International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Unnathi Suvarna. V1, Dr. Dhananjaya . V2
1 M. Tech Student, Dept of Computer Science and Engineering, Impact College of Engineering and Applied Science, Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India unnathiv95@gmail.com
2 Professor, Dept of Computer Science and Engineering, Impact College of Engineering and Applied Science, Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India csdhananjay@gmail.com ***
Abstract - The use of the internet has brought vast numbers of users online through different platforms. Unlike the old days, the internet is not just limited to email surfing, there’s so much on the internet or let’s say everything is on the internet. The Internet has solutions for almost everything, from mental health to technical issues. In this agriculture, fields cannot be untouched. The 21st Century has been the age of technology where technology has been used everywhere. So, for optimum results in each field, we use various methods which can minimize the loss and give us maximum benefits. The application of Machine learning in Crop type prediction for modern world farming is very much essential. Also, suggesting the type of fertilizer and amount can increase the usability of the application.
Crop yield prediction and fertilizer suggesting application use machine learning algorithms to predict the crops yield based on various aspects: like the amount of rainfall and other different real world parameters.
Key Words: Machine Learning, Agriculture, Crop Type, Fertilizer, KNN, Logistic Regression, Random Forest, XGB Classifier.
A Crop Yield Prediction and Fertilizer Recommender or simply agriculture assistance application is a model or system where farmers get suggestions or assistance in various aspects. The system assists farmers by providing crop yield prediction and fertilizer suggestions. These kinds of suggestions and predictions in real time can help farmers to plan their crops which can overall impact their livelihood including annual expenses, and other aspects. Indian farmers are majorly dependent on waterfall each yeartodecidewhatkindof croptosow.Eachyearsuicide of farmers has become one of the serious issues. A major reason for such cases is found to be untimely rainfall, drought, heavy rainfall, and other similar weather conditions. Due to such reasons, farmers do not get to harvest the crops after a whole struggle. If this is the case allthefarmerswillbeforcedtoleavetheiroccupationsand optforalternatives.
Agriculture and associated sectors are vital to the Indian economy. More people are working in agriculture, either directlyorindirectly.Becauseoftheincreaseinpopulation and the need for food, a significant amount of fertiliser is usedinsoil,whichmayresultincontaminationofsoiland deterioration of soil quality, causing a variety of problems for future generations. Itis critical to evaluate the amount of fertiliser needed for a specific crop in relation to soil fertility. The use of fertiliser has been measured using a varietyofmethods.
Following eachrainfall event,thereisa correlationamong rainfall intensity and nutrient loss for different fertiliser treatments. While timely and moderate rainfall can help dissolve dry fertiliser and move nutrients into the soil rooting zone, excessive rain can increase runoff and leaching of nutrients like nitrate, sulphate, chloride, and boron.
The existing system suggests us the previous works done in a specific domain, where we can refer to and get ideas from.Manyfarmingoragricultureassistancesystemshave beenimplementedorproposedfocusedinonlyaparticular aspectorcrop
In a research paper, the scholars proposed a system to predict the amount of fertiliser needed for a specific crop banana, as well as regression methods for future plantations using Neural Networks. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are the three most important soil nutrients for crop growth. The amount of NPK in the soil varies depending on where you live. The requirements for each crop differ as well. In this paper, a model is built to recommend the amount of fertiliser neededforthebananacrop[1].
