International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
1Master of technology in Civil Engineering 2Professor in Civil Department
IEC College of Engineering & Technology Greater Noida ***
Thegoalofleantechniquesinconstructionistoreducewaste,improvecommunication,andcreateteamwork.Theincreasing demandforpublicworksprojectsneedsafocusonefficientconstructionprojectservices,hencefocusingonmunicipalproject deliveryisessential.Theterm“populationworks”referstoabroadspectrumofpublic benefitinfrastructureprojectsfinanced andconstructedbylocalgovernments.Municipalconstructionpresentsparticularchallengeswhencomparedtoothersortsof projects. All around the metro area and the neighboring areas, these programmes are making a difference. The focus of this thesis is on lean construction approaches, which attempt to bring new insights into how lean techniques might reduce non physical waste connected withthe actual delivery of the project. In order tosolve difficulties, speed up project development and give recommendations for improved municipal building projects, only lean methodologies may be applied. To improve and broaden the classification of non physically controlled trash, this study employs the AHP. In this thesis, AHP is used to identifythegoal,classifythewaste,andapplythenecessaryleanmethodologies.Buildingprofessionals'experiencewasused todeterminetherelativeimportanceofagivensetofalternatives.TheAHPapproach,whichidentifiedandprioritizedissues, reducedwasteandimprovedperformance.
Keywords: leantechniques,construction,Municipalconstruction,AHP,wastereduction
A method to manufacturing that minimizes waste in materials, time and labor is known as lean construction. Improved contractualarrangements,productdesign/methodofselection,supplychain,andoperationalworkflowreliabilitywillbenefit all stakeholders if theyare made in a methodical,synergistic,andcontinuous manner [1]. Due to a variety of challenges, the building sector has been lagging behind the manufacturing industry for many years. A mixed strategy is preferable over a divided one because of its adaptability and flexibility. The complexity of the building business necessitates a higher level of technologicalinnovationthandoesmanufacturing[2].
Lean construction methods will cause a sea change in the construction industry. Companies in today's highly competitive market have improved job efficiency and quality, cut waste and costs, and raised profits as a result of their efforts to stay relevant [2]. Fewer resources are used while still satisfying customer needs in building that adheres to lean construction principles. It is essential to understand the “Physics of Building” of production management in order to implement lean construction.It'saradicaldeparturefromthewaythingsarecurrentlydone.Anyconstructionprojectcanbenefitfromthem, buttheyareparticularlywell suitedtothosethatarebothchallengingandtime sensitive[2&3]
Cuttingdownonwasteisoneofthebestwaysforabusinesstoincreaserevenues.Intheconstructionofabuilding,materials thatareeithercreateddirectlyorindirectlyarereferredtoas“constructiontrash.”Ifyou wantthemostvalueforyourmoney, lean construction (LC) is all about eliminating errors and minimizing waste [3]. All of these elements can be reduced by reducingthenumberofinputsthatareused,includinglabor,machinery,space,andtime.Itisthegoalofleanconstructionto reduce waste while increasing quality and productivity. The goals of this document mention the integration of construction facilitiesandprocedureswithconcurrentdesign.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
1. Investigate how lean construction approaches might boost the efficiency and effectiveness of municipal project delivery.
2. To contribute to the corpus of knowledge on how waste might be reduced in municipal project delivery using lean methodologies.
3. Asawaytolearnmoreabouthowconstructioncompaniesandtheirclientscommunicateandexchangeinformation.
Ankit Bhatla, et al. [1] According to the findings of a life cycle study, it is recommended that waste management for constructionand demolition be improved in orderto maximize recyclingand reduceconstruction wastedisposal.Itappears thatthisindexwillbedifficulttocontrolbecauseofthelackofprecisionwithwhichitiscalculated. AbdelrazigYE[2].Asper his analysis, in recent years, a rising number of businesses have embraced lean and environmentally friendly building practices with great success. For example, lean construction and green building concepts have shown this to be true on numerous instances.Fewstudieshaveexaminedhowtoimplementleanandgreenprinciplesinreal worldcontexts,despite thefactthattheycanbeemployedinavarietyofways.Being leanandbeingecologicallyconsciousaretwoprinciplesthatgo hand in hand, as we've seen time and time again. Aziz, R. F., and Hafez, S. M. [3] His studygoal of lean thinking to minimize wastewhilesimultaneouslyincreasingvalueandimprovingonanongoingbasis.Inordertolowerthecosts,time,andquality of road construction, the overarching purpose of this research is to use a lean construction strategy throughout the constructionprocess.Theyconductedanumberofinterviewswithspecialistsinordertohaveabettergraspoftheadvantages anddisadvantagesofleanconstructioninroadconstructionprojects.Firstandfirst,inordertobesuccessfulinthisindustry, onemustbewellinformedoftheissuesandopportunitiesthatexist.
