International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

1, Post Graduate Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur 2 Associate Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur 3 Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur ***
Abstract This study addresses the primary challenge of defining quantitative and qualitative criteria in order to proceed with a comprehensive road conditionevaluation. This method may be utilised by road authorities as a trustworthy instrument in the context of successful road upgrade management. Since ancient times, transportation has contributed to the development of civilizations by satisfying the travel and transit needs of people and products. Road and transportation have become a vital element of every person's life in the modern era. In contrast, it has been noticed that deaths have doubled in the past decade. Approximately 1.2 million Indians were murderedinautomobileaccidentsduring the past decade, or one every four minutes on average, while 5.5 million were badly wounded. Consequently, analysis and planning are of the utmost importance in a road project, taking in mind both the current and future demands of the region. This paper's primary objective is to present a complete overview of the upgrading strategy for existing highways, as well as the relevant technology to tackle the problem of traffic flow and prevent road accidents. This article investigates research on the "need for upgrading and redesigning the Nagpur Katol National Highway" The route is mostly located in an orange growing region and will benefit the orange industry. Upgrading the present two lane road to a four lane road with paved shoulders would improve transportation in terms of the speed and congestion free flow of traffic, and will also promote human interaction in adjacent communities.)
Key Words: Existing Highway, Transportation, Traffic Flow, Road, National Highway, Accidents, and the InsuranceResearchCouncil.
Highways are constructed to accommodate the traffic volumeatthetimeofdesigntogetherwithaprojectionofthe potential increase in traffic flow in subsequent years. In additiontoanincreaseinvehicleownership,factorssuchas anincreaseinhumanactivitiessuchaseducationalactivities, businessactivities,andmanyothersleadtoanincreasein traffic volume that exceeds the capacity of the highway, necessitating an upgrade of existing highways to include morelanesand,insomecases,moredurablematerials,such asanupgradefromflexibletorigidpavement.Thisarticle examines the impact of size on the design of ecologically
(sociallyandbiophysically)sustainablelinearroadways.The objectiveofthereviewistoprovidestakeholders,planners, anddecision makerswithimprovedandmoretransparent techniques for the generation of alternatives in alignment planning practise, as well as to improve the practise of environmentalassessment,whichistypicallyamandatory regulatoryprocessthatshouldprecedeandrunconcurrently with planning, implementation, and monitoring exercises. The purpose of this study is to investigate the obstacles posed by improving existing roadways, as well as the impacts that may come from taking into account aspects suchaseconomic,cultural,environmental,etc.Attemptingto give a complete overview of the upgrading technique for existingroadsaswellasrelevanttechnologytoaddressthe trafficandupgradationofexistinghighwaysisthepurpose ofthisarticle.Inaddition,thepublicationsummarizesthe study'skeyresultsandsuggestspolicy relevantoptionsfor furtherresearch.
Fundamentaltothemethodologyisthecategorizationof alltwo laneroadsintofourseparategroupsbasedontheir existingconditionandtrafficcharacteristics.
Category1roadsarecharacterisedbyahighdegreeof service and suitable geometric characteristics, hence ensuring safety and riding comfort. The alignment is appropriate, and the crossings are planned in accordance with current design requirements. The width of the pavementguaranteesadequateserviceability.Nosubstantial improvements are necessary. The primary issues to be addressed are the emergence of cracks or rutting, an increaseinslickness,andinadequatesafetyequipment.
ForCategory2,thelevelofserviceiswithintherangeof steadyflow,thegeometryistypicallyappropriate,andthe pavement width is also sufficient according to design criteria. However, the junction design is insufficient in relationtorealtrafficdemands,andthetransitiongeometry atturnsisflawed.
Categorization 3 comprises roadways with a low LOS. Themajorityofgeometriccomponentsarepoorinrelation to contemporary traffic circumstances, posing an incident risktomotorists.Thevolumeoftrafficappearstohaverisen
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3790
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

dramaticallyovertheyears,androadusagehasescalated. Roadwayandlanewidthdonotmeetcontemporarytraffic requirements. The road must be widened and maybe realigned in accordance with modern design, safety, and trafficregulations.
