International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
Richa Upadhyay1, Er. Peeyush Gupta2, Dr. Sudhakar Shukla3
Richa Upadhyay1, M tech in RS& GIS Remote Sensing Application Centre, U.P, India Er. Peeyush Gupta2 , RTIS, NMCG, Ministry of Jal Shak Dr. Sudhakar Sukla3, Scientist SE& Head of School of Geoinformatics, Remote Sensing Application Centre, U.P. India ***
The Ganga River is a major river in North India known for its fertile alluvium deposits formed by floods in the Indo Gangetic plains. Many scientists have conducted flood frequency analysis on the Ganga River using various approaches. With changes in river beds caused by anthropogenic changes, the intensity of floods hasalsochanged in the last decade, necessitatingfurtherresearch.
In recent years, the US Army Corps of Engineers Hydrologic Engineering Centres River Analysis System (HEC RAS) hydraulic model and Remote Sensing (RS) technology, in conjunction with Geographic Information System (GIS), have becomecriticalfloodmonitoringtools.Theprimaryfocusinthisfieldisthedelineationoffloodzonesandthecreationof flood hazard maps for vulnerable areas. GIS software Arc GIS and HEC Geo RAS, as well as hydraulic software HEC RAS, areusedtoanalyzeriverflowandcreatefloodhazardmaps.
A method for delineating river system floodplains using direct processing is developed. The first goal was to build and validatearivernetworkmodelofthesystemusingexistingHEC 2model generateddatafromtheHydrologicEngineering Center's River Analysis System (HEC RAS). Haridwar is one of the first towns where the Ganga emerges from the mountainsandreachestheplains.Followingthat,HEC RASsimulationswereruntogeneratewatersurfaceprofilesacross the system for six different design storm events. The HEC RAS in channel spatial data were then geo referenced and mapped in the GIS domain before being combined with digital elevation model (DEM) over bank data to create a triangularirregularnetwork(TIN)model.
The goal of this research is to use the most recent version of HEC RAS to model 1D hydrodynamic floods in the Ganga RiverinHaridwarDistrict,Uttarakhand,India,withafocusongeospatialapproaches.
Keywords:TriangularIrregularNetwork(TIN),HEC RAS,Riverflowanalysis
HEC RAS can perform alluvion mapping of water face profile results directly from HEC RAS. Using the HEC RAS figure andreckonedwaterfaceprofile,alluviondepthandlowlandboundarydatasetsarecreatedthroughtheRASMapper.To useRASMapperforanalysis,youmusthaveaterrainmodelinthedoublerasterfloating pointformat.
The USACE created HEC RAS to cover and control gutters, conduits, harbors, and other public workshop systems. Simulationssimilarasone dimensional steadyinflow, one andtwo dimensional unsteady inflow,deposition transport, bed calculations, and water temperature/ water quality models are each available using the HEC RAS program. This modelismoregenerallyusedtoexaminerivuletencroachmentsinlowlandoperationandfloodtideinsuranceexploration. Land use change is another element that could impact the circumstance of cataracts as well as the growth of socioeconomic exertion in flood tide prone areas. similar conduct has an impact on a swash's natural hydrology and floodplains' response to a flood tide hazard. These motorists aren't completely preventable due to their complexity. It's nevertheless effective flood tide threat operation strategies with information about the hazards are enforced, and it's possibletoalleviatetheassociatedtroubles.TheHydrologicEngineeringCenterRiverAnalysisSystem(HEC RAS)model wasusedtoexaminetheperformanceoftheoriginal(baseDEM)andmodifiedDEMsascrucialinputs.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

River hydraulic models similar as HEC RAS contain a wealth of detailed terrain data, generally developed from land checks. But these high resolution data are frequently stored in the match system of the hydraulic model, a format that doesn't maintain the (X, Y) chart equals of the cross sections. The primary difficulty with mapping hydraulic model data similarasHEC RASstemsfromthefactthatCiviliansandhydraulicmodelsgenerallyuseentirelydifferentmatchsystems to define their data. HEC RAS is a 1D inflow model in which the sluice morphology is represented by a series of cross sectionslistedbyaswashstation.Theswashstationnumberingincreasesfromdownstreamtoupstream.
