International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Department of Computer Science, Dr. Rammanohar Lohia Avadh University, Ayodhya, India
Abstract - Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the implementable Machine to Machine (M2M) communications which is a crucial component of recent growth in the digital market. In this paper, important agricultural applications are highlighted, and applicability of IoT towards improved performance and productivity are discussed. Characteristics of IoT are presented. Usable hard ware platforms, wireless communication technology standards, and IoT cloud services for agricultural applications are analyzed. Various sensor basedIoT systems also listed in this paper. Author also reviewed and studied the existing IoT deployments in multiple domains. IoT sensors may provide information about agriculture fields andthenactonitbasedonuserinput.Thedevelopmentof a system that can monitor temperature, level of water, wetness, and even movement if any occurs in the field that may kill the crops in an agricultural field using sensors utilizing the Arduino UNO board is termed as smart agriculture. The goal is to integrate developing technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart agriculture with automation. After the hardware has been built to meet changingneeds andtechnologies, thesoftware must be updated. The modified hardware is referred to as a new software version. This new version must be checked to ensure that the modifications are correct. It also won't introduce faults in other parts of the software. This is required because changing one component of the hardware can have unintended consequences in other parts of the hardware.
Key Words: Internet of things(IOT), Smart Agriculture using IOT, Arduino, Soil Moisture Sensor, Water Level Sensor
TheInternetofThings(IoT)isexpanding,growing,and getting more popular by the day. In today's world, approximately 5 billion things are connected to the internet. Around 50 billion things are expected to be connectedto the internet by2020,according toestimates. IoT is opening up a world of possibilities for new applications,whicharenowbeingemployedinavarietyof areas, including intelligent home monitoring systems, product supply chain management, precision agriculture, andmuchmore.
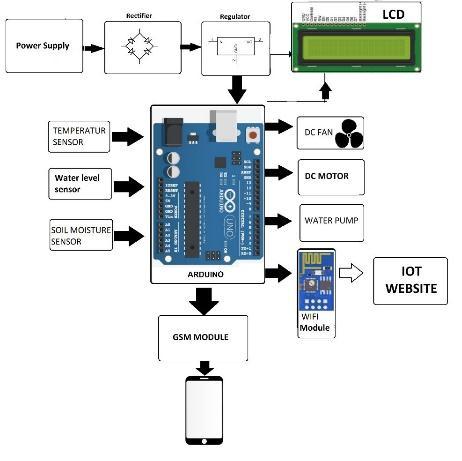
Using RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), Wireless Sensor Network (WSN), or other methods, everything in the Internet of Things is reachable, recognized, readable,
and locatable over the internet. Precision agriculture, product supply chain management, Smart Grid, environmental monitoring, cloud computing, and other sectors are all using the Internet of Things concept. IoT is gainingmuchimportancethesedaysaseveryobjectinthe network will become a computer. The idea of IoT has become successful due to the invention of recent technologieslikesensors,RFIDandWSN.
Fig.1:BlockdiagramofIoTapplications
Smart farming is a farming management concept that employs contemporary technologiesto boostthe quantity and quality of agricultural products. GPS, soil scanning, data management, and Internet of things technologies are available to farmers in the twenty first century. The purposeofsmartagricultureresearchistodevelopafarm managementdecision makingassistancesystem.
Fromcropplantingandwateringtohealthandharvesting, smart farming considers it important to address the concerns of population expansion, climate change, and labour, all of which have received a lot of technological attention.
A system is constructed for monitoring the agricultural field with the help of sensors (light, humidity, temperature,soilmoisture,etc.)andautomatingirrigation inIOT basedsmartagriculture.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
IOT (Internet of Things) refers to the use of sensors, cameras, and other devices to turn every element and actioninfarmingintodatainthecontextofagriculture.
Because smart agriculture would greatly minimize modern agriculture's negative environmental externalities, weneed ittospreadandevolvefrom where it is currently. Smart cities use Internet of Things (IOT) equipmentsuchconnectedsensors,lighting,andmetersto collectandanalyzedata.Citiesthenusethisinformationto improveinfrastructure,publicutilities,andotherservices, among other things. Farmers struggle to grasp technical concepts and applications of technology, and it is also an expensiveendeavor.
