1234
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

1234
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Palla Tejaswi1,Cheedi Dharani2,Rayavarapu Siva3,Kakara Shivani4
Guided
Abstract - Occurance of Chronic Kidney Disease doesn’t have any obvious symptoms in the earlier stages to identify, so patients most often fail to notice the disease in kidney. So that the patients are fail to take the timely treatment which enables kidney failure. CKD have an high ill and death rate in the world. Data Mining methods and Machine Learning Algorithms play a major role in this aspect of life of living beings. Machine Learning plays an key role in diagnosing of any diseases. Chronic Kidney Disease(CKD) is a condition in which the kidneys are failed and cannot filter blood properly, also cannot have an electrolyte balance steady. The causes for CKD may also includes a family history of kidney diseases or failure, high blood pressure, hypertension, obesity, age, diabetes. This is a lasting failure to the kidney when it reaches to high time or months. The complications that involves when kidney failure are heart diseases, anemia, bone diseases, high potassium and calcium, leg swelling. The last stage of situation leads to complete kidney failure and needs kidney transplant to live. An early detection of CKD can improve the great quality of life to a greater extension. So we choose a great prediction algorithms(Integrated Model Naïve Bayes Classifier and Random Forest Algorithms) to predict CKD. This paper uses data preprocessing, data selection and various classifiers (Random Forest and Naive Bayes) to predict CKD and finally it results best prediction accuracy framework for CKD. The results of the prediction accuracy framework show promising results of better prediction at an early stage of CKD.
Key Words: Chronic Kidney Disease, K Nearest Neighbour Imputation, Feature Selection, Integrated Model Naïve Bayes Classifier and Random Forest Algorithms.
Our investigations have reached great outcomes in the identificationofCKD.DatasetwastakenfromtheUniversity of California Irvine Machine Learning Repository which consists of many missing values in it. Missing values are caused due to the patients emergency or by their forgetiveness. The K Nearest Neighbour Imputation was used to fill missing values in the dataset,that is mean statistical algorithm was utilized to fill missing numerical valueswhereasmodestatisticalalgorithmwasutilizedtofill missingnominalvalues.
Kidneyillness(CKD)isakindofkidneysicknesswherethere iscontinuouslossofkidneyfilterationoveratimeofmonths
***
toyears.Atfirsttherearenoobvioussymptomstoidentify, latermanifestationsmightincorporatelegenlarging,feeling tired, heaving, loss of hunger, and frequent urination, nausea.,hypertension,bonesickness,andanemia.Causesof kidney infection incorporate diabetes, hypertension, glomerulonephritis, and polycystic kidney illness. Hazard factorsincorporateafamilybackgroundofpersistentkidney illness. Investigations be done by taking blood tests to quantifytheassessedGlomerularFiltrationRate(GFR),and apeetesttogaugeeggwhites,Ultrasoundorkidneybiopsy mightbeperformedtodecidethehiddenreasonwhichmay leadtoCKD
The investigations on computer calculations that work on naturally through experience that says it learns from the past data whithout explicitly programmed for everytime whenitneeded.MachineLearningishighlyresponsiblefor DiagnosingandPredictions.
Existing System of diagnosing of chronic kidney disease includes an integrated model of two algorithms namely LogisticRegressionandRandomForestAlgorithms.Inthis System,ithaveanproblemoflinearboundariesandunable topredictforhigherdataset.
Proposed System, includes an integrated model of Naïve BayesClassifierandRandomForestAlgorithms.Thedataset wastakenfromtheUniversityofCaliforniaIrvineMachine LearningRepository.Thedatasetconsistsofmanymissing values due to the patients forgetiveness or by their any personalissues.ThosemissingvaluescanbefilledusingK Nearest Neighbour imputation algorithm, Mean Statistical AlgorithmwasusedtofillnumericalvalueswhereasMode StatisticalAlgorithmwasusedtofillnominalvaluesinthe dataset.
Themethodologyisusedforbuildingmultipleclassification modelsatatime.Themodelmethodsaredividedintotwo sub modules.Thefirstmodulehasbeenusedtopredictthe error rates namely AAE and ARE for dataset. Also, the Kruskal wallistesthasbeenconductedtofindthesignificant
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
differenceintheperformance.Thesecondsubmoduleused fortheselectionofimportantfeatures.
