International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

2
Abstract Inrecentconstructionactivity,Flatslabbuilding hasmanyprivilegeoverconventionalslabbuildingintermsof Architectural flexibility, Easier formwork, use of space, less construction time and Better quality control. But, flat slab structures are significantly more flexible than the conventional slab structures, thus becoming more vulnerable to seismic loading. Therefore in order to upgrade the performance, flat slab are usually provided with drops. The flat slab has less stiffness and less shear strength with more flexibility feature than the conventional slab. In the present work a G+12 commercial multistoried building having conventional slab and flat slab having drop with and without shear wall. The buildings are modeled and Analyzed by using ETABS software. The seismic analysis is done as per IS 1893(Par 1) The behavior of Conventional slab and Flat slab structure with and without shear wall in seismic zone II, III, IV and V with type II (medium) soil are taken for all instances. Analysis of buildings is done by Equivalent static method and Response spectrum method. The seismic evaluation result can be done based on the parameters like Storeydisplacement,Storeydrift,StoreystiffnessandNatural time period.
Key Words: Conventionalslab,Flatslab,Shearwall,Storey displacement, Storey drift, Storey stiffness, Natural time period
Thesedays,thestructuresarebeingbuiltquicklybecauseof theexpansioninpopulation.AtpresentIndiaisthequickest developing country in economy this leads to demand in infrastructurefacilitiesalongwiththegrowthofpopulation. The demand for high rise building in urban areas is increasing day by day than the past decades. Due to urbanization,thedesiresofthepeoplehavebeenupgraded withrespecttolessconstructiontime,flexibilityintheroom layout, aesthetic appearance, better quality control, fire resistant, better diffusion of light and so on. To meet the demandofpeopledifferenttypeofconstructiontechnique has been adopted these days. Among these flat slab (i.e., beamlessslab)isone.
Generally,themultistorystructuresareconstructedwiththe conventional reinforced concrete slab which proves it to
1
have high storey stiffness and strength. But, due to the several advantages of beamless slab the old style constructioni.e.,conventionalslabarebeingslowlyreplaced byflatslabs.
The flat slab directly rest on the column and transfer the loadstothecolumnswithoutbeams.Flatslabbuildingsare prominent floor construction systems in commercial buildings, residential buildings and other multi storey buildings. Flat slab structures are favored by both architectureandclient.Intheconventionalslabstructures theslabisrestingonthebeams,theslabloadistransferred to beams and then beams to columns. But in flat slab structureloadistransferredfromslabtocolumnsdirectly.
Conventionalslabsystemisroutinemethodofconstruction consistsofcolumns,beamsandslab.Thissystemutilisedin the development of private structures and compact construction. Here all the four edges of the slab are supportedonbeamswheretheloadsaretransferredfrom slab to beams and then to columns. Hence weight of the structureincreasesandformworkisalsocostlycomparedto flatslab.Inthistype,thethicknessofslabissmallwhereas the depth of beam is large. It requires more formwork comparedwiththeflatslab.
Flatslabusuallydoesnothavebeamsissupporteddirectly bythereinforcedcolumns.Itisalsocalledasbeamlessslab. Theprojectionbelowtheslabi.e.,thethickenedportionis calledasDrop.Flatslabispreferredbybotharchitectand client because of its aesthetic view and economic advantages.Thedrawbackofbeamlessslabistheirlackof resistancetolateralloads.
Shearwallisaverticalstructuralelementdesignedtoresist the lateral loads in high rise buildings. It provides the stabilityagainstlateralforceduetoitslateralstrengthand stiffness which can be used to resist the wind loads and
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3566
M tech student, Dept of Civil Engineering, P.E.S College of Engineering, Mandya, Karnataka, India Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, P.E.S College of Engineering, Mandya, Karnataka, IndiaInternational Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
seismic loads. The position of the Shear walls is usually providedatcornersormiddleofthestructures.Theshear wallformsanefficientlateralforceresistingsystemwhenit issituatedatadvantageouspositionsofthestructure
