International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1Department of Mining Engineering, Bhagwanth University, Sikar Road, Ajmer 305004, Rajasthan, India
2Department of Mining Engineering, Aditya Engineering College, Surampalem, Andhra Pradesh, India ***
Abstract The mining activities are one of the main causes to strata movement and lack of its knowledge leads to various mining hazards such as roof fall, inrush of ground water, rock burst, coal bump, sub surface deformationanddamages tothe buildings or structures on the surface. The movement ofstrata affects the life of men, material, and machines during the course of mining operations. Therefore, a detailedstudyon the investigation and monitoring of strata behaviour and its control is becomes one of the key concern in the field of mining. In this paper a theoretical attempt has been made to understand the mechanics of the ground movement that occurred during any mining operations. The behaviour of the ground movement can be predictedby measuringthe intensity of load on the strata. Thus, the paper focused on the application of geotechnical instruments such as vibrating wire type stress cells, load cells, Tell Tale type borehole extensometers and convergence stations on the measurement of load
Words: Strata behaviour, Ground control, Roof fall, Borehole extensometer
The progress in the state of the art, technology in many branches of engineering is quite rapidly in recent years (Adomaviciuset.al.2005).Inthecaseofundergroundcoal miningindustry,aslowprogresswasobservedduringthe last one decade, due to its complex and hazardous environment. Nevertheless, a few advancements in the availability and adaptability of the modern mining machinery was observed. These advancements in the underground coal mining are also limited due to the inadequatetechnologyofstratacontrol(suitabledesignsof workingsandsupportsystems)(Minggaoet.al.1994).The Board and Pillar mining method is the most widely used technology in the scenario of Indian coal mining industry. Thismethodofcoalwinninghasthenegativeimpactonroof maintenance. During the operation of this method a large portion of roof is exposed to the external load which degradesthestrengthoftheroof.Rooffracturesandrooffall occur in this method of workings when the roadways are beingdrivenduetotimedependentdeformationorduring theextractionofpillars.Thisreducesthesafetyandincrease the probability of roof fall. Therefore, it is required to implement various innovative technologies for the extractionprocessbythismethod(RogersM.et.al.1995).
The factors influencing coal mining involves geological distributioninoreblocks,depthofdeposit,andgeologyof deposits,andsustainableminingoperationwhichimproves thesupport systeminstallation whichisoriginated by the studyofstratamechanics(Kanget.al.2010).Inearlierdays ofmining,duetolessinvestmentinminingequipmentand technology there was limited possibility of quantification coalwithgoodqualitativepossible.
However, now days, with improved technology of mining and instrumentation, such as numerical models and computerapplicationsanalysisofdata,investigatorsgained enhanced satisfaction through observational approaches (VonKimmelmannet.al.1984).Theminingindustryinthe recent scenario requires more innovative changes in the instrumentation adopts for their safer and appropriate extraction. India has large resources of coal deposits of undergroundminingandlotsofcoalwasblockedinexisting underground mines. These blocked coal needs to be extracted by the installation of proper strata reading instruments(ZhangJet.al.2010).Moreover,theaccidents whichmainlyoccurredintheundergroundminesaredueto the strata deformation and it is the one of the important factorsfortheseaccidents.
Generally, the problem of ventilation and strata control posesaverybigchallengetotheminingemployeestowork coalatgreaterdepthsat450 600m(NoackKet.al.1998). Obviously,thestrataontheface,andintheadjoiningareas (in front and behind), must require attention so that no uncontrolledfailureofgroundtakesplace.