Using Python Tool on Standalone machine Environment: The Python computer programs are essential tool for progression in the numeric examination andmachinelearningspaces.Pythonisaperfectwaytodeal withreproducible,extraordinaryexaminationprogramme. Pythonisextensibleandoffersrichvalueforarchitectsor programmerstomanufacturetheirownspecificgadgetsand proceduresforexaminingdata.Itwaseasyforprogramming tobuildmodelsalsoefficientinimplementing.Thevastness of package organic framework is indisputable one of the Python's most grounded qualities are if a true technique exists,oddsaretherewaspresentlyanPythonpackageout thereforit.Python'spositiveconditionsfalseitspackages naturalframework.Here,theaccuracyofdifferentmachine learningalgorithmshasbeenlookusingPythonToolonthe Standalone machine. Initial analysis has been done using Microsoftexcel.Acsvdatasetfilehasbeenprovidedasan input for Python. The data is gathered from web sources after that Pre processing of Dataset can be done which involves Data cleaning, Data Integration and Data Transformation.
TheconfusionmatrixisalsoknownasErrormatrix.It'sin the format of table that's often accustomed describe the performanceofaclassificationmethodonacollectionoftest datathatactualvalueareknown.Eachtupleoftheconfusion matrixdenotestheoccurrenceswithintheactualclass.Each columnofthematrixdenotestheoccurancesinanextremely predicted class. The confusion matrix is represented as shownbelow:
Predicted Yes No
Actual No FP TN
Yes TP FN
In classification, it includes two important evaluation parameters namely accuracy and precision Accuracy is definedbytheaggregationoftruepositiveandtruenegative instancesdividedby100whereasPrecisionwasdefinedby thefractionoftruepositiveandpredictedyesinstances.The AccuracyandPrecisioncanbecalculatedbythegivenbelow formulae:
Accuracy:(TP+TN)/100
Precision:TP/Predictedyes
Recall and F Square: Recallisdefinedbythefractionof TruePositiveinstancesandActualyesinstanceswhereasF
Squaredefinedbythefractionbetweenproductoftherecall and precision to the summation of recall and precision parameterofclassification.Therecallandprecisioncanbe calculatedbythegiven belowformulae:
Recall:TP/ActualYes
F Square:(2*Recall+Precision)/(Recall+Precision)
Sensitivity is defined by the fraction of true positive and actual yes instances whereas specificity is defined by the differencebetweenoneandfalsepositiveratevaluebythe actualnoinstances..ROCisdefinedbythefractionbetween truthpositiverateandthefalsepositiverate.
TheSensitivity,SpecificityandROCcanbecalculatedbythe givenbelowformulae:
Sensitivity:TP/ActualYes
Specificity:(1 FP)/ActualNo
ROC:TPR/FPR
MCC:MCCisameasurethatcapableofstudyingbothtrue andfalsepositivesandnegatives.TheMCCcanbecalculated as
MCC:((TP)(TN)(FP)(FN))
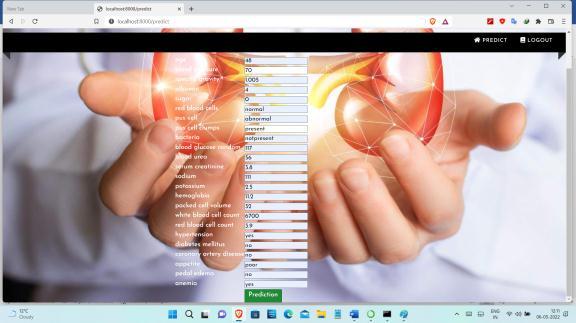
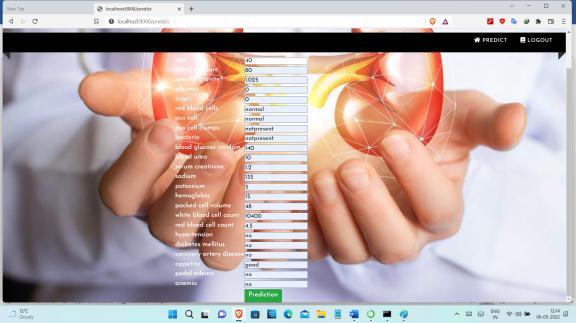
The CKD dataset was collected from the University of California Irvine Machine Learning Repository which consistsof400patientsrecords.Thedatasetconsistsof24 featureswhichweredividedinto11numericalfeaturesand 13categoricalfeatures,inadditiontotheclassfeatures,such as “ckd” and “notckd” for classification. Features involves age, blood pressure, specific gravity, albumin, sugar, red bloodcells,puscell,puscellclumps,bacteria,bloodglucose random,bloodurea,serumcreatinine,sodium,potassium, hemoglobin,packedcellvolume,whitebloodcellcount,red bloodcellcount,hypertension,diabetesmellitus,coronary artery disease, appetite, pedal edema, and anemia. The diagnosticclasscontainstwovaluesnamelyckdandnotckd. All features contained missing values except for the diagnostic feature. The dataset is unbalanced because it consistsof250casesof“ckd”classby62.5%and150cases of“notckd”by37.5%.