An Effective Method for Crop Monitoring Using Wireless Sensor Network by N. Shakthipriya (2014): In Indiaabout70%ofpopulationdependsuponfarmingand one third of the national capital comes from farming. The highlighting features of this concept includes smart GPS based remote controlled robot to perform tasks like weeding, spraying, moisture sensing, bird and animal scaring, keeping vigilance, weather forecasting, water management, canal controlling in both automatic and manualmodesandallthesedataarestoredanddisplayed inamobilesensors,WirelessFidelityetc.
Multidisciplinary Model for Smart Agriculture using IoT by Hemlata Channe, Sukhesh Kothari and Dipali Kadam (2015): Climate changes and rainfall has been regular over the past decade. Due to this, climate smart methods called as smart agriculture is adopted by many Indian farmers. Smart agriculture is an automated and directed information technology implemented with the IoT (Internet of Things). IoT is developing rapidly and widely applied in all wireless environments. The sensor technology and wireless networks integration of IoT technology has been studied and review. A combined approach with internet and wireless communications, RemoteMonitoringSystem(RMS)isdone.
Automatic Control of Agricultural Pumps based on Soil Moisture Sensing by Beza Negash Getu, Hussian A. Attia (2015): Water is always a needy part of everyone’s life. Due to environmental situation, water management and conservation will play a vital for human survivals. Recently, there were huge needs for consumer based humanitarian projects that could be rapidly developed usingInternetofThings(IoT).ThisproposesanIoTbased watermonitoringsystemthatmeasureswaterlevelinreal time. The prototypes are based on the level of the water canbeanimportantparameterwhenitcomestotheflood especiallyindisasterareas.
A Control System in an intelligent farming by using Arduino technology by Putjaika and Narayut (2016): Even now different developing countries using the traditional ways and backward techniques in agriculture sector. A little technological advancement has increased theproductionefficiencysignificantly.Andtoincreasethe productivity the inventive approach is introduced. Smart farming with Internet of Things (IoT) has been designed. By developing a motor vehicle which can be operated on both automatic and manual modes which can be used for various agriculture activities like cutting, spraying, and weeding etc.Thecontroller will monitor the temperature, humidity,soilfertility,andwatermanagementtothefield. By using green energy and smart technology the agriculture sector will find a better way to increase the productivity.
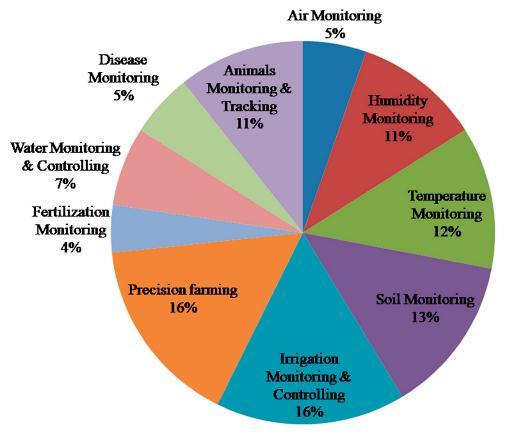
Precision agriculture, whose design incorporates IoT techniques for urban agriculture and precision agronomy in smart cities, is one of the most common uses of IoT technologiesinagriculture.
Smart cities are typically built on software defined networks (SDN) and cyber physical systems. Other possible uses for the Agricultural drones, which are very inexpensive drones with advanced technology, are an exampleofIoT. Fig.2:ApplicationsofIoTinvarioussectorsofsmart farming
Farmers will be able to use sensors to boost yields and prevent crop damage, among other things something else IntelligentgreenhousesareanotherareawhereIoTcanbe used. Hydroponic and small scale aquaponic systems are included. Intelligent Greenhouses are becoming more common in urban areas as they allow for better monitoring.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Numerous nutrient solution parameters, as well as to promotegrowth,production,andqualityandthestandard ofplants.
