International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1 , Mohammad
Sabahat2
1Final Year, M. Arch, Faculty of Architecture and Planning, Dr. APJ AKTU, Lucknow, UP 2Associate Professor, Faculty of Architecture and Planning, Dr. APJ AKTU, Lucknow, UP ***
Abstract - Transport has a significant part to play in accelerating civic mobility. Civic mobility has different confines i.e. mobility for work, education, recreationandother requirements; mobility by the public, private and individualized modes; and mobility through facilitation of colorful transport structure and services handed by the authorities concerned. In this environment, thepart ofcolorful modes of public transport in a megacity is of consummate significance for achieving effective movement pattern but the same cannot be achieved without modal integration of public transport in confluence with non motorized modes similar as climbers, bikes and cycle cabs. Hence, there's a felt need to evolve underutilized road stations particularly for Lucknow megacity through proper integration of being modes and design of physical architectures. The study suggests colorful measures to reduce vulnerability of non motorized druggies. Due to perpetration of metro, commuters shifted from road grounded modes to metro due to lower traffic, accident free script, lower pollution, as well as savings in trip time and cost. Transport is a State Government subject andhencecreationof public transport and improvement of its modal share depends on policy opinions taken by originalauthorities andconcerned transport department. Hence, expression of road as original transportation capitals is vital step to promote such a conception in medium sized metropolises also. The study also deals with policy matters related to climbers, bikes, cyclecabs, substantiated modes, original terrain, setting up of devoted civic transport fund at megacity position and state position, institutional frame, public position data bank public civic transport information system, planning morals, strategies for enhancement of sustainable transport, art and aesthetics in conveyance, control of auto business, transport as a multi sectorial policy, etc. The operations of this study workshop are numerous. The results may be used to enhance the character and image of public transport as well as planning and design of similar original transportation capitals in medium sized metropolises.
Key Words: Commuters,Transit.
Inrecentdecades,'UrbanIndia'hasgrownmanifoldbothin spatialandDemographicterms.Globalization,liberalization, privatization,theinflowofforeigncapital,etc.haveprovided the impetus for urbanization which not only leads to the growthoftownsandcitiesbutincreasethenumberofurban
centersandurbanagglomerations.Asper2011Census,the urban population of the country was 377 million, which constitutes31.16%ofthetotalpopulationconcentratedin 7935 towns and cities. The 53 metropolitan cities (2011) accountedformorethanathirdofthetotalurbanpopulation (42.6%).
The development of old railway station infrastructure to meet trip demand needs a coordinated and integrated approach amongst several agencies involved with urban services and development at the city level, in the case of Lucknow. In this context, better urban transport infrastructureandservicesleadtocityefficiencyinwhich people and goods are transported at minimal investment andoperatingcost.
Trafficcongestioniswhenvehiclestravelmoreslowly,the excursiontakesamoredrawn outtime,andexpandedthe liningofthevehicles. They areotherwisecalled gridlocks. With reasonableness and higher procuring power, it has becomesimpleforatypicalindividualtopossessavehicle. ThenumberofvehiclesthathavesoldlastyearinIndiawas alothigherthanvehiclessold20yearsback.Howeverthis haspromptedanagreeablewayoflife,numerousworkers areimpactedbygridlockconsistentlywhichhasprompted the deficiency of important time and time is cash. At the pointwhenthequantityofvehiclessurpassesthelimitofthe street,gridlockhappens.InmostIndianurbancommunities gridlock is a significant issue. Individual episodes, for example,mishapsoutandaboutorstreetbeingshutdown orawfulstreetdesignsorabruptslowingdownofavehicle inasmoothprogressionofweightytrafficmightcausetraffic congestion.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
preparation,conveyanceandsubsidizingofallmethodsof public transportation including rail based frameworks, transports and standard travel. The institutional plans shouldbesetuptogiveconsistentmetropolitantravelthat thevoyagingmetropolitantenantsbothneedarecurrently requesting. This will make it conceivable to have a productiveUrbanIndia,withfastopenvehicleframeworks setup.
