International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1
2
Abstract In recent years, rise in sea level has been one of the predominated effects of global warming caused by humans since the past century. Some of the prime cities in the world are located along coastlines can disappear in the following years to come. An increase in the frequency of floods and storms has led the cities to shut down momentarily. Many flood resistant techniques have come up such as flood walls, high discharge sewers and IoT devices. Amphibious structures are capable building that is made to withstand floods by rising due to buoyancy in the occurrence of flood and resting in the absence of the same. In this paper, a 3 storey amphibious structure is designed taking inspiration from offshore and ship design principles. The objective of this paper is to provide a brief idea of designing amphibious structures.
Key Words: Global warming, flood, Amphibious structure, Float, Buoyancy
Global warming is an increase in the average earth temperaturecausedsincethestartoftheindustrialperiod mainly due to the burning of fossil fuels which intern produces greenhouse gases that include carbon dioxide, methane,troposphericozone,etc.Sunlightafterreachingthe earth, the surface absorbs a part of sunlight energy and reradiatesasinfraredwaves.Themoleculesofgreenhouse gasesinteractwiththewavelengthofinfraredwavesandre emitshalfoftheinfraredenergybacktoearthasheatand the rest to outer space. As a result, greenhouse gases contribute to the intensity of heat waves which can imbalance the hydrological cycle sending more or less precipitationtoanarea.Inaneventofadecreaseinrainfall resultsindroughtandanincreaseinrainfallfillsmorewater in the tributaries or water bodies than it can normally handlewhichresultsinflood.
Floodsarecategorizedinto3types,coastal,riverineand shallowflooding.Coastalfloodsarecausedbystormsthat occurintheseaoroceans,duetohighwindandairpressure they are pushed towards the shore and move inland resultinginfloods.Riverinefloodsarecausedbyexcessive rainfall that results in an overflow of a tributary to the adjacent land. Shallow flooding is caused by a lack of drainage due to continuous excessive rainfall and it is typicallyseeninurbanareas.