Thedatasetcontainedoutliers,duplicationsandnoise,soit must be cleaned up in a preprocessing stage. The
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
preprocessingstageincludedbyestimatingmissingvalues andeliminatingnoise,suchasoutliers,normalization,and checkingofunbalanceddata.Somemeasurementsorvalues in dataset may be missed when patients are undergoing tests,therebycausingmissingvalues.Thedatasethad158 completed instances, and the remaining instances had missing values. The simplest method to handle missing values is to ignore or remove the records, but it is inappropriatewithsmalldataset.Sowecanusealgorithms tocomputemissingvaluesinsteadofremovingrecords.The missingvaluesfornumericalfeaturescanbefilledthrough oneofthestatisticalmeasures,suchasmean,median,and standarddeviation.Butweusedmeanstatisticalmeasures tofillnumericalvaluesinthedataset.Themissingvaluesof nominalfeaturescanbecomputedusingthemodestatistical measures, in which the missing values is replaced by the mostcommonvalueofthefeatures.Whilenumericalfeatures arethevaluesthatcanbemeasuredwhichhavetwotypes, eitherseparateorcontinuous.
After computing the missing values in the preprocessing stagemoveonto identifyingtheimportantfeatureshavinga strongandpositivecorrelationwithfeaturesofimportance for disease diagnosis is required. Taking out the vector featureseliminatesuselessfeaturesandunrelevantfeatures for predicting.we used the Recursive Feature Elimination method to take out the most important features of prediction. The Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE) algorithm was very popular with its ease of use and configurationsanditseffectivenessinselectingfeaturesin trainingdatasetsrelevanttopredictingtargetvariablesand eliminatingweakfeatures.TheRFEmethodisusedtoselect the most significant features by finding high correlation betweenspecificfeaturesandtarget.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[6] Koushal Kumar and Abhishek, on ”Artificial Neural Networks for Diagnosis of Kidney Stones Disease”, I.J. InformationTechnologyandComputerScience,2012,7,pp 20 25.
[7]TomFawcett,(2003).onROCgraphs:Notesandpractical considerationsfordataminingresearchers.Technicalreport, HPLaboratories
Conclusion:
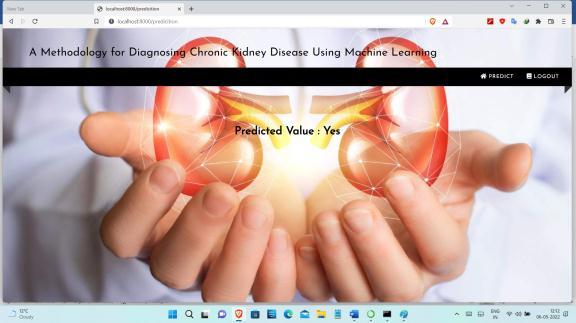
This study provides awareness into the diagnosis of CKD patients to handle their condition and receive timely treatmentofthedisease.Thedatasetwascollectedfromthe UniversityofCaliforniaIrvineMachineLearningRepository, consists of 400 patients records with 24 features. The datasetwasdividedinto75%trainingand25%testingand validationdata.Thedatasetwaspreproocessedtoremove outliersandreplacemissingnumericalandnominalvalues using mean and mode statistical algorithms, respectively. TheRecursiveFeatureEliminationalgorithmwasappliedto selectthemoststronglyidentifiedfeaturesofCKD.Selected featureswerefedintoclassificationalgorithmsnamelyNaive Bayes and Random Forest. The parameters of induced classifiersweretunedtoperformthebestclassification,so algorithmsreachedpromisingresultsfordiagnosingCKD.
InfuturewewillbefocusingonotheralgorithmslikeCNN andRNN.
[1] AKINYELU, A. A., & ADEWUMI, A. O. (2014). on “Classification of phishing email using random forest machine learning technique”. Journal of Applied Mathematics.
[2]A.Subasi,E.Alickovic,J.Kevric,on“Diagnosisofchronic kidney diseaseby using randomforest,”in Proc.Int.Conf. MedicalandBiologicalEngineering,Mar.2017,pp.589 594.