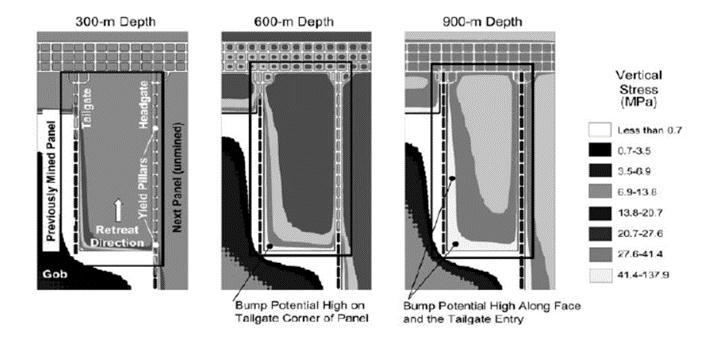
Inordertounderstandproperstratacontrolmeasures,itis importanttounderstandthemechanicsofthemovementof ground, which usually occurs as a result of mining operations. In addition to strata control problems, ventilation also poses a great challenge to the mining fraternity for designing innovative methodologies of implementation of environmental control measures in mines. The yield pillar gate road system provides no significant protection to the tailgate corner of the active longwall face from side abutment stresses (Guo H et. al. 2008).Yieldpillarsystemssucceedwhenabutmentloadsare shifted off gate road pillars, thereby avoiding potentially hazardous stress concentrations, and onto the panel edge
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
where loads can be distributed over a broader area. The figure 1 shows a significant increment in stress concentration and bump potential at the tailgate of mines usuallyatgreaterdepth.
Thesestressdistributionshavebeenproposedonthebasis of mechanics of strata behavior. Various theories for this studyarediscussedbelow:
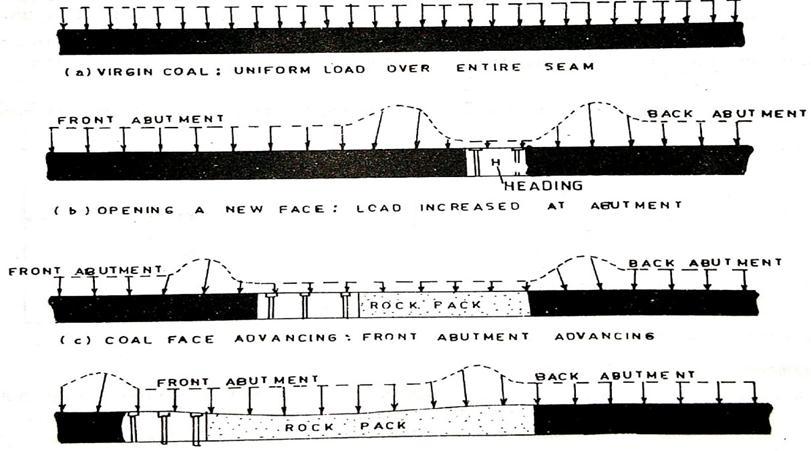
During thedrivage ofheadingsin theadvance oflongwall face, it is observed that the roof strata gets fractured to a certain distance ahead of the coal faces at a considerable distancestratummovementtakesplaceaheadoffracturing. Theabutmentloadaheadofthefacecreatessomebumps, tightening,minorsinkingandsomebulging.Theformation ofacuteangleswiththecoalfacesidewithcoalribsleft,the faceabutmentpressuregetsinvadedatagreaterdistanceat coalribs.Whentheanglebecomesgreaterthan900,thisgets displaced near to the coal ribs. The position of back abutmentandeventheirexistenceisapointofcontroversy, someresearchersbelievestheexistenceofbackabutment whileothersinthepresenceofpressurearch.Thedifferent roofbedsbendsbydifferentamountsbecauseofhavingthe propertiesofyoung’smodulusofelasticityandtheformation ofcavitiestakesplace,knownasWeber’scavity.Thelineof increasedpressureinthistheoryisknownasPressureArch, pressuredome,orPressureellipse.
The coal measure rocks found in India are full of geotechnical disturbances like joints, faults, originally formed due to the occurrence of orogenic force in the vicinity of their area. Whenever, an excavation is made in suchrocks,thestrataaroundtheexcavationtendstoexpand towardsittowarditandasaresultaregetsfracturedunder the action of new stresses arising out of the disturbances. Thistheoryhasmanylimitationswhicharediscussedbelow:
It cannot be logically applied to the coal measure strata since the symmetrical arrangement of the beds,bearsnoresemblancewithbeds.
