International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Chand Babu1 , Umesh Goyal2
1Research Scholar, Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, FCEM, Faridabad, Haryana, India
2Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, FCEM, Faridabad, Haryana, India ***
Abstract As the name of indicate, Big Data means huge collection of data that can’t be proceed without traditional computing approach. To Compute the data it’s need tool and technique. Having data bigger consequently requires different approaches, techniques, tools & architectures to manage the data in a better way. Big data technologies provide more accurate analysis which help in decision making. To manage and process huge volume of structured semi structured and unstructured data you would require an infrastructure that can secure, privacy and protect the data. There are various tools and technologies in the market from different vendors IBM, Amazon, Microsoft, etc., to handle big data. The major challenges with big data are Capturing data, Storing data, Searching, Curation, Sharing, Transfer, Analysis, Presentation, To fulfill the above challenges, organizations normally take the help of enterprise servers.
diverse methodologies (technologies/methods) based on certain parameters to chalk out which of them is best possible (optimal) or what else needs to be done, to have an optimal solution. As the data is being generated and accumulated at a very high velocity with diversity in addition to it, processing has become a tedious task. Whereas the fact remains that, by processing of this data we will uncover gold from these huge mountains but if it’s left untreated it will become Everest’s of garbage. Since the foundation of term Big Data many methodologies or technologies are present which are being used to process these data mountains. These technologies have their own area of interest due to which there are obvious drawbacks and mode of operations between them. After analysis we found that common to them is low agility and the Data management. Once the data Management issue of Cloud technology is resolved it will prove a boon and cure to the other drawbacks of cloud implementation for processing of Big Data. It makes as sure that Cloud technology with better Data Management will be implemented in every phase of life from governments to business.
Key Words: BigData,Bigdatatoolsandmethods.
Everysecondseeshugeamountsofexponentiallygrowing data,beinggenerated,acquired,stored,andanalysed.The revolution in the generation of massive data amounts comes along with the Internet usage which allows data exchangebetweenvariouselectronicdevicesandhumans. Inthisregard,thefollowingfieldsarementioned:mobile
value:
phones,socialmedia,imagingtechnologiestodeterminea medical diagnosis, etc. The volume of available data continues to grow and it grows in different formats. Conversely,thepriceofdatastoragecontinuestofallwhich results in data storing being more reachable. Although creatingdatastorageisgettingcheaperandmoreavailable, theincreasingvolumeofdataindifferentformatsandfrom diversesourcescreatesnewproblemswithregardstodata processing,includinginitsanalysisandinintegratingBig Dataintobusinessdecisionmakingprocesses.
In order to store and process Big Data, new technologies are evolving to address these problems. To deal with these challenges, there is a need for a new approach such as building a scalable and elastic architecture. The purpose of this study is to explore the domainoftheBigDataproblem;particularly,tocreatean overviewamongfreeavailablerepositoriesofbiomedical Big Data and to discover appropriate technologies and methods along with theirlimitations and use cases tobe appliedoverthechosendata.Sincethedata,technologies andmethodsarechosen,atestingscenarioiscreatedand deployedoverthisdata.
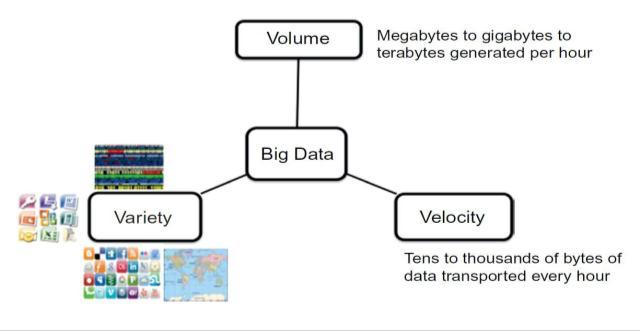
There are many definitions for Big Data. Somebody defines Big Data as data that is quite complicated rather than “easy going” and it is hard to acquire, store, manipulateandprocessit,duetothefactitis“big”.Another one,whichisfrequentlymentionediscalled“3V”described bythreewords(Volume,VarietyandVelocity).Thesetwo definitions above and others are cited and mentioned below:
“BigDatacanbedefinedasvolumesofdataavailablein varying degrees of complexity, generated at different velocitiesandvaryingdegreesofambiguity,thatcannotbe processed using traditional technologies, processing methods, algorithms, or any commercial off the shelf solutions.”[4]
Arguesthattherearethreeattributesstandingoutas definingBigDatacharacteristics:
“Huge Volume of data: Rather than thousands or millions of rows, Big Data can be billions of rows and millionsofcolumns.”
