Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072


Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

Spoorthi Hiremath1, Dr. Dhananjaya. V2
1 Student, Dept of Computer Science and Engineering, Impact College of Engineering and Applied Science, Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India spoohiremath95@gmail.com
2 Professor, Dept of Computer Science and Engineering, Impact College of Engineering and Applied Science, Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India. csdhananjay@gmail.com ***
Abstract Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a type of malignant tumour that is characterised by rapid growth and early metastasis spread. Early and accurate SCLC diagnosis is critical for improved survival. Accurate cancer segmentation assists doctors in better understanding the location and size of cancer and making better diagnostic decisions. In this project, we are using the YOLO framework to pinpoint the exact location of a lung tumour that is attached to the border of blood veins, as well as to classify the tumour. The R CNN techniques demonstrated in Part 1 primarily use regions to localise objects within an image. The network does not examine the entire image, but only the portions of the image that are more likely to contain an object. The main advantage of using YOLO is that it is extremelyfast andaccurate.
Key Words: YOLO,DeepLearning,LungCancer,CNN.
Thelungsareshapedlikeapairofspongecones.Theright lunghasthreelobes,whiletheleftlunghastwo.The right lung is significantly larger than the left lung. The inhaling process delivers oxygen to the lungs. The lungs' tissue transports oxygen into the bloodstream. Lung cancer is a disease that causes abnormal cells to multiply and grow into tumours. Cancer cells in the blood can be conducted awayfromthelungs.Becausethenaturalflowoflymphout of the lungs is toward the centre of the chest, lung cancer frequently spreads toward the centre of the chest. Lung cancer is classified into two types: small cell lung cancer and non small cell lung cancer, which has three subtypes: carcinoma, aden carcinoma, and squalors cell carcinomas. Lung cancer was found to be the second leading cause of death in men and the sixth leading cause of death in women.Imageprocessinghasawiderangeofapplications inmedicalimageprocessingfordiagnosinglungcancer.
The proposed system description of lung cancer detection system includes four basic stages. The first stage begins withacollectionofCTimages(normalandabnormal)from the IMBA Home Database (VIA ElCAP Public Access). The second stage employs several image enhancement techniques to achieve the highest level of quality and clarity.Thethirdstageemploysimagepartitionalgorithms, which play an important role in subsequent image
processing stages, and the fourth stage obtains general featuresfromenhancedpartitionedimages,whichprovide indicatorsofimagenormalityorabnormality.
A trainable neural network that learns long range 3D contextual informationusinga lightweight3Dconvolution neural network and fine grained intra slice semantic information using a 2D convolution neural network. To deal with the anisotropic dimensions of CT volumes and reduce the computational cost of the 3D convolution neural network, they use spatiotemporalseparable3D (S3D) convolutions. We use dilated convolutions in a 2D convolution neural network to enlarge the receptive field whileretaininghigh resolutiontoretaina largeamountof semantic information about smaller objects. Create a hybrid features fusion module (HFFM) to effectively fuse 2Dand3Dfeatures.Toaddresstheissueofdataimbalance training,theyalsousethegeneralisedDicelossfunction.
Inaresearchpaper,thescholarsResearchersdevelopedan algorithmthatcandetectpneumoniafromchestX raysata level exceeding practicing radiologists. The algorithm, CheXNet, is a l2l layer convolutional neural network trained on ChestX rayl4, currently the largest publicly available chest Xray dataset, containing over loo,ooo frontalview X ray images with l4 diseases. Four practicing academic radiologists annotate a test set, on which they compare the performance of CheXNet to that of radiologists. We find that CheXNet exceeds average radiologist performance on the Fl metric. They extend CheXNet to detect all l4 diseases in ChestX rayl4 and achievestateoftheartresultsonalll4diseases[1].