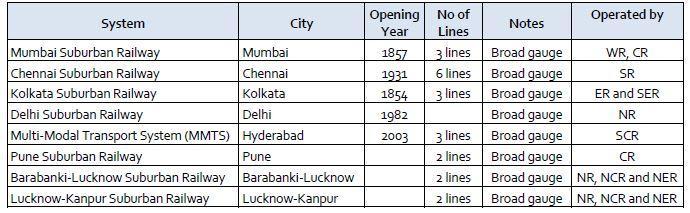
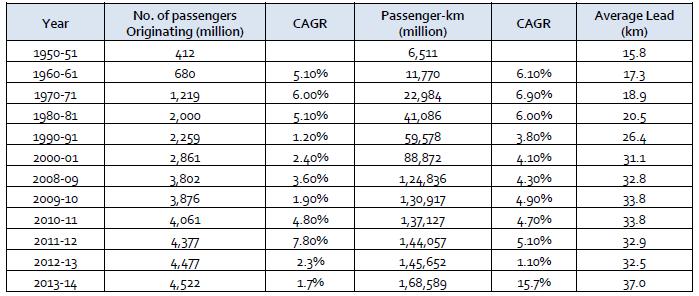
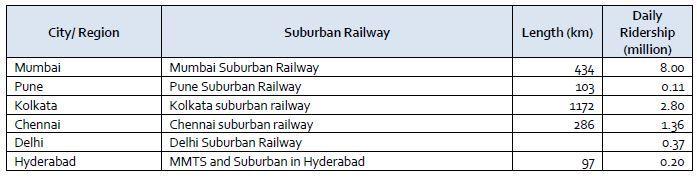
Sub urbantravelerdevelopmentinIndiahasbeenhighand reliable.
Source:SurveyofIndia(28thEdition2020)
Sub urbanrailframeworkassumesasignificantpartinthe public vehicle arrangement of a large number of India's significant urban areas. It is characterized as a rail administrationbetweenCentralBusinessDistrictandrural areas, a city or different areas that draw enormous quantitiesofindividualsconsistently.
Mumbai and Kolkata have rural train administration and haveseparatetrackslaidfortheactivitiesofruralrailroute organization. Chennai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Pune, and so on don't have committed rural tracks however share follows significant distance trains. Rural trains that handle suburbanite traffic are for the most part electric various units(EMUs).
In1950 51,thequantityoftravellersbenefitingofruralrail activities was 412 million, which developed in excess of eleven overlap to 4,552 million by 2013 14. As far as traveller km, be that as it may, it developed from 6,511 million of every 1950 51 to 1,68,589 million by 2013 14, whichismultipletimesincrementoveratimeofsixtyyears. Throughout a similar time, normal lead length multiplied from15.8kmto37.0km,becauseofthedevelopmentofthe urban communities. Interest for rural traveller travel in India has been developing at a yearly pace of 3.6% somewhereintherangeof2001and2014.Somewherein therangeof2011and2012thedevelopmentrateincreased byto7.8%andfurtherdiminishedto1.7%in2013 14.Asfar astravellerkm,theinteresthasshownadevelopmentpace of5.0%somewhereintherangeof2001and2014.
WiththisinterestcircumstancetheSuburbanframeworks mustassumeasignificantandcoordinatedpartinsatisfying the metropolitan travel need of individuals. The more moderate metropolitan locales across the world have thought that it is totally important to arrange the
Table 1: SuburbanRailPassengerGrowthinIndiaSource: IRYearBooks,IRAnnualReportandAccounts,IRFacts andFigures.
Metropolitanstructureandland useassumesasignificant partintheridershipofruralrailframework.Thisoutcomes in variety in use of rural rail routes across various urban communities. Every day ridership on rural rail route framework in Mumbai, Pune, Kolkata, Chennai, Delhi and Hyderabad.
Table 2: DailyRidershipinSuburbanRailwayofDifferent Cities(2013 14).
Source:IR YearBooks,IR Annual ReportandAccounts,IR FactsandFigures.
Table 3: Sub urbanrailsystemofvariouscities.