1. Toobtainthehighlyeffectivestructuretoresistthe horizontallateralloads.
2. Tostudytheeffectofconventionalslabandflatslab structurewithandwithoutshearwall.
3. Comparativestudyonvariousseismicparameters like storey displacement, storey drift, storey stiffnessandTimeperiod.
4. Thevariousmodelsthusgeneratedparametrically arecomparedandsuitableconclusionsaredrawn.
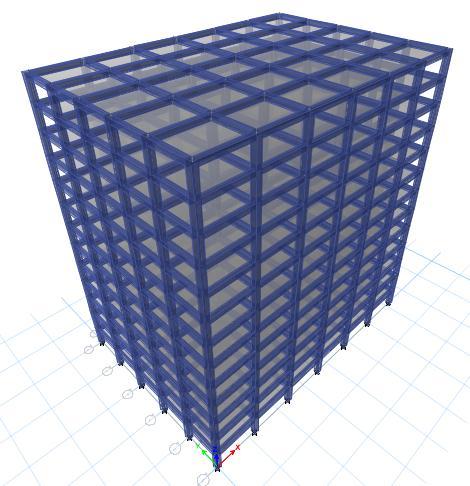
The structure considered for an analysis is RC building. A G+12 story building geometry are considered such as ConventionalslabstructureandFlatslabwithandwithout shearwall.Thebuildingsaremodeledandanalyzedbyusing software ETABS for different seismic zones. Models are consideredforzonefactorII,III,IVandVandsoiltypeisII (medium)asperIS:1893(Part1)codeofpractice.
The models of G+12 storey building are analyzed in both EquivalentstaticmethodandResponsespectrummethod. TheanalysisresultsareobtainedforseismiczoneII,III,IV andV.
1. Conventionalslabstructure(ZoneII,III,IV,V)
2. Flatslabstructurewithoutshearwall(ZoneII, III,IVandV)
3. Flatslabstructurewithshearwallatcorner (ZoneII,III,IVandV)
Table 1 StructuralandSeismicdetailsof13storey conventionalandflatslabstructure
PARAMETERS
Plandimension 36x25m
No.ofstories G+12
Heightofthestructure 39m
Bottomstoreyheight 3m
Gradeofconcrete M30
Gradeofsteel HYSD500
Floortofloorheight 3m
Slabthickness 150mm

Dropsize 2x2m
Dropthickness 200mm
Shearwallsize 200mm
Sizeofcolumn (600x600)mm
SizeofBeam (300x600)mm
Liveloadonfloors 4kN/m2
Terraceload 1.5kN/m2
Floorfinishload 1.5kN/m2
Zoneconsidered II,III,IVandV
Zonefactor 0.10,0.16,0.24and0.36
Importancefactor 1.2
Typeofsoil II(medium) Reductionfactor(SMRF) 5
Plan and 3D view
Fig 1: Conventionalslabstructure
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3567

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Fig 2: Flatslabstructurewithoutshearwall
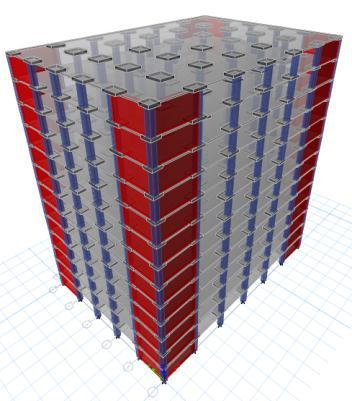
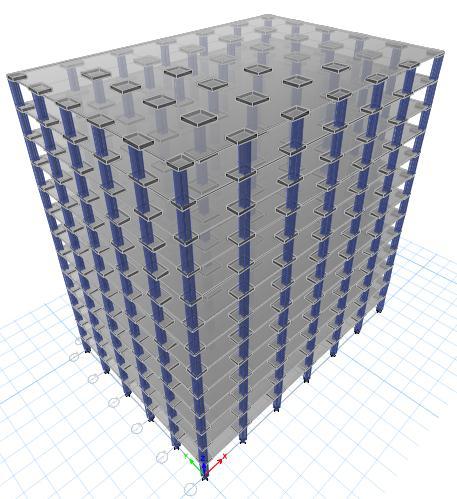
Chart 2: StoreydriftofbuildingforZoneII
Chart 3: StoreystiffnessofbuildingforZoneII
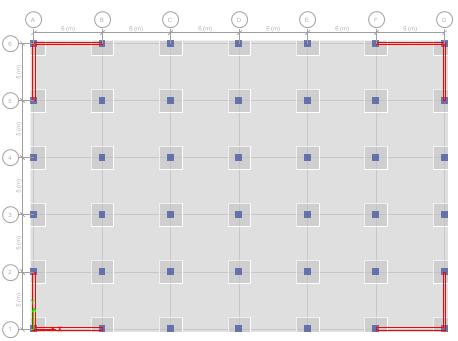
Fig 3:Flatslabstructurewithshearwallatcorner
The results of each building model are presented in this chapter. The analysis is carried out by Equivalent static method and Response spectrum method. The results are obtainedfor13storeybuildingforthezonefactorII,III,IV and V for the parameters Story Displacement, Story Drift, StoryStiffnessandNaturaltimeperiod.