AnAHPwasutilizedtoorganizethedataforthisinvestigation.Theresearchdiscoveredacollectionofgarbagefrommunicipal constructionprojectsthatmaybemanaged.JulieEmeraldJiju,etalcontrolledwastecategorizationsystembyMugheesAslam et al., lean approaches are predicted to yield substantial gains if used in conjunction with it. In order to get additional informationontheimplementationofleantechniques,asurveyofindustryexpertswassentoutandthedecisioncriteriawere organized in a hierarchical framework. Using the AHP approach, these initiatives were prioritized and reviewed to see how theyfitintothelargergoalofleanbuildingpractices[4]
In order to obtain information, the researchers had to examine secondary sources such as books and journal articles. Databases such as ABI/Inform and the General Business files, among others, have made it feasible to have access to critical information.Itwasoneofthestudy'skeyaimstodeterminewhetherornotthefindingshadanimpactonworldwidebrand trust.
Inquantitativeresearch,dataanalysisisusedtominimize,organize,andanalyzetheinformationacquiredbytheinvestigators [4].Astatisticiananalysisusedtoanalyzetheresearchdata.Therearebothvisual andnumericalrepresentationsofthedata tochoosefrom.Theaforementionedstatisticswereobtainedbyaveraging,mediating,andsummingtherelevantvariables [5] To see if there was any correlation, the variables of interest were connected using Pearson's or Spearman's methodologies. Theconfidenceintervalforthisexperimentwassetat95%.
Thestrategiesandmethodologiesfordoingresearchwere thoroughlyexploredin abovesection.Thischaptercovers,among otherthings,howthedatawasacquired,howitwasanalyzed,andhowtheresultswerevalidated [5].Thischapterdiscusses theuseoftheAHPtechniqueaswellasthethesis'findings.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

Data from the 100 survey participants were analyzed according to their location (NCR Delhi and Faridabad), sector (private versus public), and position (Director/Principal, Project Manager/Engineer, and Others), as shown in Table 1. Table 2 illustrateshowtheinformationgatheredfromthe100surveyparticipantswascategorizedandanalyzedbyposition.
Table.4.1. Waste Associated with construction Management respondents
S No. Participants based on areas Respondents categories Total respondents Percentage (%) of total respondents
Director/principal 65 65% Projectmanager 35 35% Total 100 100% 2. basedonsector private 60 60% public 40 40% Total 100 100% 3. Basedonownership contractors 70 70% owners 30 30% Total 100 100%
1. Basedonposition
10
90
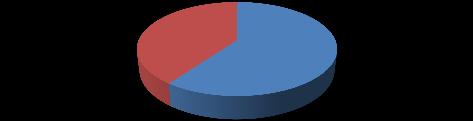
Figure.4.1. Based on location, the distribution of survey respondents
Distribution of survey respondents by locations NCR Delhi Faridabad 60%
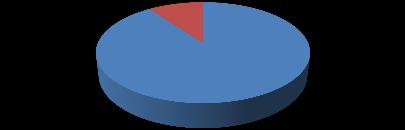
Distribution of survey respondents based on sectors private public
40%
Figure.4.2. Based on sectors, the distribution of survey respondents
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
Distribution of survey based on positions
35
65
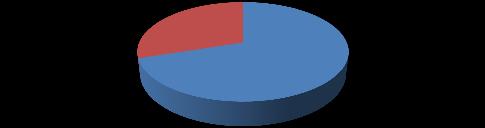
Figure.4.3. Based on position, the distribution of survey respondents
Distribution based on ownership contractors owners
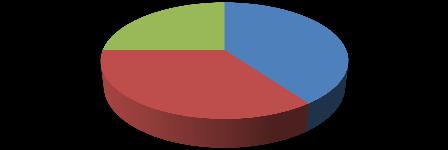
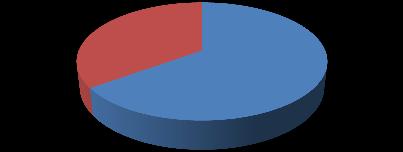
Figure.4.4. Based on ownership, the distribution of survey respondents
Table.4.2. Knowledge about lean construction concept