***
Floodsresultsinhugelossoflifeandinjurytopersonality. There is a requirement for proper shelter during an emergency. Amphibious structures are one such establishment that is made to live with the flood. Amphibious structures are made of lightweight materials andtheir baseis watertight suchthattheycanhandle the compressiveforceofthebuildingandbuoyantforcewhich makethemfloat.
1) Hydrostaticload(Fst): Linearlyvaryingpressureloadof floodwater depth. Floating structures will experience hydrostatic force but due to the gravitational force of the structure, the net hydrostatic force is zero. This force is applicableforfixedsubmergedstructuresandiscalculated by
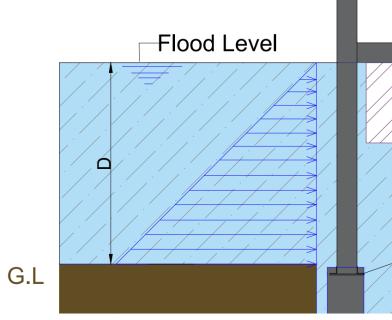
Fst=ρ.g.d [Eq1] ρ=Densityoffloodwater g=Gravity d=Floodwaterdepth
Fig 1:HydrodynamicLoad
2) HydrodynamicLoad(Fdyn):ForceImpactedonastructure duetomovingwaterVelocity
FDyn=Cd.ρ.V2.A/2 [Eq2]
Cd=DragCoefficient
ρ=Densityoffloodwater
V=Velocityoffloodwater A=Area
3)BuoyantForce(Fb):ItisanUpwardforceexertedonan objectimmersedinthefluid.Fbisequivalenttotheweightof thevolumeofwaterdisplacedbyanobject
Fb = Wt. of immersed object= Wt. the volume of water displaced.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

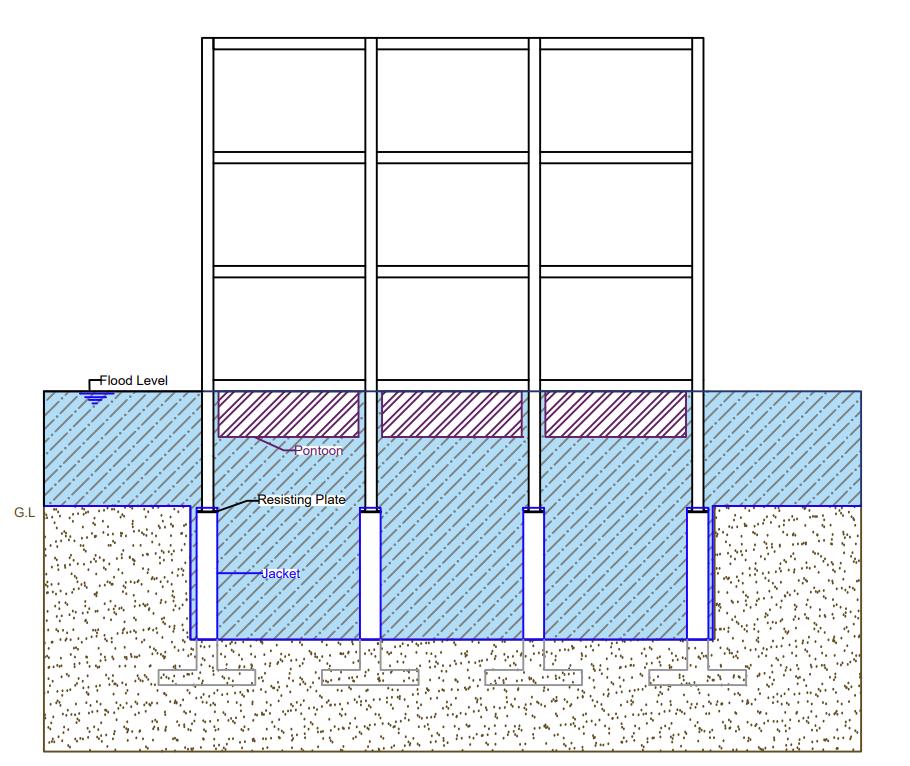
in Amphibious structures can be restricted by providing jackets. Jackets are designed for horizontal and rotational resultantforcesoffluid structureinteraction
Fig 2:Buoyantforceillustration
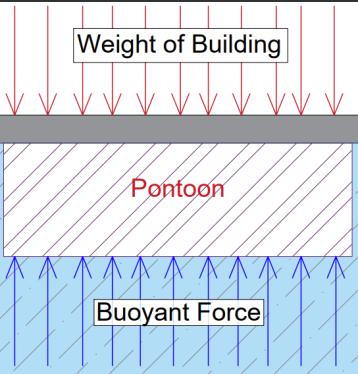
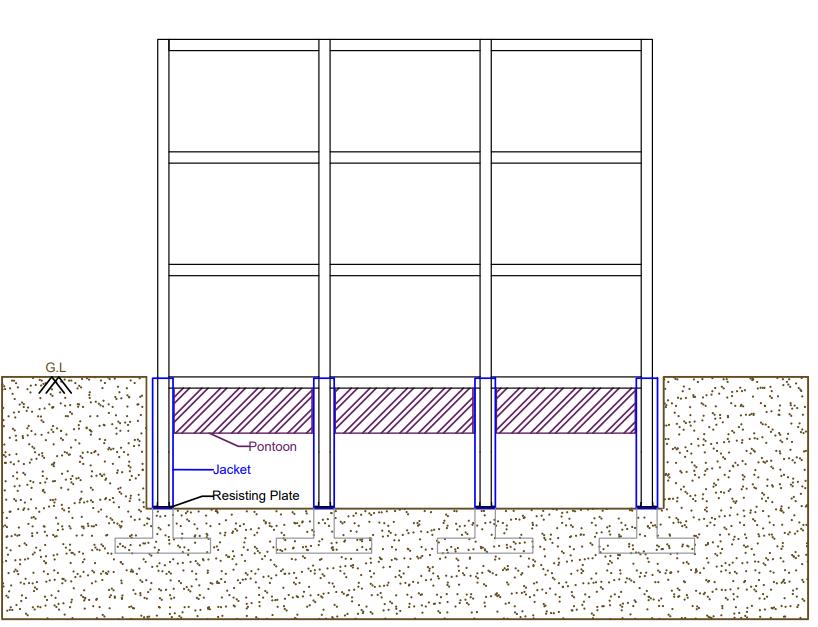
Fig 3:Floatingstability(R.KBansal)
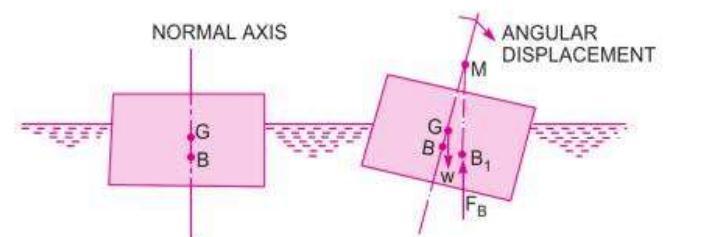
Fig 4:Amphibiousstructurepriortoflooding(nottoscale)
Pontoonsarecompressionmemberswhichundergotheload ofthebuildingaswellasbuoyancyforce.Thedepthofthe pontoonisdesignedbasedonvolumedisplaced,thevolume displacedistheequivalentweightofthestructure.
