COMPARISON OF ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF REGULAR AND IRREGULAR CONFIGURATION OF MULTI-STORY BUILDINGS IN VARIOUS SEISMIC ZONES AND VARIOUS TYPES OF SOIL
Sahil K Nayab1 , Dr.Santosh.K.Patil2 , Dr. Atul B. Pujari31PG Student, Department of Civil Engineering KJCOEMR, Pune, Maharashtra, India

2HOD, Department of Civil Engineering KJCOEMR, Pune, Maharashtra, India
3Professor, Department of Civil Engineering KJCOEMR, Pune, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract – Today's world faces some of the major problems caused by nature. One of the biggest natural disasters is earthquakes. Multi story RC construction, subject to the most dangerous earthquakes. It has been found that the main reason for the decay of RC buildings is the incorrect distribution of mass, stiffness, and strength and due to incorrect geometric configurations and different types of soil. Due to improper construction of the plan, the settlement is also diverse compared to the construction with the correct shape.
However, previous records of earthquakes show poorseismiccharacteristicsofthestructure.Thisisdueto ignoranceoftheaspectofirregularityintheformulationof methodologiesforseismicdesignthroughseismiccodes(IS 1893: 2002). These analyzes are performed by examining multi storyG+11buildingswithdifferentseismiczones3 and4andforeachzone,thebehaviorisassessedbytaking twodifferentsoiltypes,namelysolidandmediumdifferent reactionssuchasplotdeviation,displacementandbaseline shear are applied to different zones and different types of soils from the seismic regulations proposed in IS 1893 2002, using the equivalent static method and software STAADProV8i.
Key Words: Regular and irregular configuration, static analysis
1.INTRODUCTION
Much of India is vulnerable to damaging levels of seismic hazards.Soitisnecessarytotakeintoaccounttheseismic load when designing the structure. In buildings, lateral loads due to earthquakes are a problem. These lateral forces can cause critical stresses in the structure, cause unwanted vibrations or cause excessive lateral rocking of the structure. The swing or drift is the amount of lateral displacement in the upper part of the building relative to itsbase.
The limit state may correspond to the intensity of the earthquake, equal to the strongest experienced or predicted at the site. In the present study, the results wereexaminedforequivalentstaticload.
NowthedailypopulationofIndiaisincreasingdaybyday, therefore the demand for buildings, houses and apartments in row houses is also increasing. Due to the larger population, tall buildings are being built. While the construction of tall buildings, some factors are influenced bythebuildingsuchassoillayersorsoiltype,earthquake zone,windload,etc.Sideforcesforcethebuildingtomove or shake, which is why earthquake analysis is much more importantinhigh risebuildings.
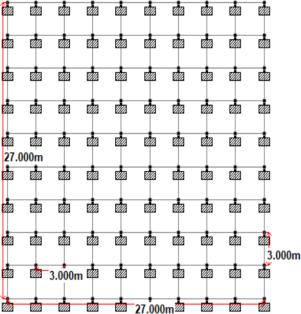
The forces of the earthquake are arbitrary and unpredictable, and static and dynamic analysis of the structure has become a major concern of civil engineers. The main part of a multi story building is the column, the beamandthefoundation.Inourproject,weanalyzeG+11 buildings in different earthquake zones with different types of soils (medium, hard) with different irregularities in the plan such as rectangular, c shaped, and l shaped buildings. SBC for medium soil is 245 KN.M ^ 2, and for hardsoilisfrom300KN/M^2to440KN/M^2.
BUILDING DETAILS:-
Numberofstories:11
Columnsize300mmX750mm
Heightofatypicalfloor:3m
Beamsize:300mmX450mm
Platethickness:125mm
thickness:230mm,150mm,100mm
Liveload:2Kn/m2
Floorcovering:1Kn/m2
Steelgrade(Fe):500N/mm2&415N/mm2
Densityofconcrete:25N/mm2
allcolumnsarefixedatthebase.
Densityofbrickmasonry:20KN/m2
Ratioofpoisonsinconcrete:0.3
Ratioofbricksofbrickwork:0.2
Modulusofelasticityofconcrete:2500N/mm2.