Category4containshighwayswithoperatingconditions at or near capacity where the usefulness of upgrading is dubious.Anaveragerestorationprojectcannotqualifyasa sustainable technical solution for an ageing road in a sensitivenaturalenvironment.Moreover,uniqueinherent limits for roads in populated areas or in the proximity of archaeologicalsitesmaypreventupgradingactivitiesonthe presentalignmentandinsteadprescribeacompletelynew path.
According on the preceding criteria, each road can be classed as one of the categories listed above. Due to the correctconditionevaluation,thiscategorizationrendersthe plan for upgrading comprehensive and well defined. For eachroadtype,auniqueupgradestrategyisenvisioned.
The National Highways Authority of India will shortly beginworkonthe50 kilometerportionoftheNagpur Katol nationalhighwayafterreceivingstage Iapprovalunderthe 1980ForestConservationAct(FCA).Theconstructionofthe highway between Kalmeshwar and Katol required an expenditureof1,350crore.AsNH 353Jbegins13kilometers from the Zero Mile near the Fetri T point, it is one of the mostimportantconnectionslinkingNagpur Katol Warud Amravati and beyond Madhya Pradesh. The 5 kilometer congestionbetweenKatolNakaandFetriwillbeeliminated if the route begins at the outer ring road, according to AbhijeetJichkar,projectdirectorofNHAI.
Theroadsegmentwillbeclassifiedasaone timeupgrade in accordance with the current policy. As the project has been divided into two parts, the 13 km section will be addressed during the second phase. The first phase is plannedsuchthathighwaytrafficwillbepermitteduptothe outerringroad(ORR)andwillthereaftercontinuealongit withoutenteringthecity.AfirmfromAurangabadhasbeen selected to finish the project following an open bidding process.
Estimated Project CostofRs.1350Cr. 14.07 Hectare of divertedforestarea3300Treestobefelled21794Existing trafficinpassengervehicleunit(Fig.1MapofNagpurKatol NationalHighway353 J)
SatelliteviewoftheNagpurKatolNationalHighway.
Rs.1350CrEstimated ProjectCost 14.07HectareForestland diverted
3300Treestobecut 21794Existingtrafficin passengercarunit
Level of service estimation for two lane split NationalHighway353 J(NagpurtoKatol).
Theentiredistanceexaminedinthestudyisaround 50kilometres.
The highway is one of the primary connections betweenNagpur Katol Warud AmravatiandMadhya Pradesh, since NH 353J begins 13 kilometres from ZeroMilenearFetriT point.
The geography and traffic factors of the research regionareinvestigated.
Thisresearchanalysestheexistingtrafficsituation andoffersmodificationstogeometricconditionsto enhancetrafficconditions.
Analyze traffic data necessary for improving a highway'strafficflow.
Toexaminethepresentroadgeometricdesignofthe Two lanesplitcarriageway,stretchfromNagpurto Katol(NH 353J).
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3791
Figure 1 Map of Nagpur Katol National Highway 353 J Figure 2 Satellite View Nagpur Katol National Highway
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Analyzethepresentgeometricconditionoftheroad underdifferentroadwayandtrafficcircumstances.
Toinvestigatenumerousroadwaygeometryfactors inordertocomprehendthecurrentstatus.
Toestablishthenecessaryreasonforupgradingthe motorway.
Toutiliseanalysedataforpavement.
thecityhasincreased.Inundertwodecades,thenumberof registeredmotorvehiclesinPatnahasincreasedby67times, from4,384in1981to294,164in2001,a67 foldrise.When calculatedfrom1981to2001,theyearlygrowthraterisesto almost 23 percent. Due to the absence of a mass transportation infrastructure, it has been noticed that the expansionofcustomizedvehiclessuchastwo wheelersand automobiles is extremely rapid. The Patna public transportationsystemasawholeisinsufficient,inefficient, and unplanned; as a result, it is unable to meet the population'stravelneedsaseffectivelyasfeasible.
