International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
123
Abstract In recent times, healthcare problems persist due to the misinterpretation of handwritten prescription and real time monitoring of the patient in the required time. Existing research monitors health parameters in real time but fails to get the advice from the doctor rapidly. Voice based prescriptions have limited work in the field and hence have a lower accuracy of the Natural Language Processing model(NLP). In order to accomplish the task of real time monitoring and acquiring a voice based prescription from the doctor instantly, this work is divided into two segments. The first segment is an Internet of Things(IoT) kit that transmits data to the cloud with the help of health sensors interfaced to a microcontroller. The second segment is a website which acts as a user interface for the doctor with a NLP model which converts speech to text and generates a medicinal prescription to the patient. The website also displays the health parameters of the patient by acquiring the data from the cloud. The doctor can view these parameters of multiple patients and can prescribe accordingly. This will save time and reduce the error in interpretation of the prescription for the patient.
Key Words: Voice based prescription, NLP, IoT, Data, Health, Cloud.
Today's world is heavily reliant on a variety of medicationsanddrugsthataidinthesmoothoperationof our society. Rapid medical advancements enable ordinary people to live longer, better, and stronger lives. However, the majority of the prescriptions given to patients are written by hand. As a result, they are more prone to interpreting errors. Such misunderstandings can result in fatal accidents. Similarity in drug brand names or pharmaceutical names can cause prescription errors due to misinterpretation. As a result, we can conclude that human factors play a significant role. The introduction of automationandtechnologycanhelptoreducethenumber oferrorsmadeduringtheprescriptionprocess.
In India, a major issue is that most prescriptions are still written by hand, and the readability of these handwritten prescriptionsispoor.Severalcaseshavesurfacedinwhich a chemist'smisinterpretationofa prescriptionresulted in the patient receiving the incorrect medication, causing serious health problems. However, for a doctor in India, usingatraditionalElectronicHealthRecordSystem(EHR)
to generate an electronic prescription is time consuming and costly. Setting up such a system would necessitate properinfrastructure.Eitherthedoctorwouldoperatethe systemonhisown,whichwouldtaketime,oranoperator wouldbehired,whichwouldbecostly.
Here, we have implemented a system enabling the doctor andthepatientwithanenvironmenttoeasilyaccesseach other and save time and energy. This system is divided intotwosections,the first section dealswithtransmitting the data from the patient using an IoT kit. The kit will be made with an ESP32 microcontroller interfaced with healthsensors.TheIoTkitsensesthehealthparametersof thepatientandtransmitsthedatatoadatabaseusingWi Fi. The patient can also send the symptoms faced by him/her to the doctor. In the second section, The doctor will be able to observe these parameters and other symptoms (if mentioned by the patient) and prescribe medicine using our voice based prescription. The patient will receive an alert for this prescription, hence the time consumed will be very less compared to the traditional methods.
WiththehelpoftheInternetofThings, Jayeeta Saha et al. [1] have proposed an easier solution for remote real time health monitoring of patients from the hospital as well as at home (IoT). Sensors collect data on a variety of parameters related to patients' health, which the Internet ofThingsstoresanddisplaysviaawebsitethatallowsfor remote monitoring. The combination of Raspberry Pi and IoT has solved this problem by introducing a new innovative technology into the healthcare system that allows for remote monitoring of the patient's health. According to the literature evidence base, the system sends data and alerts using healthcare sensors connected toa Raspberry Piandcloud integration. However,using a RaspberryPiforsuchanapplicationisinefficient because it consumes more power, and deploying such systems for every doctor is not practical because traditional sensor baseddiagnosisinthemedicalfieldrequiresmoresensors andhumaneffortwhenprocessedonalargescale.
Vani Yeri et al. [2] designed an IoT based health care applicationintheirresearchworktoaddresstheproblem raised in the previous literature. The proposed system is madeupofa webandmobileapplicationthatisbased on continuous wireless patient monitoring. The goal of the
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
paper was to develop a low cost system for transmitting patient vital signs in an emergency. Sensors are used to use the wireless network to measure the patient's vital signs. The data from the sensors is collected and sent to the cloud for storage via the controller's Wi Fi module The data is processed in the cloud, and feedback is given on the analyzed data, which can then be analyzed further by a doctor remotely. Remote viewing relieves doctors' workload and provides patients' exact health status. A message is sent to the doctor if the patient requires immediate attention. However, because the patient is unable to alert the doctor, when necessary, the doctor is only notified when there is an abnormality in the health parameters. To alert the doctors, each patient must be mappedwiththedoctor'streatmentzone.
