International
Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e ISSN:2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
1Professor, Dept. of CivilEngineering, JSPMs Rajarshi Shahu College of Engineering, Pune, Maharashtra. 2,3,4,5Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, JSPMs Rajarshi Shahu College of Engineering, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
ABSTRACT
The point of the review is to figure out the impact of geogrid in radiates. The reason for utilizing geogrid in radiatesatdifferentfocusestonoticeitsadvantagesover the design. Presently a days structure having short life expectancy reason for material quality, ill advised execution,naturalconditionandsoforth.Inlightofthese reasonsstructureshavingdecreaseintheircompressive strength and flexural qualities which prompts its disappointment. Various examinations have been performed to bring answers for development industry, which shows extraordinary interest in geogrid material. Geogrid is a geosynthetic material like geonets which is utilized in street developments, holding dividers, dams, waterrepositories,building development,establishment and some more. In this review putting geogrid in primaryindividualslikeshaftsistotestwhethergeogrid isexpansionorsubstitutiontosteelinthepart.Geogrids areincludedtheshaftsandresulsaredeterminedinthis review.
INTRODUCTION
A geogrid is a geosynthetic material with normal for its solidness. It is regularly utilized as sub bases or dirt underneath the streets and designs, to build up holding dividers. Geogrids are solid in pressure. Geogrids comprisedofpolymermaterialslikepolyester,polyvinyl liquor, high thickness polyethylene and polypropylene. Inlightofwhichbearingtheextendingisfinishedduring make, geogrids are delegated uniaxial geogrids, biaxial Geogrids and triaxial geogrids. Uniaxial geogrid has a rigidityinonecourse.

Differentopeningsortsareformedinviewofthemanner in which the polymer sheet is attracted possibly at least onedifferentways.Drawingone,twoandthreeheadings resultsinuniaxial,biaxialandtriaxialgeogridseparately. They are effectively accessible in market including weldedgeogrid,wovengeogridandexpelledgeogrid.
PROBLEM STATEMENT
Thesedaysbecauseofadditioninhumanprogress enormousmeasureofdesignsarebuiltwithconcrete. The substantial individuals are fragile materials to endure the rigidity of individuals as they are supported by steel bars as of late because of natural wellbeing idea the substitution of development materials are generally done in investigate field specifically,halfwaysubstitutionofconcreteandsteel has got more huge in research field on account of its high outflow of carbon vaporous during the creation. In research mechanical applications, utilization of Geo textures materials have acquired significance in CivilEngineeringworksGeo Technical,transportation frameworks and different applications like bank, water system structures and so forth. So we need to examine conduct of Geo Grid support in cement to track down it as elective support material and legitimizeitsreasonablenesspivotsatexplicitlocales.
Thedisappointmentlocalesaresoffitofcrystaland spiral if there should arise an occurrence of parted tractable test. Likewise, if there should arise an occurrence of 3D shapes, Geo Grids are set over the soffitofpart,Ineveryoneoftheparticulars,Geo Grids are put opposite to the stacking of examples. The geogrid layer will be put at 30 mm over the base surfaceofthebar.Asimilararrangementwillbetaken
“EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES AND RESPONSE OF GEOGRID IN CONCRETE STRUCTURES”Prof. Mrs. S. S. Kakade1 , Mr. Vinit Rawale2 , Ms. Aditi Bari3 , Ms. Priyanka Khade4 , Mr. Nitish Zope 5
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022
onfordifferentbarsandblocks.
1. GEO-GRID APERTURE