Upgradethecurrenttwo laneroadwaytoafour lane highwaywithoptimalshoulderandmedianwidths accordingtoIRCcriteria.
Proposeanalignmentthatisassimilaraspracticable tothepresentalignmentinordertoincreasevehicle speedandqualityofservicewhiledecreasingtravel time,delays,andqueuelengths.
Donotuseabbreviationsinthetitleorheadsunlesstheyare unavoidable.
Karim et al. (2009) researched road safety issues and difficulties.Intheearlyyearsofthetwenty firstcentury,a relativelynewmechanismwasenactedtouncoverpotential road safety issues at various phases of road construction projects. The road safety audit examines both new road infrastructureprojectsandroadrepairinitiatives.Theroad safetyauditmethodshavebeendesignedtoencompassall phases of project execution, including the planning, preliminary design, detailed design, construction (or pre opening),andoperatingphases.
Singh and Mishra (2006) conductedaroadaccidentstudy inthecityofPatnaandanalysedthemaincausesofaccidents. InthemajorityofIndiancities,urbantransportinfrastructure is poor and decaying over time. The growth of the public transportation system has not kept pace with the traffic demandintermsofbothquantityandquality.Asaresult,the usage of unwanted modes such as private transport, primarily two wheeled vehicles, and intermediate public transit, namely three wheeled vehicles, is increasing at a rapid rate. Today, parked automobiles, hawkers, and roadsidebusinessesencroachextensivelyonroadwaysand pathways,forcingpeopletowalkontheroad.Thisnotonly impedestheflowoftrafficbutalsoplacespedestrians'livesin gravedanger.Biharisoneofthepoorestandmostpopulous states in India, and its maincity, Patna, isloud, congested, filthy,andoftenchaotic.Thecity'sroadwaysarecloggedand invaded by other activity. Particularly, bus services have worsened, and their efficiency and quality of service have declined,causingpassengerstoswitchtocustomisedmodes andIPTs.Thisnotonlyimpedestheflowoftraffic,butalso placesthelivesofroadusersingravedanger.Overtheyears, theoverallnumberoffatalaccidentsandrelatedfatalitiesin
Jain et al. (2009) conductedasafetyassessmentoffour lane nationalroads.TheRoadSafetyAudit(RSA)isasystematic method for evaluating the accident risk and safety performance of new and existing roadways. RSA is an efficient,cost effective,andproactivemethodforenhancing road safety. It has been demonstrated that RSA has the capacitytosavelives.TheRSAwasinventedinGreatBritain and has now spread to the United States, Australia, New Zealand, Denmark, Canada, Malaysia, and Singapore. DevelopingnationssuchasIndia,SouthAfrica,Thailand,and Bangladeshareatvariedphasesofadoption.RSAlookstobe asuitableinstrumentforenhancingroadsafetyinIndia,since fundamentalandprecisedataonincidentshavenotyetbeen gathered.

DevarajHanumappa and Parthasarathy Ramachandran (2009) did research titled "Cellular Automata Model for Mixed Traffic Flow with Lane Changing Behavior." Indian citiesarecharacterisedbylargelymixed trafficstreets.The modellingofmixedtrafficcombiningvehicleswithvarying speeds,lengths,andwidthsisacomplexproblem.Basedon thefinercellsystemofcellularautomata(CA)models,this research offers to analyse the mixed traffic behaviour of vehiclesandmotorbikesinIndiantownswithintermediate lane width. Even with the presence of motorbikes, the maximum automobile flow seen in the data is more than predictedbytheNa Schmodelforcars.Thisriseismostlythe resultofalteredbehaviour.Theautomobileflowreducesas the motorbike density increases. In addition, the research intendstoexaminetheimpactoflanechangebehaviouron the speed and flow of the traffic stream by employing the fundamental diagrams of speed flow density curves. The
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3792

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
simulationresultrevealsthatthelikelihoodoflanechanges hasminimalimpactonthepaceandflowoftraffic.