AsproposedbySarfrazFayazKhan[3],IoTandRFIDtags are used to create a comprehensive and effective healthcare monitoring system that aids in the monitoring andweighingofthepatient'shealth.Hospitalshavebegun to use cell instruments for communication purposes, and internetofthings(loT)hasbeenusedandfusedwithwi fi sensor nodes resembling Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Near field communication (NFC) tags, and small sensor nodes for this purpose. RFID can be used with an Android phone over the Internet. The parameter is detected by RFID and sent to a mobile device. Patients mustbewithinRFIDrangeinordertodoso;thesedevices are placed at the entrance or in the desired location of patients. Active RFID systems work in the ultra high frequency (UHF) band and have a range of up to 100 meters, but they can't be used remotely in an emergency. Itdoesnotincludemedicationorprecautionsbasedonthe patient's health status, which are administered by controlling the appliances that deliver the prescribed medication.
Asif Mehmood et al. [4] proposes a system based on android and a web application in which a doctor can prescribe patients using an android application and a styluspen,andotherusers suchaspatients,receptionists, pharmacists, and administrators can interact with the systemusingtheirwebaccessibility.Theproposedsystem is based on the use of Arduino and E Health sensors to integrate Internet of Things and Cloud Computing technologies. The general concept is to collect data using anIoTsetupwithhealthsensorsandsendittothedoctor via API (Application Programming Interface) and MQTT (Message Queue Telemetry Transport) protocol on the cloud.Amobileapplicationandastyluscanbeusedbythe doctor to write prescriptions. However, styluses require smartphones or tablets to function, which are generally more expensive than the alternatives. In the case of poor handwriting, the issue of handwritten prescriptions may also arise. This also necessitates practical experience in ordertoachievethedesiredoutcomes.
The patient’s parameters can be monitored by using various types of health sensors. The data from these sensorswillhavetobeaccurateasthedatawillbeseenby the doctor before prescribing medicines. All this data will be parsed by a micro controller into JSON format. The parsed data will also need to have a timestamp to keep track of the time of the monitored parameter. This will alsoallowforarealtimeseriesdata,whichcanbeusedto keeptrackofanyanomaliesinthepatient'sroutine.
A user interface for both patients and doctors will be made. The patients will be able to send their health parameters and symptoms to the doctor and ask for the advice. The doctor will have a user interface to observe his/her patient's parameters and symptoms. Using this interface, the doctor will be able to diagnose the patient andgivehisadviceusingvoicerecognition.
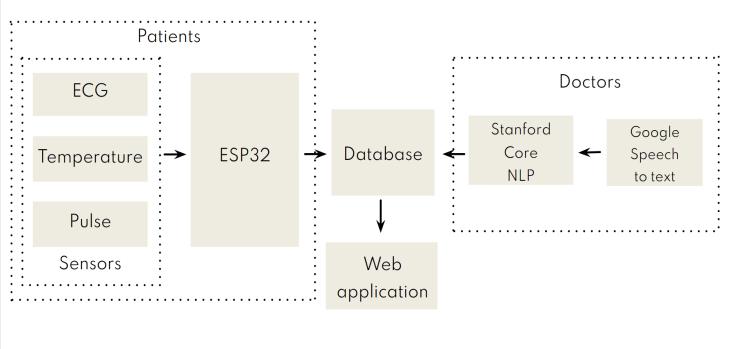
The doctor will prescribe the patient using voice recognition. To implement a voice based prescription, an NLPmodelwillbeusedtopreprocessthetextdictated by the doctor by removing the stop words and using tokenization. Once the text is processed, NER tagging will be performed on the text to get annotated data of tagged entitiesinit.Usingthetaggedlabels,theprescriptiondata willbeextractedfromthetext.
ThearchitecturediagramshownintheaboveFig.1shows variouscomponentsandentitiesintheapplication.
Health parameters of patients: Retrieval of information on patient's temperature, heart's rhythm and its electrical activity, oxygen level,
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
pulse rate, etc. using the various sensors which areconnectedtoESP32micro controller.