[3]L.Zhangetal.,on“Prevalenceofchronickidneydisease inchina:acrosssectionalsurvey,”Lancet,vol.379,pp.815 822,Aug.2012.
[4]A.Singhetal.,on“IncorporatingtemporalEHRdatain predictive models for risk stratification of renal function deterioration,”J.Biomed.Inform.,vol.53,pp.220 228,Feb. 2015.
[5] A. M. Cueto Manzano et al., on “Prevalence of chronic kidneydiseaseinanadultpopulation,”Arch.Med.Res.,vol. 45,no.6,pp.507 513,Aug.2014.
[8]J.VanEyck,J.Ramon,F.Guiza,G.Meyfroidt,M.Bruynooghe, G.Van den Berghe, K.U.Leuven, on ” used Data mining techniquesforpredictingacutekidneyinjuryafterelective cardiacsurgery”,Springer,2012.
[9] DSVGK Kaladhar, Krishna Apparao Rayavarapu* and VarahalaraoVadlapudi,on”usedStatisticalandDataMining AspectsonKidneyStones:ASystematicReviewandMeta analysis”,OpenAccessScientificReports,Volume1•Issue 12•2012.
[10]K.R.Lakshmi,Y.NageshandM.VeeraKrishna,on”done performanceoncomparisonofthreedataminingtechniques for predicting kidney disease survivability”, International JournalofAdvancesinEngineering&Technology,Mar.2014.
[11] Morteza Khavanin Zadeh, Mohammad Rezapour, and Mohammad Mehdi Sepehri, on ” used Data Mining for fundingperformanceinIdentifyingtheRiskFactorsofEarly Arteriovenous Fistula Failure in Hemodialysis Patients”, Internationaljournalofhospitalresearch,Volume2,Issue 1,2013,pp49 54.
[12] Abeer Y. Al Hyari, on ” chronic kidney disease predictionsystemusingclassifyingdataminingtechniques”, library of university of Jordan, 2012. Manish Kumar, International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing,Vol.5Issue.2,February 2016,pg.24 33©2016, IJCSMCAllRightsReserved31.
[13]Xudong Song,Zhanzhi Qiu,JianweiMu,on” Study on DataMiningTechnologyanditsApplicationforRenalFailure Hemodialysis Medical Field”, International Journal of AdvancementsinComputingTechnology(IJACT),Volume4, Number3,February2012.
[14] N. SRIRAAM, V. NATASHA and H. KAUR, on ” data miningapproachesforkidneydialysistreatment”,journalof Mechanics in Medicine and Biology, Volume 06, Issue 02, June2006.
[15] Jicksy Susan Jose, R.Sivakami, N. Uma Maheswari, R.Venkatesh,on ”AnEfficientDiagnosis of KidneyImages usingAssociationRules”,InternationalJournalofComputer TechnologyandElectronicsEngineering(IJCTEE),Volume2, Issue2,april2012.
[16]DivyaJain,SumanlataGautam,on”PredictingtheEffect of Diabetes on Kidney using Classification in Tanagra”,
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing,Volume3,Issue4,April2014.
[17] M. M. Hossn et al., on “Mechanical anisotropy assessmentinkidneycortexusingARFIpeakdisplacement: Preclinical validation and pilot in vivo clinical results in kidneyallografts,”IEEETrans.Ultrason.Ferr.,vol.66,no.3, pp.551 562,Mar.2019.
[18]M.Alloghanietal.,on“Applicationsofmachinelearning techniques for software engineering learning and early predictionofstudents’performance,”inProc.Int.Conf.Soft ComputinginDataScience,Dec.2018,pp.246 258.
[19]D.Gupta,S.Khare,A.Aggarwal,on“Amethodtopredict diagnosticcodesforchronicdiseasesusingmachinelearning techniques,”inProc.Int.Conf.Computing,Communication andAutomation,Apr.2016,pp.281 287.
[20]L.Duetal.,on“Amachinelearningbasedapproachto identify protected health information in Chinese clinical text,”Int.J.Med.Inform.,vol.116,pp.24 32,Aug.2018.

Dr.K.N.S.Lakshmi
Currentlyworkingasprofessor in Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Sanketika Vidya Parisad EngineeringCollege.
Pursuing B.Tech final year in Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Sanketika Vidya Parisad EngineeringCollege.
Pursuing B.Tech final year in Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Sanketika Vidya Parisad EngineeringCollege.

Pursuing B.Tech final year in Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Sanketika Vidya Parisad EngineeringCollege.


Pursuing B.Tech final year in Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Sanketika Vidya Parisad EngineeringCollege.