4) Stability: Floating bodies have a tendency to oscillate whenthebodyistiltedbyasmallangle.Freedomtooscillate
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Fig 5:Amphibiousstructureduringflooding(nottoscale)
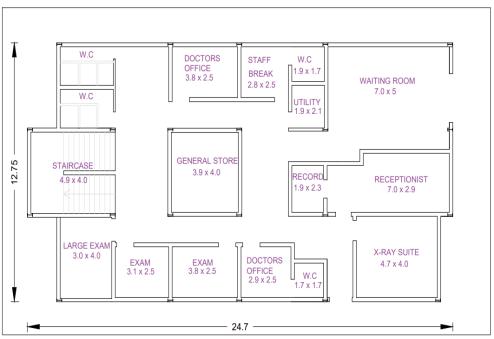
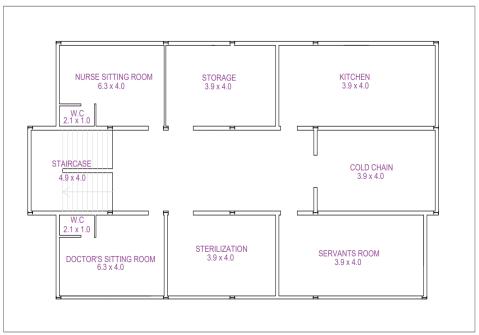
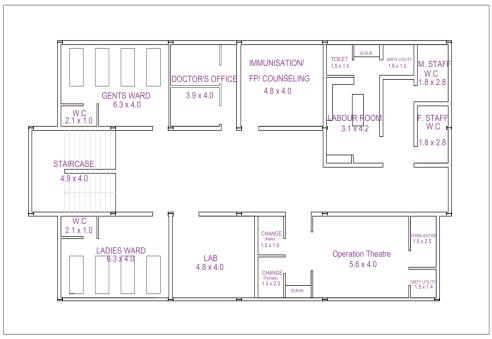
During an emergency such as floods and earthquakes, importantbuildingsplayamajorroleinservice.Someofthe top tier important buildings are hospitals, fire stations, governmentbuildings,telephoneexchange,etc.Inthispaper, aplanof3storeyprimaryhealthcarecentre ofplot24.7x 12.7mwitha storeyheightof3.2m isprepared asper the recommendationofIndianPublicHealthStandards[Fig.6]. Inordertomakethestructurelightinweight,steelframeis chosenasloadbearingmembers.Forwallsurfaces,loadsand properties of lightweight concrete sandwiched panels of density720kg/m3isconsidered.
The design of the building is divided into two main parts superstructure and substructure. The superstructure consistsofabuildingframework(columnsandbeams)that are modelled and evaluated by load combinations in staad.pro. The substructure consists of pontoons and resistingjacketswhichareconsideredasplatesandanalysed in staad.pro rather than Ansys/Abaqus due to of ease modificationandoptimization.Lastly,asimplifiedmodelofa pontoonwiththeappliedloadofthesuperstructureistested tofloatinAbaqus.
Fig 6:PlanlayoutofPrimaryHealthCareCentre
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Assumptionandloadparametersappliedforthestructureis listedbelow:
Consideringfloodwaterdepthas3mandfloodvelocity of0.5m/s.