In a different paper proposed system's goal is to assist farmers in cultivating crops for higher yield. The crops chosen for this work are based on important crops from the chosen location. Rice, Jowar, Wheat, Soyabean, Sunflower, Cotton, Sugarcane, Tobacco, Onion, Dry Chili, and other crops have been chosen. Crop yield data is
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
compiled from various sources over the last five years. Scholars proposed the system in 3 steps: a. Soil Classification b. Crop Yield Prediction and c. Fertilizer Recommendation[2]
A paper published at IEEE predicts the yield of nearly all types of cropsgrown inIndia.This script is novel because it uses simple parameters such as state, district, season, and area to predict crop yields in whatever year the user desires. The paper predicts yield using advanced regression techniques such as Kernel Ridge, Lasso, and ENet algorithms, as well as the concept of Stacking Regressiontoimprovethealgorithms[3]
Rainfall regimes, P application rates, soil P content, and field management practices such as field bund and open ditch construction can all influence phosphorus losses in rice wheat cropping systems. Heavy rainfalls shortly after Papplications,inparticular, causesignificant Ploss,andP lossincreaseswithincreasingPapplicationratesandsoilP content. During the rice growing season, P concentrations infieldpondingwaterregulatePconcentrationsinsurface runoff. The construction of open ditches can increase phosphorus loss during the winter wheat growing season. As a result, we propose that rice wheat cropping systems be managed to avoid heavy rain events while also balancingcrop P removal (20 30kg P ha 1inthisstudy). Furthermore,appropriatewatermanagementpracticesare recommended, such as increasing the capacity of field pondingwaterorusingcontrolledirrigationinconjunction with natural drying of the field rather than open ditches duringthewheatgrowingseason[4].
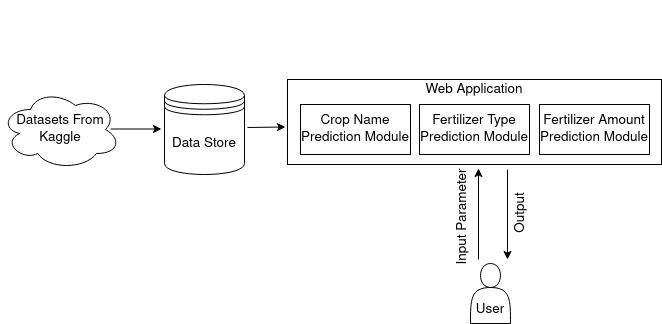
The previously proposed methods for predicting fertiliser type are based on crop type and crop production. The amountoffertiliserisonlyclassifiedusingimagedata.We propose in this paper a method for predicting the amount andtypeof fertiliser based ontabulardata. Topredictthe amount and type of fertiliser, multiple machine learning algorithmsareused.
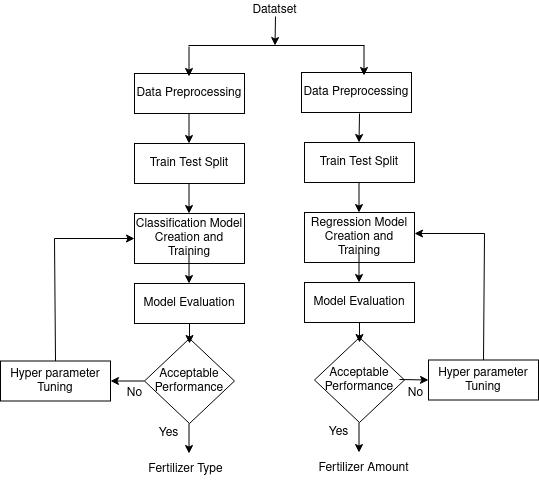
Dataset: A dataset containing information about fertilizer isgainedfromKaggle.
Pre processing: Various preprocessing methods used in the tabular dataset are done. Different techniques are employed for preparing datasets for classification and regression.
Model Creation and training: Different machine models basedonoperationarecreated.Eachmodelistrainedwith thecorrespondingdataset.
Model Tuning: Models are compared based on metric values.Thebestoneisfurthertunedandusedforthefinal prediction.