Noconsiderationoftimeanddipofstrata.
Load on support will be more than the load on brokendebris.
Ingeneral,theroadsdriven inlongwall methodof mining shouldhavefourcharacteristics:a)Theboundarysurfaceof influence; b) The surface of fracture; c) The surface of aspiration; d) the surface envelope of separate beds. This theoryreliesonthedynamicworkingofthefacesandcope upwith variousstressesinvolved.Thistakesintoaccount thetimefactorandthepropertiesofthesupportsandthe theoryaccordswellwithintheobservationmadeinactual practice.
ThecoalmeasurestrataofIndiancoalfieldsconsistsmainly ofsandstone,shaleandanalluviumcapofvaryingthickness atthesurface.InthelightoflimitedcoalreserveinIndian Territory,limitedqualitycoalreserve,qualitycoalreserve within 300m depth cover extensively disturbed by pillar mining and poor recovery with pillar mining, it is
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
recommendedtogoforextensivesurfacemininginallthe majorcoalbasinsuptothestrippingratioof1:10.
Thecoal seams belowin selected basins of qualitycoals Sohagpur, E&W Bokaro, N&S Karanpura, Jharia, Raniganj, Wardha and Godavari valleys are recommended to go for underground longwall, pillar mining with continuous miner and mining with vertical production concentration technologyispreferred.Thetypeandradialextentofcoal measure strata are influenced by tectonic setting. Many researchandacademicinstitutionsinitiatedmanystudiesto helpcoalindustryforbetter,efficientandsafeextractionof coalthrough
i)Analyticalanalysisandmathematicalmodels,
ii)Empiricalanalysisandmodels,and
iii)Numericalmodellingwithcomputerization
MechanicalpropertiesofIndiancoalmeasurerocksvaries from place to place in respect of volatile matter, depth of Burial, their compaction, Moisture content etc. The compressivestrengthofthesestratagenerallyliesbetween 56kg/cm2and396kg/cm2.Onthebasisofthebehaviorof coalseams,theroofiscategorizedintothree:
Thickstrongroofs; Fragileroof: Stratifiedcompetentroof.
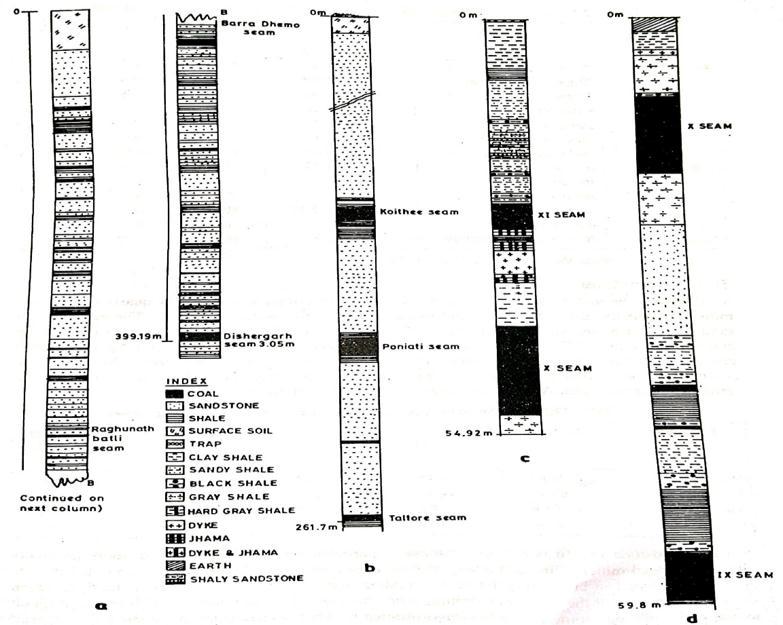
Proper Investigations were conducted at the mine to understandthebehaviorofthestratainthelongwallpanel. Themainaimoftheseinvestigationsistomeasurethefront abutment,andthedeformationofthestratasurroundingthe gateroadsaheadofthelongwallface.Themeasurementof these parameters is done with the help of geotechnical instruments such as vibrating wire type stress cells, load cells, Tell Tale type borehole extensometers, and convergencestations.Theboreholesectionsforthestudyof strata control of some Indian underground coalfields is showninFigure3.