Geogrid opening can be classified in three fundamental gatherings in view of their gap uniaxial, biaxial and triaxial.Uniaxialgeogridhasanelasticityinoneheading. Biaxial geogrids have elasticity in two aspects and they are frequently utilized for support of asphalts including unpaved streets,rail lines,andadaptableasphalts.Dong etal.(Dong,Han,&Bai, 2010) uncovered that biaxial geogrid can't give steady elastic qualities when exposed to strain in multiple headings, and it has rigidities in only two bearings. This isonethelimitsofbiaxialgeogrids.
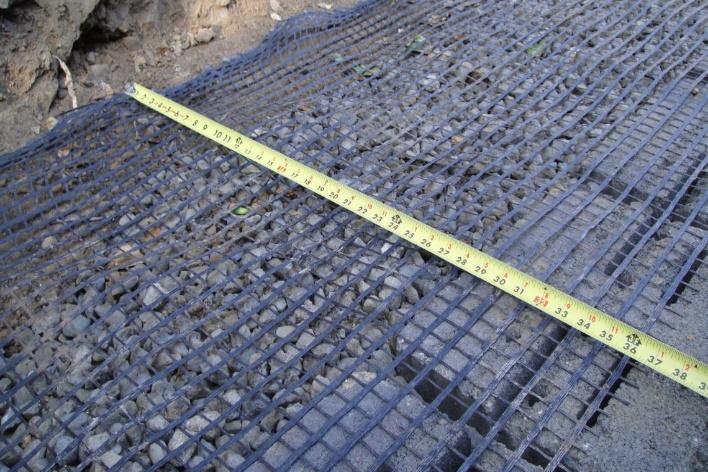


SingleLayer. DoubleLayer
e ISSN:2395 0056
p ISSN:2395 0072
3. Conventional Cube (L 150mm x B 150mm x D 150mm).
4. Cube with geogrid (L 150mm x B 150mm x D 150mm).
SingleLayer. DoubleLayer.
PCC mixtures having normal strength with target strength of 35 MPa will be used in the study. Eighteen specimens will be fabricated: one beam, one cube with conventional reinforcement to serve as control, and other beams and cubes with Biaxial geogrid, and Uniaxialgeogridasdescribedabove
IV. PLACING OF GEOGRID
Geo Grids putting play an Important job to additionally work on the nature of substantial individuals. In this work the Geo Grids can be put regarding exploratory examination on control examples. It flops because of most extreme burden anddevelopmentofplasticonthesubstantialpart
II. TESTS FOR GEOGRID PROPERTIES
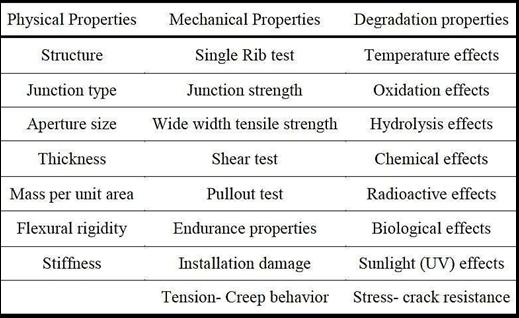
III. TESTING PROGRAM AND MATERIALS