These enhancements provide a substantial contributionto theachievementofthegoal.infrastructuresinsmartcities that allow forautomation, optimization,and improvement Precision agronomy and urban agriculture another area whereIoTtechnologiesarebeingusedisinhealthcare.
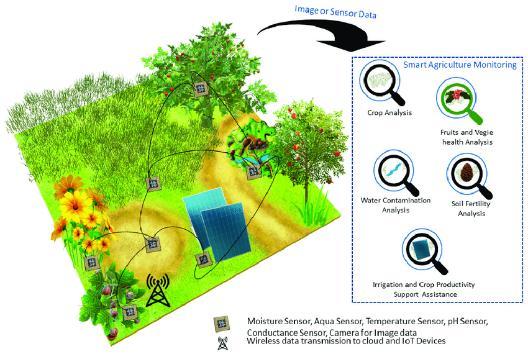
Vertical agriculture is used, which permits soil moisture and water to becontrolledmaterial throughcomputers or mobiledevicesliketabletsandsmartphones.Finally,there are applications that mix Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) such as Malthouse , an Artificial Intelligencesystemthatallowsprecisionfarmingandfood manufacture to prescribe configurations and timetables areas.
Many businesses and marketplaces throughout the world have embraced IoT based devices. Agriculture is one of these businesses, which benefits from IoT technologies in a variety of ways. In Indiana, for example, LoRa is a frequently utilizednetwork radiobecauselong range,low power consumption, and low cost are just a few of its benefits a financial investment. Another example of IoT based device application is the utilization of cameras to checkthequalityoffood.
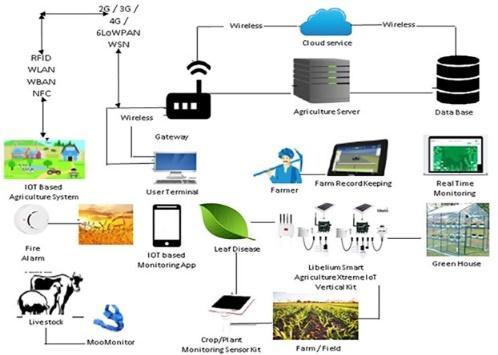
Fig.4:WirelessdatatransmissiontocloudandIoT devices.
There are, on the other hand, techniques that mix cloud computing and wireless sensor networks to provide a comprehensivesolutionAgriculture as a Service(AaaS)is aservicethatallowsyoutomanageagriculturaldata.
UsingBigDatatechnologiesThePhytecfirm,forexample, provides A Systematic Literature Review of IoT Applications in Agriculture. Plan IoT is a platform for automatically detecting changes in plant status, analysing data,andmakingrecommendations.
IoT based solutions have been effectively implemented in a variety of situations. As a result, various companies are investing in IoT based farm software development. There are numerous software programmes available on the market nowadays centred on assisting various farming operations AG IoT , for example, is a unmanned aerial vehicle that searches for and assists IoT enabled devices toconstructdatatransmissiongroupsonthegroundAgro 4.0.
On the other hand, High performance computing algorithms, a sensor network, and connectivity are all implemented to process enormous amounts of data using mobile devices, cloud computing, and analytical methods large amounts of data and provide decision making aids. Agro Tech is a company that produces, sells, and distributes agricultural technology and updates data collected from various sensors in a certain area of the worldcrop.Furthermore,thisprogrammeenablesfarmers toaccessthisinformationaimingtomonitortheirharvest Malthouse is an Artificial Intelligence system that enables for the prescription of medications precise farming and foodmanufacturingconfigurationsandschedules.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The major advantages of IoT in agriculture are described below:
• Using hardware and software to support community agriculture in both urban and rural regions enormous volumesofdataandsoftwareresources.
• Food production may be traced logistically and qualitatively, lowering costs, reducing the waste of inputs throughdecision makingbasedonreal timedata.
• Creation of agricultural business models that allow a directlinkwiththeconsumertobeestablished.
• Crop surveillance, which provides for cost savings as wellasthepreventionofmachinerytheft.