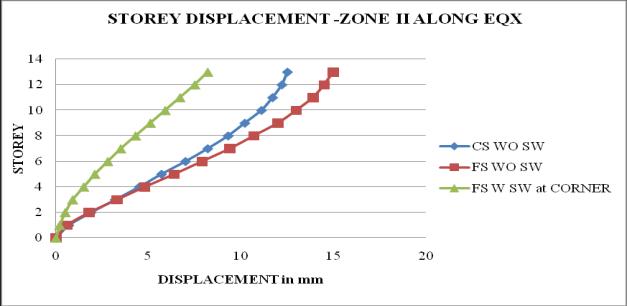
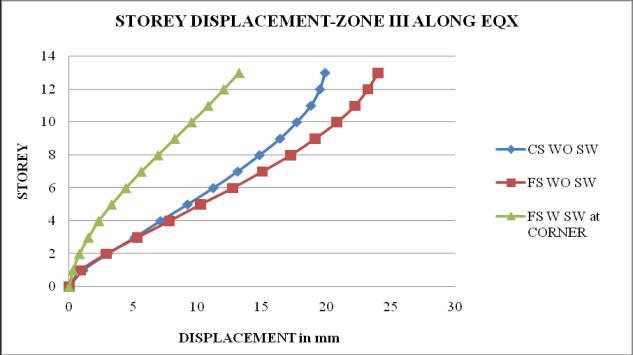
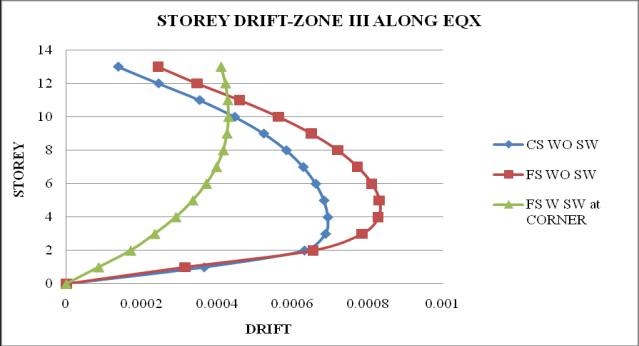

Chart 1: StoreydisplacementofbuildingforZoneII
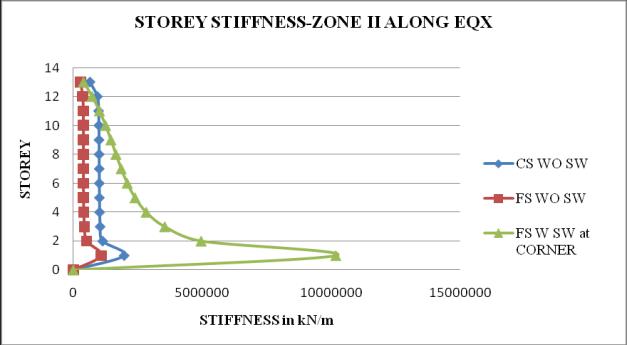
Chart-4: StoreydisplacementofbuildingforZoneIII

Chart-5: StoreydriftofbuildingforZoneIII
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3568
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
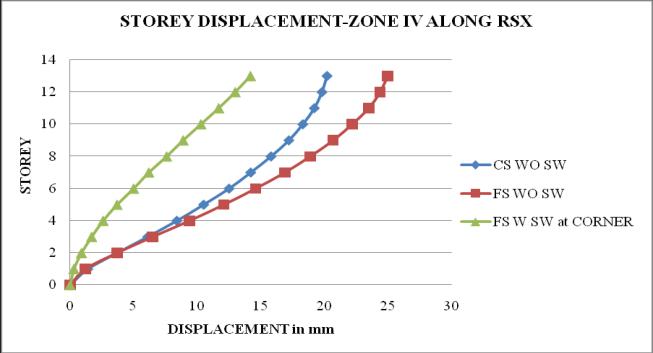
Chart 6: StoreydisplacementofbuildingforZoneIV