Thehydrodynamicforcefrom[Eq2]is5kn/m
Liveloadof3kn/m2
Wallload2kn/m
EarthquakeCharacteristicasperIS1893
Zone 2
ResponseReductionFactor 3
Importancefactor 1.5
Soil Hard
Combinationsused
1.5DL+1.5LL+1.5WL
1.5DL+1.5EQX+1.5WL
1.5DL 1.5EQX+1.5WL
1.5DL+1.5EQZ+1.5WL
1.5DL 1.5EQZ+1.5WL
1.2DL+1.2LL+1.2EQX+1.2WL
1.2DL+1.2LL 1.2EQX+1.2WL
1.2DL+1.2LL 1.2EQZ+1.2WL
1.2DL+1.2LL+1.2EQZ+1.2WL
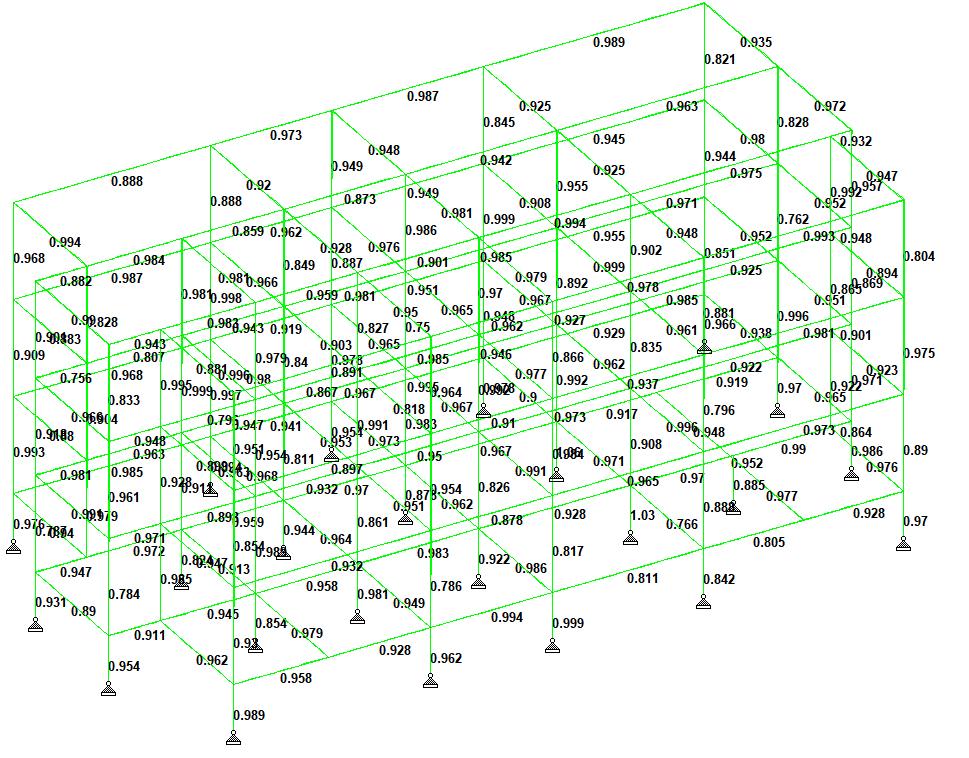
ISMB300memberwaschosenforallthemembersofthe building.ResultsareevaluatedbasedontheUtilizationratio. The utilization ratio is the ratio of allowable to maximum strength of members. A Member is failed if the utilization ratio is >1. All the values of members do not exceed the valueof1hencetheycansatisfactorilytakeuptheloads.Fig 7 is the utilization ratio of the structure that includes the deadloadofthepontoonandtheloadparameterslisted.