ForconnectinghydraulicmodelingwithCivilians,numerousofthesesoftwareresultsfollowananalogousthemesampling parameters that are recaptured from a terrain model and integrated into a hydraulic model. The affair of the hydraulic model is reused for display and analysis in a Civilians once the stoner runs it. still, as the source of input sampling descriptions,thisfashionrequiresahigh resolutionDEM.Unfortunately,DEMswithsuitableresolutioninsluicechannels forhydraulicmodelingisn’tconstantlyavailableandmustgenerallybeattainedbyremoteseeing.likewise,thesestudies are unfit to gather precise topographical data for locales that are constantly swamped by water and must calculate on bathymetric biographies attained through land checks to condense their findings. As a result, a system for combining availableDEMswithbeingsurveyedchannelelevationshasbeendeveloped.
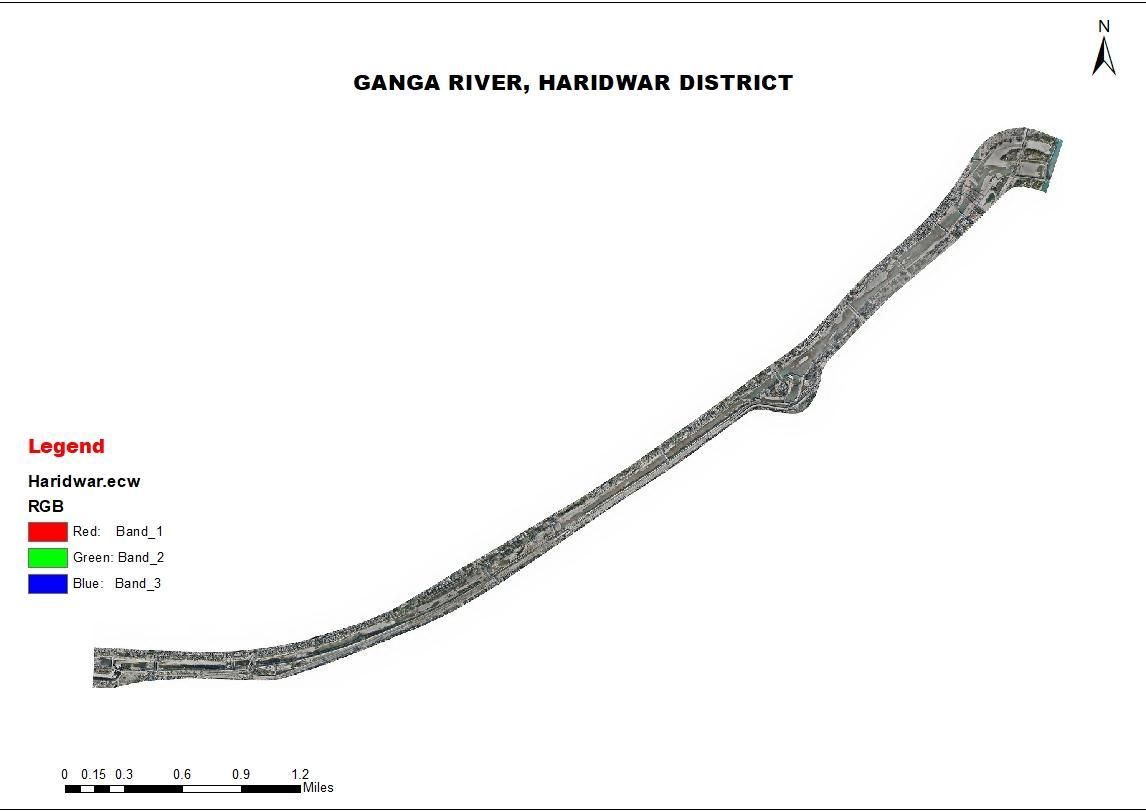
Thestudy was carriedout inGanga River,Haridwar,Uttarakhand. Thisstudywasdone tocheck the waterflow analysis. Haridwar'slocationdenotesthenorthIndiancity'sgeographicallocation,andit’sknownforthegreatsourceofthenatural resources. Haridwarsituatedat thelatitudedistanceof 29°58'N tothelongitudinal of78°10'E, surroundinga regionof 2,360sq.km.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
DOWNLOADED 30m(resolution) DEM OF THE AREA FROM BHUVAN AND THEN IN ARCGIS CLIPPING ACQUIRED DEM.