BUILDING FORM:
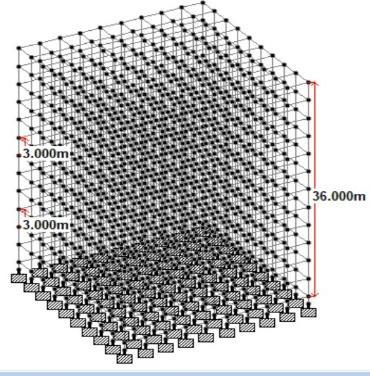
Rectangular building: Inabuildingwitharegularshape, thenumberofbaysintheXandYdirectionsis9.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
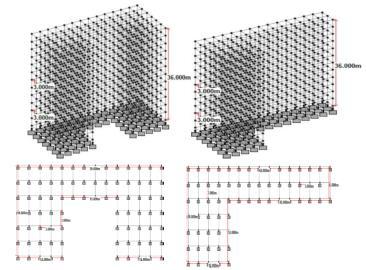
C shaped building: The socket number in the X directionis13andthesocketnumberinthezdirectionis 6.
L-shaped building: - The socket number in the X direction is 14 and the socket number in the Y direction is6.
2. METHODOLOGY
Seismic weight of the building: Theseismicweightof the construction tools is calculated on the total floor weightofthe building.Basic natural periodaccording to IS1893(part1):2002.
Theapproximatebasicnaturalperiodofvibration: Ta=0.075h^0.75forabuildingwithanRCframe Ta=0.085h^0.75forabuildingwithasteelframe Billy,h=heightofthebuilding. LOAD COMBINATIONS:
LOAD CASE DETAILS:
Earthquake load: TherearetwotypesofearthquakesintheX andZdirectionsdirection(i.e.EQXandEQZ). Fig4&5 EARTHQUAKELOADINXANDZDIRECTION
Dead Load: Self weight:Automaticallydefinedbysoftware. Wall Load:
ExternalWall:20x1x0.23x3=13.8kN/m
InternalWall:20x1x0.15x3=9kN/m
ParapetWall:20x1x0.1x1=2kN/m Fig6&7.DEAD&WALLLOADINXANDZDIRECTION
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
1.2(DL+LL±EQZ)
1.5(DL±EQX)
1.5(DL±EQZ)
0.9DL±1.5EQX
0.9DL±1.5EQZ
875(Part2):
figno11.
Output for analysis and design in STAAD pro: Afterentering all values and some values are automatically taken from on software such as own weight, SBC on soil, etc. After this, ontheresultisgivenbelow. Fig12
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
Figno13
3: RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Hardsoil
Shape/Direct ion/Zone
Rect. shape C shape L shape
X dir. Z dir. X dir. Z dir. X dir. Z dir.