Chart 10: StoreydisplacementofbuildingforZoneII
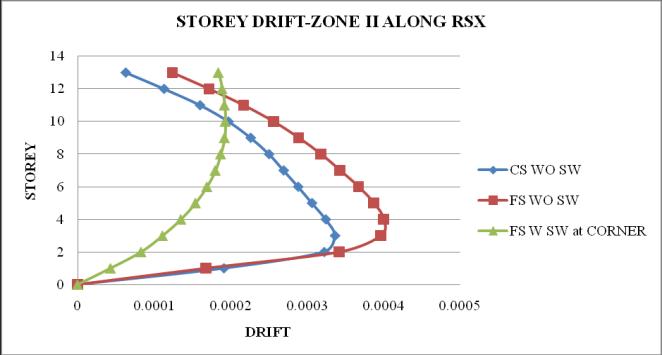
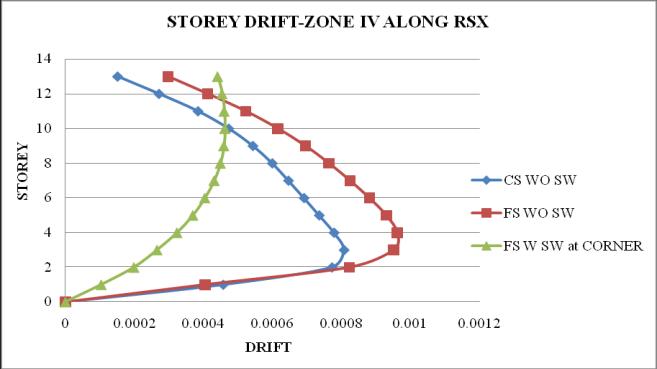
Chart 7: StoreydriftofbuildingforZoneIV
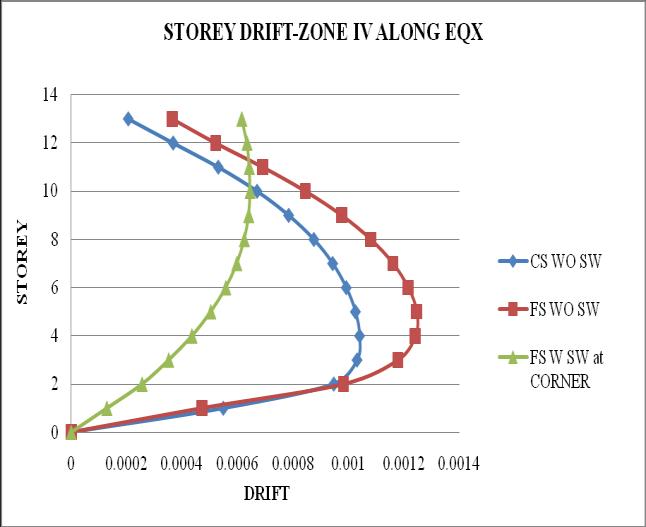
Chart 11: StoreydriftofbuildingforZoneII
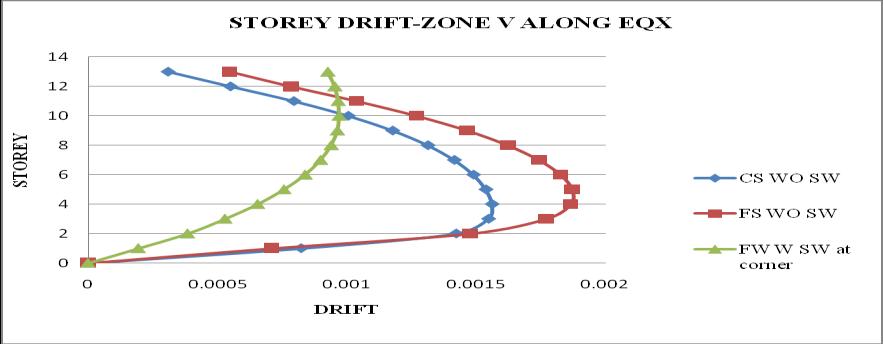
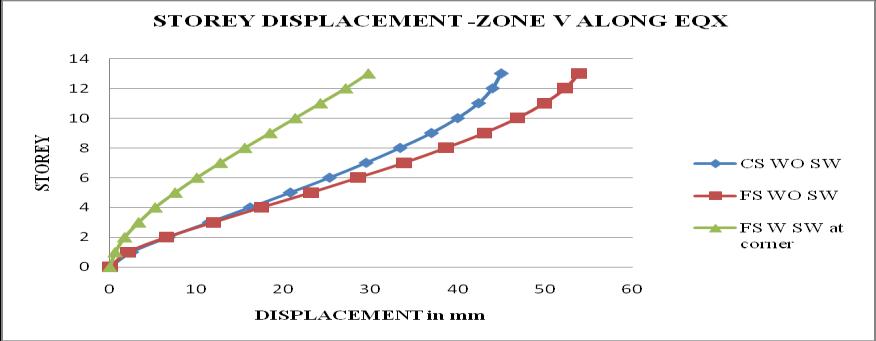
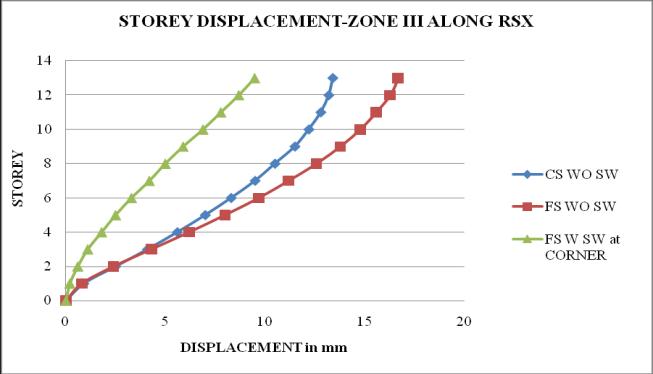
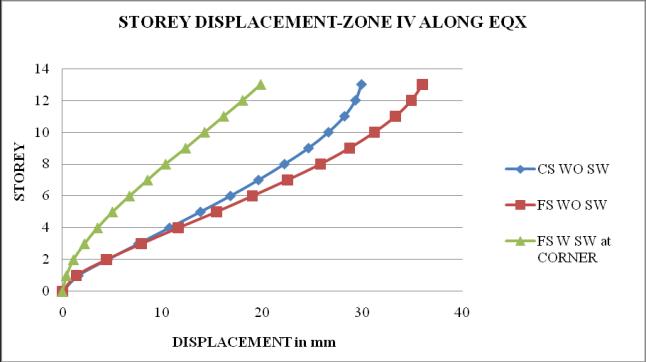
Chart 8: StoreydisplacementofbuildingforZoneV
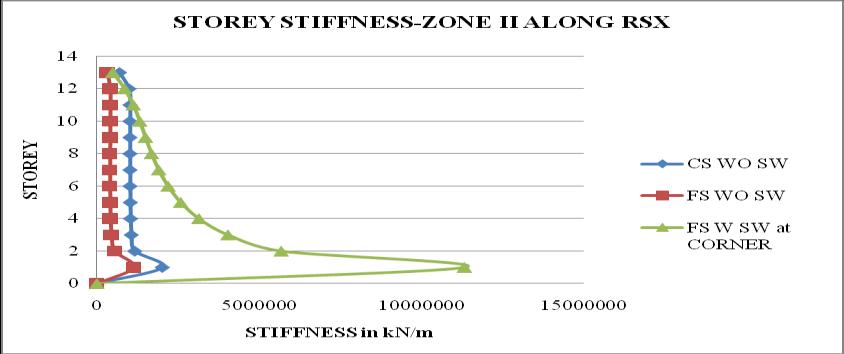