Aim is to understand the geo mechanical behavior of the stratainthegateroadsandintheface.Theseobservations wereaimedatmeasuringthelocationandmagnitudeofthe front abutment, and the deformation of the strata surroundingthegateroads,andloadonsupportsaheadof thelongwallface.Fourvibratingwiretypestresscellswere installed, a continuous convergence recorders and convergencepoints,andloadcellswereinstalledintheTail Gate and Main Gate. The location of these instruments is showninFigure4.
Thetelescopicconvergenceindicatorisusedtodetermine theconvergenceatthemainandtailroadoflongwallmines. The efficiency of the supports is monitored by measuring loadvariationontheOCpropsbyinstallingloadcellsand convergenceofGateroadways.Theabutment loadonthe pillarsduringtheextractioncanbemonitoredbyinstalling fourvibrating wiretypestresscells.Twostresscellswere installedinmaingateandtwointailgate.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
span,theinsitustress,andthemining inducedstress.The schematicgroundreactioncurveisshowninfigure5.
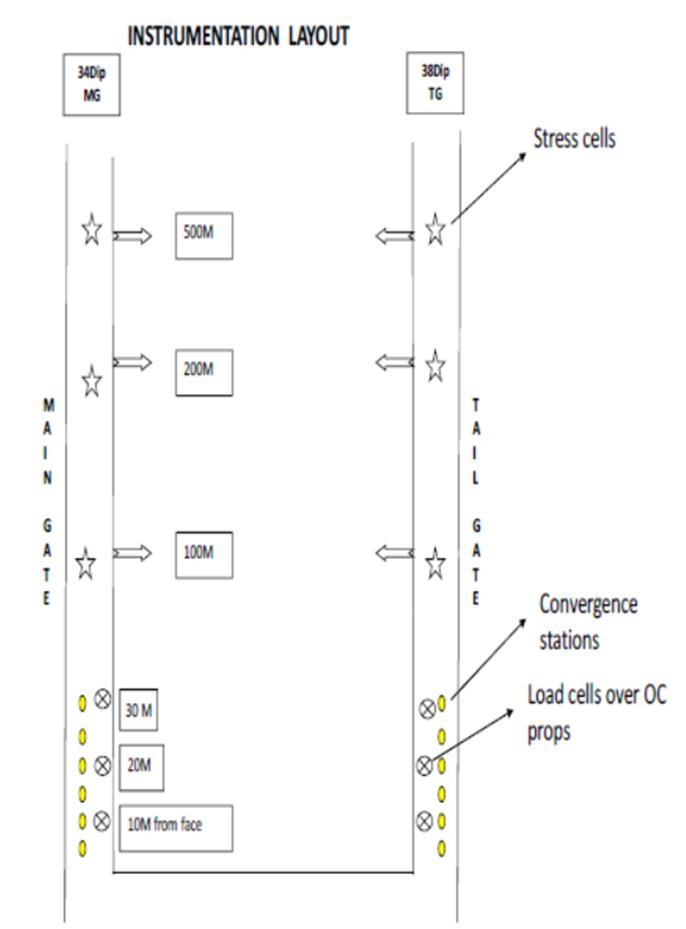
Fig 4 locationofinstrumentinlongwallpanel.