Kumar A., Dhananjay A. S., Agarwal A., Badage G., BhagatC., Devkar A., Kadam S. (2015), Theauthorshows that the construction of an efficient road transportation infrastructureisaprerequisiteforeachdevelopingnation.In addition,updatingthecurrentroadnetworkisnecessaryfor industrialisednationstocarryouttheirtransportationtasks efficiently,sinceurbanandnon urbanhighwaysreachtheir saturationpointwithgrowingtrafficvolume.Thedesignof theroutealignmentandpavementstructuredeterminesthe project'scost,whichisentirelydependentonthedurationof theproject.Therefore,thebestaccessibleHighwayGeometric Design Software must be utilised for this task. In consideration of this, the author has utilised MXROAD Software for the geometric design of the existing state highway (SH 131) in Maharashtra in order to improve its geometric characteristics and expand it from two to four lanes.Thesoftwareemploys3Dstringmodellingtechnology and provides the appropriate values for many geometric designcomponents,suchashorizontalandverticalcurves, superelevation,shoulder,etc.JournalArticle6(Summary)
VikasGolakoti (2015), His dissertation consists of road geometryfactors,datacollecting,andgeometricparameter analysis. This study aims to determine the effect of road geometryvariablesonaccidentratesonflatterrain,aswellas theextenttowhichtheseparametersimpactaccidentratesin rural regions. Thestudy intends to determine the effectof elementssuchas additional width,horizontal radius,sight distance, K value, super elevation, horizontal arc length, verticalarclength,andverticalgradientontheaccidentrate, as well as to determine the values for future road design. JournalArticle7(Summary)Shukla(2008)investigatedthe mixedtrafficflowbehaviouronafour lanedividedhighway undervariedcircumstancesoftrafficvolumeandshoulder andcreatedasimulationmodeltopredictroadwaycapacity under theseconditions based on the observedtraffic flow. The arrival pattern of cars, speed characteristics, lateral positioning of vehicles, and overtaking behaviour were investigated in order to comprehend the traffic flow behaviour on four lane divided roads under mixed traffic conditions.Thisexhaustivereviewoftheliteraturereveals that no substantial work has been done to establish the roadwaycapacityforvaryingcarriagewaywidthsonmulti lanehighways,urbanroads,andurbanexpresswaysforthe heterogeneoustrafficmixprevalentonIndianhighwayswith areasonabledegreeofconfidence;therefore,thisresearch effortcanbeconsideredasignificanteffortinthisdirection
ToxicologyattheIndiraGandhiGovernmentMedicalCollege in Nagpur has conducted retrospective research spanning two years. There was a total of 460 road traffic accident related fatalities, which accounted for 22.24 percent of all
autopsies of unnatural deaths. Greatest numbers of road traffic casualties were men (87.61 percent) and maximum deaths in the 20 39 age group (55.43 percent), with a significantmalepredominanceacrossallagecategories.In themajorityofincidents,pedestriansweretargeted(43.91 percent). 60 percent of victims died at the scene of the accident,and84.58percentperishedwithin24hours.The majority of deaths were caused by damage to essential organs (49.13 percent), followed by head injury, bleeding, andshock(37.17percent,10.65percent,and10.65percent, respectively).