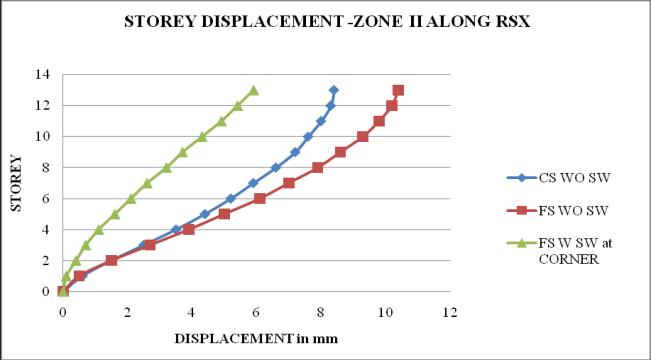
Chart 12: StoreystiffnessofbuildingforZoneII
Chart-9: StoreydriftofbuildingforZoneV
Chart 13: StoreydisplacementofbuildingforZoneIII
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3569

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
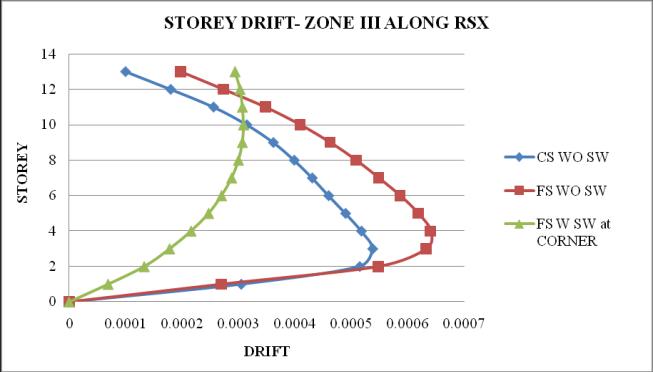
Chart 14: StoreydriftofbuildingforZoneIII
Chart 18: StoreydriftofbuildingforZoneV
Chart 15: StoreydisplacementofbuildingforZoneIV
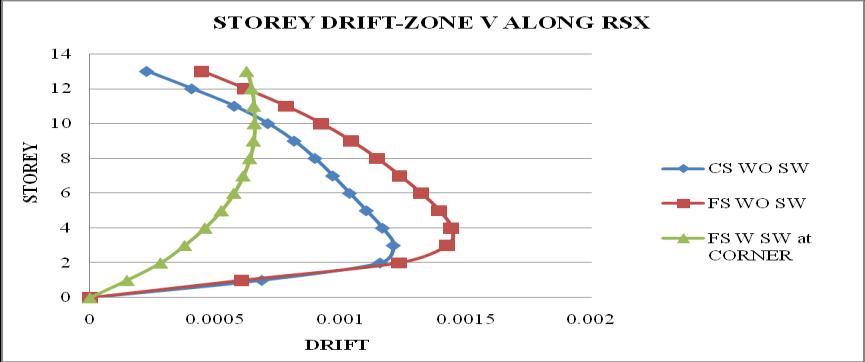