Zone 3 24.23 43.78 25.93 47.05 25.17 55.90
Zone 4 36.29 65.63 38.82 70.43 37.70 83.81
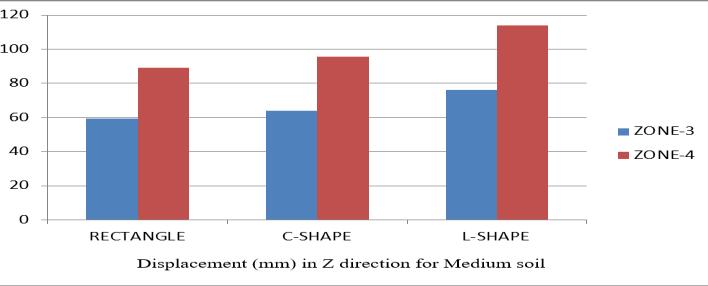
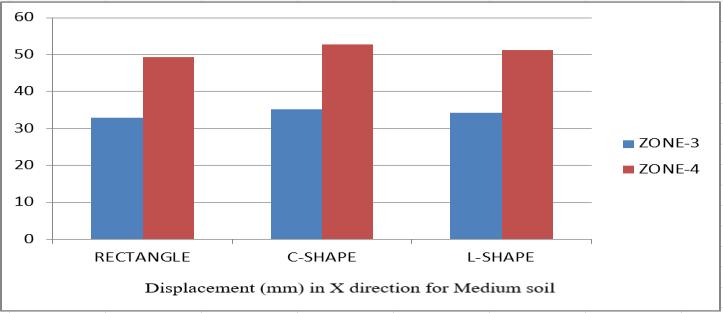
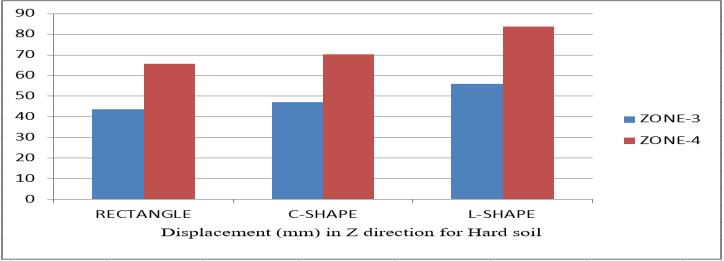
Table1 COMPARISONOFLATERALDISPLACEMENTINX AND ZDIRECTIONINHARDSOIL.
Shape /Direc tion
Medium soil Rect. shape C shape L shape
X dir. Z dir. X dir. Z dir. X dir. Z dir.
Zone 3 32.91 59.52 35.21 63.88 34.19 76.00
Zone 4 49.32 89.24 52.74 95.69 51.24 113.9
Table2 Comparisonoflateraldisplacement(mm)inXandZ directionforMediumsoil chart 12
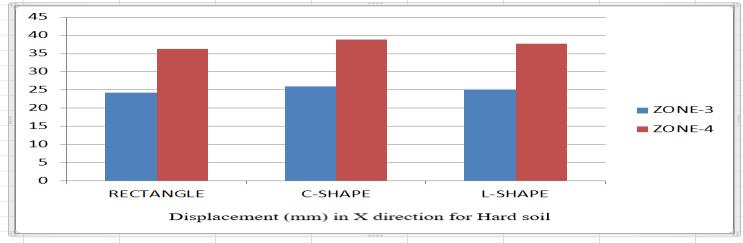
1. The above diagram and table show the X and Z offset for MeanandHardsoil.
2. I can observe that displacement in Z direction is bigger than on displacement in direction X for medium and hard soil.
3. For solid soil type, the displacement is 30.14% minimum comparedtotheaveragetypeofsoil.
4. Given the solid soil, the more stable or minimal displacement of the shape of the building is a rectangle and maximum displacement in an L shaped building. Andalsothesameformediumsoil.
5.Alsoweobservethatondisplacementinzone3is16.95% minimumanddisplacementinthearea4eMore▼inthe XandZdirections.