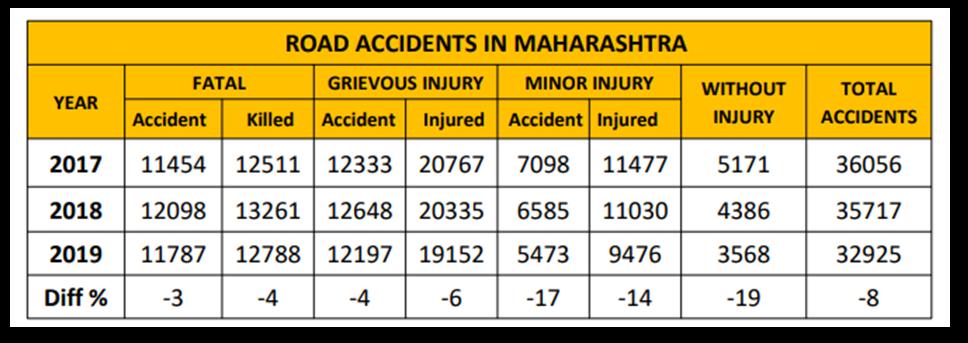
The following information indicates that there was an increaseindeathsandseriousinjuriesin2018comparedto 2017, however there has been a decrease of 4 percent in fatalities,6percentinseriousinjuries,and8percentintotal accidentscomparedto2018.In2019,therewere32,925total roadtrafficaccidents,areductionof8percentcomparedto 2018.In2019,12,788 people perishedasa resultofthese accidents.Basedontheavailablestatistics,therewillbe38.8 percentmorefatalaccidentsinMaharashtrain2019thanin 2018. Approximately 90 accidents and 35 fatalities occur dailyonthestate'sroadways,whichequatestoanaverageof 3liveslosteverytwohours.Thetotalnumberofregistered motorvehiclesin2019was23,1million.Inthesameyear,the total length of roads was 2,67,451 kilometers. These road networksincludeinterstates,statehighways,districtroads, andruralandvillageroads.3,7percentofthenation'sgross domesticproductislostduetotrafficaccidents.
25percentofthe12,788fatalitieshappenedinthreedistricts: Pune (1,329), Nashik (960), and Ahmednagar (873). The 2872 accidents recorded in Mumbai City resulted in 447 fatalities.In2019,thedistrictofSatarahasanalarming83 percentincreaseinaccidentsanda120percentincreasein deaths compared to 2018, whereas Ratnagiri has a 37 percent decrease in accidents. Thane Rural (accidents by 21%,deathsby26%)andWashimdistrict(accidentsby16%, fatalities by 23%) indicate a decline in accidents and fatalities.Eventhoughroadaccidentsareoneofthetopten leadingcausesofhumanmortality,theyareoftenoverlooked
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3793

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
due to the widespread notion that they are random, unavoidable, and unexpected. The biggest cause of traffic accidentsinMaharashtrais,amongotherthings,drivererror.
The highest number of accidents, 3228 and 3245 respectively, and deaths, 1203 and 1146 respectively, happenedinthemonths ofMayandJanuary,possiblyasa resultoftheincreasednumberofcars onunfamiliarroads duringtheholidayseason.
Octoberhadthefewestaccidents(2201)andSeptemberhad the fewest fatalities (784), possibly due to the wet season causinglessautomobilestobeontheroad.Additionally,less agriculturalgoodsistransportedduringthisseason.Table2: Scenario of Road Accidents in Nagpur S.No. Year Total AccidentTotalKilledTotalInjured
Year Total Accident Total Killed Total Injured
2017 897 350 887
2018 996 346 981
2019 843 384 950
2020 195 283 373
2021 958 269 950
Thisstudydiscussestheupgradeofgeometricdesignforthe wideningofNH 353JinthestateofMaharashtrainorderto decongesttheurbanboundariesoftheNagpur Katolsection. Thegeometricdesignofahighwayentailsthedesignofthe highway's visible physical characteristics, including cross sectional components, sight distances, alignment, bends, super elevation, and other auxiliary features based on available topography data. The traffic regulatory system, vehiclespeeds,accelerationanddecelerationcharacteristics ofdifferentvehicleclasses(Bus,trucks,auto rickshaw,cars, bikes,LMV,HMV),intersection,rotary,rotaryintersection, signalintersection,andsignalinterlockingmustbestudiedin ordertocompletetheresearch.
Selection of topic and formulating objectives and scope of research
Collection of data
of a current
Initially, an appropriate topic is chosen and all pertinent informationisgathered.Existinggeometricdesignisutilized toconductastudyofthepresenttrafficenvironment.Ifthe outputdatacollectedbythesimulationmodelaredeemed insufficient according to design standards, a geometric redesign of the road is performed in which the road is enlargedandthealignmentsaremodifiedinaccordancewith IRCcriteria.Therebuiltmodelundergoesasimulationcheck inwhichitsLevelofServiceismonitoredandadjusteduntil therequiredvaluesarereached.Theflowchartdepictsthe stages of the research procedure. Selection of topic and formulationofresearchobjectivesandscopeDatacollection Developmentofacurrentscenariotrafficsimulationmodel RedesignofroadutilisingCADDsoftwareDevelopmentofa redesignedscenariotrafficsimulationmodelComparisonand validation of current and redesigned simulation models. National Highway Authority of India, Ministry of Road Transport andHighways (MORT&H), Government of India havecarriedouttheWideningandStrengtheningofExisting National Highway Development in India. Existing road condition,trafficvolume,androadcompositiontoanticipate roaddeteriorationinaccordancewithurbanandruralroad circumstancesdidnotmeetIRIstandards.
