International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1 ME design Engineering student at SVPM’s College of Engineering Malegaon, Maharashtra, India
2 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Dept. of SVPM’s College of Engineering Malegaon, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract – Vibrations in a machine or rotating mechanicalscomponentsaremainlycausedbythebearing defectsandfaults.Bythevirtueofitsconstructionand its characteristics,bearingstendtoproducevibration. Asthe condition of the bearing changes over time the vibration signalanditscharacteristicsalsochanges.Inthispaperwe shall discuss various vibration signal based techniques in conditionmonitoring.Theinnerraceandouterraceofthe bearing can feature the defects of variable nature. The vibrationdadaisobtainedfromthebearinghousingandits effectonthefunctionalityandtheseriousnessofthedefectis analyzed..Atotalrankingoftheparametersistriedwiththe aimofevaluatingeffectivedamageidentificationparameters fromdiagnosisoftherollingelementbearings.
Key Words: Bearings, Vibrations, Defects, Damage, Defectiveness, Frequency
If there a considerable fault in the rolling bearings is not detectedinadvance,itcancauseamajormechanicalaswell as economical loss. For the proper functioning of any mechanicalpartcontainingthistypeofrollingbearings,they need to operate smoothly and stably. Causes behind localizeddefectsofrollingbearingscanbeoneormorelike inappropriateinstallation,materialfatigue,faultybearings etc When a rolling bearing with a defect is rotated in an operation a certain amount of vibration and the vibration signalisgenerated.Therearemainlytwotypesofmethods that are used to detect these types of defects in a rolling bearings vibration monitoring, acoustic monitoring, temperature measurements and wear debris analysis. Among these techniques the vibration measurement techniqueismostwidelyusedinthedefectevaluation.To measure the vibration signal and acoustic measurement, manytypesoftechniquesareemployed,suchas,timeand frequencydomainanalysis,theshockpulsemethod,sound pressure and sound intensity techniques and the acoustic emissionmethod.Allroundsoundperformanceandstability oftherollingbearingisimportantforthefunctionalityand failureavoidanceinthemachine.
Bearinghealthmonitoringtechniquesisimportantstepfor evaluatingthebearinghealthanditsperformance Forthis purposetheconditionmonitoringiscarriedoutbyusingthe
various condition monitoring techniques. Since it is very reliableandverysensitive,vibrationanalysistechnique is mostcommonlyusedconditionmonitoringtechniqueused nowadays. Bearings are a source of vibration and noise becauseofdefectspresentorvariableperformanceinparts ofbearing.Wecanassessthebearinghealthbyanalysisthe vibrationsignalcomingoutofthebearingwhenitisinthe operatingortherunningcondition.
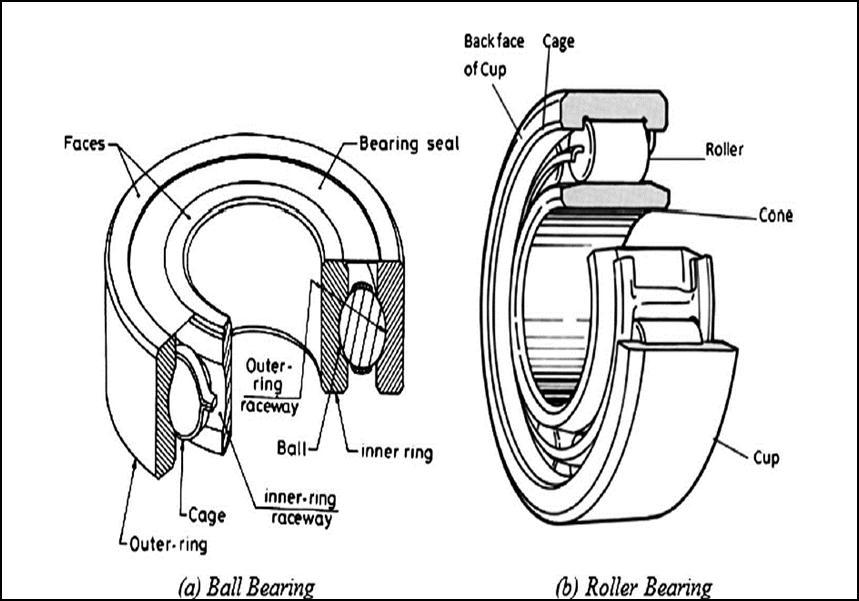