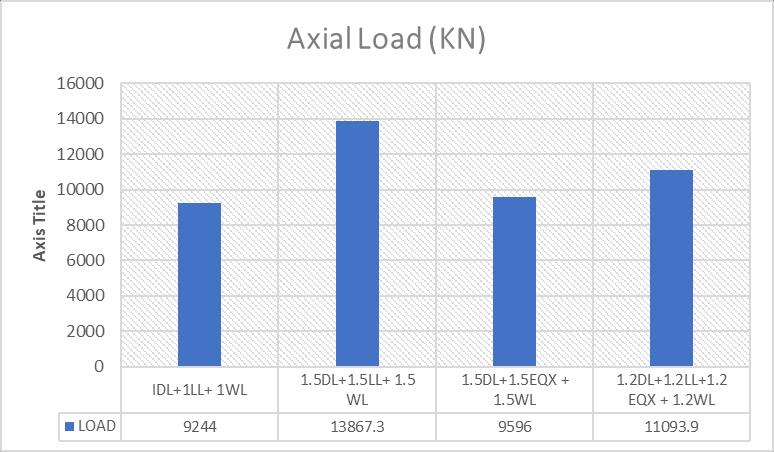
Chart 1:AxialloadofSuperstructuresubjectedto differentCombinations
Fig 7:Staad.proResults(Utilizationratio)
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
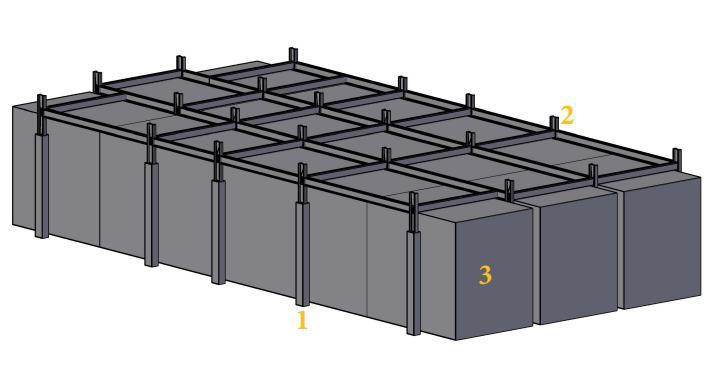
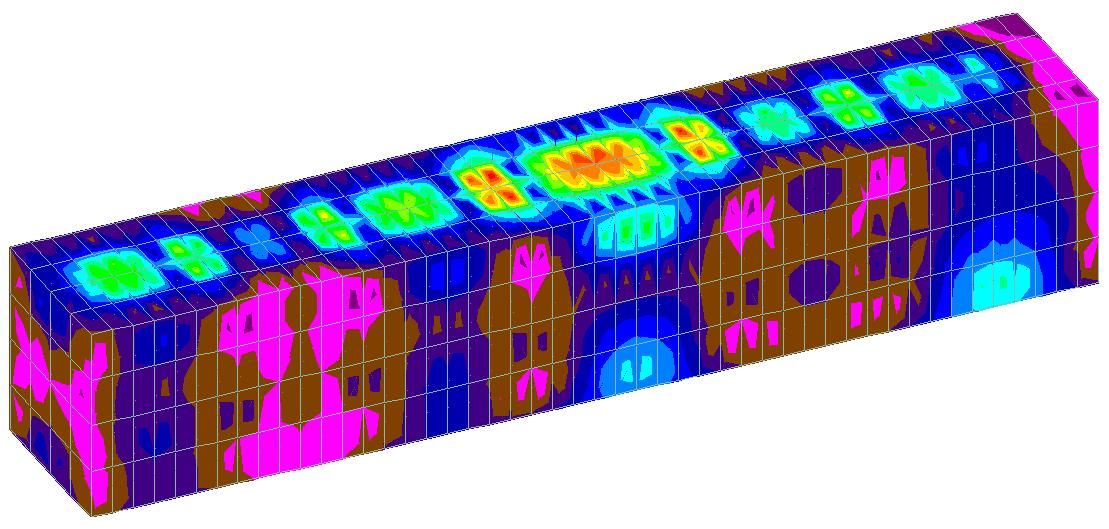
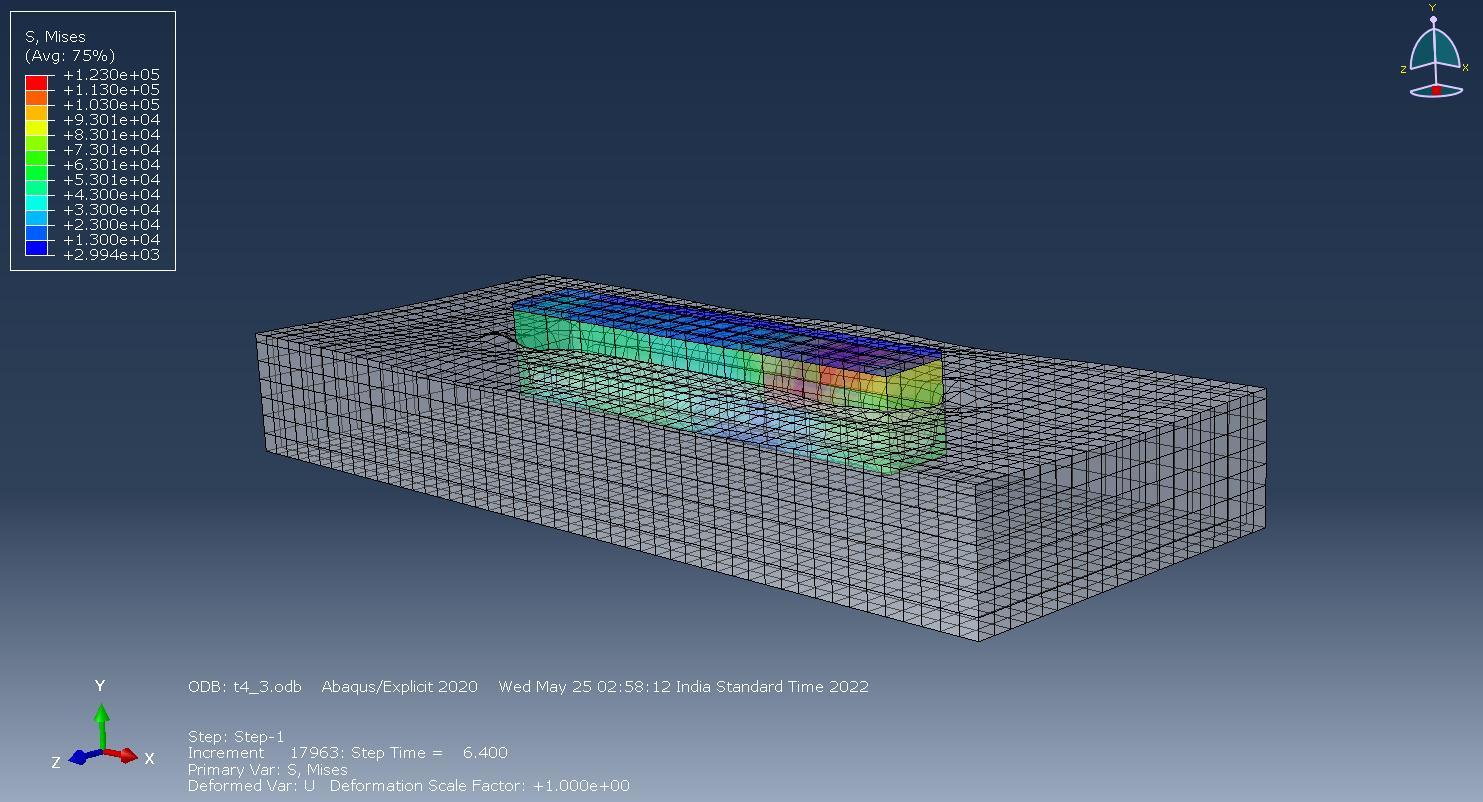
Fig 8:3DModelofsubstructure,1.Restingjacket,2.Superstructureframe,3.Pontoon(Deck1)
BothPontoonandJacketweredesignedinstaad.produeto its ease of modification. When a pontoon failed to achieve strengthrequirements,Itiseasytochangethethicknessor increase the dimensions of the model using Staad.pro Whereas in Ansys/Abaqus the model needed to be resketchedandmeshingwasahugeconcernsincetheauto meshwouldn’tworkevenwithtetmesh.Inordertomeshthe model,apartitionneededtobecreatedateveryend
Pontoonsarecompressionmemberswhichareprovidedto displacemorewatertomakethestructureafloat.3Pontoons namelydeck1,2,3areprovidedinthestructure i. PontoonDepth:Totalaxialloadondeck1is3080kn,
self weightofdeck1is890knandthetotalweightis3970kn Volume=Force/Densityofwater Volume=404.68m3
Depth=Volume/(BxD) TotalDepth=4.0m+0.6m(Freeboard)=4.6m
ii. StructuralProperties
Pontoonisdesignedtowithstandacompressiveforceof35 kn/m2.Thethicknessofthepontoonisoptimizedfor24mm. Steelpontoonisusedforthedesignwithyieldstrength,the ultimatestrengthof250N/mm2 and420n/mm2 Wherever thesuperstructurebeamswererun,verticalsupportswere giveninthepontoonstoreducestressForfloatingobjects, the hydrostatic forces are considered to be zero and hydrodynamicload [eq2]of 5kn/m isapplied
Fig 9: Max Absolute Stressdiagramofpontoonsubjectedtoloads(Deck1)