• Automatic watering systems that adjust based on temperature, humidity, and other factors sensors, as well assoilmoisturereadingsderivedbysensors.
• Automatic environmental parameter gathering using sensornetworksformoreanalysisandprocessing.
• Assisting with decisions systems that analyze large amounts of data to improve operational efficiency and productivity.
IoTtechnologyenableefficientremotecropmonitoring by providing information on climate, humidity, temperature, and soil fertility, among other things. Farmers may know the state of their crop at any time thanks to these technology any time and from any location Wireless sensor networks, on the other hand, provide for control the farm's environment, as well as automatecertainprocesses.
For instance, some wireless cameras are used in several of the experiments examined in this paper to determinecropstatusinthepresentmomentDroneshave also been used in other research to assist with precise tasks.
Smartphones are being used in agriculture to keep farmers updated about the present state of their crops wireless sensor networks and cloud computing are being used to develop agricultural solutions, mobile apps, computing,andmiddlewaresystems.
1. Patil VC, Al Gaadi KA, Biradar DP, Rangaswamy M (2012) Internet of things (Iot) and cloud computing for agriculture: an overview. AgroInformatics Precis Agric(i):292 296
Dlodlo N, Kalezhi J (2015) The internet of things in agriculture for sustainable rural development. In: 2015 international conference on Emerging trends in networks and computer communication (ETNCC), pp 13 18
Yan E D (2011) Design of intelligent agriculture management information system based on IoT. In: Proceedings of the 4th international conference on intelligent computation technology automation ICICTA2011,vol1,pp1045 1049
Li J, Gu W, Yuan H (2016) Proceedings of the 5th internationalconferenceonelectrical engineeringand automaticcontrol,vol367,pp1217 1224
Lee M, Hwang J, Yoe H (2013) Agricultural production systembasedonIoT.In:2013IEEE16thinternational conference computer science engineering, pp 833 837
Bo Y, Wang H (2011) The application of cloud computing and the internet of things in agriculture and forestry. In: Proceeding of the 2011 international joint conferenceonservicescienceIJCSS2011,pp168 172
MohanrajI,AshokumarK,NarenJ(2016)Fieldmonitoring and automation using IOT in agriculture domain. ProcediaComputSci93:931 939
8. Tongke F (2013) Smart agriculture based on cloud computing and IOT. J Converge InfTechnol 8(2):210 216
Karim F, Karim F, Frihida A (2017) Monitoring system using web of things in precision agriculture. Procedia ComputerSci110:402 409
Zhao JC, Zhang JF, Feng Y, Guo, JX (2010) The study and application of the IOT technology in agriculture. In: Proceedings of the 2010 3rd IEEE international conference computer science information technology ICCSIT2010,vol2,pp462 465
Patra L, Rao UP (2016) Internet of things architecture, applications, security and other major challenges. In: 2016 international conference on computing for sustainable global development (INDIACom), pp 1201 1206
Jayaraman PP, Palmer D, Zaslavsky A, Georgakopoulos D (2015) Do it yourself digital agriculture applications with semantically enhanced IoT platform. In: 2015 IEEE 10th International conference on intelligent sensors, sensor networks information processing ISSNIP2015,pp7 9
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page886

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | Jun 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072




Dr. D. K. Verma have done MCA from University of Lucknow in 2011 and Doctorate in Computer Science in 2016. Dr. Verma is currently working as Assistant Professor of Computer Science at Dr Ram Manohar Lohia Awadh University, Ayodhya, India. His research interests are Artificial Intelligence, IoT and Data Mining He has published several research papers in National and International journals & Conferences. He has 10 years of teaching experience and 6 years of Research Experience.


Ms. Apurnima Mishra is final year student of graduation with computer science from Dr Rammanohar Lohia Avadh University, Ayodhya. Her research interests are Internet of Things, Smart Farming and Robotics.
Ms. Komal Mishra is final year student of graduation with computer science from Dr Rammanohar Lohia Avadh University, Ayodhya. Her research interests are Internet of Things, Big Data and Cloud Computing