Strata and support behavior monitoring is required for understanding the performance of support system. To minimize the dangers from weighting on the pillar due to overhangingofroofinthegoafandtoensurethatassmallan areaofun collapsedroofaspossibleisallowedinthegoaf,a suitable code of practice for induced blasting shall be evolved in consultation with a scientific organization keepinginviewthedepthofinduceshotholesbeingnotless than2.7m,direction&spacingofshot holes,explosivesused etc. so as tolimit the rate of convergence [i.e., the ratio of C1/C2isequalorlessthan2,whereC1isdailyconvergence atasiteinaday"n"andC2istheaveragedailyconvergence atthesiteuptothepreviousdayi.e.day(n 1)]andalsoto ensure complete filling of the goaf and release of any abutmentpressures.
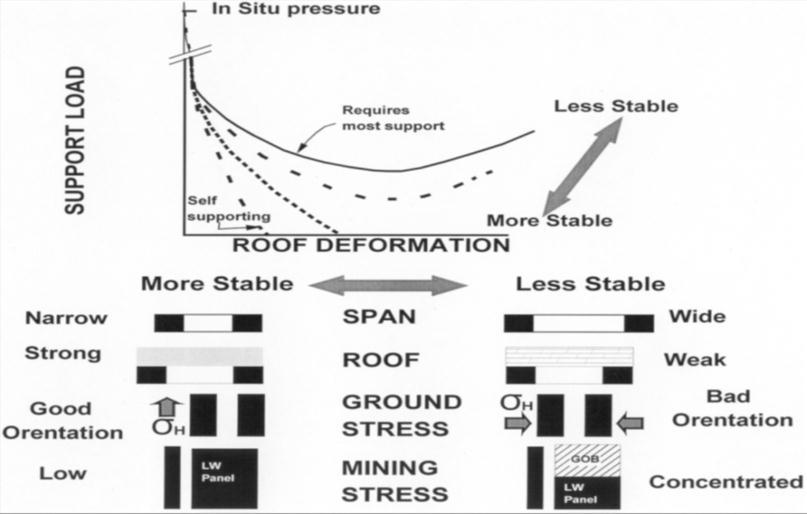
In general, roof supporting is done to create a stable rock structure. The factors governing the installation of roof supportinvolvesthepropertiesofrock,andthemagnitude of stress distribution. To study the strata behavior in undergroundlongwallmines,aconceptsofGroundreaction curveisestablished.Thiscurveisdefinedastherequirement ofallpossiblesetofloadstoachievemaximumstability.The groundreactioncurvedependsontherockmassquality,the
Asillustratedbythegroundreactioncurve,the"ideal"roof supporthasthefollowingproperties:
High initial stiffness, so that only small ground movementsareneededtomobilizethecapacityof thesupport;
Largeload bearingcapacity;and
High residual strength over a large range of displacement
Thisisthecasewhereoverloadingandpressureonthecoal seamroofisatudiesinconjunctionwithstratabehaviorand groundcontrol.Themainfactorsgoverningtheover break androckaregivenbelow:
Spacingbetweenthejoints.
Shattering effect of blasting on the rock located beyondthepay line.
Distance between the working phase and roof support.
Lengthoftimewhichelapsesbetweentheremoval of the natural support of the roof by blasting and theinstallationoftheartificialsupport
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
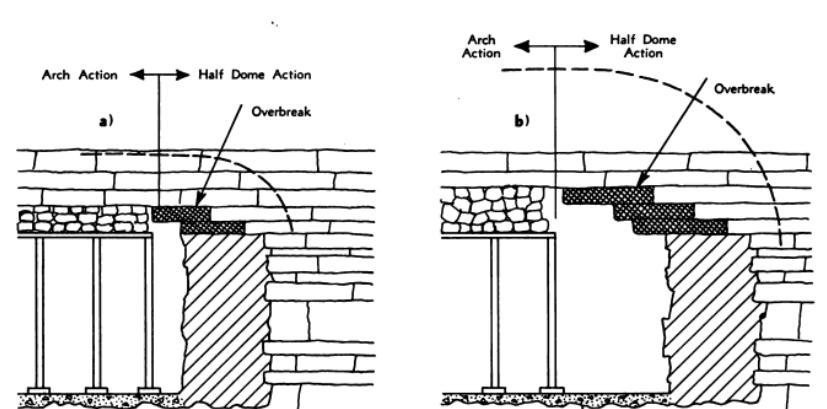
Figure5andFigure6showsthehowtheworkingphaseand thesupportedroofisinfluencedbythedistanceontheover break in closely jointed, horizontally stratified rock. The smaller this distance, the smaller is the quantity of rock which is likely to drop out of the roof when the round is fired.