Database: The parameters which are captured usingamicro controllerarestoredinaMongoDB database. These parameters are referred by doctors for prescribing the patient. The data is stored as a time series data which can be used to observe the changes with respect to the time, to studythedirectionofthepatient'shealth.
Web Application: A User interface enabling the doctors and patients with an environment to communicatewitheachother.
Doctors’ portal: Doctors can give prescriptions based on voice using the Google Speech to Text APIandextractdatausingStanfordNLPpackage.
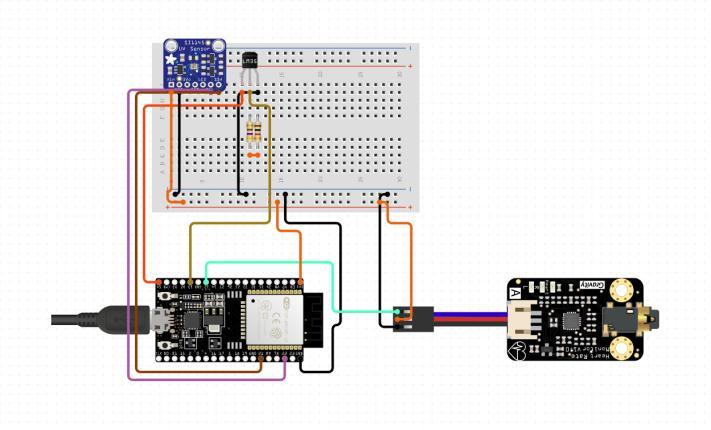
● ESP32: It's a feature packed micro controller with built in Wi Fi and Bluetooth connectivity that can be used in a variety of IoT applications.
Features:
○ Single or Dual Core 32 bit LX6 Microprocessor with clock frequency up to240MHz
○ The ESP32 uses a combination of proprietarysoftwaretoachieveultra low powerconsumption.
○
520 KB of SRAM, 448 KB of ROM and 16 KBofRTCSRAM.
○ Supports 802.11 b/g/n Wi Fi connectivitywithspeedsupto150Mbps.
○
34ProgrammableGPIOs.
○ It can provide Wi Fi and Bluetooth functionalitytoothersystemsviaitsSPI/ SDIO or I2C / UART interfaces. (such as theADC).[6]
● AD8232 ECG Sensor: The AD8232 Heart Rate Monitor is a low cost board that monitors the electrical activity of the heart. An ECG (Electrocardiogram) can be used to visualize this electrical activity and can be read as an analog reading. Because ECGs are notoriously noisy, the AD8232 Heart Rate Monitor acts as an op amp to helpobtaina clearsignal.It'sdesigned to extract, amplify, and filter small signals in noisy environments, suchasthosecaused by motionor theplacementofremoteelectrodes.
Features: ○
OperatingVoltage 3.3V ○ AnalogOutput ○ 3.5mm Jack for Biomedical Pad Connection.[7]
● LM35 Temperature Sensor: The LM35 is a temperature sensor that produces a proportional signal to the current temperature. The output voltage can be easily translated into a Celsius temperature reading. The advantage of the LM35 over the thermistor is that it does not require externalcalibration.
Features: ○ OperatingVoltage 3.3V 30V ○ Calibrated Directly in Celsius (Centigrade) ○ Linear+10 mV/°CScaleFactor ○ 0.5°CEnsuredAccuracy(at25°C) ○ Lessthan60 µACurrentDrain.[8]
● MAX30102 Heart Rate Pulse Sensor: A pulse oximeterandaheartratemonitorareincludedin theMAX30102biosensormodule.IthasaredLED and an infrared LED, as well as a photo detector, optical components, and low noise electronic circuitry that suppresses ambient light. The MAX30102 has a 1.8V power supply and a separate 5.0V power supply for internal LEDs in wearabledevicesforheart rateandbloodoxygen acquisitionthatarewornonthefingers,earlobes, andwrists.
Features: ○
OperatingVoltage 3.3V ○ Ultra lowshutdowncurrent 0.7µA ○ Low powerheartratemonitor.(<1mW)
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

○ Tiny 5.6mm x 3.3mm x 1.55mm 14 pin opticalmodule.[9]
The user interface will be a website consisting of portals for both patients and doctors. For the website the followingtechnologiesareused.