Fig
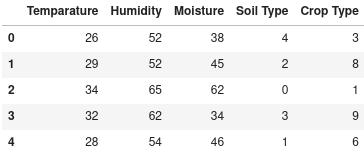
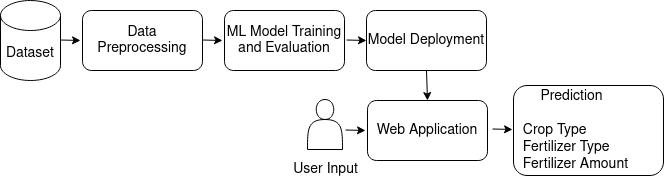
Fig 1 :ProposedSystem
:DatasetforCropPrediction
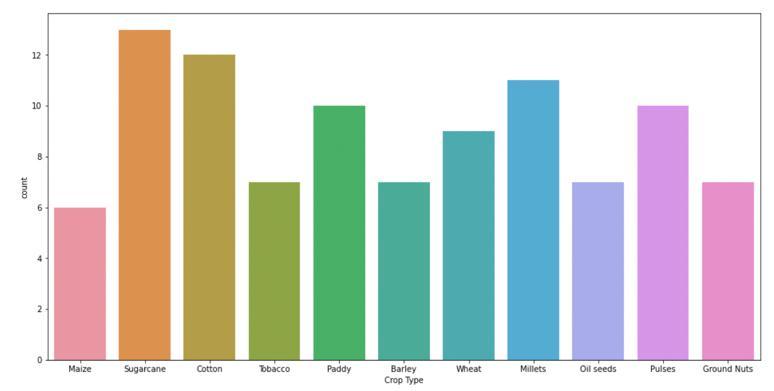
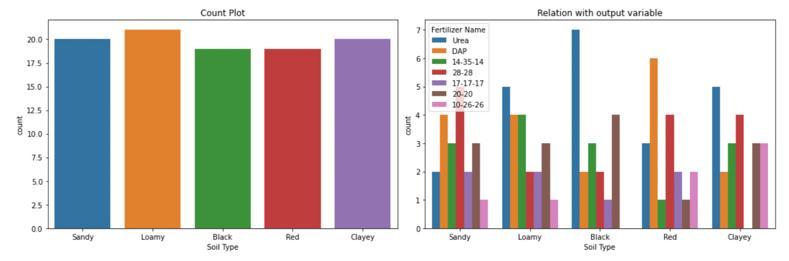
TableforTemperature,Humidity,Moisture,andSoilType isusedasfeatures.CropTypeisthetargetLabel.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Fig 8 : Comparisonoftheresultoftheimplementation
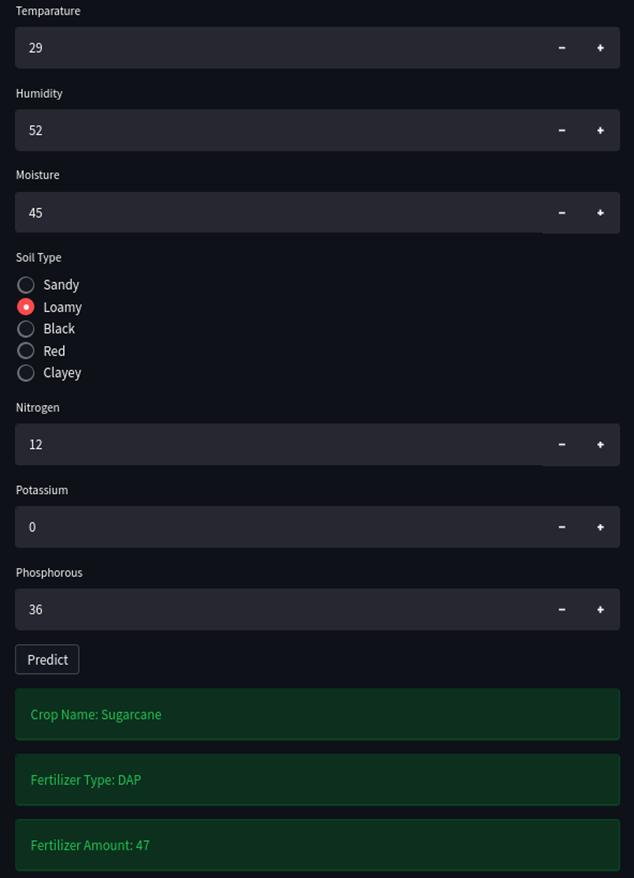
Alltheinputsfromthepreviousmodulearetaken.Besides that,thecroptypegivenasoutputbythepreviousmodule is taken, and the Nitrogen, Potassium, and Phosphorus valueistaken.