Source:IRYearBooks,IRAnnualReportandAccounts,IR FactsandFigures
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The multicultural province of Uttar Pradesh is at present home to 16% of India's complete populace. Uttar Pradesh assumesavitalpartinEconomicadvancementofIndiaasit besttheoutlineinmanycrowdedterritoryofIndia.Thestate additionally stands firm on top footing in high populace developmentrateinIndia.UttarPradeshhasseena quick developmentinitspopulaceoverthemostrecent50years. Everyyear,thestateaddsalargernumberofindividualsto its always expanding populace than some other state in India. From 1991 to 2001, Population of Uttar Pradesh expandedby26%,accordinglyshowingthatstatehasahigh populacedevelopmentrate.PopulacethicknessinUP(Uttar Pradesh) as of now remains at 828 individuals for every square kilometre, making it one of the thickly populated statesinIndia.Allahabadisthemostpopulatedlocaleinthe state. Kanpur and Lucknow are the two most populated urbanareasinUttarPradesh.Asofnow,thetwourbanareas arehometonorthof6millionindividualsinIndia.Thestate isseeingayearlydevelopmentof2%initspopulacewhichis exceptionallyhighwhencontrastedwithdifferentstatesin India. Starting at 2021, Population in territory of Uttar Pradeshisassessedtobe241millionindividuals.Thewhole stateaddressesthicklypopulatedregionswithahighrateof birth.Thenumberofinhabitantsinthestatewasassessedto be around 207 million out of 2013. This tremendous populace lives in 75 areas of Uttar Pradesh which are additionallypartitionedintovariousurbancommunitiesand towns.
Lucknow Division ofN.E.Railwaycameintoexistenceon 1st of May 1969 Lucknow Division’s working is on broad gauge&metregaugeboth.Thedivisionserves14districtsof northernandeasternpartsofUttarPradesh.Thisdivisionis enrichedwithmanyimportantriversviz.Gomti,Saryu,Rapti &Ganga,whichalsodefinetheculture&religionofthearea. Therearealsomanyplacesoftourist&religiousinterest.
Barabanki Lucknow and Lucknow Kanpur Barabanki Lucknow Suburban Railway (36 km) is a suburbanite rail administrationworkedbyNorthernRailways,NorthCentral Railway and North Eastern Railway to interface Lucknow withBarabanki.Theseadministrationsareforthemostpart runutilizingEMUandMEMUrakes.Inanycase,itdoesn't havedevotedrural trackshoweversharesthetrackswith significant distance trains. Locally it is called BL meaning BarabankiLucknow.
Lucknow Kanpur Suburban Railway (72 km) is a suburbanite rail administration worked by Northern Railways,NorthCentralRailwayandNorthEasternRailway tointerfaceauthoritativecapitalLucknowwiththemonetary andmoderncapitalKanpurofthestateUttarPradesh.These administrationsaregenerallyrunutilizingEMUandMEMU
rakes. In any case, it doesn't have devoted rural tracks howeversharesthetrackswithsignificantdistancetrains.It isaffectionatelycalledLCmeaningLucknowCawnpore(old nameofKanpur).
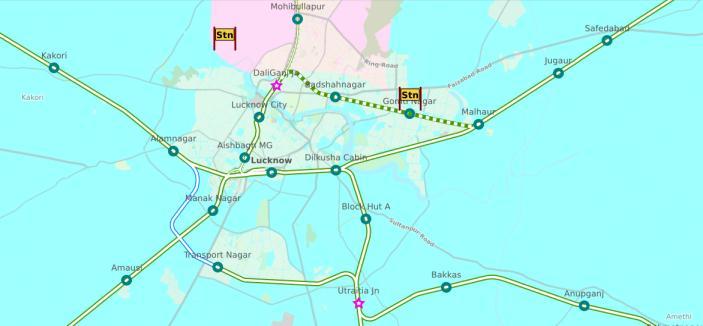
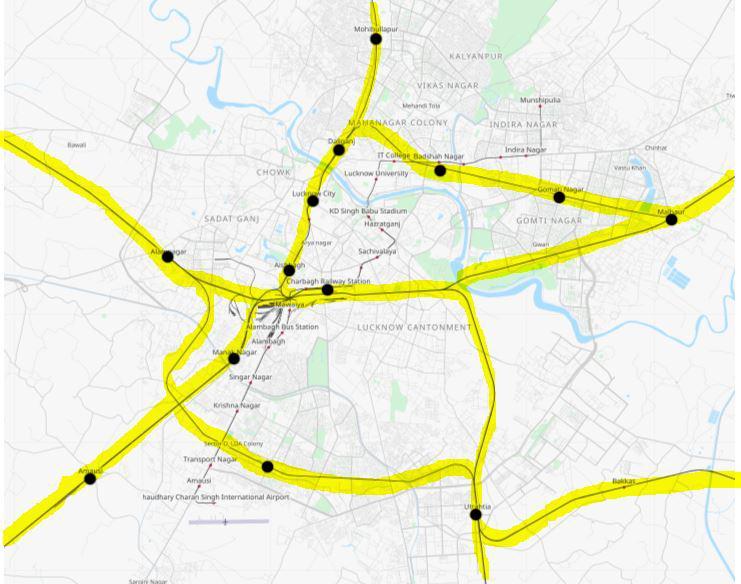
Fig 2: Lucknowcityrailwaynetwork
Source:https://indiarailinfo.com/station/map/lucknow charbagh nr lko/336
To share the load of traffic on roads through Railwaystationswhichhavelesstraffic.