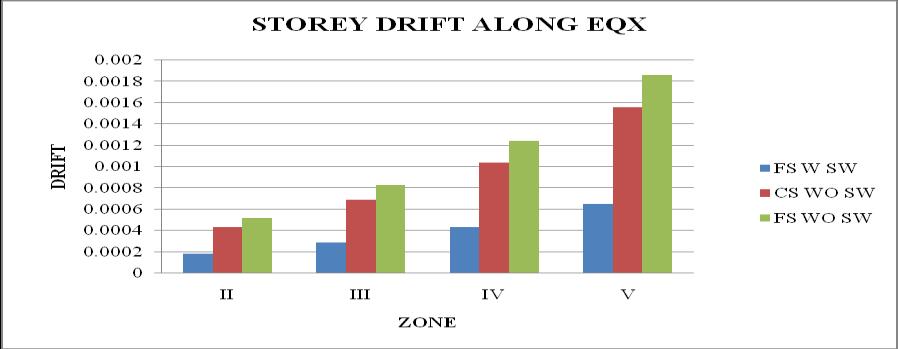
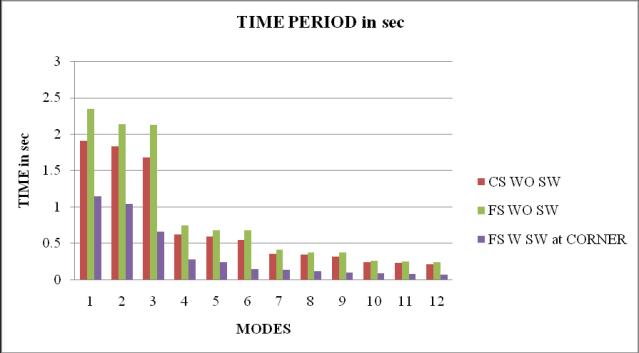
Chart 19: NaturalTimeperiodofbuilding
5.3 COMPARISION OF STRUCTURES FOR DIFFERENT SEISMIC ZONES BY EQUIVALENT STATIC ANALYSIS
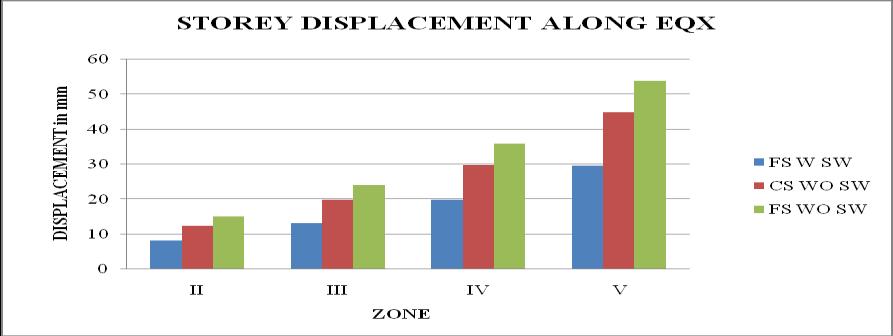
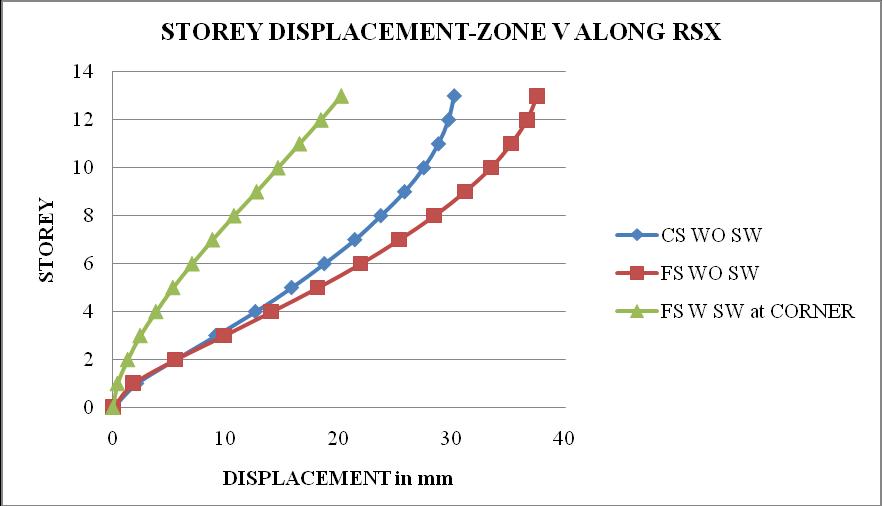
Chart 16: StoreydriftofbuildingforZoneIV
Chart 20: DisplacementvsZoneforstructures
Chart 17: StoreydisplacementofbuildingforZoneV
Chart-21: DriftvsZoneforstructures
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3570