Fertilizer Amount Prediction Module
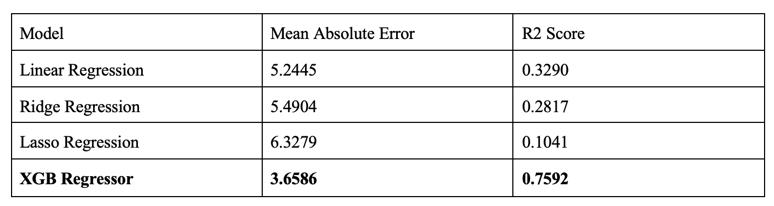
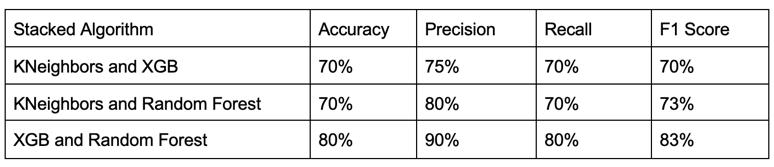
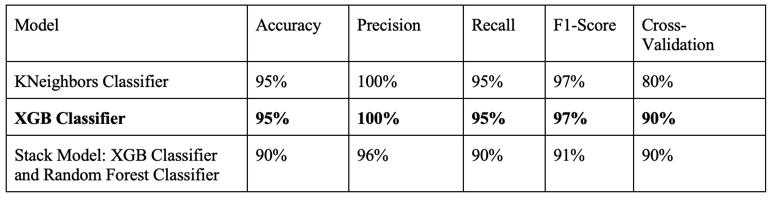
From the above table, it can be clearly seen that the stackedXGBandRandomForestperformthebest.
Thetablebelowprovidestheinformationaboutthesecond partwherethefertilizetypepredictionisdone.
From the Table, it can be clearly seen that all models performsimilarlyinthefourbasicmetricsused.So,cross validation is used to check the model performance in a different split of data. Among all the classifiers, XGB Classifierperformsthebest.
A complex feature (Total Fertilizer) is gained from the Nitrogen, Potassium, and Phosphorus value. Since this feature can be gained from the NPK value, these features might be biased, so they are removed. The Crop Type and FertilizerNamearegainedfrompreviousmodules.
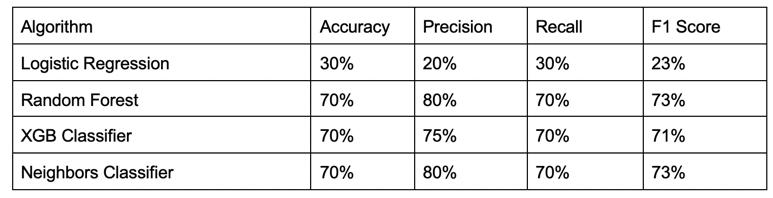
The macro average gives each prediction a similar weight while calculating loss but there might be cases when your datamightbeimbalancedandyouwanttogiveimportance to some predictions more (based on their proportion), there you use a 'weighted' average. So, the weighted averagevalueformetricsisused.
Fig 9 :Comparisonofdifferentparametersinthe differentalgorithms.
Finally, in the third module fertilizer amount is calculated using regression models. The table provides information aboutmodelperformance.
Fig 10 :ComparisonofModelPerformance.
Fig
Besides Random Forest, all other algorithms are performing good and they have similar metric values In order to increase model performance hyperparameter tuning and Isolation forest is done but there is no improvement in model performance. So, a concept of stacking multiple models is used and there is some improvementinthemodelperformance.
Graph – 1: PlotforFertilizeramount
When we use stacked regression, the results are far superior to when those models were used individually. This system is expected to solve modern life agriculture related problems. To make it best usable for Indian farmers we have kept the parameters according to Indian weather conditions. Also, system developed is more user friendly since it has web app as well. Use of mobile phone is very much, so in future implementing the solution as mobileappwouldbebetterforcommonuse.
[1] JuhiReshma, S. R., and D. John Aravindhar. "Fertilizer Estimation using Deep Learning Approach." NVEO NATURAL VOLATILES & ESSENTIAL OILS Journal| NVEO (2021): 5745 5752.