SinceinLucknowroadcross sectionsarenotgood enough to cater the present and future needs of transportation.
Soitwilldecreasetheloadbyusingrailwaystations sincetheyareunderutilized.
Studywilldevelopfurthergroundsforothersuch cities.
The aim of the research use under utilized small railway stationsaslocaltransportationhubsinLucknow.
1.
Toidentifythelocalrailwaystationswithinthecity andtoanalyzetheamenities.
2. To study the traffic movement and railway movement within the city in order to understand the basic needs of the public and also how will railwaystationscaterslocalpublicmovementand tonotgetmixedwiththenormal railwaypublic.
3. To provide better and convenient intra transportationsystemusingrailwaystationswithin Lucknowcity
4. Tryreducingtheloadsonthecityroadsandtraffic.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
5. Alsotoimprovetheamenitiesandfacilities.
6. Toreducetheuseofprivatetransport.
Inordertoachievetheobjectivesstatedthestudy willincludethefollowingsequentialstages
To understand issues and potentials of transportation systems in Lucknow through literaturestudies.
Identifyingthesmallrailwaystationswhichcanbe convertedinthelocaltransportationhubs.
LiteratureandcasestudyofLocalrailwaystation.
Findinginferencesandgivingrecommendationsfor futureproposal.
Thisstudycanboosttheframeworktothebusiest modeoftransportsysteminIndia.
Itwillalsoprovidethebasicparameterstostartthe researchonprojectsimilartothis.
Thisstudywillhelpinreducingtrafficcongestion, pollution and will help the urban designers to understandthescienceofintegration,accessibility, circulationintheirdesigns.
This research will only be limited to railway stationswithinLucknow.
Transport is the lifeline of physical and socioeconomic growth ofanytown,city,stateandnation.Inurbanareas, efficientmodesoftransport,betterfacilitiesandpassenger friendlyservicesleadtocityefficiency.
Transport is the lifeline of physical and socioeconomic growthofanytown,city,stateandnation.Inurbanareas, efficientmodesoftransport,betterfacilitiesandpassenger friendlyservicesleadtocityefficiency.
Better planning, designing, operation and management of facilitiescombinetwoormoremodestoprovideutilityand service for safe, rapid, convenient and environmentally compatiblemovementofpeople.
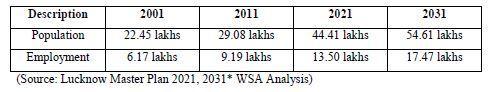
Withits2.2million(COI,2001Estimates)residents Lucknowhascurrentlyover3millionpopulationin urbanareas.Themasterplanhasenvisagedthata populationofabout3.2millionand4.0millionby years2011&2021respectively.
The rapid growth of the city and the associated urban region has accentuated the demand supply mismatch amidst the constrained transport infrastructure resulting in economic and social externalities.
The inadequate public transportation system in Lucknow is overwhelmed by upsurge of private automobiles.Privatevehiclesconstitute90percent oftotalvehiclesregisteredinLucknowCity.