The total specimens will be tested under monotonic constantdisplacementrateloadinguntilfailure.Typesof specimens&theirdimensionsareasfollows:
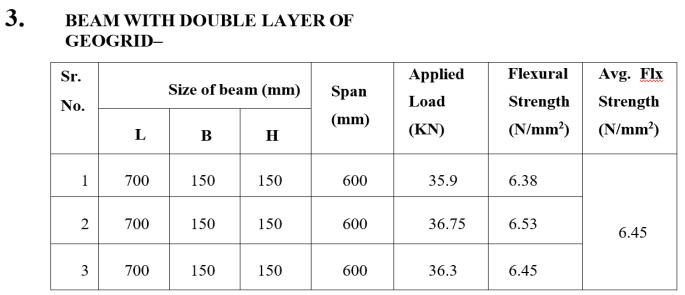
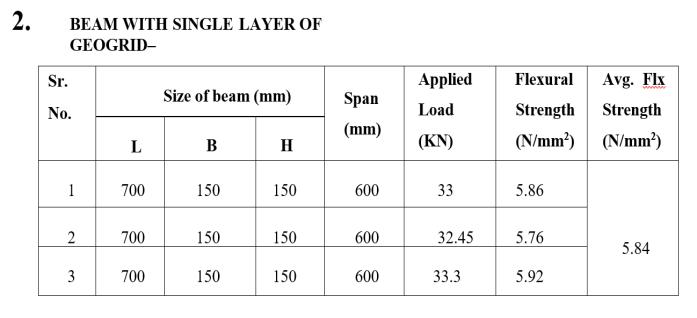
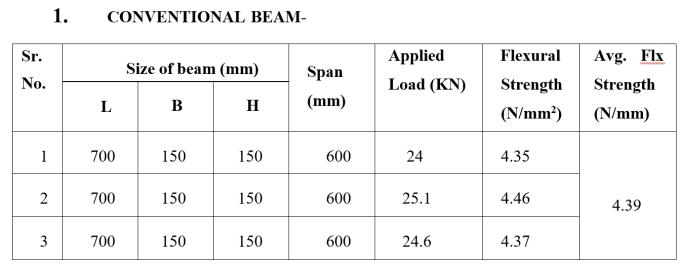
1. Conventional Beam (B 150mm x D 150mm xL 700mm).
2. Beams with geogrid (B 150mm x D 150mm xL 700mm).
V. PORTLAND CEMENT CONCRETE.
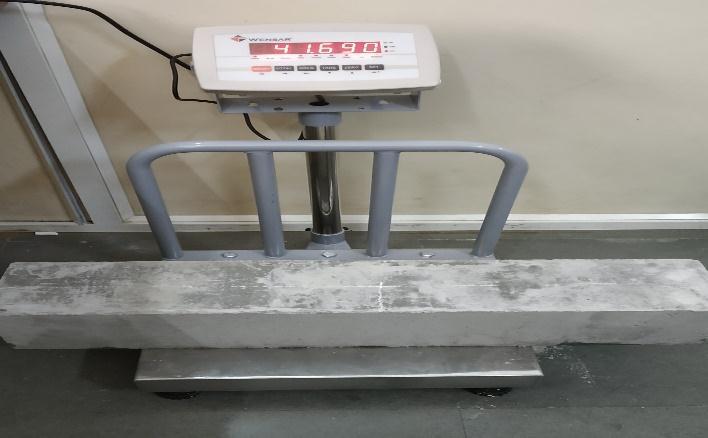
The Concrete Mixture is made utilizing Portland Concrete, fine totals comprising of regular sand, medium size totals with 10 mm, and coarse totals with 20 mm. The Ratio extents by mass were 1:1.6:2.907 with a water concrete proportionof0.45 for concrete. It was plan for 7 and 28 Days to check the compressive strength of 35MPa The substantial blend was intended for creating substantial cube to testcompressivestrengthof35MPa at7daysand28 days.12
Table.1 Test for geogridFig.2 geogrid
05
ISSN:2395 0072

economical solutions as Compared to conventionalsolutionswithconcrete,theyoften have the benefit of lower costs and less environmentalimpact.
2. Geogridsarealsoused for Dewatering Drainage Filtration, Landfill and Environmental Barrier andSurfacingReinforcement.
3. It has high durability reducing maintenance cost. They are highly resistant against environmentalinfluences.
4. Geogrid provides quality construction & excellentflexuralstrength.
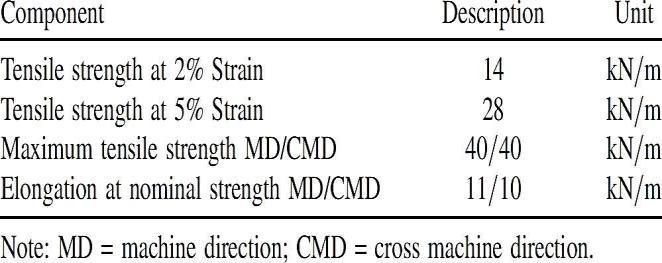
PHYSICAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE UNIAXIAL GEOGRIDS USED
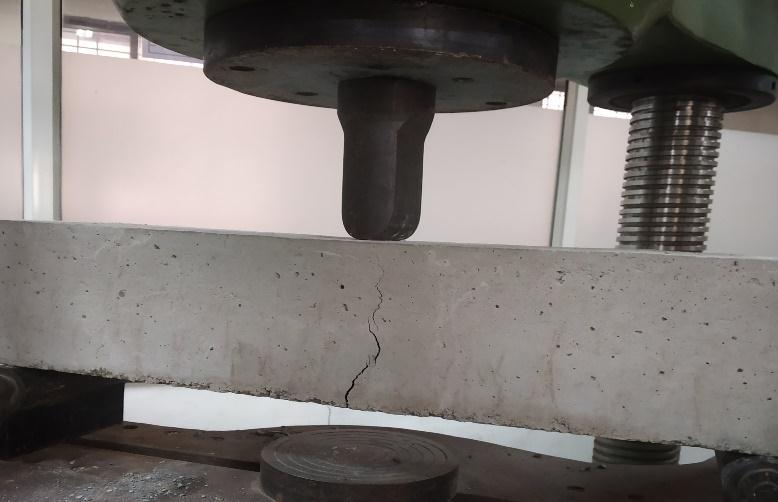