A deep learning framework for covidl9 screening from radiographs. The novel pandemic has spread all over the world in the last few months, according to arXiv preprint arXiv:2oo3.l4395,2o2oBecauseofitseaseoftransmission, developing techniques to accurately and easily detect it anddistinguishitfromothertypesoffluandpneumoniais critical. According to recent research, the chest CT of patients suffering from shows certain abnormalities in radiography.However,thoseapproachesareclosedsource andarenotmadeavailable totheresearchcommunity for replication and deeper understanding. The goal of this
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
work is to create open source and open access datasets and to present an accurate CNN framework for machine learning. It's known as ResNet. This is accomplished by resizing input images progressively to l28xl28x3, 224x224x3, and 229x229x3 pixels and fine tuning the network at each stage. Using this approach and automatic learning rate selection, we were able to achieve state of the art accuracy of 96.23 percent (on all classes) on the dataset in only 4l epochs. This study presented a computationally efficient and highly accurate model for multi class classification of three different infection types in addition to normal people. This model can help with early case screening and reduce the burden on healthcare systems[2]
A deep learning classifier framework for diagnosing covidl9 in x ray images. arXiv preprint arXiv.org. Background and Goal: Coronaviruses are dangerous viruses that can cause SARS and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS CoV). At the end of 2ol9, the novel 2ol9 Coronavirus disease was discovered as a novel disease pneumonia in the city of Wuhan, China. According to the World Health Organization's most recent reports, the world is experiencing a Coronavirus outbreak, with the number of infected people and deaths increasing rapidly every day(WHo). Asa result,the purpose of this article is tointroduceanewdeeplearningframeworkthatwillhelp radiologists automatically diagnose in X ray images. Materials and Procedures: Due to a lack of publicly available datasets, the study is based on 50 chest X ray images with 25 confirmed positive cases. There are seven different deep convolutional neural network architectures included, such as the modified Visual Geometry Group Network (VGGl9) and the second version of Google MobileNet. Each deep neural network model can analyse the normalised intensities of an X ray image and classify thepatientstatusasnegativeorpositive.Experiments and evaluation of the have been completed successfully using 8o 2o percent of X ray images for the model training and testing phases, respectively. The VGGl9 and Dense Convolutional Network models demonstrated good and comparable automated classification performance, with fl scores of o.89 and o.9l for normal and, respectively. Conclusions:Basedontheproposedframework,thisstudy demonstrated the useful application of deep learning models to classifyX rayimages.Clinical trialsare the next stepinthisresearch[3]
Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks in mobilenetv2. 2ol8 in the Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on ComputerVisionandPatternRecognition.Inthispaper,we describe MobileNetV2, a new mobile architecture that improves the state of the art performance of mobile models on multiple tasks and benchmarks, as well as across a range of model sizes. In addition, we describe efficient methods of applying these mobile models to object detection in a novel framework we call SSDlite. Furthermore, we show how to build mobile semantic
partition models using MobileDeeplabv3, a reduced form of Deeplabv3 that is based on an inverted residual structure with shortcut connections between the thin bottleneck layers. As a source of non linearity, the intermediate expansion layer filters features using lightweight convolutions. In order to maintain representational power, we also discovered that non linearitiesinthenarrowlayersmustberemoved.Weshow how this improves performance and provide the inspiration for this design. Finally, our method decouples the input/output domains from the expressiveness of the transformation, providing a convenient framework for furtherinvestigation[4].
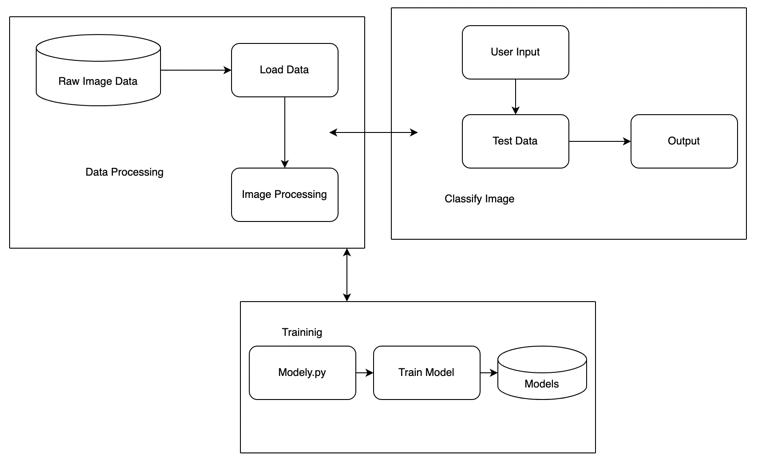
The proposed system is based on the YOLO framework. Where we try to study and understand the existing vision module systems. Where we look into working of YOLO frameworksfor the imageacquisitionsystem. Also,we try to build an Image classifier to find tumours and cancer in CT images. With that, we train a YOLO object detection to automaticallydetectTumorandcancerwithimagesviathe dataset collected. Finally, Evaluate the results from the trainedmodel.