THEN CLIPPED DEM IS CONVERTED INTO TIN IN ARCGIS (BY CONVERSION TOOL)
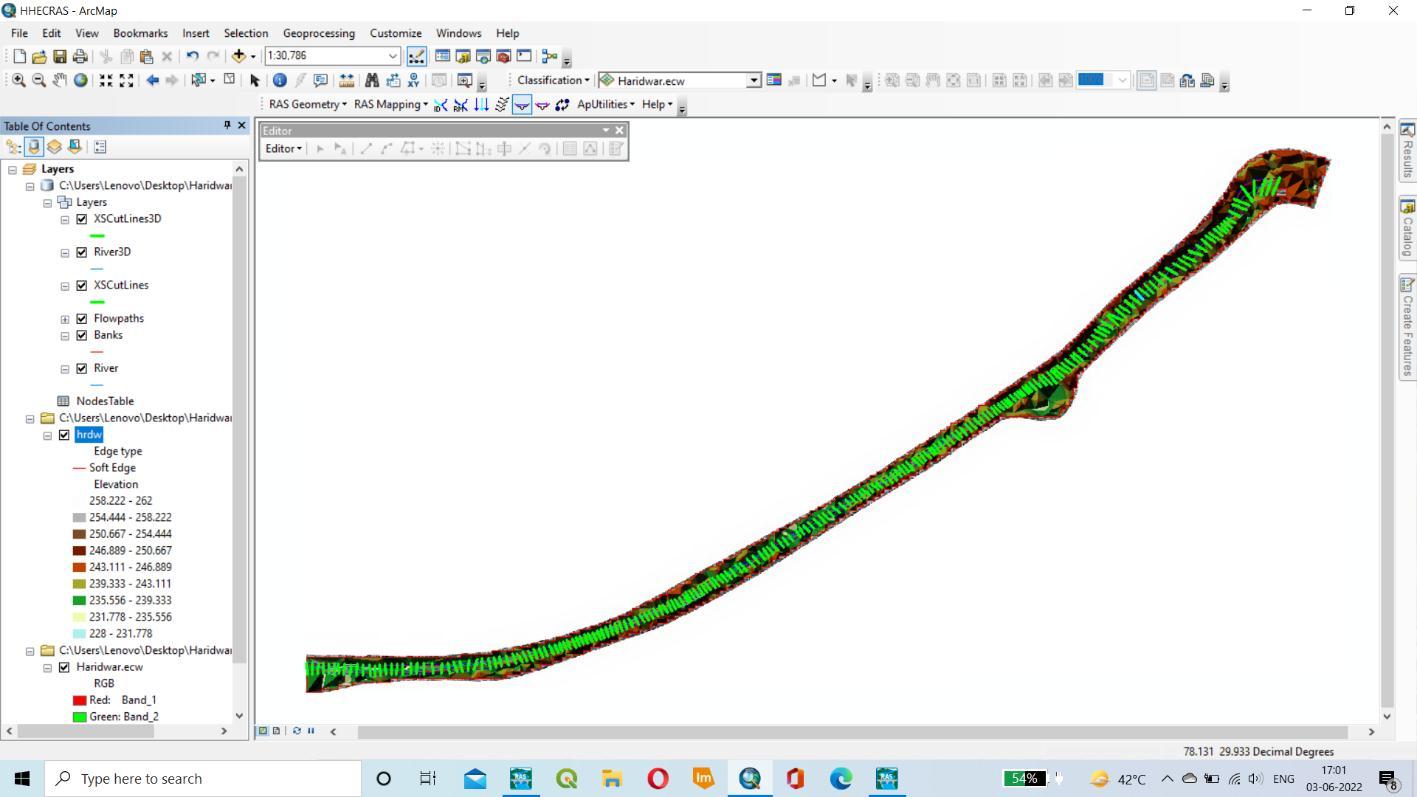
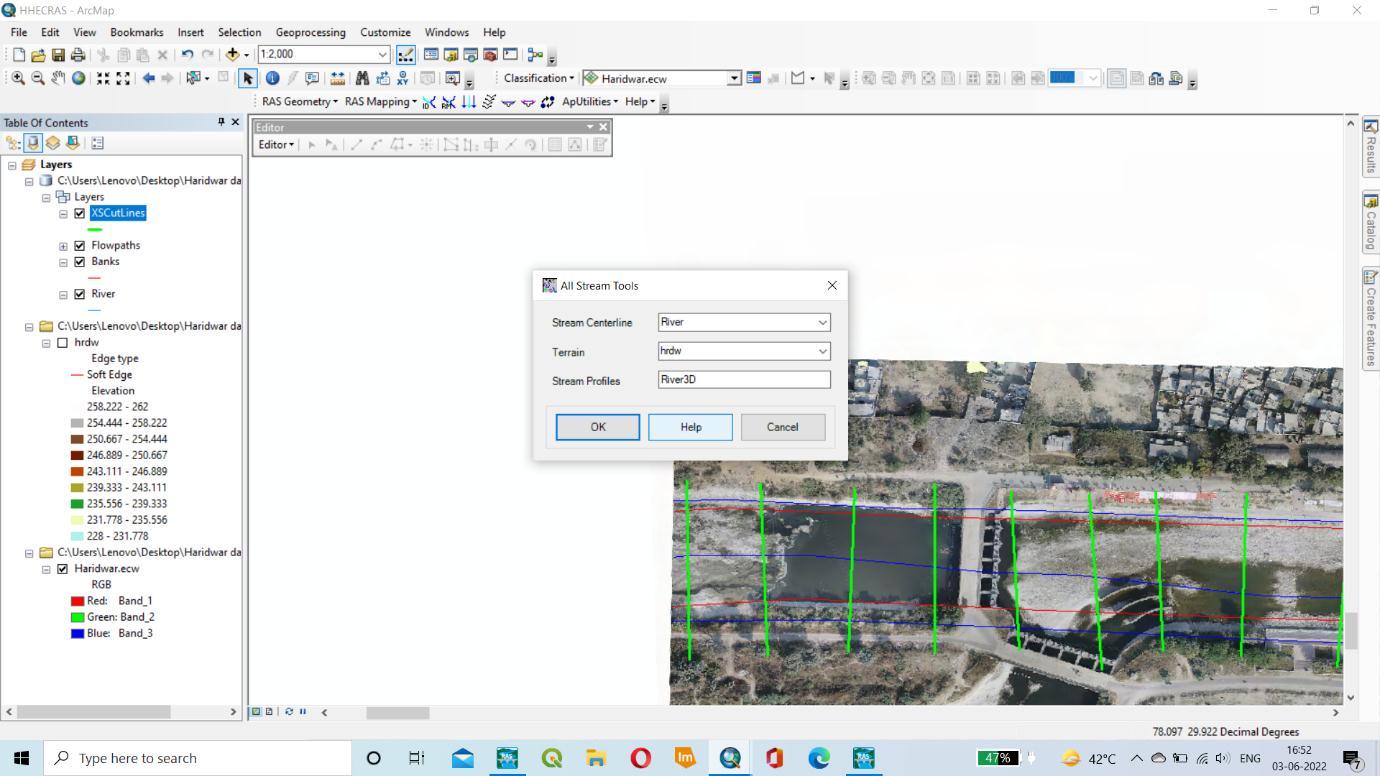
AFTER THAT BY CREATING THE RAS LAYER IN THAT STREAMLINE, RIVER, BANK LINES, FLOWPATH, AND XS CUTLINES ARE CREATED.
BY SELECTING THE STREAMLINE ATTRIBUTES AND ALL CROESS SECTION TOOLS. ITS USED TO RECHECK OUR PROCESS. AFTER THAT EXPORT OUR RAS DATA INTO GIS.
NOW IN HEC-RAS IN THE FILE ADD OUR EXPORT DATA AND SAVE THE GEOMETRY DATA. THEN IMPORTING THE DATA, FINALLY FLOW DIRECTION, DOWNSTREAM, AND CROSSSECTION ARE CREATED.