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
“Complexity of data types and structures: BigData reflects the variety of new data sources, formats and structures, including digital traces being left on the web andotherdigitalrepositoriesforsubsequentanalysis.”
“Speed of new data creation and growth: BigDatacan describehighvelocitydata,withrapiddataingestionand nearrealtimeanalysis.”
The most known and used definition is originally describedas“3V”(seeFigure).Sincethenvariousauthors havecomeupwithotherdefinitionsanddescriptions.The combinationofthesethoughtsisdescribedbelow:
1.1.1 Volume the volume is increasing exponentially. Therearemanysourcesgeneratingahugeamount ofdatawhichtakesalongtimetoprocess.
1.1.2 Variety Big Data is not always structured data. Actually, most parts of it are unstructured. In addition, it comes in different formats due to the variety of data sources; dealing with the data formatsvariety,increasesthecomplexityofstoring andanalysing.
1.1.3 Velocity describes the rate of data change. Data volume changes dynamically. There is a need to manipulate with data in real time. However, for some tasks in fields such as business and health care,itcanbesomehowdemanding.
1.1.4 Value itisoftenarguedthatthevalueisthemost critical part of Big Data. Most of projects have to produce appropriate results, unless the company/institutioncanwastefinancialsources.It costsalotofmoneytoimplementITinfrastructure systems to store data. If the subject which stores dataisnotabletoextractdatavalue,itisdesirableto consider if the intention of the investment to an implementation of IT infrastructure systems was suitable.
1.1.5 Veracity – notalldatahastobeperfectlygood,butit doesneedtobealmostgoodtogiverelevantsight. Upon considering the errors rate and the data incompleteness,ambiguityinthedatasetisdesirable and even necessary for further data analysis. Credibilityisanotheraspectofdataveracitywhichis worthmentioning.
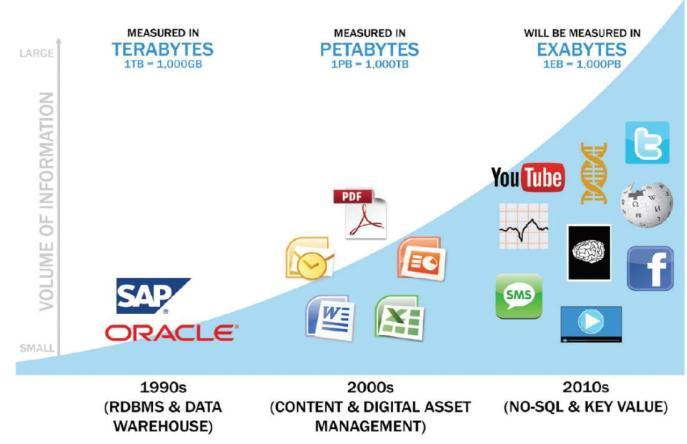
To better understand what Big Data is and where it comes from, it is crucial to first understand some past historyof data storage, repositories and tools tomanage them.AsshowninFigure,therehasbeenahugeincreaseof datavolumeduringthelastthreedecades.
Aswecanseeinthedecadeof1990sthedatavolume was measured in terabytes. Relation databases and data warehouses representing structured data in rows and columnswerethetypicaltechnologiestostoreandmanage enterpriseinformation.
Subsequent decade data started dealing with different kindsofdatasourcesdrivenbyproductivityandpublishing toolssuchascontentmanagedrepositoriesandnetworked attached storage systems. Consequently, the data volume wasstartedbeingmeasuredinpetabytes.
Typically,thefirsttypeisboundupwiththespreadof machines digitalisation which is related to sensors integration, the connectivity increase, and devices recording sounds, images or videos and to machines communicationbetweeneachother.Particularly,devices such as cameras recording videos, cell phones collecting
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
geospatialdata,machinesinproductionlinesofindustrial systems, are exchanging important information while processingtheiractivities.Moreexamplesarementioned below:
Medical information machines recording EEG (Electroencephalography), heartbeats, genomic sequencing
Multimedia photos and videos uploaded on the Internet,
Mobile devices provide geospatial data (location, gyroscope), as well as metadata about phone calls, messages, internet usage and data gathered by mobile applications,
Other devices Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) providing inside location realised by Wi Fi, identification of stored products or material by BAR, QR (Quick Response) codes or RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chips. There is a presence of many other technologies such as navigation systems, seismic processing,etc.