[1] Adomavicius,G.,&Tuzhilin,A.(2005).Towardthenext generation of recommender systems: A survey of the state of the art and possible extensions. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge & Data Engineering, (6), 734 749.
[2] Minggao, Q., Fuliang, H., Zuotang, W., & Cunbao, G. (1994).AFurtherDiscussionontheTheoryoftheStrata Behaviors in Longwall Mining [J]. Journal of China UniversityofMining&Technology,
[3] RogersM.(1998).Thedefinitionand measurement of innovation.
Fig 6 Unsupportedaction longveryshort
If the mine support is installed and wedged soon after blasting,thefrictionforcesonthesidesoftherockfragments occupyingthespacebetweentheroofsupportandthevault transferpartoftheweightofthisrockontotherocklocated beyondthesidesofthevault.
Inthefoldedmassofrock,thedipofthestratamayrange anywherebetween00and900,andthestrikemayintersect thecentrelineoftunnelatanyanglebetween00and900. Theangleoffrictionϕdependsnotonlyonthenatureofthe surfaceofcontactbutalsoonthehydrostaticpressureinthe water which percolates into the space between the two surfaces.
The strata behavior and ground control is an important concernintheviewofsafetyaspectandtheproposedstress distributiontheoriesalsohelptounderstandthebasicsof stratabehavior.Thetelescopicconvergenceindicatorisused todeterminetheconvergenceatthemainandtail roadof longwallmines.Theefficiencyofthesupportsismonitored bymeasuringloadvariation ontheOCprops byinstalling load cells and convergence of Gate road ways. Strata and supportbehaviourmonitoringisrequiredforunderstanding theperformanceofsupportsystem.Tominimizethedangers fromweightingonthepillarduetooverhangingofroofin thegoafandtoensurethatassmallanareaofun collapsed roof as possible is allowed in the goaf, a suitable code of practiceforinducedblastingshallbeevolvedinconsultation withascientificorganization.
[4] KANG, H., NIU, D., Zhang, Z., LIN, J., LI, Z., & FAN, M. (2010).Deformationcharacteristicsofsurroundingrock andsupportingtechnologyofgob sideentryretainingin deepcoal mine[j].ChineseJournal ofRock Mechanics andEngineering,10(29).
[5] Von Kimmelmann, M. R., Hyde, B., & Madgwick, R. J. (1984).TheuseofcomputerapplicationsatBCLLimited in planning pillar extraction and the design of mining layouts. In Design and Performance of Underground Excavations: ISRM Symposium Cambridge, UK, 3 6 September 1984 (pp. 53 63). Thomas Telford Publishing.
[6] ZhangJ.X.,WuQ.Huang,Y.L.,&Zhou,Y.J.(2010).Strata pressurebehaviorbyrawwastebackfillingwithfully mechanized coal mining technology. J China Coal Soc, 35(8),1 4.
[7] Noack K. (1998). Control of gas emissions in undergroundcoalmines.InternationalJournalofCoal Geology,35(1 4),57 82.
[8] GuoH.,YuanL.,ShenB.,QuQ.,&XueJ.(2012).Mining induced strata stress changes, fractures and gas flow dynamicsinmulti seamlongwallmining.International JournalofRockMechanicsandMiningSciences,54,129 139.