NationalHighwayNo. 353J: Theconditionoftheexisting pavement is poor to good. Generally, the existing road is having2laneswithpavedshoulders

The information provided in this schedule is for the Concessionaire'sfirstcomprehensionanddirection.NHAIis not responsible for any inaccuracies in the submitted informationandisnotaccountablefororconstrainedbythe Concessionaire's use of data. pertinent to the main course Thefollowingsummaryofthecriteriaforthevariousaspects oftheProjectHighwayisthebareminimumforthe'Project' Theterm'Project'hasthesamemeaningasestablishedinthe concessionagreement'ssection1.1.
Intheplanning,design,andexecutionoftheworksandother works associated with the repair, maintenance, or improvement of the Project Highway and functions associatedwiththeconstructionoftheProjecthighwayand roadside facilities, the concessionaire shall take all such actionsanddoallsuchthings(including,butnotlimitedto,
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3794

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
organisingitself,adoptingmeasuresandstandards,executing proceduresincludinginspections,etc.)asmaybenecessary.
EnableNHAItoprovideanacceptablysafehighwayinterms ofitscondition(structuralsafety)anduse(roadsafety)and. Enable NHAI to fulfil its statutory and common law obligationsand.EnableNHAItoprovidealevelofservicein the public not inferior to that provided on the trunk road during construction or improvements works and. Enable NHAI to provide a congestion free, uninterrupted flow of trafficontheProjectHighwayand.Enablethe
Providea safe,clear,andinformativesystemofroadsigns and, Comply with any specified programme requirements including for the completion of the new road and, Enable standards of fitness for the purpose appropriate for a highway to the character of the Project Highway to be achieved throughout the contract period and, Ensure adequatebusbaysforstoppingofbusesandbussheltersfor commuterstowaitundercoverand,Provideadequateoff streetparkingand,Provideadequateon streetparking.
The so called maintenance approach comprises of inexpensivelocalrepairsandpavementresurfacing.Theroad alignmentisappropriate,andthejunctionsarewell designed. Onthepavementsurface,thetypicalindicationsofmodest surface deterioration are visible. Functional aspects contributetoanexceptionaldegreeofservice.Thereareno timedelaysortrafficcongestion,andnosubstantialactionis necessary.Thesurfaceofthepavementmustberestored,and inadequatesignageandguardrailsmustbefixed.Ingeneral, the first option does not contain any enhancements to alignment characteristics and consists primarily of basic maintenance.Thecostofoperationsremainsminimal.Thus defined, maintenance operations do not involve pavement reconstructionorroadwidening.
Rehabilitation,thesecondtechniqueforimproving,entails moreextensiveprocedures.Thepavementwidthprovidesa satisfactorylevelofservice,butthealignmentcharacteristics at turns are poor, intersections have inadequate approach anglesasindicatedbytherightarrowornoturninglanesas indicated by the left arrow, and safety and traffic control equipmenthasdegradedorisobsolete.Adjustingthecurrent alignment is not part of the engineering tasks required to effectively improve the roadway. Where necessary, the pavementmustberesurfaced,shouldersandbermsmustbe reshaped,roadsafetydevicesmustbeupgraded,andat grade junctionsandbendsmustbeplanned.