Itisappropriatetoconsiderothersourcesgeneratedby activitiesontheInternetingeneral.Letusimaginehavinga setofserverswhichrunwebpagesthatcanbedetermined for retail business. The servers can collect records of all activities of the websites’ customers, users, transactions, applicationsandserversownactivityandbehaviour.For instance,therearelogswhichcanbecollectedof[2]
Inrelationtothedefinitions,thereasonwhythere isintensecomplexityinprocessingBigDataisshown. Alongwith theBigData therealso exists ambiguity, viscosityandvirality(seeFigure).
Ambiguity emerges when there is less or no metadata in BigData.Anexamplecanbea graphor somethingthatusuallyneedsadescription.LettersM andFinagraphcandepictgendersortheycaneven representMondayandFriday.
Viscosity this term is often used to describe the latencytimeinthedatarelativetotheeventofbeing described.
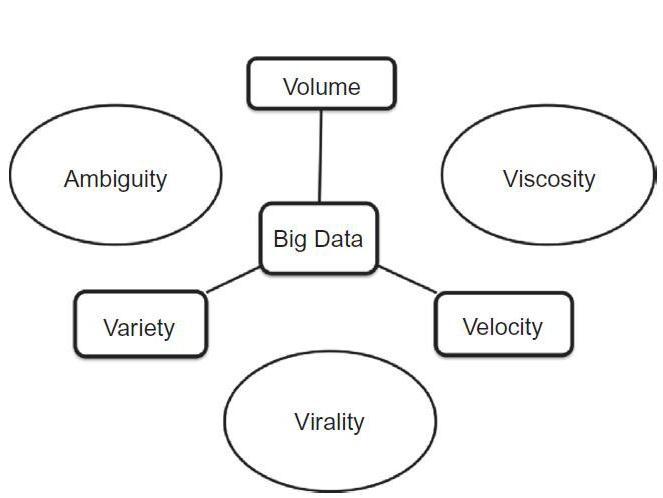
Virality describes how quickly data is shared throughout a network among people who are connected. The measurement result is the rate of spreadofdataintime.Forinstance,Twittercanbea relevantexamplewhenthetweetsarespreadingfrom the first (root one) original tweet among people throughoutthenetwork.
Figure3:BigDatacharacteristicsderivedfrom‘3V’ definition
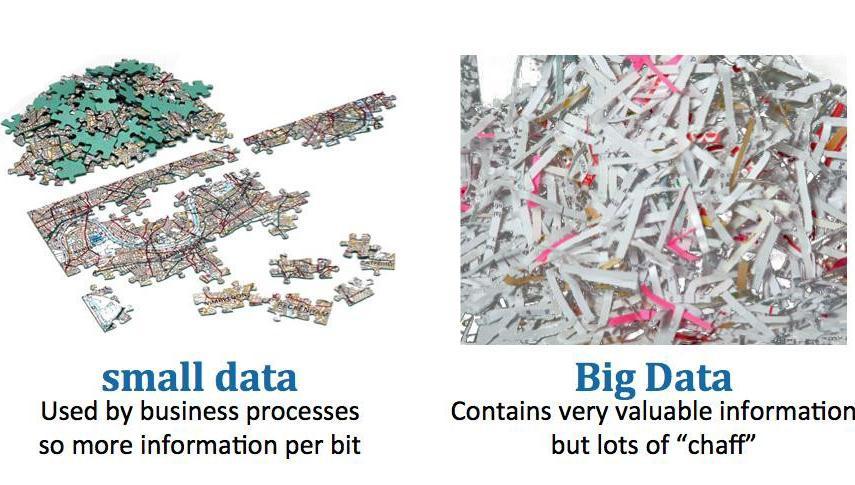
BigDataisnotsimplysmalldatathathasgrown.There aremoreaspectsthatdefinedifferences betweenthese two categories. A subset of the aspects can be derived fromthe“3V”definitiondescribedaboveandtheothers arearguedby[6](seeTable1).