Base shear: Thefollowingtableshowsthevalueofbaseshear in hard, medium soil and zone 3, zone 4. The values of base shear in the X and Z direction are the same as per software output.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

STEEL PERCENTAGE:
Zone/So il/ shape
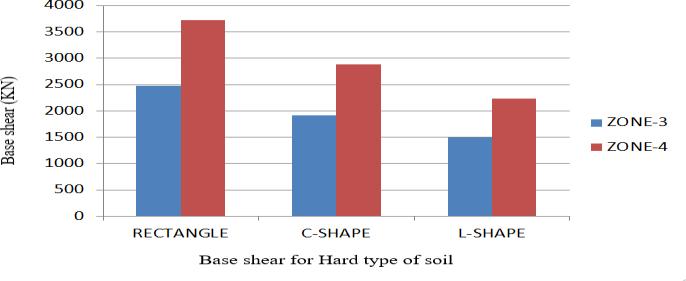
HARD SOIL Rec. Shape C Shape L Shape Zone3 2480.09 1918.34 1491.69 Zone4 3720.13 2877.50 2237.53
Therequirementofsteelforallbuildingsisgiveninthebelow table
Zone/Soil /Shape Hardsoil Rec.Shape C Shape L Shape Zone3 14.19 7.42 14.08 Zone4 14.21 14.12 14.11
Table9.Comparisonofsteelpercentage(%)forHardsoil
Chart13ComparisonofBaseshearinXandZ direction forhardsoil
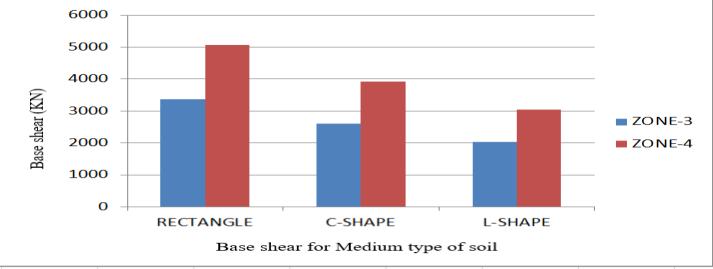
Zone/Soil /Shape Medium soil Rec.Shape C Shape L Shape Zone3 3372.92 2608.94 2028.69 Zone4 5059.38 3913.41 3043.04
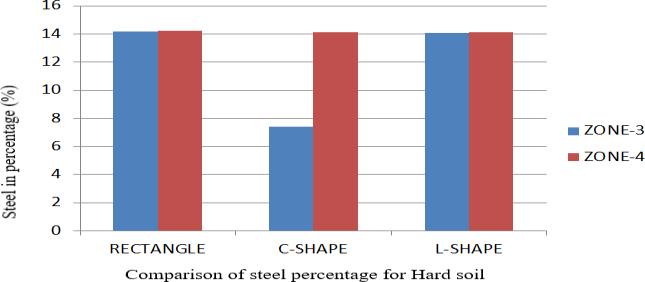
Chart7.Comparisonofsteelpercentage(%)forHardsoil
Comparison of steel percentage (%) for Medium soil
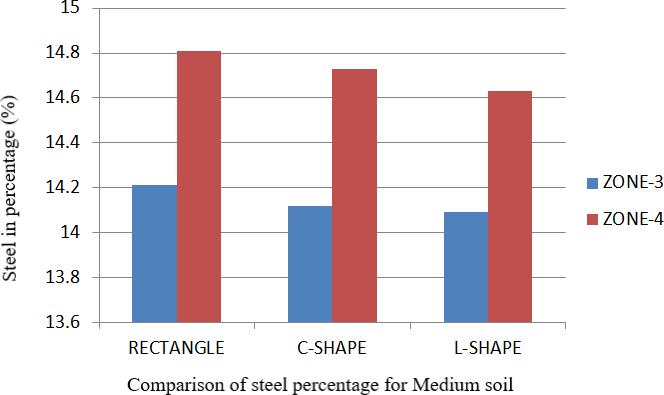
Zone/Soil /Shape Mediumsoil Rec.Shape C Shape L Shape
Zone3 14.21 14.12 14.09 Zone4 14.81 14.73 14.63
Table9.Comparisonofsteelpercentage(%)formediumsoil
chart14.ComparisonofBaseshear inXandZ direction formedium soil
Discussionsaidsuchasfollows:
1. We observe that in everything from building with and everything zones, on b share is maximum in zone 4 in a rectangle form buildings.Andatleastinarea3inanL shaped building.
2. In everything from building on base share is 49,01% maximum in zone 4 in average soil suchascomparedwithzone3inhardsoil.
3.Сconsideringhardandaveragesoilonminimum value on base shearing is in zone 3,in L. form building
Chart8.Comparisonofsteelpercentage(%)forMediumsoil
Discussionasfollow:
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page30
1. InallShapebuildings(i.e.Rect.,CandLshape)the steel percentage is more in zone 4,in medium soil, andminimuminzone3inhardsoil.