ReconstructionThethirdmethod,so calledrebuilding,refers to worldwide upgrading activities and consists mostly of extensiveroadwideningandinfrastructureexpansion.The alignment may be conserved and maintained, but inferior lanewidthandlowroadcapacitynecessitateinthisinstance pavementandshoulderwidening,pipeandculvertextension, andextensiveearthworkworks.Engineeringworksinclude the expansion of roads and the rebuilding of bridges. In numerousinstances,thealignmentmaybegood,butthelane width is insufficient. Due to large scale engineering works and expropriations, the level of service is poor, and the operational expenses are substantial. Typically, reconstruction entails a significant construction effort to rebuild the current roadway to full geometric and safety requirements.
Considerationofanentirelynewalignment,routeselection, androadbuildingisthefourthmethod.Thismethodmaybe favoured above others because to the high expense of restoration reconstructionactivitiesorareevaluationofthe entire project's environmental effect and social benefit implications. This may be the case for older roadways in ecologicallysensitiveordenselypopulatedregions.Ifthisis the case, the existing road should be abandoned or eliminated, and a completely new route site should be researched. Expropriations and the construction of new interchanges and bridges are examples of important and priceyissuesthatfrequentlyariseduringtheexecutionofa newproject.Technicallyenticingattimes,thishigh priced solutionmaybeimpossibletoimplementduetopoliticalor financialrestrictions.
The present road geometric design of the two lane split carriageway from Nagpur to Katol (NH 353J) has been analysed.
Foreachsignificantintersectionintheresearchregion,the analysisoftheexistinggeometricconditionoftheroadunder diverseroadwayandtrafficcircumstancesisundertaken.
Basedontheanalysesconductedinthisstudy,anefforthas beenmadetoenhancethecapacityoftheNationalhighway fortwo lanesplitcarriagewaybyupgradingittofour lane carriageway with optimal shoulder and median widths accordingtoIRCcriteria.
Thesignificanceofupgradingexistingtwo laneNagpurKatol highwaystofour lanesisasfollows:
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3795

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Decrease in number of accidents due to less congestion. Provides better riding quality and also reduction in fuel requirementleadingtoadecreaseinpollution.Theroadis primarily an orange producing belt and will benefit the orange industry. Upgrading the existing two lane road to four lane with paved shoulders will facilitate better transportationintermsoffast,congestion freemovementof traffic.
1. Ashok Kumar, Dhananjay A.S, Agarwal Alkesh, Badage Ganesh, ChavanBhagatsinh, Devkar Anil, Kadam Shubham, (2015). “Up Gradation of GeometricDesignofSh 131(Ch.9.35km 15.575km) Using MX Road Software A Case Study”, International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology,Volume6,Issue6.
2. AASHTO, 2004. A Policy on Geometric Design of Highways and Streets, Green Book. American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials.
3. American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO). A Policy on Geometric Design of Highways and Streets. Washington,DC.2004.
4. KumarA.etal,(2015).“UpgradationofGeometric Design of Sh 131(Ch. 9.35km 15.575km) Using Mxroad Software”, International Journal of TransportationEngineering,6(6),67 78.
5. Singh, S. K., Mishra, A. “Road Accident Analysis: A case study of Patna city”, Urban Transportation Journal
6. Karim, M. R., Marjan, J., Abdullah, S. “Road Safety Audit:challengesfromtheMalaysianexperience.
7. Khanna,S.K.,Justo,C.E.,&Veeraragavan,A.(2015). Road side Development. In Highway engineering(10thed.,pp.736 743).Roorkee:Nem Chand.
8. Vardaki,S.,Papadimitriou,F.,&Kopelias,P.(2014). “Road safety audit on a major freeway: implementing safety improvements”. European TransportResearchReview
9. IRC: SP: 88 2010. “Manual on Road Safety Audit”, IndianRoadCongress,NewDelhi,India.
10. IRC:SP:73 1980.“GeometricDesignStandardsfor Rural (non Urban) Highways”, Indian Road Congress,NewDelhi,India.
11. IRC: SP: 23 1993. “Vertical Curves for Highways”. IndianRoadCongress,NewDelhi,India
12. IRC: SP: 88 2010. “Manual on Road Safety Audit” IndianRoadCongress,NewDelhi,India.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3796