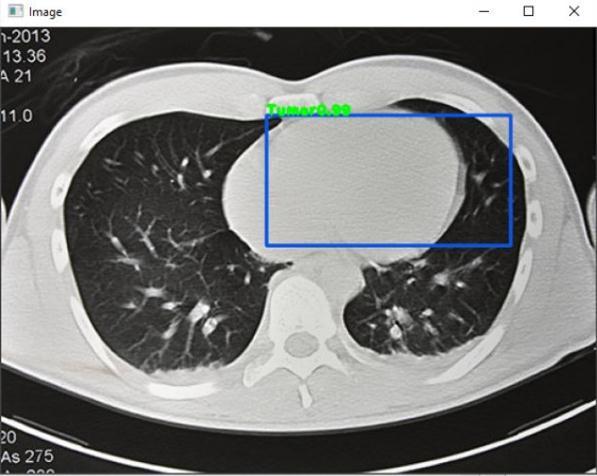
Training and testing are two modules in our proposed system. The cropped CT scan image is input to the system in the Training module, followed by Pre Processing to enhancetheimage.IntheTestingmodule,theCTimageis sent to the Pre Processing phase, where it is divided into two parts to extract the lung region and the region of interest. The first two parts are feature extraction and selection, which are used to extract the tumour’s main characteristics.Thefinalcomponentistheclassifier,which determines whether the cancer was detected or not. We areusing the YOLOalgorithmandthe YOLOframework to determine the exact location of the lung tumour and tumourattachedtotheborderofbloodvessels.
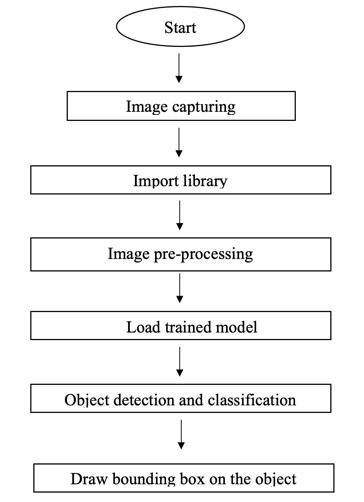
Image Capturing: In this step image captured from an Xray.
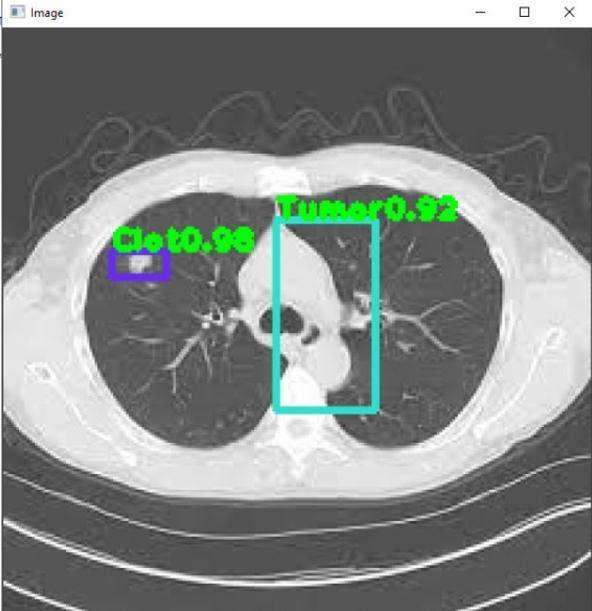

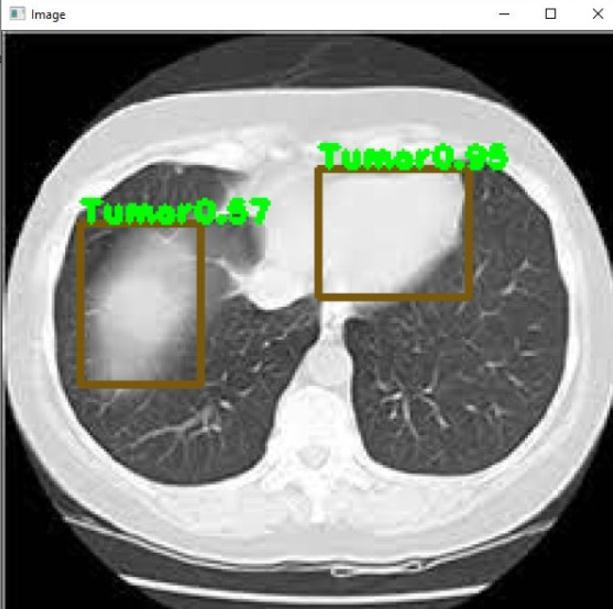
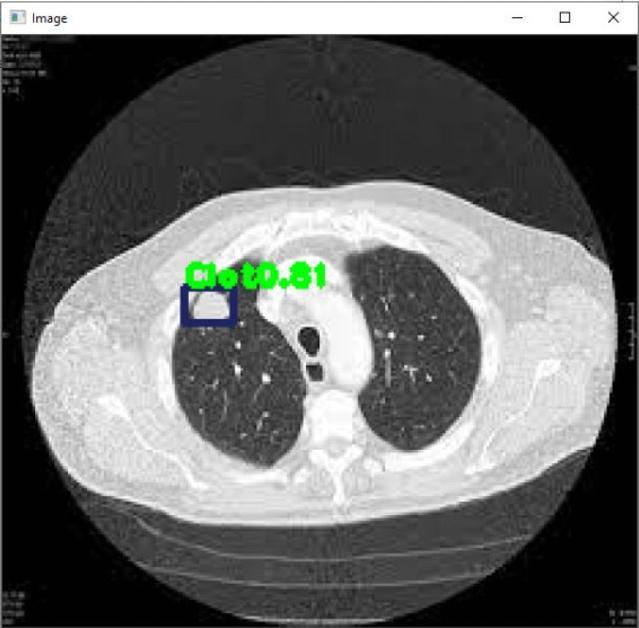
Import Library: Respective libraries required are imported.
Image Pre Processing: Acquired images are pre processedandunwanteddataiserasedoff.
Load Trained Model: Trained model isloaded to procced withfurtherimplementation.
Object Detection & Classification: Object isdetectedin a frame and classified into different categories based on differentmodels.
Draw bounding box on the object: A box with border is builtaroundtheaffectedregion.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
blood veins, as well as tumourclassification. We are using the deep convolution neural network YOLO framework to pinpoint the exact location of the lung tumour. We intend to expand the dataset in the future by incorporating new lungCTimages.Inaddition,weplantotestthemodelwith an imbalanced dataset and gain more knowledge about updated CNN frameworks. We also plan to volumize the pixelsizeoftheimagesinthedatasettoimproveaccuracy.
[1] Rajpurkar,P., Irvin, J.,Zhu, K., Yang, B.,Mehta, H., Duan, T., Ding, D., Bagul, A., Langlotz, C., Shpanskaya, K., Lungren, M.P., Ng, A.Y., 2017. Chexnet: Radiologist level pneumonia detection on chest x rays with deep learning. arXiv:1711.05225.