S.No. Level of respondents Total respondents Percentage (%) of total respondents 1. Excellent 40 40.00% Good 35 35.00% Fair 25 25.00% Neverheard 0 0.00% Total 100 100%
0%
30 40% 35% 25%
Figure.4.5. Knowledge about lean construction concept
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Table.4.3. Controllable waste from management vs. controllable waste from flows
S.No. Level of respondents
Total respondents Percentage (%) of total respondents

1. Significantlylessimportant 0 0.00% Lessimportant 25 25.00% Equallyimportant 45 45% Moreimportant 20 20% Significantlymoreimportant 10 10% Total 100 100%
Waste association with construction management respondents
0.00% 10.00% 20.00% 30.00% 40.00% 50.00%
Series 1
Figure.4.6. Controllable waste from management vs. controllable waste from flows
This chapter contains a summary of this thesis as well as the findings of the research into the use of lean techniques to municipal project delivery improvement. This chapter also looked at the limits of the research and made some recommendationsforfutureworkinthisarea.
Accordingtothisresearch,thefollowingfindingscanbedrawn:
1. Itwasdeterminedthatbuildingwastewasatypeofcontrollablewastethatneededtobemanaged.
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3879
2. An in depth look at waste control and enhancement as it is applied by lean concepts was also gained from this research.
3. A wide range of lean approaches have been established in order to reach the ultimate aim of reducing waste and improvingperformanceandproduction.
4. The survey results helped decision makers achieve their aim by displaying the decision making problem as a hierarchyofcriteriaandalternativesthroughtheAHPapproach.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

5. Itwaspossibletomakecompromisesbetweenwastecausesandleanmethodchoicesbasedonthesurveydata.
6. Basedontheresultsofthepoll,themostimportantvariablestofocusonaremanagementactivitiesandflows,witha rateof43percentforeach.
7. Leantechniqueswereoutlinedandprioritizedforimplementationateachlevelofwaste.
1. To serve as a model for future research on lean construction and the application of lean concepts throughout the constructionindustry,thisstudywasconducted.
2. Asaresultofthisstudy'sfocusonasingleindustryanddeliverymechanism,futureresearchshouldlookatdifferent projecttypes.
3. However,thisresearchwasunabletoinvestigatethebuildingbusinessglobally.
1. Ankit Bhatla, Bulu Pradhan and Jin Ouk Choi, (2016). Identifying Wastes in Construction Process and Implementing the LastPlanner System inIndia. KICEM Journal ofConstructionEngineering and Project Management, Vol. 6, No.1, 2016,pp.11 19,http://dx.doi.org/10.6106/JCEPM.2016.6.1.011
2. AbdelrazigYE(2015).UsingLeanTechniquestoReduce WasteAndImprovePerformanceInMunicipalConstruction ProjectDelivery.TheUniversityofTexasatArlington.
3. Aziz, R. F., and Hafez, S. M. (2013). Applying lean thinking in construction and performanceimprovement.AlexandriaEngineeringJournal,52(4),679 695.
4. Ahmed, S., and Forbes, L. (2011). Modern Construction: Lean Project Delivery and IntegratedPractices.CRCPress,NewYork,NY.
5. Anon (2006). Lean construction defined. https://www.leanconstruction.org/wp content/uploads 2016/02/TDC CH04.pdf.
6. Bjorn Andersen, (2012). Lean Construction Practices and its Effects: A Case study at St.Olav’s Integrated Hospital, Norway.LeanConstructionJournal,2012.