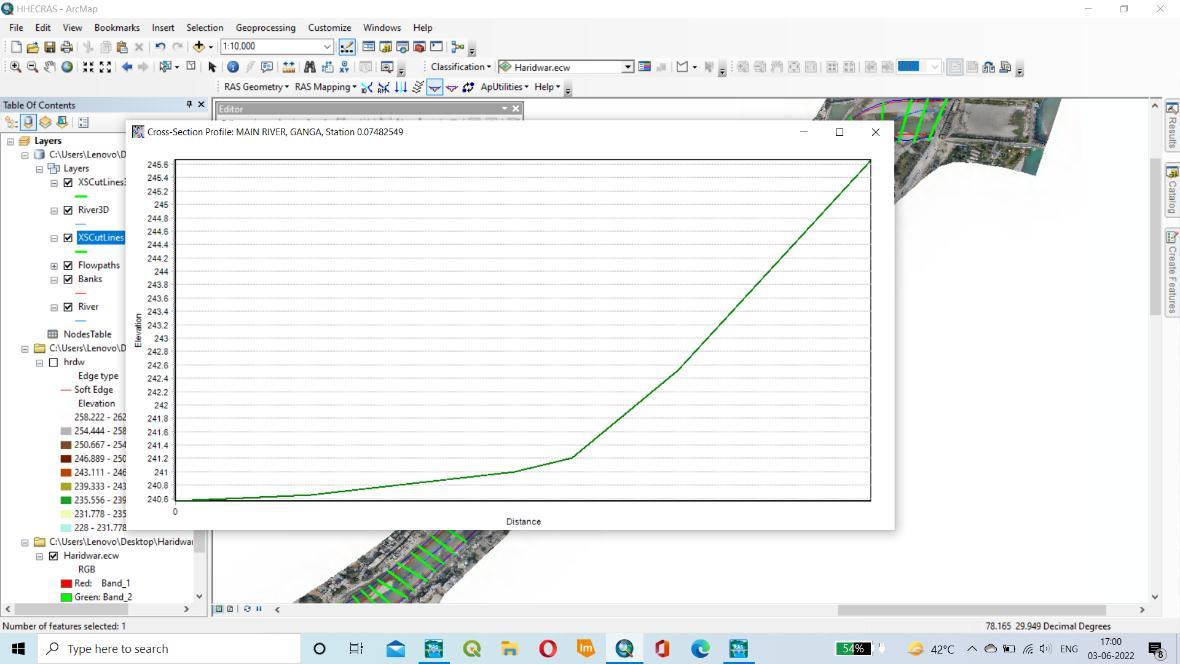
TINisusedastheprofilecreationinputdata.ItcomesfromCartoDEM(30m).TheHEC RASmodelwasusedtocreatethe profiles.ThelongitudinalprofileofaGangaRiver,HaridwarDistrict,Uttarakhand.Thisisgeneratedovertimeasaresultof erosionanddepositionalongtheriver'scourse. AGangariver’slengthyprofileisusuallyasmoothcurve.Theprofileofa riverissmoothanddoesnotshowthevariationsinthecross sectiongraph.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
ThisresearchlookedDEMs(derivedfromBhuvan)affecthydraulicmodellingresults.Thestudyalsofoundthatthequality andaccuracyoftheDEMaremoreimportantthanitsresolutionandprecisioninsupportingfloodinundationmodels.For example, the model is based on the 30m DEM These outcomes are inextricably linked to the particular test. The methodology described here, on the other hand, can offer a comprehensive examination of the impact of various topographydataonfloodhydraulicmodellingforvariousriversaroundtheworld.
A Bharath, Anand VShivapur, CGHiremath, Ramesh Maddamsetty, “Dam break analysis using HEC RAS and HEC GeoRAS:AcasestudyofHidkaldam,Karnatakastate,India”,ScienceDirect,EnvironmentalChallengesVolume5, December2021
BennettTH,WaltonR,DickersonPD,HowardJW.ComparisonofHEC RASandMIKE11unsteadyflowmodeling fortheTillamookValley.Bridges.2004.
BrunnerGW.HEC RASRiverAnalysisSystem.HydraulicReferenceManual.Version4.1.Davis,CA:USArmyCorps ofEngineers,InstituteforWaterResources,HydrologicEngineeringCenter;2010
Brunner GW. HEC R AS River Analysis System: User’s Manual. US Army Corps of Engineers, Institute for Water Resources,HydrologicEngineeringCenter,Davis,CA;2001.
FanC,KoC H,WangW S.AninnovativemodelingapproachusingQual2KandHEC RASintegrationtoassessthe impactoftidale ectonRiverWaterqualitysimulation.JEnvironManage.2009;90(5):1824 1832
Goodell CR. Dam break modeling for tandem reservoirs a case study using HEC RAS and HEC HMS. Paper presentedatImpactsofGlobalClimateChange,Salem,OR;2005.
Gee MD, Bru nner GW. Dam Break Flood Routing Using HEC RA S and NWS FLDWAV. ASCE/EWRI. American SocietyofCivilEngineering (ASCE),St.,Davis,CA;2005.
Kotal, S.D., et, al. 2014. Catastrophic heavy rainfall episode over Uttarakhand during 16 18 June 2013, observationalaspects.CurrentScience,107,2,234 245.