Graph 1: TrainingLoss Graph 2: TrainingAccuracy
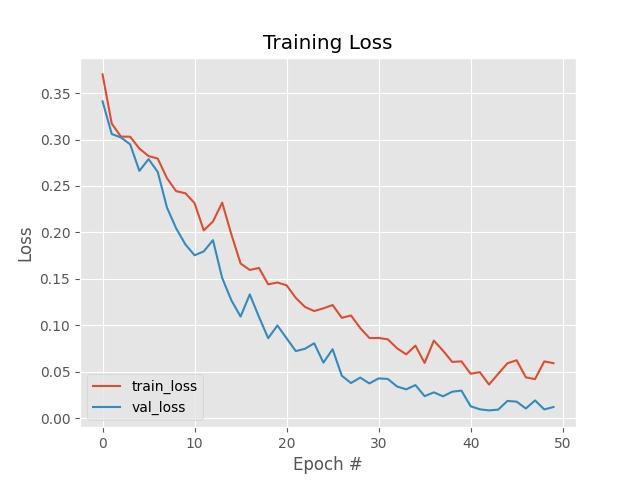
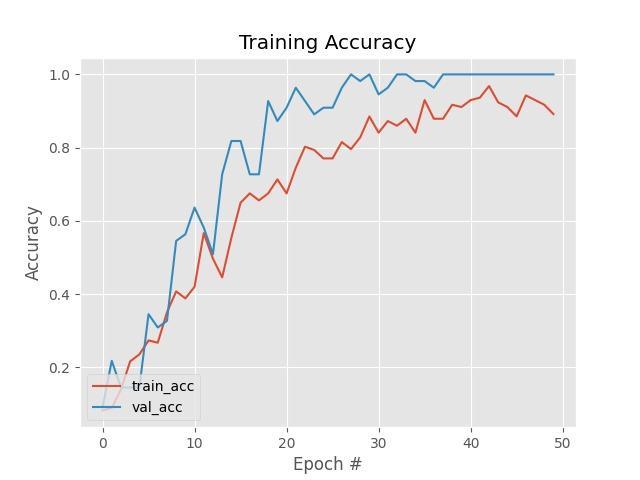
SystembuiltwithYOLOframeworkiscompletelyusefulfor detecting any lung cancer related disease. A novel non smallcelllungcancerpartitionofCTimageby,YOLOframe work non small cell lung cancer partition of CT image can provide precise cancer tumour contours and contribute to theconstructionofCADdiagnosticsystems.Smallcelllung cancer is a type of uncontrolled growth tumour that is distinguishedbyrapidgrowthandearlymetastasisspread. Ahottopicinthefieldofmedicalimageanalysisishowto effectivelydesignamodelforaccuratecancerpartitioning. Deep learning techniques, particularly deep CNN, have been widely used for medical image partitioning in recent years. The dataset is divided into two parts: testing and training.Thetrainingsetisfurthersubdivided.80%ofthe time is spent on training and 20% on validation. In this paper, we proposed a novel convolution neural network for small cell lung cancer image partitioning and finding the exact location of the tumour attached to the border of
[2] Muhammad Farooq and Abdul Hafeez. Covid resnet: A deep learning framework for screening of covid19 from radiographs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.14395,2020.
[3] Ezz El Din Hemdan, Marwa A Shouman, and Mohamed EsmailKarar. Covidx net: A framework ofdeeplearningclassifierstodiagnosecovid19in x ray images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.11055, 2020
[4] Xiang Yu, Nianyin Zeng, Shuai Liu, and Yu Dong Zhang.Utilizationofdensenet201fordiagnosisof breast abnormality. Machine Vision and Applications,30(7 8):1135 1144,2019.
[5] Mark Sandler, Andrew Howard, Menglong Zhu, Andrey Zhmoginov, and Liang Chieh Chen. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition,pages4510 4520,2018.