Bearinggeometryisanimportantcomponentwhichisused toevaluatethedefectsbecausethegeometryofballbearings isthedeterminingfactorinthedynamicsofcomponentsand theirvibrationcharacteristics.Aschematicdiagramofdeep grooveballbearingisshowninfigure1.1 Ballbearingsare generally characterized as having smaller size and lower loadcarryingcapacitythanmostoftheircounterparts.Still with all these limitations they can support both axial and radial loads. Axial force is defined as the force applied paralleltotheshaft Theradialforceisappliedperpendicular to the shaft. To maximize the life span of the component, placementorlocationofthebearing,amountandthetypeof lubricationused,correctalignmentplaysanimportantrole. Themaincomponentsofaballbearingisinnerrotatingrace, outer rotating race, roller balls and the cage structure holdingtheracesandballstogether. Theloadzoneandload distributionarealsogivenwiththedirectionofappliedforce inthefigure.Mostofthetimestheinnerraceandtheroller balls rotate along with the shaft and the outer race is remaining stationary Majority of the defects occur on the inner race and the roller balls as they are continuously rotating and most of the force such as static and dynamic load,torqueandacceleration.Alsotheinnerraceandroller ballscomeundertheloadzonesotheytendtobeexposedto most amount of wear and tear happening in any rotating partorcomponentina machine. Sothe mainfocusofany conditionmonitoringscheduleofmaintenanceismostlyon analysisofinnerraceandtherollerballsofthebearing,the outer race is secondarily analyzed because of before mentionedreasons.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Basic condition monitoring is mainly done through elementaryobservations.Thereareamplenumbersoftools that can magnify, amplify the results to make them more recordable.
Visual monitoring of the bearings typically includes observationofdeformationofconditionofbearing,corrosion ifpresentandthelubricantquantityandquality Ifamounted bearingislubricatedproperlythenitwillpurgethegrease fromitssealing.Theanalysisofthispurgedgrazecanbeused todeterminethequalityandamountofthelubrication.Milky, dark and caked grease found can imply that lubrication scheduleandproceduresmayneedtobeimproved.
Tofindoutthecharacteristicsofthevibrationsignaloutput due to inherent faults, it is assumed that the bearings are continuousandisolatedsystems Itisalsoassumedthat:(1) Allrollersofthebearingareequalindiameter;(2)Thereis only pure rolling contact between rollers, inner race and outerrace;(3)Noslippagebetweentherotatingshaftand the bearing; (4) Outer race is stationary and inner race rotating Since there is pure rolling contact between the inner race, outer race and the roller balls, the relative velocity between all of them is also zero. The theoretical characteristicfaultfrequenciesforafixedouterracebearing canbecalculatedusingfollowingequations 1.Outerracedefectfrequency: …Eq.2 2.Innerracedefectfrequency …Eq.3 3.Rollerdefectfrequency: …Eq.4
Audiblemonitoringorsimplelisteningismostcommonand traditionalwayoftheconditionmonitoring.Oddnoisesare anindicationoffaultyoperationofthebearing Thiscanbe sensedevenbyanyuntrainedworker.Thistaskcanbeapart ofworkersdailyroutine
2.4
Monitoringtheoperatingtemperatureofanybearingisthe mist simple technique that does not require any tool. Monitoringoperatingtemperatureisimportantasoperating temperature has direct effect on failure If the operating temperatureishighthenitimpliesthatbearinghasafault andviceversa.Loggingthedailyoperatingtemperaturewill helpindetectingfaultinearlystagestoavoidcatastrophic failure.Thermocouplesandresistancetemperaturedetectors (RTDs)arethetoolsthatcanbepermanentlymountedonthe bearinghousingforcontinuousreal timemonitoring.