Fig.3 Testing of Beam.
VI. GEOGRIDS
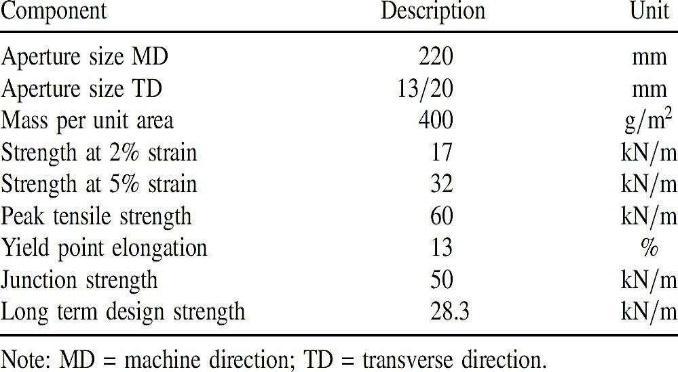
Every one of the 3 sorts of geogrids will be firm geogrids. They comprise of firm, unwoven, punch drawn geosynthetic material theuniaxial type is made ofhigh thicknesspolyethylene,whilethetwodifferent sorts are made of polypropylene. The uniaxial type is made of high thickness polyethylene, while the two different sorts are made of polypropylene. Varieties present in the opening math and aspects and in the physicalandmechanicalproperties.
Varieties exist in the gap math and aspects and in the physical and mechanical properties and are introducedintablesgivenbeneath.
VII. ADVANTAGES
1. EaseofConstruction:Geogridcanbeinstalledin any weather conditions, this makes it more demanding&placementtechniquesaresimple.
2. Instructural components,thegeogridsareused as additional reinforcement and as shear reinforcement.
3. To achieve good strength fibers like polypropyleneandsteelareused.
4. The geogrid reinforcement results in high ultimateload bearingcapacity,improvedenergy absorption and reduced slippage, shear and bondstrength.
VIII. ENVIRONMENTAL BENEFITS
1. Geogrid reinforced constructions are increasingly used as safe, ecological and
7.529
Table.2 properties of uniaxial geogrid.
PHYSICAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE BIAXIAL GEOGRIDS USED
Table.3 properties of biaxial geogrid.
PROPORTIONING :
Gradedesignation:M35
TypeofCement:OPC53gradeconformingtoIS 8112
Maximumnominalsizeof:20mmaggregate
Minimumcementcontent:320Kg/m3
MaximumWatercementratio:0.45
Beam Specimen
REVIEW:
Thispaperillustratesthebehaviour ofreinforced concrete(RC)beamwithbiaxialgeogridasanadditional reinforcement. They have done experimental investigationconsistsofonecontrolbeams(CB)andfive geogrid reinforced concrete beams (GB) with varying geogrid layer from one to five. These beams were subjected to gradually increased two point load until collapse occurred. The first crack load, ultimate load carrying capacity and behaviour was observed till collapseoccurred.Thebehaviourandflexuralstrengthof these geogrid beams were compared with that of a controlbeamthathadthesteelreinforcementsalone.
2]. El Meski and Chehab (2013)
Have conducted an experimental program on plain and geo grid reinforced beam specimens under four pointbending.Resultsfromtestingconfirmthatthe reinforcing benefit of the geo grids are evidenced from the load deflection response in terms of post peck behavior, load capacity, crack mouth opening displacement,andfailuremode.
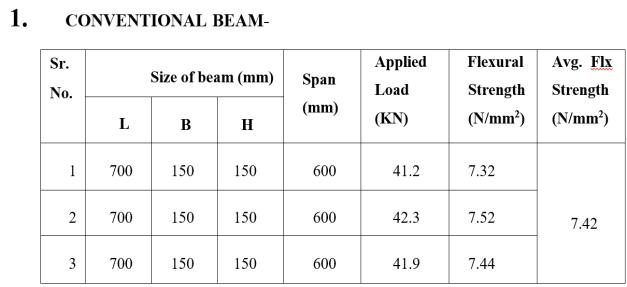