[6] Asmaa Abbas, Mohammed M Abdelsamea, and Mohamed Medhat Gaber. Classification of covid 19 in chest x ray images using detrac deep convolutional neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.13815,2020.
[7] Thomas Brox Olaf Ronneberger, Philipp Fischer. U net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv:1505.04597 [cs.CV], 2015.
[8] North America, R. S. RSNA pneumonia detection challenge. https://www.kaggle.com/c/rsna pneumonia detection challenge/data(2019).
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[9] NavdeepKanwal, AkshayGirdhar, and Savita Gupta. Region based adaptive contrast enhancement of medical x ray images. In 2011 5th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, pages 1 5. IEEE, 2011.
[10] Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A., Bengio, Y., 2016. Deep learning. volume 1. MIT press Cambridge.
[11] J.Deng,W.Dong,R.Socher,L.Li,KaiLiandLiFei Fei, "ImageNet: A large scale hierarchical image database," 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, 2009, pp.248 255,doi:10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848
[12] Gandhi,N.,Armstrong,L.J.,Petkar,O.,&Tripathy, A. K. (2016, July). Rice crop yield prediction in India using support vector machines. In 2016 13thInternational Joint Conference on Computer ScienceandSoftwareEngineering(JCSSE) (pp.1 5).IEEE
[13] Gandhi, N., Armstrong, L. J., & Petkar, O. (2016, July).Proposeddecisionsupportsystem(DSS)for I ndian rice crop yield prediction. In 2016 IEEE Technological Innovations in ICT for Agriculture andRuralDevelopment(TIAR)(pp.13 18).IEEE.
[14] Islam, T., Chisty, T. A., & Ch akrabarty, A. (2018, December).ADeepNeuralNetworkApproachfor Crop Selection and Yield Prediction in Bangladesh. In 2018 IEEE Region 10 Humanitarian Technology Conference (R10 HTC) (pp.1 6).IEEE.
[15] Jaikla, R., Auephanwiriyakul, S. , & Jintrawet, A. (2008,May).Riceyieldpredictionusingasupport vecto r regression method. In 2008 5th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, TelecommunicationsandInformationTechnology (Vol.1,pp.29 32).IEEE.