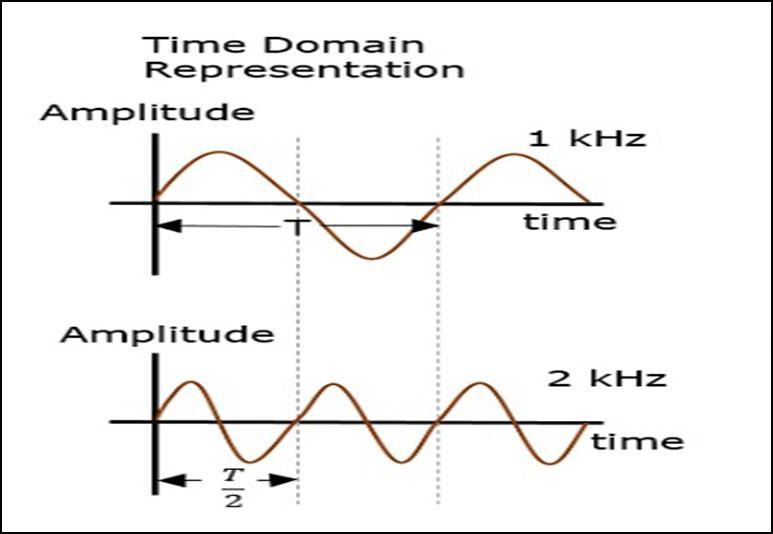
Whenadefectispresent,itproducesvibrationwhichcanbe sensedusingvibrationtransduceroraccelerometers There aresomeanalysistechniquesthatareusedtoprocessraw data fortheconditionmonitoringof bearings.Theycanbe classifiedasfollowing:time domain,frequencydomainand timefrequencyortime scaleanalysismethods.
Series ofdigital values representing proximity,velocity,or accelerationinthetimedomainareknownasthevibration signals.The displayand analysis of the vibrationdata as a functionoftimeiscalledasthe“time domainanalysis”of
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
theobtainedvibrationsignal.Themainadvantageofthistype ofanalysisisthatnegligibledadaislostbeforetheinspection.
whichvibrationswhicharenotassociatedwiththefaultis generallysmaller.
Thistechniquecanplayaveryimportantroleincondition monitoring of the simpler machines but they are not very viable for a complex machine It is useful in detecting a simpledefectpriortofailure Sinceitdetectsthefaultafter forming it, the bearing needs to be replaced but the economicimplicationsofchangingabearingismuchlesser thanhavingtofacea catastrophicfailureofa component. DyerandStewart(1978)statedthattheprobabilitydensity. Generally used time domain metrics consist of waveform analysisandvibrationfeatures
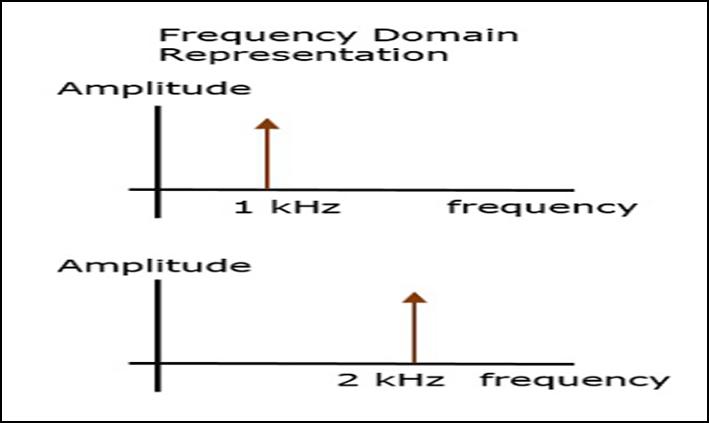
Extractingthefrequencycontentofthetimedomainsignal spectrum analysis is known as the “frequency domain analysis” of the vibration signal. It is the most common techniqueusedforhealthinspectioninrollingbearings.It canbeconsideredasanimportantwaytofindoutfaultand perform its diagnosis in simple rotating machinery. Frequency analysis is a measure of the vibrations over a large number of discrete neighboring narrow frequency bands. At constant speed and specific geometry, the frequencies of the vibrations which are produced by the many components in the bearing can be established. Generally, the defect diagnosis with the help of vibration level along with wave shape features can be improved by dividing the vibration signal in to number of frequency bands prior to analysis. A fault or defect present may not causeasignificantvariationinthesignalanditcanalsobe maskedorhiddenunderotherhighenergysignalsdetected whichisnotrootedindefect. But,thedefectorafaultcan generateaconsiderablevariationinabandoffrequenciesin
Tohandlestationaryandnon stationaryvibrationsignals, wemayhavetouseacombinationoftimefrequencydomain analysis.Thisprovestobetheconsiderableadvantagefor the same. This analysis can show the signal frequency components and it can also illustrate their time variant features. Methods such as the Wavelet Transform (WT Wigner VilleDistribution(WVD),.
