Test is carried out to determine the appropriateness of factor analysis.
Cumulative loading variance is 68.879% which is above 60%,thatmeanstheidentifiedfactorwhichweregrouped in 9 components has 68.870% of impact based on the analysiswhichisgood.
Code NameofViability Parameter Component 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
O1 WorkProcess Reengineering 0.107 0.474 0.154 0.244 0.208 0.039 0.267 0.132 0.521
O2 Implementation PriorityofERP 0.046 0.047 0.048 0.096 0.020 0.065 0.035 0.132 0.882
O3 ITInfrastructureof theOrganization 0.056 0.111 0.099 0.024 0.330 0.067 0.056 0.797 0.028
O4 AvailabilityofData 0.175 0.457 0.050 0.300 0.049 0.266 0.074 0.575 0.017
O5 FinancialHealthof Organization 0.279 0.154 0.274 0.050 0.171 0.232 0.174 0.553 0.218
O6 DataVolumeofthe Organization 0.278 0.031 0.027 0.695 0.198 0.023 0.038 0.113 0.026
O7 GeographicSpread oftheOrganization 0.743 0.001 0.029 0.248 0.034 0.093 0.028 0.054 0.123
O8 Organization Strength 0.763 0.017 0.122 0.054 0.054 0.030 0.287 0.020 0.101
O9 Organization Structure 0.314 0.531 0.137 0.395 0.285 0.320 0.078 0.040 0.006
O10 TypeofProjects 0.651 0.318 0.288 0.030 0.203 0.141 0.248 0.115 0.107
O11 Organization's GrowthPlan 0.064 0.408 0.004 0.013 0.536 0.009 0.106 0.020 0.288
O12 NumberofProjects 0.567 0.341 0.373 0.056 0.027 0.241 0.045 0.016 0.064
O13 AcceptanceofNew Technology 0.012 0.703 0.057 0.273 0.157 0.081 0.304 0.144 0.003
The result indicates the Kaiser Meyer Olkin measure of sampling adequacy is 0.625 which is above 0.5 hence the measureisadequate.Bartlett’sTestofsignificanceshould havevalueofsignificancelessthan0.05,hereits0.01,that means that the variables are correlated high enough to carryoutfactoranalysis.

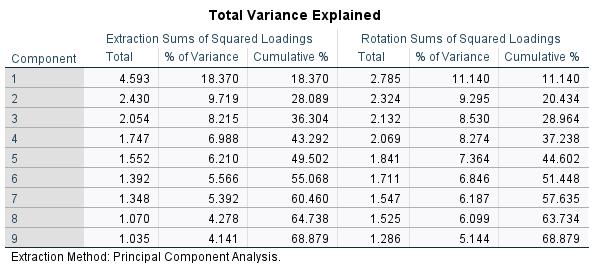
A total of 9 components are extracted from the factor analysis through SPSS Software. These 9 components consist of viability parameters groups. Each component contains 1 group of viability parameters and each parameter in single components has equal impact on the results.Hereintotalvariancetableexplainsthevarianceis dividedinto25viabilityparameters.Pleasenotethatall9 components have eigen values more than 1 which means all these components has greater impact on the outcome.
O14 ParticipantRoles 0.218 0.681 0.125 0.238 0.150 0.171 0.103 0.074 0.045
S1 Customization 0.611 0.105 0.164 0.129 0.041 0.190 0.121 0.286 0.035
S2 InitialTraining Time 0.066 0.099 0.494 0.519 0.037 0.069 0.150 0.153 0.130
S3 Software Competency 0.120 0.131 0.060 0.081 0.028 0.032 0.783 0.000 0.029
S4 Userfriendlinessof ERP 0.078 0.026 0.043 0.414 0.540 0.099 0.071 0.021 0.088
S5 AvailableERP Softwareinthe Market 0.314 0.257 0.266 0.171 0.409 0.051 0.551 0.038 0.065
S6
Applicabilityof AvailableERP Softwareinthe Markettothe Organization
0.113 0.011 0.038 0.054 0.824 0.120 0.042 0.162 0.008
C1 InitialCost 0.106 0.017 0.578 0.303 0.105 0.387 0.290 0.027 0.082
C2 RunningCost 0.009 0.237 0.559 0.390 0.022 0.329 0.322 0.147 0.071
C3 MaintenanceCost 0.072 0.060 0.852 0.071 0.018 0.063 0.063 0.028 0.031
C4 Development/ CustomizationCost 0.017 0.080 0.138 0.064 0.051 0.840 0.097 0.070 0.026
C5 TrainingCost 0.158 0.234 0.064 0.565 0.032 0.560 0.070 0.006 0.127
TherotatedcomponentmatrixasshownintheTable 13 above was used with 0.7 as a cut off point. In the SEM (Structural Equation Modeling) approach, as a rule of thumb, 0.7 or higher factor loading represents that the factor extracts sufficient variance from that variable for factor loading for grouping the factors. Factor Loading is basically the correlation coefficient for the variable and factor. It shows the variance explained by the variable on thatparticularfactor.