2. Theminimumsteel(7.42%)isrequiredforCshape building which is in zone 3 inhard soils and it is alsoeconomical.
3. The maximum steel (14.81%) is required for Rect. shapebuildingwhichisinzone4,inmediumsoil.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
3. CONCLUSION
1.Instructureisanalyzedinzone3andzone4.I findonthe resultinBaseshearingvalueisMore▼ inzone4thcenturyaveragesoil(incorrect configuration).
2.Basis shearing value is More ▼ in zone 4 and that in onaveragesoil (regularconfiguration).
3.Basisseismicshear4ishigherthan73.53%compared totheZone3.
4Comparedto bothregular andincorrectconfiguration basic shear value is more in the ordinary configuration asthestructureismoresymmetricaldimensions.
5.Reachingthedisplacementsofthefloorinzone4there arehigherdisplacements thanintheZone3.
6.MinimumMovingismeetinginrectangularformat_on thebuilding.
7.Maximum history drift is meeting in theintermediate history of rectangle formbuilding while the minimum driftstoryoccursinL shapeonthebuilding.
8. When comparing the two on regular and irregular configurationis history driftvalueisMore▼inregular configuration because on structure there are more dimensions.
9.Steelamountofseismiczone4ishigherthanZone3.
10. When comparing the two on regular and irregular configuration is the steel quantity isMore in regular configuration.
11.Fromonaboveresultszone4iscriticalforon G+11structure.
12. seismic zones zone 4 thereisa higher zone factor than zone 3. Yes zone 4 values on Baseshear, 13. 13. RelocationsandtheamountofsteelareMore thanzone 3.
14. Basis shearing, displacement, and steel quantity are According On The area factor so these values are more inZone4.
15. Given rectangle C and L shaped building. 16. An L shaped building is More effective in Zone 3 and hardtypesoil. AnL shapedbuildingismoreefficientforBase share,Floor Driftinseismiczone3
REFERENCES
1) Mohd Abdul Aqib Farhan, Jagadish Bomizeti , "Seismic Analysis on Multi storey RCC buildings with correct and incorrect plan ”, IJERT , ISSN: 2278 0181, volume 8 Number November11,2019
2) M. Seetha , KEViswanathan , “Comparison of Multi storey Building with Regular and irregular shape in different seismic zones ”, IJRIAS, ISSN 2454 6194, vol III, no VI, June 2018
3) Mr. S. Mahesh , Dr. B. Panduranga Rao, “Comparison of analysis and design of the
correct and incorrect configuration of a multi storey building in different seismic zones and differenttypesofsoilsusingETABSandSTAAD”, IOSR JMCE, p ISSN: 2320 334X, Sound volume 11,Issue6,Ver.me,novemberDecember2014
4) Pritam C. Pawade , Dr. PP Saklecha , Milind R. Nikhar , “Comparison and analysis of the correct and incorrect configuration of a multi storey building in different seismic zones and different typesofsoil",IARJSET,ISSN(Online)2393 8021, SSN(Print)2394 1588,vol.5,noJune62018
5) Girum Mindy , Dr. Shake Yajdani , “Seismic analysis of a multi storey RC frame Construction in different seismic zones ", IJIRSET, ISSN (online): 2319 8753, ISSN (Print): 2347 6710, vol.5,noSeptember9,2016
6) Asha, “Comparison of the seismic behavior of a typical multi storey structure with Composite columns and steel columns ”, International Journal of Civil and Structural Engineering Research (IJSER), vol. 3, pp. 360 367, September 2015
7) IS 1893 (part 1): 2002, "Criteria for earthquake resistant structures", part 1 General Provisions and Buildings, Fifth Revision, Bureau of Indian Standards,newDelhi.
8) IS 456: 2000, Ordinary and reinforced concrete Code of Practice, Fourth Revision, desk on Indian standards,NewDelhi.
9) IS875(Part1):1987,"CodeonPracticeforDesign Loads for Building and constructions ”, part 1 dead Loads unit _ weight on building materials and preserved materials second revision, The BureauofIndianStandards,NewDelhi.
IS875(Part2):1987,"CodeonPracticeforDesign LoadsforBuildingandStructures”,part2Load imposed,secondrevision,BureauofIndian Standards,newDelhi.