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Chart 22: stiffnessvsZoneforstructures
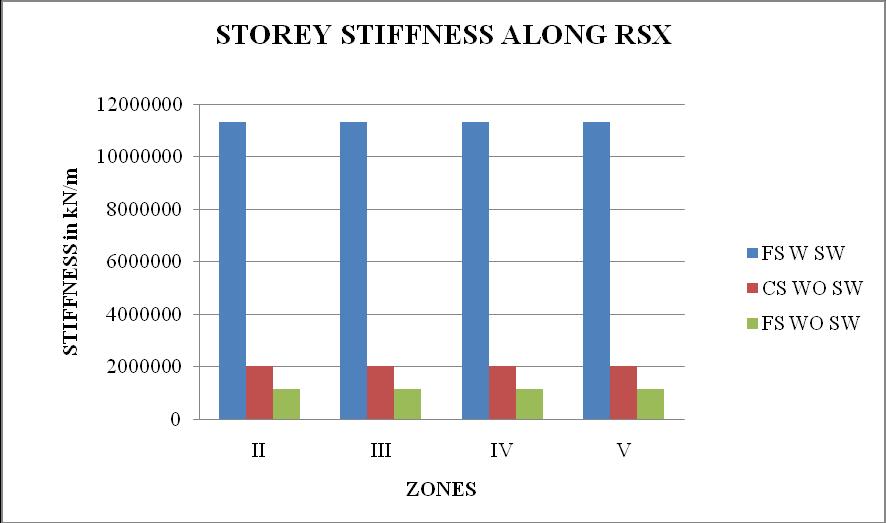
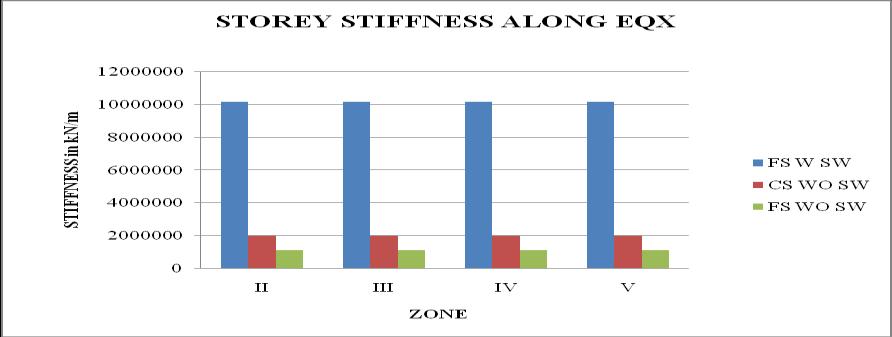
Chart 26: stiffnessvsZoneforstructures

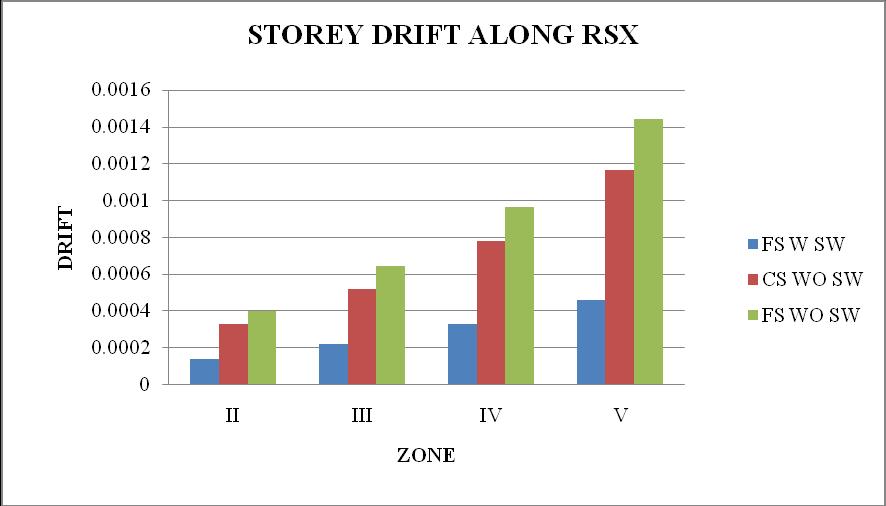
1. The storey displacement is high at the top storey andlessatthebase.Withtheincreaseintheheight ofthestructurethedisplacementgoesonincreases. Storeydisplacementofflatslabstructurewithout shearwallshowsmaximumvalue.