[2] Bondre, Devdatta A., and Santosh Mahagaonkar. "Prediction of crop yield and fertilizer recommendation using machine learning algorithms." International Journal of Engineering Applied Sciences and Technology 4.5 (2019): 371 376.

[3] Potnuru Sai Nishant; Pinapa Sai Venkat; Bollu Lakshmi Avinash; B. Jabber. “Crop Yield Prediction based on Indian Agriculture using MachineLearning”IEEE2020.
[4] LIUJian,ZUOQiang3,ZHAILi mei,LUOChun yan, LIU Hong bin, WANG Hong yuan, LIU Shen, ZOU Guo yuan, REN Tian zhi. “Phosphorus losses via surface runoff in rice wheat cropping systems as impacted by rainfall regimes and fertilizer applications” Science Direct, Journal of IntegrativeAgriculture2016.
[5] Yulong Yin, Hao Ying,Huifang Zheng, Qingsong Zhang, Yanfang Xue, Zhenling Cui. “Estimation of NPK requirements for rice production in diverse Chineseenvironmentsunderoptimal fertilization rates.” Science Direct: Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,Dec2020.
[6] Ananthara,M.G.,Arunkumar,T.,&Hemavathy,R. (2013, February). CRY an improved crop yield prediction model using bee hive clustering approach for agricultural data sets. In 2013 International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Informatics and Mobile Engineering (pp. 473 478).IEEE.
[7] Awan, A. M., & Sap, M. N. M. (2006, April). An intelligent system based on kernel methods for crop yield prediction. In Pacific Asia Conference
[8]
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (pp. 841 846).Springer,Berlin,Heidelberg.
Bang,S.,Bishnoi,R.,Chauhan,A.S., Dixit,A.K.,& Chawla,I.(2019,August).FuzzyLogicbasedCrop Yield Prediction using Temperature and Rainfall parameters predicted through ARMA, SARIMA, and ARMAX models. In 2019 Twelfth International Conference on Contemporary Computing(IC3)(pp.1 6).IEEE.
[9] Bhosale, S. V., Thombare, R. A., Dhemey, P. G., & Chaudhari, A. N. (2018, August). Crop Yield Prediction Using Data Analytics and Hybrid Approach. In 2018 Fourth International Conference on Computing Communication Control and Automation (ICCUBEA) (pp. 1 5). IEEE.
[10] Gandge, Y. (2017, December). A study on various data mining techniques for crop yield prediction. In 2017 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computer, and Optimization Techniques (ICEECCOT) (pp. 420 423).IEEE.
[11] Gandhi, N., Petkar, O., & Armstrong, L. J. (2016, July). Rice crop yield prediction using artificial neural networks. In 2016 IEEE Technological Innovations in ICT for Agriculture and Rural Development(TIAR)(pp.105 110).IEEE.
[12] Gandhi,N.,Armstrong,L.J.,Petkar,O.,&Tripathy, A. K. (2016, July). Rice crop yield prediction in India using support vector machines. In 2016 13thInternational Joint Conference on Computer ScienceandSoftwareEngineering(JCSSE) (pp.1 5).IEEE
[13] Gandhi, N., Armstrong, L. J., & Petkar, O. (2016, July).Proposeddecisionsupportsystem(DSS)for I ndian rice crop yield prediction. In 2016 IEEE Technological Innovations in ICT for Agriculture andRuralDevelopment(TIAR)(pp 13 18) IEEE
[14] Islam, T., Chisty, T. A., & Ch akrabarty, A. (2018, December) ADeepNeuralNetworkApproachfor Crop Selection and Yield Prediction in Bangladesh. In 2018 IEEE Region 10 Humanitarian Technology Conference (R10 HTC) (pp 1 6) IEEE
[15] Jaikla, R., Auephanwiriyakul, S. , & Jintrawet, A (2008,May) Riceyieldpredictionusingasupport vecto r regression method. In 2008 5th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer,
Telecommunications, and Information Technology(Vol.1,pp.29 32).IEEE.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3266