Flask: Flask is a web framework that is free and open source. It is written in Python and requires noORM(ObjectRelationalManager)touse.
Features:
○ URLRouting.
○ TemplateEngine. ○ RESTfulrequestdispatching. ○ Support for secure cookies (client side sessions).[10]
MongoDB: MongoDBisa NoSQL databaseandan open source document database. It stores data in databases called collections in the form of documents. It uses JSON format to store the data inthedocument.
Features:
○ Ad hoc queries for optimized, real time analytics.
○ Indexing appropriately for better query executions.
○ Replication for better data availability andstability.
HTML, CSS, JavaScript: Forthefrontend,HTMLis used to design the basic layout of the website using Jinja2 templating by Flask. Jinja2 parses HTMLcontentanddisplaysitontothewebsiteby workingincollaborationwithFlask.CSSisusedto style the web pages and add padding with a CSS framework called Bootstrap. JavaScript helps in makingthewebpagesinteractiveintherealtime.
The recorded voice from the doctor is converted into speech by the Google Speech to Text API. The text is extractedbyusingNLTKtopreprocessthetext,andfinally performing Named Entity Recognition on the preprocessed data. NER is performed by using the StanfordNERpackage.
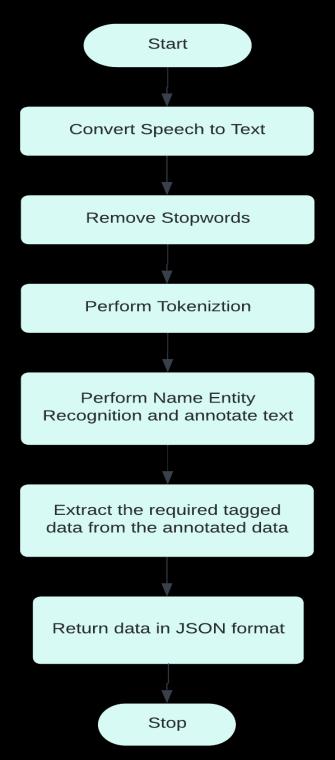
Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK): It includes a suiteoftextprocessinglibrariesforclassification, tokenization, stemming, tagging, parsing, and semantic reasoning, as well as wrappers for industrial strength NLP libraries. It also includes easy to use interfaces to over 50 corpora and lexicalresources.[14]NLTKisusedtopreprocess the data by removing redundancies and then performing NER tagging on the words to extract therequiredinformationinthisimplementation.
Stanford NER Tagger: It'saJavaimplementation ofaRecognizerforNamedEntities.Theprocessof extractingfeaturesandlabelingentitiesinatextis knownasnamedentity recognition.Itusesa CRF (ConditionalRandomFields)Classifier,whichisa supervised learning technique. [12] The CRF training features selected for a given application domain can have a significant impact on entity recognition performance [13]. Simple token level training of CRFs, for example, yields poor results, but text features such as word prefix/suffix/shape, word/phrasal clustering, and Part Of Speech(POS)tagscanbeusedtocreatea CRF language model that is very effective at recognizing the intended entities. The model was re trained using suitable Indian drug names for increasing the accuracy for extracting data from anIndiandoctor.
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 3447
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
The following results were obtained from the implementationofthissystem.
problems with two major advantages over the existing healthcaresystem.
The prescription is computer generated and in textformatwhichcansolvetheproblemofsloppy handwriting. The doctor’s notes are comprehendedeasilyasitperformsNERtaskson both normal English medical phrases as well as doctor’sabbreviations.
Fig.4 displays the health parameters of the patient, as receivedbytheIoTkitofthepatient.Itconsistsofanarray of health parameters with the timestamp and the patient ID which refers to a particular patient in the patient collectionofMongoDB.

The patient can get real time feedback from the doctoraboutthesymptomsandtheparametersof the patient, thereby saving the time of both the doctorandthepatient.
Voice-based E-prescription requires only a subtle influence in a doctor's workflow, but it will have a significant impact on the development of a digital ecosystemforpatientsinthelongrun.
The monitoring IoT kit can be made patient specific. For instance, if a patient has Diabetes, then a glucometer can be used and interfaced with the kit easily, making the hardwarescalableandflexible.Themodelnowworksonly with the English language. To make models compatible with many more languages to make it user friendly for doctors as well as the patients. Discontinuity in speech (For example, Coughing, sneezing, stammering, etc.) may affect the accuracy of the speech to text conversion. Find ways to eradicate these errors. A graph of the health parameterscanbedisplayedonthewebsite.
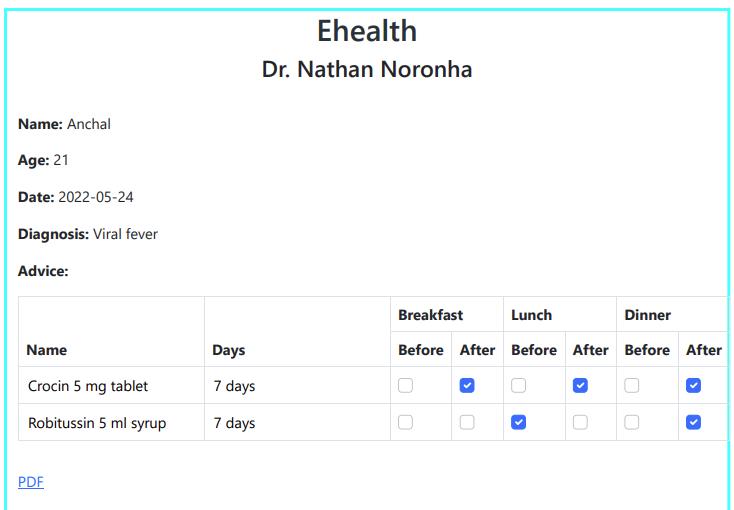
Fig.5 is the generated prescription that is obtained after performing speech to text conversion and extracting data fromthetextusingStanford NER tagger.Theprescription canalsobeverified bythedoctorandanychangescan be made to the prescription, if needed, by using JavaScript. The prescription shows the name of the doctor, patient, with the date, diagnosis and the medicines prescribed by thedoctor.
The main aim of the project was to solve the problem of illegible handwritten prescriptions and provide an interface for the patients and doctors to get in touch with each other. The implemented system overcomes these
[1] “J.Saha et al., "Advanced IOT based combined remote health monitoring, home automation and alarm system," 2018 IEEE 8th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), 2018, pp. 602 606, doi: 10.1109/CCWC.2018.8301659.
[2] V. Yeri and D. C. Shubhangi, "IoT based Real Time Health Monitoring," 2020 Second International Conference on Inventive Research in Computing Applications (ICIRCA), 2020, pp. 980 984, doi: 10.1109/ICIRCA48905.2020.9183194.
[3] S.F.Khan,"HealthcaremonitoringsysteminInternet ofThings(IoT)byusingRFID,"20176thInternational Conference on Industrial Technology and Management (ICITM), 2017, pp. 198 204, doi: 10.1109/ICITM.2017.7917920
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |

[4] A. Mehmood, F. Mehmood and W. C. Song, "Cloud based E Prescription management system for healthcare services using IoT devices," 2019 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), 2019, pp. 1380 1386, doi: 10.1109/ICTC46691.2019.8939916.
[5] S. Deshmukh, R. Balani, V. Rohane and A. Singh, "Sia: An interactive medical assistant using natural language processing," 2016 International Conference on Global Trends in Signal Processing, Information Computing and Communication (ICGTSPICC), 2016, pp.584 586,doi:10.1109/ICGTSPICC.2016.7955368.
[6] ESP32 Datasheet: https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/docu mentation/esp32_datasheet_en.pdf
[7] AD8232 Datasheet: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical documentation/data sheets/ad8232.pdf
[8] LM35 Datasheet: https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/lm35.pdf
[9] MAX30102 Datasheet: https://datasheets.maximintegrated.com/en/ds/MAX 30102.pdf
[10] Flask:https://flask.palletsprojects.com/en/2.1.x/
[11] MongoDB:https://www.mongodb.com/docs/
[12] Stanford NER Tagger: https://nlp.stanford.edu/software/CRF NER.html
[13] M. Tkachenko and A. Simanovsky, “Named entity recognition: Exploring features,” in Proceedings of KONVENS2012,J.Jancsary,Ed.ÖGAI,September2012, pp.118 127,maintrack:oralpresentations.
[14] Bird, Steven, Edward Loper and Ewan Klein (2009), Natural Language Processing with Python. O’Reilly MediaInc.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page