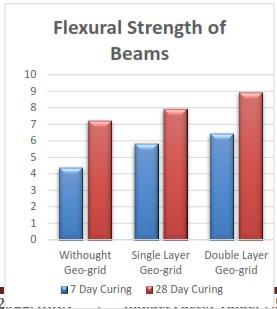
RESULTS
7 DAY CURING PERIOD.
28 DAY CURING PERIOD.
1]. S. Ramakrishnan, M. Arun, S. Loganayagan, M. Mugeshkanna (2018)
Volume: 09 Issue: 05
May
Compressive Strength of Cube
Withought Geo-grid
Layer Geo-grid Double Layer Geo-grid
7 Day Curing 28 Day Curing
With Single & Double Layer Of






(At 7th Day & 28th Day).
(At 7th Day & 28th Day).
CONCLUSION
Experimental investigation concluded the beams proportioned with layers of biaxial geogrid shows luminouslyriseincompressivestrengthandsignificantly incrementinflexuralstrength.Geogridinconcreteactas a ductile member by taking tensile load. Also geogrid layer shows increase in bending strength of beam. Geogrid found to be economical source and no harm to theenvironmentfollows:
Compressive strength at full age of concrete rise significantly.
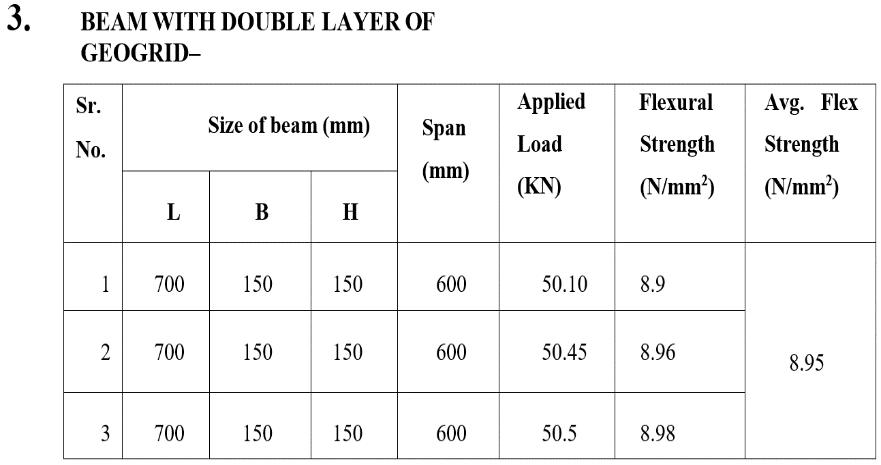
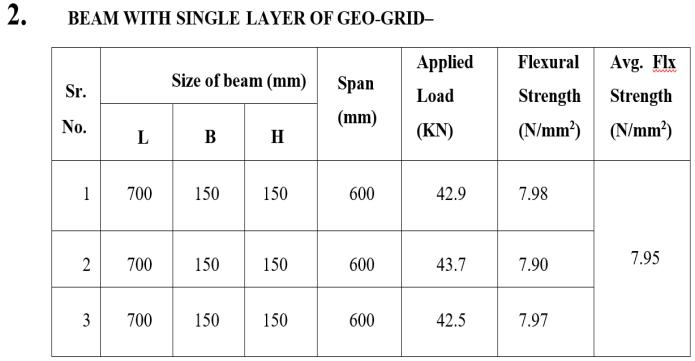
Flexural strength shows significant increment above 18%.