The bearing defects can be widely categorized as the localized defects and generalized defects. They are briefly describedbelow
Whentheamountandtypeoflubricationisinadequateor incorrect or if a foreign particle infiltrates the rollers, the bearingwearmayoccur Ifthereisvibrationinacomponent whenthebearingisnotrotatingthenthewearmayhappen inthatcasealso
Smearingisaconceptwhentwopoorlylubricatedsurfaces slideagainstoneanotherandsomeamountofmaterialgets transferredfromonesurfacetoanother.Thisisknown as smearing.Thesurfacesundergoingsmearingappeartobe swollen,andtheyappeartobetorn,thematerialisheatedto atemperaturethatre hardeningofthatsamesurfacetakes place. This results in production of localized stress concentrationswhichinresultcausesflakingandcracking
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
on the surface. When the rollers are subjected to high amountofaccelerationwhentheyareintheloadzone,then smearingmayoccur.
Corrosion may take place in any bearing when a dust or other corroding materials intrude then bearing surface beyond a level at which lubricant can resist the corrosion fromtakingplace.Oncethecorrosionstartstakingplaceon any surface, it leads to the formation of deep seated extensiverustonthesurface.Deepseatedrustcausesagreat harmtobearingsbecauseitcanleadtoflakingandcracks. Whileitisimportanttonotethatacidicliquidcorrodesthe bearingsurfacequicklythanthebasicliquid.
Brinelling can be described as the regularly spaced indentationswhicharedistributedovertheentireraceway circumferenceandwhicharecorrespondingapproximately in shape to the Hertzian contact area. The main causes of brinelling are, (1) Static overloading which can cause the plasticdeformationofthebearingraces,(2)Whenashock loadandvibrationsareappliedtoastationarybearingand (3)whenandelectriccurrentiscausedbyaloopofpassage.
When a bearing is inadequately lubricated or the type of lubricantisimproper,itmayleadtoproblemslikesticking, skidding, excessive heat generation. Region of Hertzian contactwhenthelubricationisnotproper,thesurfacesin contactwillweldtogetherduetoheating,thentheyaretorn apartasthebearingstartsrollingmore.
Faultyinstallationofthebearingatthebeginningandother mishapssuchasmisalignment,loosefits,excessiveaxialor radialpreloadingcanleadtofaultybehaviorandultimately failure.
If the size of the bearing required for a specific set of operationisnotproperanditiscalculatedincorrectlythen designmalfunctionmayoccur.Thisincorrectdesigncanlead toseriouseffectsonlowladandlowspeedoperationstoo.
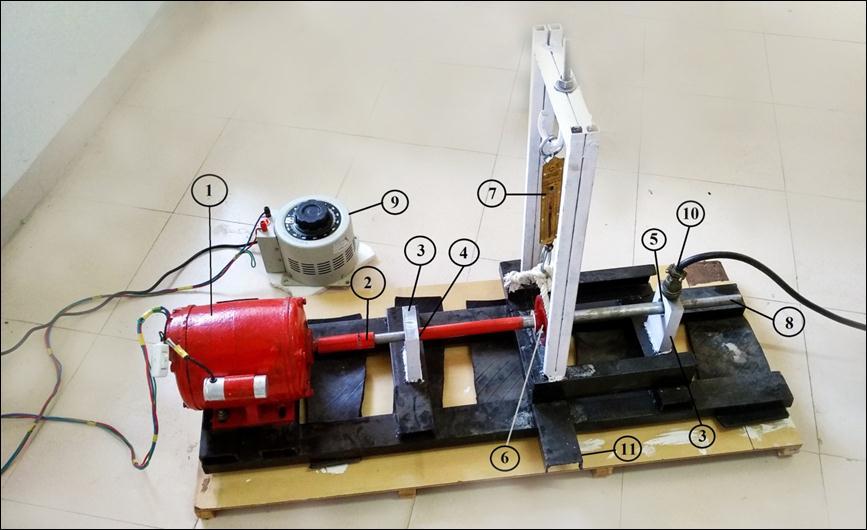
(1)1H.P.singleϕMotor(2)Coupling(3)BearingHousing (4)Standard(Healthy)Bearing(5)Test(Fault)Bearing(6) Pulley(7)SpringBalance(8)Shaft(9)Dimmerstat(10)
The adjacent figure shows the model of the proposed experimentalsetup Themainshaftissupportedbyusing thetwosupportbearings.Theinductionmotorisconnected withshaftendwiththehelpofacoupling.Thedimmerstatis usedforchangingthespeedoftheinductionmotor.Italso consistsofthearrangementofaspring balanceinorderto varytheloadontheshaftwiththehelpofpulleymountedon the shaft. The coupling connecting the main shaft to the motor alsoactsthe vibrationisolatingsetup. Thesamples takenaredescribedbelow.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
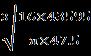
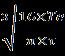
d= = =16.72mm
Forshaftdiameter(d)=20mmandCo =2.432kNbearing selectedis HCH 6004 2RS
d 20mm
D 42mm B 12mm d1 24.65mm D2 37.19mm r1,2(min.) 0.6mm
Table3BearingDimensions
Sr. No. Speed, N (RPM) ShaftFrequency, Fs (Hz)