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) is a multivariate statistical analysis technique that is used to analyze structuralrelationships.Thistechniqueisthecombination offactoranalysisandmultipleregressionanalysis,anditis
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
used to analyze the structural relationship between measured variables and latent constructs. In the table below, nine factors were formed having linear variables intoeachfactor.Onefactor,factorno.4whichdidnothave any variable crossing the cut off point. The variables in eachfactorwerelistedasbelow:
Component ViabilityParameters
LoadingVariance
Component1 GeographicSpreadoftheOrganization 11.14%
OrganizationStrength
Component2 AcceptanceofNewTechnology 9.30%
Component3 MaintenanceCost 8.53%
Component4 Didnotmeetthecutoffpoint(0.7) 8.27%
Component5 ApplicabilityofAvailableERPSoftwarein theMarkettotheOrganization 7.36%
Component6 Development/CustomizationCost 6.85%
Component7 SoftwareCompetency 6.19%
Component8 ITInfrastructureoftheOrganization 6.10%
Component9 ImplementationPriorityofERP 5.14%
CumulativeLoadingVariance 68.88%
Dataanalysiswerecarriedoutusingboth RIIandFactor Analysis methods to identify the most important viability parameters impacting the decision making of investing and implementing ERP software in construction organizations.
Based on the analysis done through RII method, the important viability parameters are User friendliness of ERPSoftware,AcceptanceofNewTechnology,Availability ofData,InitialTrainingTime,Organization'sGrowthPlan, Work Process Reengineering, Implementation Priority of ERP, IT Infrastructure of the Organization, Customization andSoftwareCompetency,respectively.
Whereas the factor analysis is an entirely different approachthanRIImethod.AspertheRotatedComponent Matrix, the most important viability parameters are Geographic Spread of the Organization, Organization Strength, Acceptance of New Technology, Maintenance Cost,ApplicabilityofAvailableERPSoftwareintheMarket to the Organization, Development/Customization Cost, Software Competency, IT Infrastructure of the Organization and Implementation Priority of ERP, respectively.
Understanding the need of the organization before investing & implementing an ERP software is a vital step for a successful adaption of the new technology. This research aimed to identify such viability parameters by conductingqualitativeandquantitativestudybyinvolving variousindustryexperts.
Based on the reviewed literatures & interviews, a total of 25viabilityparameterswereidentified.Theseparameters werethenratedonLikertscalebasedontheirimportance by 83 experienced professionals through a questionnaire survey.TheresponseswereanalyzedusingRIIandFactor analysismethod.
User friendliness of ERP Software, Acceptance of New Technology, Availability of Data, Initial Training Time, Organization's Growth Plan, Work Process Reengineering, ERP Implementation Priority, IT Infrastructure of the Organization, Customization, and Software Competency are the important viability parameters, according to the analysisdoneusingtheRIImethod.Factoranalysis,onthe other hand, is a completely different technique than the RII method. Geographic Spread of the Organization, Organization Strength, Acceptance of New Technology, MaintenanceCost,ApplicabilityofAvailableERPSoftware in the Market to the Organization, Development/Customization Cost, Software Competency, IT Infrastructure of the Organization, and ERP Implementation Priority are the most important viability parameters,accordingtotheRotatedComponentMatrix.
Identifiedviabilityparametersdiffersforboththeanalysis methodsasRIIisanabsolutemethodand focused on one variable at a time, whereas factor analysis being the relative method focusing on group of factors simultaneously. Factor analysis provides group of factors cumulatively impact the decision making for the viability ofanyERPsoftwareinconstructionorganization.
These significant viability parameters can be used while making crucial decisions about testing the viability of any ERPsoftwareinconstructionorganizations.
The current research work identified important viability parameters using RII and Factor analysis method where results were found to be different for both. Future research work can focus on identifying the most suitable method. Apart from this, the research is limited to identifyingviabilityparametersanditsimportancerating. The future research work may focus on conducting a live casestudytovalidatetheanalysisresults.Thisresearchis centered on the Indian environment and conditions; however,similarfactorscanberesearchedglobally.
[1] Sharma, D., Sharma, A., & Shekhawat, N. (2012). The Best Performance Practices in Project Management of SAP ERP Accomplishment. International Journal of Information and ElectronicsEngineering,2(5).
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[2]A.Panayiotou,N.,P.Gayialis,S.,&K.Katimertzoglou,P. (2015). A business process modeling enabled requirements engineering framework for ERP implementation. Business Process Management Journal,21(3).
[3] W. Halpin,, D., & Shi, J. (2003). Enterprise Resource Planning for Construction Business Management. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management,129(2).
[4] Mallikarjuna, S., Azhar, S., Ahmad, I., & M. Ahmed, S. (2003). Implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems in the Construction Industry.ConstructionResearchCongress.
[5] Singh, R., & Arora, S. (2016). ERP Implementation in Indian Prespective: Critical Issues. International JournalofManagementandAppliedScience
[6] XU, X. H., WANG, L., & ZENG, Y. R. (2017). An Integrated Model to Select AN ERP System For Small and Medium Sized Enterprise Under Uncertainty. Technological and Economic DevelopmentofEconomy,23(1).
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