The supply of city buses being only 6 per lakhs populationisinadequateforcity.Thebenchmarkis between 70 to 80 buses per lakhs residents in an urbanareainIndia.
Amovementrequestmodularandfuturebeginningobjective dependent on the projected populace and business were readyintheitemizedoverviewdirectedbytheDMRCforthe arrangement oftheDPRof Lucknowmetroproject.In the DPRwholereviewregionhasbeenisolatedinto127zones among them 119 are inner zones and the remaining are outer.
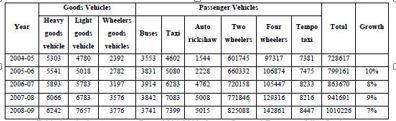
There were 1010226 registered vehicles in Lucknow till March2009withagrowthrateof7%infiscal2008 2009. Privatetransportationprovidersconstituteaverysizeable portionofpublictransport.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Consideringtheabovesurgingvolumeoftrafficinthecityan alternative transportation solution is required in order to fulfiltheneedsofLucknow.BesidesthisinoldLucknowarea thereafrequenttrafficjamcausedduetoheavytrafficand lowavailabilityofamasstransitsystem.
LucknowisthecapitalofthestateofUttarPradeshaswellas thesecondlargestcityinNorthIndia,afterNewDelhi.Asa cityknownforitsdeliciousfoodandculture,Lucknowisalso one of the transportation hubs in North India. It iswell connectedwithothermajorcitiesbyair,road,andrail.Here we will talk about small and less used railway stations of Lucknow.
Sourcehttps://www.openstreetmap.org/
Metropolitan regions are development magnets. Consequently, for advancement, consideration should be given to metropolitan regions. The urban communities in India have been becoming throughout the long term. The requirementsofnetworksadditionallybecomegreater.To addresstheseissuesthefoundationprerequisite,including thatofthevehicleframeworks,isadditionallygoingup,and is additionally expected to increment in future in every singlemetropolitanregion.
Sourcehttps://www.openstreetmap.org/
Ruralrail,metropolitanrail,suburbaniterail,orterritorial rail, assumes a significant part in the public vehicle arrangementofaconsiderablelotofIndia'ssignificanturban communities. Rural rail is characterized as a rail administration between focal business region and rural areas, a city or different areas that draw enormous quantities of individuals consistently. The trains offering suchtypes ofassistance are ordinarily named rural trains andaretheonesthatstopbyanystretchoftheimagination, orpracticallyall,ofthestationsalongacourse.InMumbai, thesearealludedas"neighborhoodtrains"or"localpeople". Thevastmajorityofthesewillmoreoftenthannotbevery sluggish.
RuralrailinIndiaworksonlinesimpartedtoothertraveler andcargotrains(likeLucknow KanpurSuburbanRailway) orablendofcommittedrurallinesandlinesforsignificant distancetrains(liketheMumbaiSuburbanRailway).
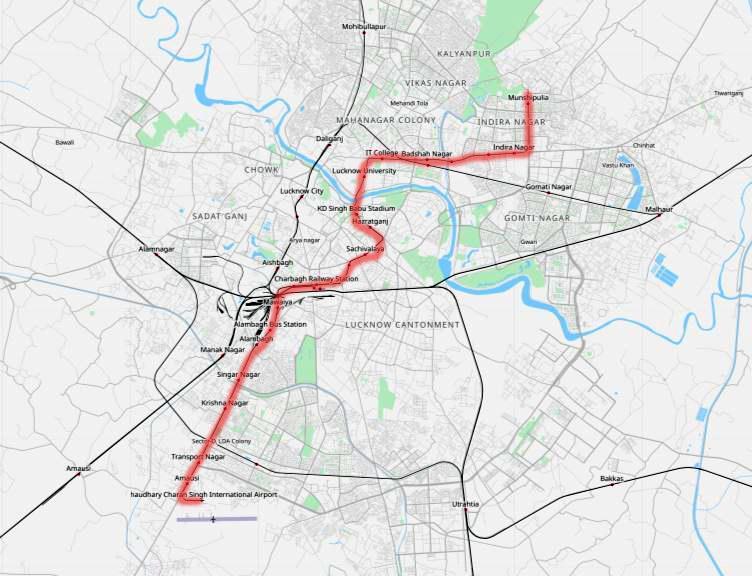
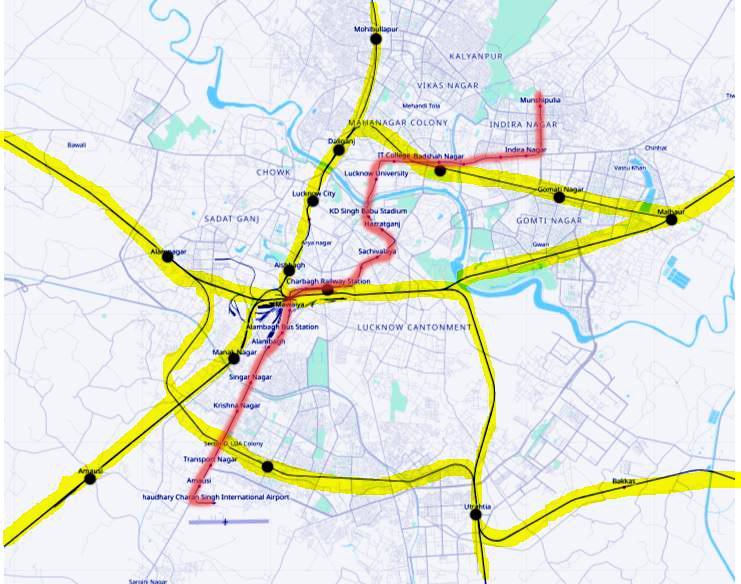
Fig 4: LucknowMetro
Sourcehttps://www.openstreetmap.org/
Itisnecessarytotakeappropriatestepsforoptimallyusing the carrying capacity of public transport modes and their properintegrationwithothermodes.Oflate,shareofpublic transportinDelhihasdeclinedto43%ascomparedtothe desirablefigureof70 75%.Now a days;thereisriseinthe
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
number of middle class population desirous of owning personalized modes. Further, automobile companies have also been coming up with new models of mini cars at affordable price. Hence, personalized vehicles have been increasing. It is important to synchronize metro, bus, personalized modes, etc. to evolve multi modal transport systemalongwithnon motorizedtransport.
Literature review and various research studies clearly indicatethattheimpactofatransithubismanifestedinthe changeinlandattributesof adjoiningareas.Inthecaseof transithub,itisthestationareawherethechangeismost prominent.Theparametersofstudyandbasisforanalysing thecontextinordertoassesstheimpactoftransitsystem thathavebeenselectedare:
Amplespaceforpedestrianmovement.
Designatedbuslanesandboulevards.
Physical barriers erected in street to direct pedestrianflow.
Extensive space should be provided for pick and dropforthepassengers.
Varietyinright of wayallocationparking/loading typesaredispersedratherthanconcentrated.
Heavyfocusonpedestriansanddesignatedurban parkandplazaspace.
Formalized vehicular and pedestrian zones with partitions,andthereshouldbecategorizedareasfor arangeofparkingoptions.
A Comprehensive, iconic way to find multitude of vehiculartypes.
Adaptive reuse of ‘leftover’ spaces and under performingasphaltassignaturepedestrianspaces.
Extensiveuseofone wayvehicularcirculation.
Maximizationofprimaryvehicularlooparoundthe station.
These parameters will be studied in response to the passengerdispersalatstationsselectedastheintentofthe studyistorelatepassengerattributeswithlandattributes associatedwithatransitstationandthecorridorbetween stations.
Afteranalyzingtheabovecasestudiesandliteraturestudies weconcludethattodevelopamultimodaltransithub,we needtoconcentrateonfollowingaspectssuchas:
There should be Integration of non motorized vehiclesininfrastructure.
A facility of proper Auto court to accommodate largevolumesandtypesofvehiculartraffic.
Designated loop for different modes of transport mustbeplanned.
Parkingspaceshouldbeenormous.
Extensivebicycleinfrastructure(widewell marked bike lanes and enormous formalized ‘bike beds’ parking)isrequired.
Notenoughinfrastructureattheserailwaystations tocaterlocalpublic.
Little used,footbridge.
Metroisdoesn’thaveawellspreadnetworktocater localpublicallaroundthecity.
Railwaystationsarenotorunder utilized.
In light of conversation in the previous passages, the accompanying methodologies for expansion of the travel limit might be proposed for the Sub Urban Rail route of Lucknow
Resuscitate:TheSub UrbanRailwayoughttoberestoredas amethodofmetropolitantransportationinDelhi.Itoughtto becreatedasanoptionincontrasttoRoadTransportandas aFeeder/ConnectortotheLucknowMetro.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1. Redesign:ThecurrentfoundationoftheSub Urban Railwayoughttoberedesignedforthereason.The stations ought to be made effectively available what's more noticeable. The arrangements of obstructionfreeclimateandprogrammedtagging ought to be consolidated for the accommodation andconsistentexchangeofthesuburbanites.
2. Expand:Therecurrenceofthetrainsonthecourse ought to be expanded to increase the conveying limit and decrease the hanging tight an ideal opportunityforthesuburbanites.
3. Improve:Initiativestoproducemindfulnessabout theSub UrbanRailwayoughttobetakentomakeit well known with suburbanites. As a significant numberofthestationsaresituatednearbylegacy and sporting destinations, social or the travel industryextraordinarytrainscouldlikewisework duringnon tophoursorduringoccasions.
Thereisneedtoseethesetransithubsinnewformbecause in present time and in future these are the destinations whichprovidepacetothepeoplelifeanddevelopments.
Inpresenttime70%ofpeopleprefertheirownvehiclefor travel,sothereisneedtoreducethesestatsforthatweneed todevelopthetransporthubinawaywherepeopleloveto go.
[1] Nisarkhan,augmentingtheTransitCapacityofDelhi byRenewaloftheSub Urban.
[2] Sunil Kumar Sharma and Anil Kumar A comparative studyofIndianandworldwiderailways.
[3] P C Sehgal and Teki Surayya Innovative strategic management:ThecaseofMumbaisuburbanRailway system
Easy to Use: The hub should be easily discernibletoresidentsandvisitors
Connected: The hub should connect as many transit systems and routes as possible within the shortest distance possible
Imbedded: The hub should offer convenient access to adjacent areas of CentreCity
Iconic: The hub should be iconic and memorable
Lucknow is evolving as a complex and complicated Mega City.ThesolutionstotheproblemsofLucknowhavetobe indigenousandinnovative.InthespecificcaseofitsUrban Transit,havinganetworkofmultiplemodeswithseamless integration will improve the carrying capacity and effectivenessofthesystem.Sub UrbanRailwayisamodeof transportationwhichmaybeemployedtofillthemodalgap existinginthepresentsystem.Theinfrastructureisalready inplaceandcanberenewedwithverylittleinvestmentto substantiallyaugmentthetransitcapacityofLucknow.
Therearenoprescribedguidelinesforthedevelopmentof local transportation hub in Lucknow, and because of the heavy traffic and footfall load there is need to redevelop thesetransithubsasacomponent,sothattheycanserveto maximumno.ofpeopleandprovidethemeasyaccessand betterfacilities.
[4] PrashantAgrawal1,Dr.KedarBhagwat2Comparative studyonMumbai’sSuburbanRailwayNetworkwith Tokyo, London and New York Suburban Railway Network.
[5] Shumank Srivastava, Ruchin Agrawal and Dr. A K NigamPersonalRapidTransit:AFeasibilityAnalysis InLucknow.
[6] Vinod Kumar Maurya and Dr. omprakash Netula Analysis of transportation system of trans gomti in Lucknow.
[7] Prof. Nishith Rai and Dr. Awadhesh Kumar Singh StrategicissuesininfrastructureDevelopment:acase studyoflucknowcity.
[8] Wetetsou Losou1, Dr Ravi Prakash Verma2, Mr Kekhriesituo Sachu3Study of Traffic Congestion in Lucknow.
[9] Institutional Development of the Suburban Rail System:SupporttoIndianRailwaysintheDesignand ImplementationoftheirSuburbanRailStrategy