Inner race Frequency,Fi (Hz) A E A E
1 1080 18 18.125 97.90 99.375 2 1820 30.33 30 164.96 165
Table4Faultfrequenciesatvariousspeeds.(Analytical& Experimental)
Sr. No. Speed, N (RPM) Outer Race Frequency,Fo (Hz)
Roller (ball) Rotational Frequency,Fr (Hz) A E A E
1 1080 64.09 65.125 82.49 81.625
2 1820 108 107.5 136.8 135.875
Table4Faultfrequenciesatvariousspeeds.(Analytical& Experimental)
Inthispaper,westudiedabouttherollingbearinggeometry, types of failure in rolling bearing, condition monitoring techniquesandthevibrationanalysis.Experimental setup forcarryingoutthestudywasdesignedandmanufactured. Themethodusedforthestudywasthefrequencydomain analysisalongwiththemodalanalysisofthebearing.During theexperimentationvariousbearingdefectslikeinnerrace defect,roller(ball)defectsandouterrace weretakeninto consideration. The metal Burr was used as solid contaminant. Finally the results obtained from vibration spectra illustrate firmly, that, as the speed of defective bearingincreasesthefrequencyandaccelerationvaluesalso startincreasing.Substantialvariationinthevibrationsignals were observed when the contamination was added in the vibration lubricant. The acceleration values also change according to the variation in speed and load. The particle size also has a major impact on the outcome of the study. Whenthesizeisincreasedthecorrespondingacceleration values go on increasing up to point, and then start decreasing. The reason is that the contaminants start bto occupy the corners present in the bearing. The same outcomewasobservedwhencontaminationconcentration andsizewasincreased.Atthespeedof1080RPM,withsmall particlesizeandvaryingconcentrationofthecontamination, we found the desired results. At other instance, there is a mismatchobservedinexperimentalandactualresults.This may be happening because the particles may not come in directcontactwithrotatingelements.
IwouldliketothankmyprojectguideProf.V.B.Rajmanesir whohelpedandmotivatedmetoworkonthisproject.
1. SumitNawale,P.D.Kulkarni,“AnalysisofEffectof Solid Contaminants in Lubrication on Vibration Response of Ball Bearing”, IJIRSET Vol. 6, Issue 6, June2017
2. Tandon N, “A comparison of some condition monitoringtechniquesforthedetectionofdefectin inductionmotorballbearings”,MechanicalSystems andSignalProcessing21(2007)244 256.
3. V. N. Patel, N. Tandon, R. K. Pandey, “Vibration Studies of Dynamically Loaded Deep Groove Ball BearingsinPresenceofLocalDefectsonRaces”.
4. Ragini Sidar, Prakash Kumar Sen, Gopal Sahu, “Review of Vibration Based Fault Diagnosis in Rolling Element Bearing and Vibration Analysis Techniques”.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

5. Yogeshrao Y. More et al, “Study of Effect of Solid Contaminants in Grease On Performance of Ball Bearing by Vibration Analysis”, IJIERT ISSN: 2394 3696Volume2,Issue5,MAY 2015
6. R. Serrato, M.M. Maru, L.R. Padovese, “Effect of lubricant oil viscosity and contamination on mechanical signature of roller bearings”, Twelfth Internationalcongressonsoundandvibration,11 14July2005,Lisbon,Brazil.
7. L.Kahlman,IanM.Hutchings,“Effectofparticulate contaminationinGrease lubricatedhybrid rolling bearings”, Tribology Transactions 42 (1999), 4, 842 850.
8. R. Serrato, M.M. Maru, L.R. Padovese, “Effect of lubricantviscositygradeonmechanicalvibrationof rollerbearings”,TribologyInternational40(2007) 1270 1275.
9. M.M. Maru, R.S. Castillo, “Study of solid contamination in ball bearings through vibration and wear analyses”, Tribology International 40 (2007)433 440.