Usuallydesignedto answeraspecific questionortoachievea particulargoal
LOCATION
Typically,smalldatais containedwithinone institution,oftenon onecomputeroreven inonefile
Nobodyknowswhatthe exactoutputoftheprojectis. Usuallyitisdesignedwitha goalinmind,butthegoalis flexible
Bigdataarelocated throughoutthecompany networkorthroughoutthe Internet.Typically,itiskept ontomultipleservers,which canbeeverywhere
Ordinarilycontains highlystructureddata. Commonly,thedata domainisrestrictedto asingledisciplineorits sub sequence.The typicalformsofits storageareuniform recordsor spreadsheets
Hastobecapableof absorbingunstructureddata suchastextdocuments, images,soundsandphysical objects.Thesubjectof disciplinescanvary throughoutthedata
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Inmanycases,thedata ispreparedbyitsown userforhisown purposes
The data is kept for a limited time (academic life). After few years whenthedataprojectis finished, the data is usuallydiscarded
Typically,thedatais measuredusingone experimentalprotocol
Theprojectsare typicallyrepeatable.If thereisaproblemwith thedataquality,the entireprojectcanbe repeated
Projectcostsare limited.Theinstitution canusuallyrecover fromsmalldatafailure
Datapointsare identifiedbyrowsand columnswithina spreadsheetora database.Itenablesto addressaparticular datapoint unambiguously
Inmostcases,allthe dataintheprojectcan beanalysedtogether
Thedataiscollectedfrom manydifferentsources. Peoplewhothedatacomes fromarerarelythesame peoplewhousethedata
ABigDataprojecttypically containsdatawhichhasto bestoredinperpetuity
to avoid the incompleteness together with the other attributesofBigData(seeFigure).
Manyvarioustypesofdata aremeasuredinmany differentelectronicformats
Replicationoftheprojectis seldomfeasible.Thereis nothingmorethanoptimism thatthebadqualitydatais foundandflagged,rather thanbereplacedbyabetter one
Bigdataprojectscanbe reallyexpensive.AfailedBig Dataprojectcanleadto bankruptcy
Itismoredifficulttoaccess thedata.Theorganisation andthecontextcanbe inscrutable.Accesstothe dataisachievedbyaspecial techniquereferredtoas introspection
Bigdataistypicallyanalysed inincrementalsteps.Itis extracted,reviewed, reduced,normalised, transformed,visualised, interpretedandreanalysed withdifferentmethods
Additionally,inrelationtothevolumeofBigDataandits incompleteness,corruptionandambiguitythatarecaused by its large volume, the Small Data is generally more organised,structuredanditisalsopossibleanddesirable
AlthoughBigDataprinciplesandapproachesarefrequently discussed, there are not many technologies which are convenienttodealwithsuchdata.Duetothedefinitionsof thevolumeandthevelocity,thetoolswhicharesupposed todealwithBigDatahavetoofferadistributedcomputing approach. There are the following approaches: multiple data and single program, and single data and multiple program.
Inthefirstcase,thereisasingleprogram,whichisrun onmorenodes,whereallnodesprocessdifferentdata.On thecontrary,thesecondcaseisconsideredtohaveonlyone dataset,whichisprocessedbyaprogramdividedonsmall tasksthatarerunondifferentnodesinparallel.
Due to it, there are tools that try toabstract from the physicaldistributionasmuchaspossible.SincetheApache companyreleaseditsnewimplementationofMapReduce paradigm, a whole ecosystem called Hadoop has started evolving. The MapReduce paradigm offers the means to break a large task into smallertasks, runin parallel,and consolidatetheoutputsoftheindividualtasksintothefinal output.Thesignificantecosystemexpansionwascausedby usingsimpleprogrammingmodelstoprocesslargedatasets acrossclustersaswellaswasamplifiedbythefactthatthe wholesolutionhasstartedasopensourcesoftware.
Hadoop as the first publicly known and discussed technologyofBigDataprocessinghasbeenusedasthebase ofopensourceandcommercialextensions.Inotherwords, mostofthesetofBigDatatoolsarebasedontheHadoop solution.
Thesesolutionsoffermethodsandapproachestoload, pre process,store,queryandanalysedata.
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
InthefollowingsubchapterstheHadoopecosystemwill be described along with other technologies which have been evolved from it or others which are using its technologies.
As mentioned earlier, the MapReduce paradigm providesthemeanstobreakalargetaskintosmallertasks, runthetasksinparallelandconsolidatetheoutputsofthe individualtasksintothefinaloutput.MapReduceconsists oftwobasicparts:amapstepandareducestep.[1]
• Map performsanoperationtoapieceofdatawhich generatessomeintermediateoutput.
• Reduce gathers the intermediate outputs from the map steps, processes it and provides the collected final output.
The main advantage of MapReduce is the workload distribution over a cluster of computers (to run tasks in parallel). Particularly, MapReduce provides a technique, which allows the processing of one portion of the input whichcanberunindependentlyoftheotherinputparts.In otherwords,theworkloadcanbeeasilydistributedover thecluster.