placing Geo grid in concrete it act as a ductile memberbytakingtensileloads.
geogrid beams compare to Conventional beam can help to increase Flexural strength as per aboveresults.
grid in concrete can found to be economical sourceinconcretemembers.
layer of geogrid increased towards the CG of beam thebending strength ofbeamincreases.






International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to thank Project Guide Pro S. S Kakade (RSCOE) for their valuable guidance throughout this Project.
REFERENCES
1. S. Ramakrishnan, M. Arun, S. Loganayagan, M. Mugeshkanna, “STRENGTH AND BEHAVIOUR OF GEOGRID REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAMS” International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology,2018,Volume9,Issue6.

2. MartinZiegler,“Applicationofgeogridreinforced constructions: history, recent and future developments”Elesvier,2017,P 42 51.
3. P.RAJESH KUMAR M.E, A/P, VSB College Of Engineering Varun Shankar,Singarajan,Hariharan,Bharathi kannan (Students), , VSB College Of Engineering International Journal of Scientific & Engineering ResearchVolume11,Issue3,March 2020
4. F. El Meski, G. R. Chehab, "Flexural Behaviour of ConcreteBeamsReinforced with Different Types of Geogrids" American Society of Civil Engineers(ASCE), 2014.
5. P.K. Kolay, S. Kumar, and D.Tiwari, “Application of geogrid reinforced constructions: history, recent and future developments”Elesvier, 2013, P 42 51.
6. Guray Arslan , "Shear Strength of Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete (SFRC) Slender Beams Korean Society of Civil Engineers (KSCE) Journal ofCivilEngineering" 2014,587 594.
7. M. Chandrasekahar, M.V. Sehagirirao, M Janardhana , “A Comparative Study On Stress Strain Behaviour Of Standard Grade HFRSC Under Confined AndUnconfined States", InternationalJournalOfAdvancesinEngineering &Technology,Volume01,2011,pp 162 170
8. Raju ,"Review on Shear Behaviour of Reinforced Concrete Beam Without Transverse Reinforcement", International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications, 2014, Volume8,pp116 121.
9. R. Siva Chidambaram and Pankaj Agarwal, "The Confining effect of Geo grid on the mechanical propertiesofconcretespecimenswithsteel fiber ndercompressionandflexure",Elesvier2015,pp 628 637.
BIOGRAPHIES
e ISSN:2395 0056
p ISSN:2395 0072
PROF.SUCHETA KAKADE , Assistant Professor at JSPM’s Rajarshi Shahu College of Engineering Pune. M.E-Civil (WaterResourceEngineering) Maharashtra,Pune.

Ms. ADITI BARI , StudyingFinalYearofB.E-Civil at JSPM’sRajarshiShahuCollegeof EngineeringPune. Maharashtra,Pune.


© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008
Mr. VINIT RAWALE , StudyingFinalYearofB.E-Civil at JSPM’sRajarshiShahuCollegeof EngineeringPune. Maharashtra,Pune.
Ms. PRIYANKA KHADE , Studying Final Year of B.E-Civil at JSPM’s Rajarshi Shahu College of EngineeringPune. Maharashtra,Pune.
Mr. NITISH ZOPE , Studying Final Year of B.E-Civil at JSPM’s Rajarshi Shahu College of Engineering Pune. Maharashtra , Pune.