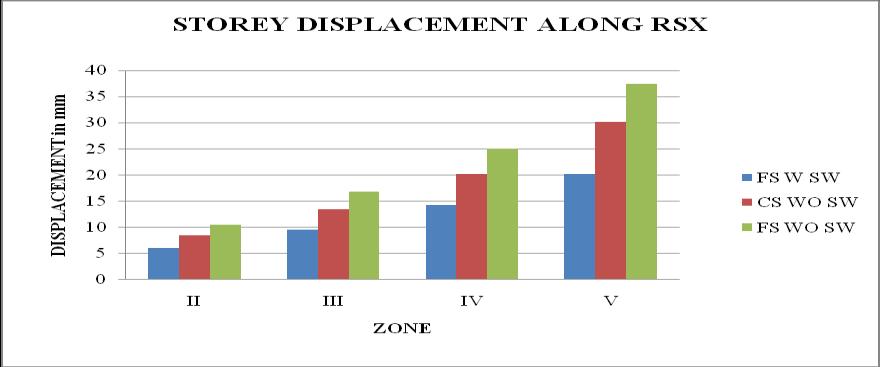
Chart 23: TimevsZoneforstructures 5.4
OF STRUCTURES FOR DIFFERENT SEISMIC ZONES BY RESPONSE SPECTRUM ANALYSIS Chart 24: DisplacementvsZoneforstructures
Chart 25: DriftvsZoneforstructures
2. Thestoreydriftfollowsaparabolicpathalongthe storey height. Storey drift of flat slab structure withoutshearwallismaximum
3. Thestoreystiffnessismoreatbaseanditdecreases as the height of the structure increases. Storey stiffness of flat slab structure with shear wall at cornerismaximum
4. Thetimeperiodofflatslabstructurewithoutshear wallismaximum.
5. It is observed that as the seismic zone increases from zone II to V, the storey displacement and storeydriftincreasesandstoreystiffnessandtime periodremainssame.
6. Flatslabstructurewithshearwallatcornergives the best results, because the Time period, Storey displacement,storydriftislessandStorystiffnessis morethanothertwostructures
[1] SandeshD.Bothara,Dr.ValssonVarghese.(July August 2012) “Dynamicanalysisofspecialmoment resistingframebuildingwithflatslabandgridslab” ,Vol.2,Issue4,pp.275 280,ISSN:2248 9622.
[2] M A Rahman (2012) “Effects of openings in shearwall onseismicresponseofstructures”, Vol 2,issue10july2012.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

[3] R.S.More,V.S.Sawant,Y.R.Suryawanshi.(2013) “Analytical study of different types of flat slab subjectedtodynamicloading”,IJSR,ISSN(Online): 2319 7064.
[4] SharadP.Desai,SwapnilB.Cholekar(2013) “Seismic performance of reinforced Concrete building with flat slab”; Volume 2, Number 10; April June,2013.
[5] Lakshmi K O (2014), “Effect of shear wall locationinbuildingssubjectedtoseismicloads”,ISOI JournalEngineeringandComputerScience,Volume 01,December2014.
[6] Salman I Khan and Ashok R Mundhada. (February 2015) “Comparative study of seismic performanceofmultistoriedrccbuildingswithflat slabandgridslab”,Vol.4,No.1,,ISSN2319 6009.
[7] NKRISHNARAJUBookofadvancedreinforced concretedesign”.
[8] Government of Bureau of Indian Standards: IS 875, part 2 (1987), Live Loads on Buildings and Structures,NewDelhi,India.
[9] Plain&ReinforcedConcreteCodeof Practice” FourthRevisionIS:456:2000.
[10] IS 1893 (Part I) : Criteria for Earthquake Resistant Design of Structures, Part I General ProvisionsandBuildings,FifthRevision,Bureauof IndianStandards,NewDelhi.
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3572