The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is a file system which provides the capability to distribute data acrossaclustertotakeadvantageoftheparallelprocessing ofMapReduce.
HDFSisdesignedtorunoncommonlow costhardware. Consequently,itmeansthereisnoneedtodeployitonlyon supercomputers.Although,itisimplementedinJava,HDFS canbedeployedonawiderangeofmachinesapartfroma node, which is dedicated to manage namespace services (seeArchitecturebelow).
HDFS has a master/slave architecture as shown in Figure.Itconsistsofasinglemasterserverwhichmanages thefilesystemnamespaceandmanagesaccesstofilesby clients and a single NameNode. In addition, there are DataNodeswhichareusuallyboundupwithanodeinthe cluster. These DataNodes manage storage within their nodesthattheyrunon.AfileinHDFSissplitintooneor more blocks that are stored by a set of DataNodes. Moreover,theyareresponsibleforservingreadandwrite requests from the file system clients and performing blocks’ creations, deletions and replications which are requestedbyNameNode.Wheneverthereisarequestfor an operation as opening, closing, renaming of a file or a
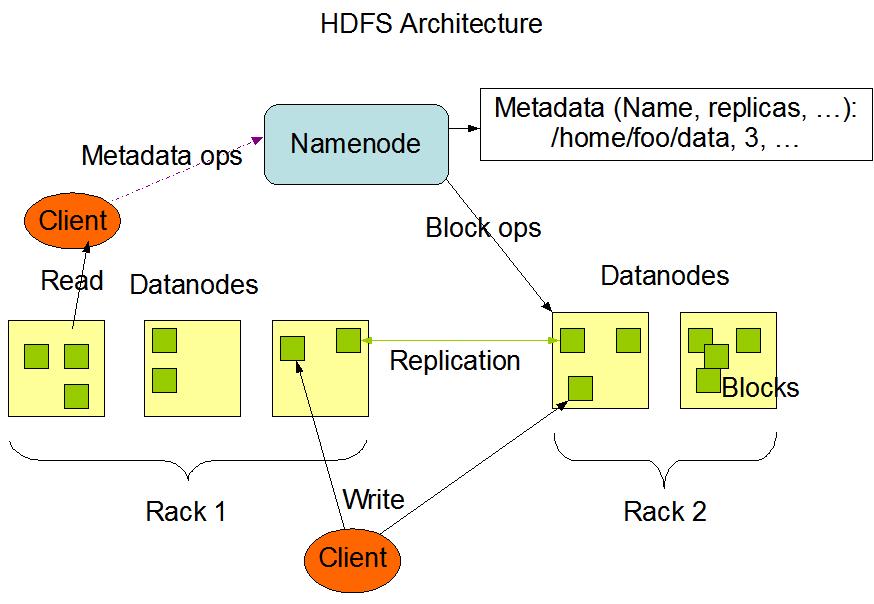
folder, it is handled by the NameNode. Additionally, it is alsoinchargeoftheblocksmappingtoDataNodes.[11]
HDFSbreaksfilestypicallyinto64MBblocksandstores the blocks throughout the cluster. Whenever possible, HDFSattemptstostorefileblocksondifferentmachinesto allow the map step to operate on each block of a file in parallel. If a file size is 200 MB, the file is stored in four blocks:three64MBblocksandone8MBblock.Ifthefileis smaller than 64 MB, the block represents the whole file. HDFSisdeterminedtodealwithlargefilessuchasfilesof up to 1 GB. Files with a size smaller than 64 MB are considered as small sizes which are not efficiently maintainedbyHDFS.
Atypical MapReduceprogramin Java iscomposedof threeclasses:thedriver,mapperandreducer.
Thedriver containsthejobdetailsanditsconfigurations suchasinputfilelocations,detailsforassigningtheinput filetothemaptask,thenamesofthemapperandreducer Javaclassesanditalsocontainsthelocationofthereducer taskoutput.
Themapper representsthelogictobeprocessedoneach data block relatedtothedefinedinputfilesin the driver code.
The reducer represents the logic of the gathering of intermediateresultsfromthemappers.
Asmentionedabove,Hadoopevolutioncomesallalong with open source and commercial extensions to make Apache Hadoop easier to use and provide additional functionalityandfeatures.Thissubchapterexaminesthe
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
following Hadoop related Apache projects which all togetherformtheHadoopEcosystem.
ItisanopensourceBigDataprocessingframeworkfor performing data analytics on a distributed computing cluster such as Hadoop. Spark supports in memory processing to increase speed and data process over MapReduce. It is discussed as a more powerful analysis replacement of Hadoop. Spark is deployed on the top of existingHadoopclusterwhichenablesSparktoaccessdata viaHDFS.Additionally,itcanalsoprocessstructureddata viaHiveandstreamdatafromHDFS.[13]
Nowadays, there are two databases where the data is beingstoredwithinthevirtualmachinewhichhas100GB allocated. As result of the data analysis, without external stimulithedatavolumewillprobablyreachthelevelof1TB in approximately the year 2032. The current data storage system is sufficient for next following years. Most of PostgreSQLdatabasesizeisoccupiedbybinaryfiles,which cannot be queries. With this in mind, there is no need to exchange this RDBMS for other more scalable technology suchasadistributedfilesystem.Moreover,themetadataof experimentsarecurrentlybeingstoredinaNoSQLdatabase whereitcanbequeriedinamoreefficientway.
As said before, the whole process of analysis is performed either within Matlab along with EEGLAB or by applicationswritteninJava.
Mostoftechnologiesprovidingascalablesolution fordealingwithBigDataarebasedonHadoop.Duetothe factthatHadoopisimplementedinJava,itprovidessuitable APIwhichenableswritingdistributedJavaprogramsbased onMapReduceparadigm.
Hadoop is built on its distributed file system HDFS. HDFS solutionisnotefficientwhenthefilesystemissupposedto dealwithahugeamountofsmallfileswhereasmallfileis thefilewhichissmalleroralmostequaltothesizeofblock (default 64 MB). With this in mind, we can state that this solutioncouldnotbeefficientinthedomainoftheEEG/ERP becausethesizeofthemostofthedatafilesislessthan27 MBin63%ofcases.Moreover,theremainingrest37%of otherfileshavedifferentsizes,itmeans,whichmeans,thatif ittheywerestoredinHDFS,mostof thefiles wouldnotfill HDFSblocksappropriatelyduetoitsinnerfragmentation.
Although Hadoop provides some approaches how to deal withsmallfiles,neitherofthemisconvenienttobeapplied inthiscontext.Theprocessofthedatagenerationcannotbe changed because the generated files are associated with particularexperiments.Similarly,thesameproblemwould occur if we used the method of batch file consolidation. Sequenced files technique, seems to be better, but if we considerthatwewouldliketorunamethodoverthedataset ofoneexperiment,itwouldnotbeefficienteitherbecause onemapoperationisrunoveronedatablock,wherethefiles of one dataset could be stored anywhere. In general, the solutions based on Hadoop are not appropriate Big Data technology for the domain of the department’s EEG/ERP project. Moreover, there is no need to store data in a distributedfilesystem.
Matlab provides a number of techniques and approachestohandleBigData.Althoughtherearetoolssuch asmemorymappedvariables,discvariablesanddatastore whichenabletodealwithproblemsthatoccurwhenalarge data has to be loaded into a computer’s memory at once, theyareconsideredasamethodwhichprovidesascalable solution.ThisfunctionalityisenabledbyParallelComputing Toolbox along with Distributed Computing Server that provideascalabledistributedsolution.Thissolutionenables torunmethodsfordatapre processingandanalysingovera scalableMatlabcluster.
A Matlab cluster seems to be the best solution for the application of a Big Data approach within the EEG/ERP project. Moreover, the researchers are familiar with this environment, which contains many available methods for data pre processing and analysis either _rogrammed as Matlabscriptsbytheresearchersorasfunctionsprovided by EEGLAB plugin which is widely used among this community.
ThecharacteristicsofBigDatawerefirstdescribedin2001, whenLaney[4]identifiedthreekeyattributesoflargedata amounts:highvariety,volume,andvelocity.Todate,these attributes have become the defining characteristics of Big Data. However, contemporary authors and business specialists enlarged these defining characteristics with furtheraspectssuchasdedicatedstorage,management,and analysistechniques[8],[9],[10].Furtheramendmentstothe definitionincludetheadditionofafourthV,veracity,byIBM [11], emphasizing the aspect of data quality. Taking these differentextensionsoftheoriginaldefinitionintoaccount, we define Big Data as a phenomenon characterized by an ongoingincreaseinvolume,variety,velocity,andveracityof
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
datathatrequiresadvancedtechniquesandtechnologiesto capture,store,distribute,manage,andanalyzethesedata.
Mark Beyer,DouglasLaneyPublishedon21June2012"Big data"warrantsinnovativeprocessingsolutionsforavariety ofnewandexistingdatatoproviderealbusinessbenefits. But processing large volumes or wide varieties of data remainsmerelyatechnologicalsolutionunlessitistiedto businessgoalsandobjectives.
Ming Ke, Yuxin Shi publishedonSeptember17,2014“Big Data, Big Change: In the Financial Management” In recent years, "Big Data" hasattracted increasing attention. It has already proved its importance and value in several areas, suchasaerospaceresearch,biomedicine,andsoon.In"Big Data"era,financialworkwhichisdominatedbytransaction, businessrecord,businessaccountingandpredictionsmay spring to life. This paper makes an analysis about what changethat"BigData"bringstoAccountingDataProcessing, Comprehensive Budget Management, and Management Accountingthroughaffectingtheidea,function,mode,and methodoffinancialmanagement.Thenthepaperstatesthe challenges that "Big Data" brings to enterprise aiming to illustrate that only through fostering strengths and circumventing weaknesses can an enterprise remain invinciblein"BigData"era.
Aicha Ben Salem, Faouzi Boufares, Sebastiao Correia published on April 2014 “Semantic Recognition of a Data StructureinBig Data”Infact,goodgovernancedataallows improvedinteractionsbetweenemployeesofoneormore organizations. Data quality represents a great challenge becausethecostofnon qualitycanbeveryhigh.Therefore theuseofdataqualitybecomesanabsolutenecessitywithin anorganization.ToimprovethedataqualityinaBig Data source,ourpurposeistoaddsemanticstodataandhelpuser to recognize the Big Data schema. The originality of this approach lies in the semantic aspect it offers. It detects issuesindataandproposesadataschemabyapplyingase manticdataprofiling
Each second sees a huge amount of data being generated eitherbyhumancollaborationorbymachineswhichareall aroundus.TheAgeofBigDatahascomeandthereisaneed toaddressthechallengeswhichcomealongwithit.
Consequently,theproblemofBigDataiswidelydiscussed; manybooksandjournalshavebeenpublishedtoaddressits challenges,definitionsandrecommendationsonhowtodeal with it. Moreover, the terms such as privacy, security and ethicalproblemsarealsoconsidered.
Although Big Data is a frequently discussed topic in theoreticalmanners,thereisdeficiencyinpublicationsand sourcesdedicatedtoitspracticalusage.Nevertheless,there
are some evolving technologies such as Apache Hadoop alongwithitsecosystem.Thistechnologyisconsideredas thefirstopen sourceandwidelyusedBigDatatechnology, building upon a distributed filesystem and an implementationofMapReduceparadigm.Mostoftheother technologiesdedicatedtodeal withBigData arebasedon theHadoopsolution.AlthoughHadoopisoftendiscussedas auniversalBigDataplatform,itcannotaddressallBigData problems.Therearestillsomeavailablesolutionswhichare not based on Hadoop such as Matlab, a system which providesadifferentapproachofaclustercomputationrun overasharedfilesystem.
Furthermore,itisconvenienttomentionwhereBigDatais stored and how much it is available. Although there are many possibilities on how to access Big Data of various types,biomedicaldataismostlynotmuchavailable.Thereis only one publicly opened biomedical Big Data database whichisintendedtopreservegenomes.Ontheotherhand, duetoitsbigvolume,thereisconsiderablequalityvariety amongpublicationswherethedatabaseisdescribed.Other availabledatabasescannotcompetewiththevolumeofthe genomedatabase.However,theyarestillcharacterisedby some qualities which should be considered. (consider revisingsentencetomakeitclearer)Nevertheless,duetoits domain, availability, many publications and information withintheproject,thedatabaseoftheEEG/ERPprojectwas evaluatedasthemostsuitableone.
Depending on the EEG data characteristics, which were obtainedbythedeepdatabaseanalysis,Matlabsolutionwas evaluatedassuitabletechnologyforapplicationonEEGdata. Additionally,MatlabiswidelyusedwithintheEEGproject for the data processing and its programs can be deployed overaMatlabcluster.AlthoughtheComputerScienceand Engineering Department does not possess all required licences, there is the possibility to use the project Metacentrum where all licences are available along with countlesshardwareresources.
ToconfirmthataMatlabclusterisasolutionwhichcanbean asset for the EEG/ERP project, a model which allows the runningofaMatlabprogramovermultipledataonaMatlab cluster was created. The model was tested by performing two use case, where EEG signals were either divided on epochsorfilteredovertwoexperimentdatasets.Thistesting has shown that the model is functional and can be consideredasanassetfortheEEG/ERPproject.Additionally, a few recommendations are proposed on how the project canbeimprovedfurther.
[1] EMC Education Services. Data Science & Big Data Analytics. Indianapolis: JohnWiley&Sons,2015. 978 1 118 87613 8.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

[2] Splunk Inc. Machine Data. Splunk. [Online] Splunk Inc., 2005 2016. [Cited: March8, 2016.] http://www.splunk.com/en_us/resources/machin e data.html.
[3] Mayer-Schönberger, Viktor and Cukier, Kenneth. A Revolution That Will Transform How We Live, Work and Think. New York : Houghton MifflinHarcourt PublishingCompany,2013.978 0 544 00269 2.
[4] Krishnan, Krish. Data Warehousing in the Age of Big Data. San Francisco : Morgan Kaufmann Publishers,2013.9780124059207.
[5] Manyika, James and Chui, Michael. Big data: The next frontier for innovation, competition, and productivity. s.l.:McKinseyGlobalInstitute,2011. 978 0983179696.
[6] Berman, Jules J. Principles of Big Data. Boston : Elsevier, 2013. 9780124045767.
[7] Iafrate, Fernando and Front, Matter. From Big Data to Smart Data. Chap : John Wiley & Sons, 2015.
[8] Jagadish, H. V., Gehrke, Johannes and Labrinidis, Alexandros. Big Data and Its TechnicalChallenges. Communications of the ACM. Month, 2014, Vol. 57,7.
[9] Hurvitz, Judith, Kaufman, Marcia and Bowles, Adrian. Cognitive Computing and Big Data Analytics. Hoboken:JohnWiley&Sons,,2012. 978 1 118 89662 4.
[10] Minelli, Michael, Chambers, Michele and Dhiraj, Ambiga. Big Data, Big Analytics: Emerging Business Intelligence and Analytic Trends for Today's Businesses. s.l. : John Wiley & Sons, 2013.9781118562260.
[11] Borthakur, Dhruba. HDFS Architecture Guide. Hadoop.apache.org. [Online] The Apache Software Foundation, 8 4 2013. [Cited: 19 April 2016.] https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r1.2.1/hdfs_desig n.html#Data+Organization.
[12] The Apache Software Foundation. Hadoop. Hadoop. [Online] The Apache Software Foundation. [Cited: 15 May 2016.] http://hadoop.apache.org/.
[13] Spark. Spark. [Online] The Apache Software Foundation. [Cited: 22 May 2016.] http://spark.apache.org/.
[14] Zaharia, Matei; Chowdhury, Mosharaf; Das, Tahagata; Dave, Ankur; Ma, Justin; McCauley, Murphy; Franklin, Michael; Shenker, Scott; Stoica, Ion;. Resilient Distributed Datasets: A Fault Tolerant. Berkeley: University of CaliforniaatBerkeley,ElectricalEngineeringand ComputerSciences,2011.
[15] MathWorks. Makers of MATLAB and Simulink. Mathworks.com. [Online] [Cited:24April2016.] http://www.mathworks.com/.
[16] Holubová, Irena, a další. Big Data a NoSQL databaze.Praha:Grada,2015. 978 80 247 54666.
[17] Rigden, Daniel J. , et al. The 2016 database issue of Nucleic Acids Research. Nucleic Acids Research. 2016,,Vol.44,D1 D6.
[18] Pennisi, Elizabeth. 1000 Genomes Project Gives New Map of Genetic Diversity. Science. 2010,Vol.330,6004.
[19] Citizen Science: The Law and Ethics of Public Access to Medical Big Data. Hoffman, Sharona. 3, Cleveland : Case Western Reserve University Schoolof Law,2014,Vol.30.
[20] The GovLab. The Open Data Era in Health and Social Care. GOVLAB. [Online] May 2014. [Cited: 5 June 2016.] http://images.thegovlab.org/wordpress/wp content/uploads/2014/10/nhs full report 21.pdf.
[21] Bydžovský, Martin. Relational and non relational modeling for portal of electrophysiologicalexperiments. Pilsen:University of West Bohemia, Faculty of Applied Sciences, DepartmentofComputerScienceandEngineering, 2014.
[22] Řeřicha, Jan. Software tool for management of neuroinformatics data. Pilsen:UniversityofWest Bohemia,FacultyofAppliedSciences,Department of ComputerScienceandEngineering,2013.
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |