International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
123Student, Department of Information Technology, Bharati Vidyapeeth’s College of Engineering for Women, Pune, Maharashtra, INDIA
4 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Information Technology Engineering, Bharati Vidyapeeth’s College of Engineering for Women, Pune, Maharashtra, INDIA
5Software Engineer, Veritas Technologies LLC, Pune, Maharashtra, INDIA ***
Abstract: In today’s world where we depend on internet for every small piece of information or for sharing the data, we generate new data every second. This data can include texts, videos, audios, images, etc. and storing or maintaining this big data is of concern. Businesses invest heavily in data storage and this is why there is a need to manage big data. De duplication is emerging technology for removing redundant or duplicate data. De duplication can be applied to any type of storage data like primary storage, secondary storage and also for cloud storage. De duplication reduces the data to be stored hence the cost is reduced, also the bandwidth required for data sharing is reduced considerably. These are some of the advantages of using de duplication. Data de duplication is efficient for large scale storage systems rather than traditional approaches. This paper focuses on data de duplication and its various types and the main stream is the implementation of de dupe engine.
Key Words: Big data, de-duplication, client-server, chunking,fingerprints,inter processcommunication
In the era where data, specifically digital data has self evidentimportanceintheageofglobalization,ithasbecome essentialtoeliminateanycircumstancesordrawbacksinthe field of data processing and management. One such challengeisdataredundancyorduplication,wheremultiple copies of same digital data take up storage space on our system, and numerous other issues like bandwidth inefficiency, increased hardware and backup cost and networkinefficiency.Reasonsofredundancy:
An enormous portion of internet data is redundant for 2 reasons. Firstly, because of the significant decline in the storage cost per GB, people tend to store multiple copies of same file for data safety or user convenience. Secondly, while incremental (differential) data backups or disk image files for virtual desktops tend not to have duplicated whole
file copies, there is still large fraction of duplicated data portionfromthemodificationandrevisionofthefiles.
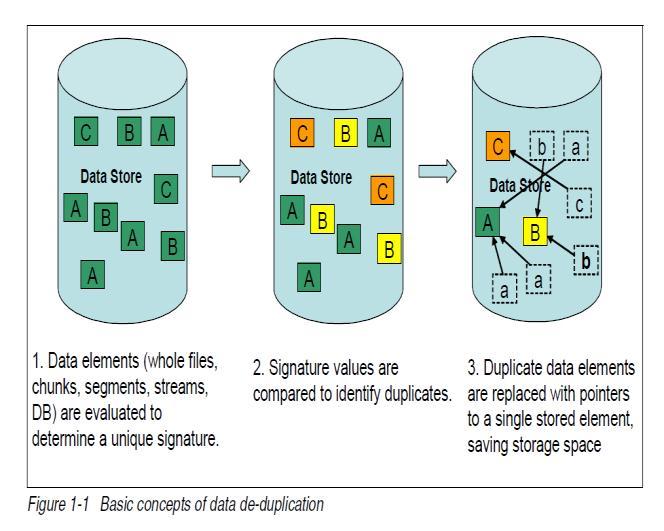
Chunks are the small divided portion of the complete data that may be fixed sized or variable sized. The techniques thattrack andeliminateany duplicatechunksofdata in the specific storage unit are implemented, such techniques are calleddatade duplicationtechniques.Datade duplicationis more important at the shared storage level, however implemented in software as well as database. Basically, de duplication takes place at file level and block level. In file level de duplication, it eliminates duplicate or redundant copies of same file. This type of de duplication is called SingleInstanceStorage(SIS).Inblocklevelde duplication,it eliminates redundant or duplicate blocks of data which is present in unique files. Block level de duplication reduces morespacethanSIS,thistypeofde duplicationisknownas variable block or variable length de duplication. De duplication on more finely grained chunks at block level shows better performance in removing duplicate data and thus creates more opportunities for space savings, but it mayreducethesequentiallayoutofsomefiles.Alternatively, whole file de duplication is simpler and eliminate file fragmentationconcerns.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
With the help of data de duplication on our storage environment, only one and unique copy of data is retained onstoragemedia,andredundantorduplicatedataisplaced withpointertouniquedatacopy.Thatis,itlooksatthedata onasubfileorblocklevel,andattemptstodetermineifitis seenthedatabefore.Ifithasnot,itstoresit.Ifithasseenit before, it ensures that it is stored only once, and all other references to that duplicate data are mere pointers. De duplicationprovidesthebenefitssuchasincreasednetwork efficiency, bandwidth efficiency and storage efficiency, improved speed replication, reducing backup window and therebycost.
There are various ways to classify, but generally 4 ways of classificationare
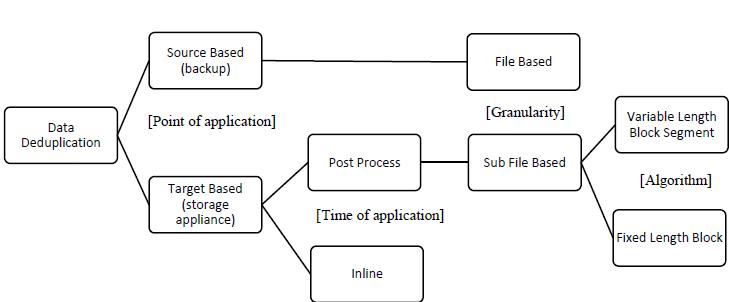
i. Pointofapplication ii. Timeofapplication iii. Granularity iv. Algorithm
Source de duplication is in where the redundancies are removedbeforetransmittingthedatatobackuptarget This
offer a reduced bandwidth and network storage. For large amounts of data, source de duplication may be slower than the target de duplication but the rate of transfer is pretty good as the duplicate data has been removed before the backup transmission. Due to extensiveworkloadontheserversoveralltimerequired for backup may increase. This type of de duplication is suitedforbackingupsmallbackupsets.
This de duplication takes place at client side or at server side. Only the unique segments or block of data which has been changed since previous backup is only considered for the backup. The cost of traditional backup infrastructure like hardware, software, tapes, courier, drives, etc. gets eliminated. Advantages of sourcebasedde dupeare
1. Rapidbackupwindow 2. Reductioninnetworktraffic 3. Datatransfersareefficient
2.2.
The redundancies are removed from the backup transmissionasitpassesthroughtheappliancebetween source and the backup target. Intelligent Target Disks (ITD) and Virtual Tape Libraries (VTL) use target de duplication. Same as source de duplication, target de duplication reducestheamountofstorage required but itdoesnotreducetheamountofdatatobetransferred
for backup. This type of de duplication requires hardware butitissometimesconsideredasadrawback.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
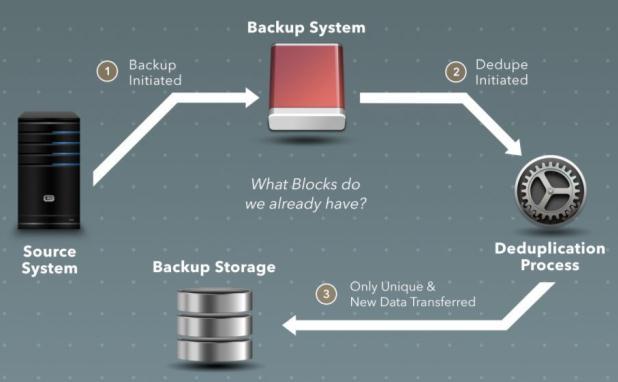
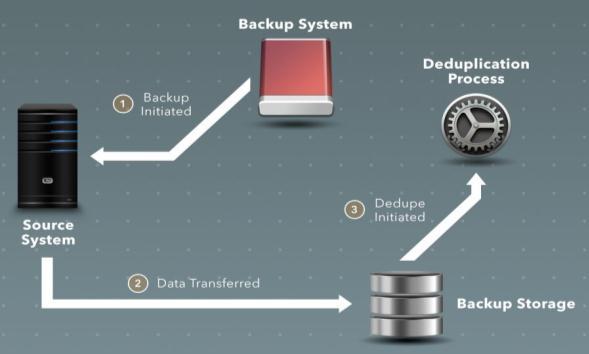
Inline de duplication is also called as synchronous or online de duplication. Redundancies and duplicate data is removed while writing data on backup device. Inline de duplication can make system work slower because thedevicesareinthedatapathbetweentheserversand backupdisksystems.Thissystemcanworkassourceor target based.
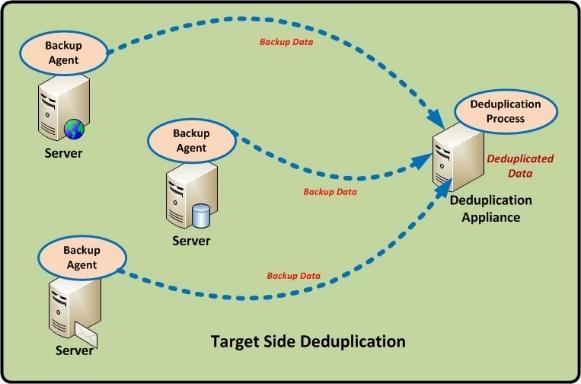
Target de duplication provides faster performance for big datasets. This de duplication can be used for protecting large SQL or Oracle databases. Target de duplication can integrate with the existing infrastructure of the backup system. This de duplication reduces the consumption of primary storage resources. Advantages of target de duplication
1. Reductioninbackupwindows
2. Makeminorchangesinsystemtoimprove efficiency
Post process de duplication is also called as asynchronous or offline de duplication. In this, the removal of redundant data is done after backup is complete and data has been written on storage. As compared to inline de duplication post process de duplication is faster. In this technique, duplicatedata isremovedandreplaced with a pointer. This requires a lot of storage space as duplicates are removed after storing data and this is a drawback Advantage of this de duplication is that it is straight forward and takes less time.PostprocessproductsareExaGridEX.
Inline de duplication requires less space than post process as the redundancies are removed before storing and do not require temporary space Inline de duplication can cause bottleneck slowing down the overall process. NetApp’s SolidFire division offer products with inline de duplication. Some famous inline de duplication products are IBM SpectrumVirtualize,VeritasNetBackup.
File based de duplication is commonly known as Single InstanceStorage(SIS).Inthisde duplication,wholefile is compared with the files already stored by checking its attributes.Ifthenewfileisuniquethenitisstoredandifthe file is repeated only a pointer to existing file is stored. Duplicates are not stored. This technique requires less processingpowerduetosmallerindexesandlessnumberof comparisons.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
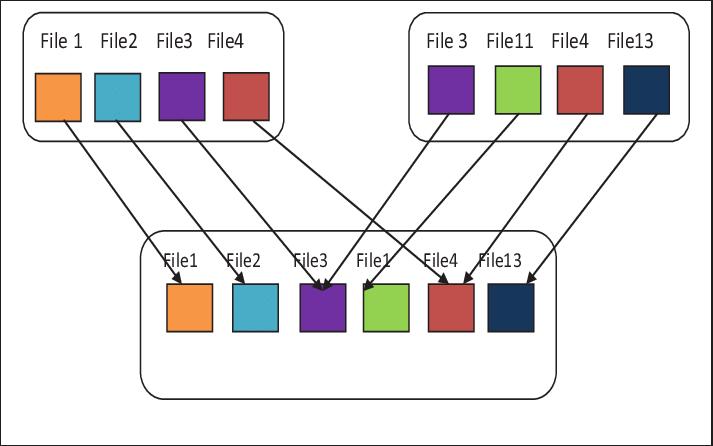
The time required for computation is less. The main big advantage of file level de duplication is that it requires less resources but it also has a major drawback that it cannot eliminate smaller redundant chunks of data. Hashing algorithms like MD5 or SHA 1 are used for calculating the hash of file and then comparing hash values to find the duplicates.
Block level de duplication works on sub file level. In this, a fileisbrokenintochunksorblocksthatarethencheckedfor redundancy with previously stored information. For this hashingalgorithmisthebest.Usingthehashingalgorithm,it creates a unique id or fingerprint for each block. If the id existspreviouslythentheblockisalreadyprocessed.
The size of block depends on different peoples. Some may havefixedsizeblockandsomehavevariable sizeblock.For fixedblocktheusualsizeis8KBor64KB.Smallerblocksize has more probability of finding the redundancies. This meansverylessstoragespaceisrequiredasthereisalmost noduplicatesavailableafterprocessingthedata.Thereisan issue with this fixed size blocks that if a file is updated and thesystemusesthesameoldblocksofdatathenitmightnot detectanyredundancy.
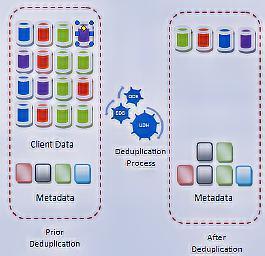
Thevariablesizesofblocksusedinvariable sizedblock de duplicationcreatesconfusion.Thisapproachcanfind redundantdataevenifthefileisbeenshiftedtoanother place.Thereishighde duplicationratioascomparedto file basede duplication.
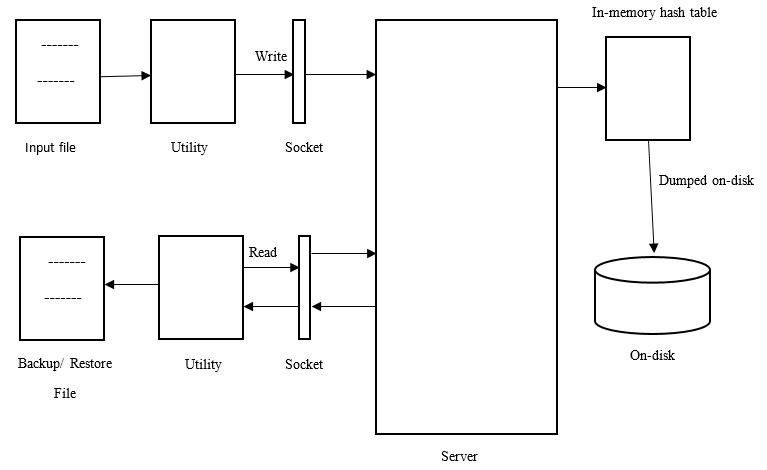
For implementing de dupe engine for files with de duplicate data, we established client server communication using sockets for inter process communications. We first created server that will be a daemon process. When client requests server to fulfill its requirements, server receives those messages through sockets. Thus, server could bind and listen to client before accepting the client requests. The messages betweenclientandserveraresimultaneously stored at log file created. The client utility is basically a process that could parse user entered arguments and performactionsaccordingly.Ourimplementationisable to parse arguments that could either be name of input fileornameofoutputfile.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
calculated. Checksum is calculated using md5sum checksum algorithm. Since each unique chunk has unique checksum, and duplicate chunks have same checksum being calculated, we will be using this fact of matter during our project implementation. We search thatchecksuminin memoryfingerprint.
Theinputfileisusedbyclientforaskingtheserverto fulfill its different kind of requirements for the given file. The requirements(tasks)mayinclude: identifyinguniquechunksofdata,
writingtheuniquechunksanditsrelatedinformationto metadatafile,
incrementing the reference count of any duplicate chunksinthemetadatafileatthe
correspondingmetadataposition,
creating backup file for original file using only the metadatafilecreatedabove.
The output file name is given so that it is used to read or restore from metadata created. The in memory fingerprint is dumped on disk, which is referred to as metadata file. Dumping is done to have the in memory fingerprints available for reference all time. The metadata is essentially anarrayofuserdefinedstructurenamelyde dupefootprint. Theelementsofthisstructureare:
databuffer
datalength
datachecksum
referencecount
dedupeoffset
submeta (sub structure which includes the elements filenameandoffset)
next pointer referencing this structure type itself (for purposeofaddingstructuresdynamically)
Suppose client utility wants to write a file, server process readthatinputfileinchunkof128KB.Whilereadingthefile frombeginning,thefirst128KBdataisreadandstoredinto data buffer, which forms our chunk that we are stating throughoutproject.Thechecksumofthisdatachunkgets
At the start the first data chunk will be unique with its respective checksum. This checksum is also used to determine the hash index position in the in memory fingerprint and metadata file. The remainder obtained ondividingthechecksumvaluebythehashtablesize,is usedasourhash index positionwherethedata andthe metadataofthechunkgetsstoreddirectly.
Aswemovefurthertoreadnext128KBofdata,wemay facefollowingsituations:
1. The checksum of this data chunk is found in the in memoryfingerprint
In this case, data and metadata of this duplicate chunk is not stored, just the reference count of respectivemetadatawillbeincremented,itsde dupe offset will be stored and submeta for additional informationoftheduplicatechunkwillbeupdatedin the in memory fingerprint as well as metadata file for backup or restore purpose. This optimizes the storagespaceandcost.
2. The checksum is not found in the in memory fingerprint but hash index calculated will be one whichisoccupiedbymetadataofearlierchunks
Inthiscase,thechunkisunique,butsincehashindex positionisalreadyoccupied,itwillappendthisnode of metadata to the previous node at that particular hash index using its next pointer, in the in memory fingerprintaswellasinthemetadatafile.Thisallows dynamic insertion of data structures and optimize spacebyeradicatingtheuseofstaticstructureswith largehashindexvalues.
3. The checksum is not found in the in memory fingerprintaswellashashindexwillbeonewhichis unoccupied
In this case, the chunk is unique as well as its hash index position is unoccupied, so the data of this chunkanditsmetadatacanbedirectly storedatthis hash index position of the in memory fingerprint as wellasofthemetadatafile.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
Whateverthedataremainingatend,whichmaybelessthan 128KB are stored in metadata file along withits respective metadata,similarly.
Thus, the complete data file is read and simultaneously its chunks are searched and identified if duplicate or not, and insteadofstoringeachchunkinsystemandoccupyingmore storage space, we use it to create metadata that optimizes storage space as well as cost. This could also be used for backup purpose, when original file contents may be lost. This is done by creating a restore file that completely replicates the original file, without any data loss, by only usingthismetadatafilecreated.
Therestorefileiscreatedasdescribedbelow: The particular filename in in memory fingerprint is searched for and matched with filename of original file of whose restore file is to be created. If found, we look for the corresponding offset and accordingly write the corresponding complete data from its data buffer at the offsetpositioninrestorefile.Thefilenameandoffsetofnext nodeinin memoryfingerprintissearchedandwrittentoits restorefileatparticularoffsetinsimilarway.Thisisdonein iteration until complete restore file is written of original inputfileiswritten.
Thus, we used de duplication technique with fingerprinting phenomenonisusedtowritede dupedmetadataforbackup and storage efficiency purposes, and log files for referring thecommunicationbetweenclientandserverprocesses.
Forinitialtestingofcode,a largetextfile ofsize50 MB was taken onto the system which is having LINUX environment (Ubuntu). For ease, we took small portion of this file of around 1 MB which also includes duplicate data portions insideit.Ourtask wastoperformblocklevelde duplication over this file. We divided this file into fixed size chunks or blocksofdataofsize128KB,performedhashingoverthese chunksandstoredtheresultanthashvalueintothememory.
We used MD5 hashing algorithm for generating the checksum. This checksum will be unique for every unique chunk. Small changes to any particular block of data or chunk produces different checksum that is uncorrelated withitspreviouschecksum.Thus,weverifiedthataddingor deleting some portion of data into the file at some places, producesdifferentchecksumandassuredthatthealgorithm performed well cryptographically. Thus, the chunks are
produced in the cryptographic algorithm to yield a correspondingchecksumordigitalprintforit.
Because of the hash properties each and every block maintainitsuniqueidentifierifthoseblocksareunique,that is, there is no any duplication. If the block is repeated, we canidentifyiteasilywiththehelpofitsrepeatedchecksum. Using this principle, only the unique blocks are saved into the hard disk or secondary memory, and its metadata is created into the hash table with its reference count of occurrence. This hash table is implemented using arrays of linkedlistandthenodesoftheselinkedlistbeingstructures thatrepresentsthemetadata.
Even though, same hash index is generated from any hashing formula for two or more chunks, its checksum will be different for different chunks. Thus, metadata of these chunks will be stored at same index in the hash table array withthehelpoflinkedlistattheparticularindex.
If duplicate chunks are already present in the memory, according to user requirement we have implemented function to search and delete those duplicate chunks, and corresponding changes are made to the hash table. Such kindofhashtableisdumpedintotheharddiskorsecondary memory, which is then used by the client server architecturemodel.
Intheclient servermodel,theserveracceptsandprocesses the requests from clients, with the help of sockets. Sockets actascarrierofutilityrequestsandrequiredinputsbetween clients and server, which are requested by clients. Server accepts and performs the utilities with the help of the hash table in hard disks, and successfully returns the result to clients. Server thus acts as daemon process in this architecture which continuously feed utilities to clients when requested. Thus, we aim to perform block level de duplicationwiththehelpofclient serverarchitecture.
Intheresults,wefoundthatafterde duplicationprocessthe read/write time required for a particular time is decreased. Forthis,wetooktextfileoffewkilobytes(KB).Wechunked it and created a metadata in hash table and dumped it into memory.Thein memoryfingerprintofhashtableisusedfor maintainingtherecordsevenaftertheprogramtermination. The server can read data from this file and create a restore fileifthereisanydatacorruptionordataloss.
Asthechunksareofsmallsize,duplicatedataidentification isdoneonlargescale.Itisverydifficulttoidentifyduplicate data in a larger chunk size. Also, for future use if the client
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
requiresonaspecificdatachunkthenonlythatcanbesend. Thisalsorequireslessbandwidthandtransmissiontime.
Theclient servercommunicationallowsmanyclients/users to connect at a time with the single server. Simultaneous read/write processes can be done. This saves time of users andthereisusersatisfaction.Thechecksumalgorithmhelps to detect if the data is corrupted or not. Fingerprints are veryusefultoidentifytheduplicatedatachunks.Theywork asuniqueidentifiersforeachuniquechunk.
Hence, we can measure de duplication engine performance based on time and space. It can be used for backup and restoreofdata.Inbigorganizations,the performanceof de dupeenginewillhelpgainmoreprofit.
Data storageisimportantissue.Manyindividualsaswell as organizations face this issue. There are many ways for storagewhicharen’tcosteffective.Alsothemethodsshould bereliable.Thedatamustremainsafe.Duetobigdatathere isproblemofnetworktraffic.Duetomultiplecopiesofsame data there is a lot of confusion between employees and end consumers.
Data de duplicationis efficient way for storing backups and big data. De duplication reduces the space required for the storage. As the space is reduced the cost also reduces. The problem of network traffic reduces and bandwidth wastage for transferring the data is also reduced. As de duplication cleans the data and stores only the unique copies of data, productivityincreases.
Also the brand reputation is intact as there is no confusion for end consumers. Time is saved to greater extent and can be utilized for more creativity and productivity rather than cleaningdatamanually.
In the future, we will add an important module of deleting the duplicate chunks from the input file and receive a file without duplicate data. This will reduce the storage space requiredandreducetheread/writetimerequired.
To complete any type of project work is team work. It involves all the technical/non technical expertise from various sources. The contribution from the experts in the formofknows howandothertechnicalsupportisofitsvital importance. We are indebted to our inspiring guide Prof. A.V. Kanade and our project coordinator Prof. Dr. K.A.
Malgi. Wearethankfulto Mr. Swapnil Ujgare forguidingus in technical coding part of the project and for lending supportthroughouttheproject.
We are also very thankful to Prof. Dr. D. A. Godse for her valuable guidance. We have great pleasure in offering big thanks to our honorable principal Prof. Dr. S. R. Patil. Last but not least, we would like to thank all the direct and indirecthelpprovidedbyallthestaffandourentireclassfor successfulcompletionofthisproject.
1. E.Manogar,S.Abirami,InternationalConferenceon Advanced Computing (ICoAC), “A Study on Deduplication Techniques for Optimized Storage”, 2014.
2. Wen Xia,HongJiang,DanFeng,FredDouglis,Philip Shilane, Yu Hua, Min Fu, Yucheng Zhang, Yukun Zhou, “A Comprehensive Study of the Past, Present and Future of Data Deduplication”, IEEE 2016, Vol. 104.
3. ZhouLei,ZhaoXinLi,YuLei,YanLingBi,LuokaiHu, Wenfeng Shen, “An Improved Image File Storage MethodUsingDataDeduplication”,IEEE2014.
4. Chao Tan, Luyu Li, Chentao Wu, Jie Li, “DASM: A Dynamic Adaptive Forward Assembly Area Method toAccelerateRestoreSpeedforDeduplicationbased Backup Systems”, published by Springer InternationalPublishingAAG2016.
5. Panfeng Zhang, Ping Huang, Xubin He, Hua Wang, Ke Zhou, “Resemblance and Mergence based IndexingforHighPerformanceDataDeduplication”, Journal of Systems and Software, Science Direct, 2017.
6. Meyer D. T., & Bolosky W. J., “A Study of Practical Deduplication”, ACM Transactions on Storage, 7(4), 1 20.doi:10.1145/2078861.2078864
7. Ahmed Sardar M. Saeed, Loay E. George, “Fingerprint based Data Deduplication Using a Mathematical Bounded Linear Hash Function”, Symmetry2021,13.
8. Dutch T. Meyer, William J. Bolosky, “A Study of Practical Deduplication”, ACM Transactions on Storage,Vol.7,No.4,Article14,January2012
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

9. https://linux kernel labs.github.io/refs/heads/master/lectures/intro.ht ml 10. https://www.tutorialspoint.com/unix/unix file system.htm 11. https://github.com/libfuse/libfuse 12. https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/filesyste ms/fuse.html 13. https://docs.microsoft.com/en us/windows server/storage/data deduplication/overview 14. https://opensource.com/article/19/4/interprocess communication linux networking 15. https://beta.computer networking.info/syllabus/default/exercises/socket s.html
16. https://vdc repo.vmware.com/vmwb repository/dcr public/c509579b fc98 4ec2 bf0c cadaebc51017/f572d815 0e80 4448 a354 dff39a1d545e/doc/vsockAppendix.8.3.html





17. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyclic_redundancy_c heck#:~:text=This%20is%20a%20practical%20alg orithm,%C2%A7%20Multi%2Dbit%20computation ).
18. https://www.thegeekstuff.com/2012/02/c daemon process/
Ms Kajol Pawar is perusing B.E (IT) from Bharati Vidyapeeth College of Engineering for Women, Pune and presently is in FourthYear.





Ms. Vrushali Phatale is perusing B.E.(IT)fromBharatiVidyapeeth College of Engineering for Women, Pune and presently is in FourthYear
Ms Ranu Kumari is perusing B.E (IT) from Bharati Vidyapeeth College of Engineering for Women, Pune and presently is in FourthYear
Mrs A.V. Kanade is working as a assistantprofessorindepartment of IT, Bharati Vidyapeeth College ofEngineeringforWomen.
Mr. Swapnil Ujgare is currently working as Software Engineer in VeritasTechnologiesLLC.