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)


e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
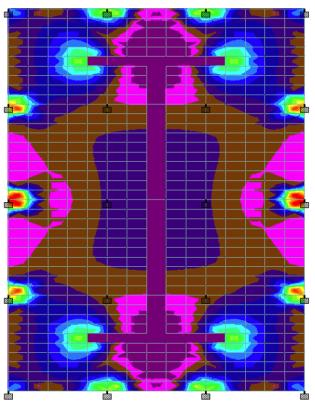
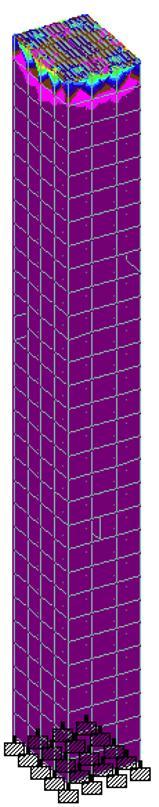
Thepurposeoftheresistingjacketistoguidethesuperstructurefrommovingawayandrestricttherotationalmovement ofthestructureduetodynamicforces.ThisJacketwillstaycompletelysubmergedincaseofaflood.Adrainplugmaybe requiredincaseofanysandparticlessettinginthebottom.Theresistingjacketisdesignedwithasteelplateofthicknessof 17mmandyieldstrength,theultimatestrengthof250N/mm2,420N/mm2.Case1(fig13)isastressdiagramofajacket subjectedtoaloadof160knatthe3mend.Case2(fig14)isastressdiagramcausedbytheupwardpressureofthebuilding tothetopjacketplate.
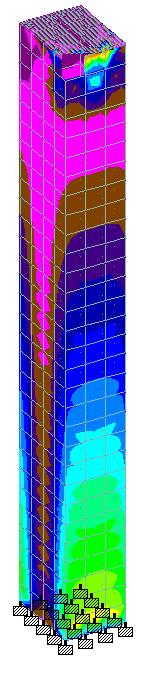
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The floatation test is performed in Abaqus to verify the manualcalculationsandstaad.proresults.The3Dgeometry wasmadeusingAutoCAD3dandimportedtoAbaqusasa ACISfiletype.Propertyandmaterialassignmentaremade similar to properties assigned in staad. General explicit solverwasusedtoperformtheanalysis.TheAssemblyofthe model consisted of a base eulerian part (water) with dimensions of 30x50x12m out of which 6m of height was consideredasvoid.Pontoon isplacedinthemiddleofthe model as dropped onto the eulerian part. An overlay materialwasusedtoapplytheloadofthestructureonthe pontoon.Fig11showsthesuccessfulfloatationofthemodel.
In the case of designing structures for dynamic wave conditions, fig12 shows the fluid structure interaction of pontoon. This figure is presented in a book written by Subrata k. Chakrabarti on ‘Handbook of Offshore Engineering‘,Volume1
Theamphibiousrequiresprecisestructuralcalculationfor thefunctioningofelements.Inthispaper,apontoonbased amphibious structure was simplified into finer parts and designed Loadonthepontoonwasconsideredbasedon a combinationof1DL+1LL+1WLandaddingafreeboarddepth of 0.6m for the design of depth. Considering other combinationswouldmakethestructureinefficient.
The pontoon depth required for 3 storey structure was foundtobe4.6mwhichisquiteuneconomical. Apontoon based structure must be constructed only if its required depthis2mi.e.asingle storeystructure.Forpontoondepth, greater than 2m providing a watertight sub storey would serve as an efficient design Further research needs to be conducted on making amphibious structures containing watertight sub storey, utilization of sustainable materials anddesignofflexibleMEPelements. Foradvanceddesign consideringwaveslam,debrisimpact,dynamicwaveimpact wouldmakethisstructurepreparedforanyfloodstocome.
The evolution of amphibious houses would serve a great purposeforsociety.Theapplicationscanextendtoatown planned amphibious system that can withstand 1 in 500 yearfloods
[1] Chakrabarti,Subrata.HandbookofOffshoreEngineering (1 volumeset).Elsevier,2005.
[2] Bansal, R. K. A textbook of fluid mechanics. Firewall Media,2005.
Fig 12:Shearandmomentofpontoonsubjectedtowave (Subratak.Chakrabarti
[3] FEMA 55 (2011) Coastal Construction Manual: PrinciplesandPracticesofPlanning,Siting,Designing, Constructing,andMaintainingResidentialBuildingsin Coastal Areas (4th edn). Washington, DC: Federal EmergencyManagementAgency.
[4] Wang,C.M.,andB.T.Wang."Largefloatingstructures." OceanEngineering&Oceanography3(2015).
[5] ElizabethC.English,MeiyiChen,RebeccaZarins,Poorna Patange & Jeana C. Wiser (2021) Building Resilience through Flood Risk Reduction: The Benefits of AmphibiousFoundationRetrofitstoHeritageStructures, International Journal of Architectural Heritage, 15:7, 976984,DOI:10.1080/15583058.2019.1695154
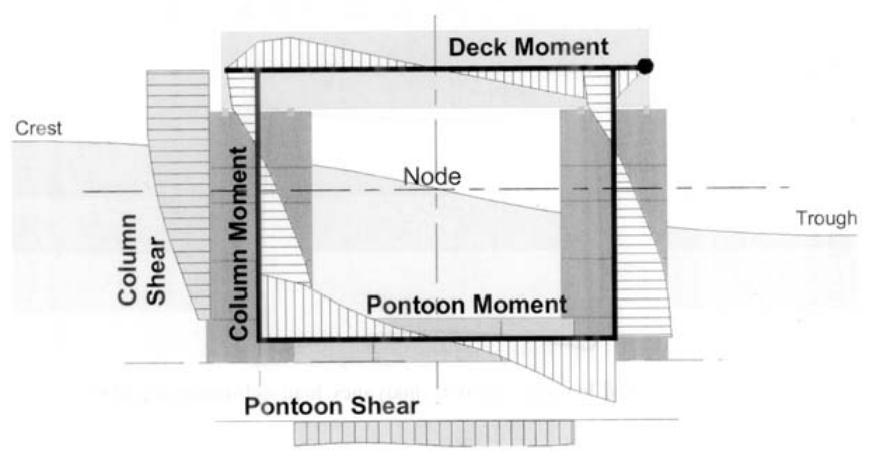
Fig 13:Gravity/Buoyancydeformationpatternof pontoon(Subratak.Chakrabarti)
[6] MohammadAliNekooie,MohamadIbrahimMohamad& ZulhilmiIsmail(2017)Dragcoefficientforamphibious house, Urban Water Journal, 14:10, 1045 1057, DOI: 10.1080/1573062X.2017.1325914
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

[7] Thriving with water: Developments in amphibious architecture in North America Elizabeth English, Natasha Klink , and Scott Turner E3S Web Conf., 7 (2016)13009;DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20160713009
[8] Nilubon, Polpat & Veerbeek, William & Zevenbergen, Chris.(2016).Amphibious ArchitectureandDesign:A Catalyst of Opportunistic Adaptation? Case Study Bangkok.Procedia SocialandBehavioralSciences.216.
[9] Sumantha,Snehanjali,andElizabethEnglishb."ALoss Avoidance Study of Amphibious Housing." In InternationalConferenceonAmphibiousArchitecture, DesignandEngineering.2015.
[10] Mohamad,Mohamad&Nekooie,MohammadAli& Ismail, Zulhilmi & Taherkhani, Roohollah. (2012). Amphibious Urbanization as a Sustainable Flood Mitigation Strategy in South East Asia. Advanced Materials Research. 622 623. 1696 1700. 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.622 623.1696.
[11] Norberto C. Nadal and Raúl E. Zapata and Ismael Pagán and Ricardo López and Jairo Agudelo (2010) BuildingDamageduetoRiverineandCoastalFloods;[9] JournalofWaterResourcesPlanningandManagement 136 3.327 336; DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943 5452.0000036
[12] SumayyaRK,Prof.VishalBV,Prof.MamathaPG,& Prof. Shiva Shankar K M (2021). Analysis, Design And PerformanceEvaluationOfFloatingBuildingUsingFea, International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology,Volume:8,Issue:8
[13] Manual, Abaqus Scripting User’S. "Abaqus 6.11." http://130.14989,no.2080(2012):v6.
[14] Pike,Kenton,GangDuan,JasonSun,andPaulJukes. "Comprehensive FEA of thermal mitigation buoyancy module (TMBM) soil interaction using the coupled Eulerian Lagrangian (CEL) method." In International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering,vol.49132,pp.865 870.2010.
[15] Aleyaasin, Majid. "An elementary finite element exercise to stimulate computational thinking in engineering education." Computer Applications in Engineering Education 30,no.1(2022):31 41.
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal