International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

Abstract The coronavirus (COVID 19) outbreak remains impacting the fitness or wellbeing of the worldwide population, with an excessive price of transmission affecting tens of thousands and thousands of people. In maximum situations, strategies utilized in pathogen laboratories, which include polymerase chain reaction (PCR), take greater time and regularly produce fake poor results, however are the usual strategies for diagnosis. Therefore, there may be a want for quicker and greater correct diagnostic strategies to locate early level COVID 19 instances to forestall and combat the unfolding of the pandemic. The speedy screening process, primarily based totally on current technology which include X rays and computed tomography scans, can assist lessen the quantity of labor concerned in big diagnostic tests. A chest X ray is one of the handiest approaches to diagnose a pneumonia symptom,that'stheprimarysymptomofCOVID 19.
This paper aims to propose a model for detecting COVID 19 effectively utilizing digital chest x ray images with the highest level of accuracy in detection and classifying the imagesbyusingInceptionV3methodandDNN.
Key Words: COVID 19, Convolutional Neural Network, Deep Learning, Inception V3, Deep Neural Network
Coronavirus (COVID 19) disease is a virus borne infectious disease. The World Health Organization (WHO) labeleditapandemiconMarch11,2020,duetoitsglobal expansionanditsfrighteningvelocityatwhichthedisease spreads and the intensity with which it is manifested. Authorities in a lot of countries have established peripheral limitations, flight restrictions, home quarantine, social isolation, and increased cleanliness awareness. The virus, on the other hand, continues to spread at a quick speed. The majority of the patients infected with COVID 19 developed mild to moderate respiratory illness, but a few people suffered from life threateningpneumonia.
The following are some of the major issues with current methodsforidentifyingCOVID 19patients.
1. Healthcare providers must obtain respiratory tract samples. Nasopharyngeal swab collection is a typical procedurethatrequiresthenursetobeincloseproximity
tothepatient[6].Crossinfectionmaybecomemorelikely asaresultofthis.
2. The WHO recommended RT PCR kits for testing COVID cases are expensive, and the number of kits available in underdeveloped countries is insufficient to test the huge population. As a result, establishing cost effective testing methodsisrequired[7].
3.Thesensitivityoffastantigentestingisnothighenough tobeutilizedaloneforfirstscreening[8].
4. A delay in receiving the test result will cause a delayin tracking the afflicted individual's connections with anotherhealthyperson.
It has already been stated that obligatory patient screening and rapid clinical response for contaminated patients are crucial in preventing the spread of COVID 19 disease. The Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Response(RT PCR)testisthehighestqualityleveltesting approach used for assessing COVID 19 patients. Although it is the most commonly used technique for COVID 19 identification,itisa difficult,time consuming processand sometimes it gives false negative test results. Additional COVID 19diagnosticapproachesincludeclinicalsymptom evaluation,epidemiologic record,affirmativeradiographic screening(CT)/(CXR),andpositivepathogenictesting[4]. Due to a paucity of testing kits, it will be hard to examine every patient with a respiratory illness using routine techniques (RT PCR), X rays were the first technology to playasignificantroleinCOVID 19illnessdiagnosis.Chest X rays and computerized tomography (CT) imaging are considered viable screening methods because of their sensitivity and speed [2]. Chest X rays might yield more accurateresultsthanexistingtechniques.
Many biological problems (for example, detection of breastcancer,identificationofbraintumor,andsoon)are now being addressed with Solutions that are based on artificial intelligence (AI). Image features that were not included in the original photos can be revealed using a variety of Deep learning methods [4]. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in particular have been shown to be extremely effective in the extraction and learning of data, and as a result, they have earned universal support among scientists. In low light images from a high speed videoendoscopy,CNN wasusedtoimproveimagequality and to distinguish the idea of aspiratory knobs using CT
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
images.ThegoalofthisstudyistousechestX raypictures to identify and classify Covid 19 disease, healthy people, andpneumoniapatients.
In the paper "COVID19 detection using transfer learning and convolutional neural networks". To detect COVID19,theconceptofdeeplearningoftransferlearning is provided. Chest x ray analysis to assess lung disease, compared to the total number of affected people, has become an essential technique for both diagnosis and prognosis of COVID 19 patients in the current situation. This study describes a metastatic learning (CNN) technique for detecting COVID 19 infections in X ray images. A multivariate Neural network model (CNN) with TransferlearningapproachInceptionV3hasbeencreated inthe proposedmodel.Itusesconvolutionand pooling to extract features in the same manner as CNN does, except this transfer learning model contains weights from the ImageNet dataset. As a result, it can recognize characteristics rather successfully, providing it an advantageintermsofaccuracy.Thismodelhighlightshow computer vision has the potential to change radiological image analysis. The recommended model performs well with a small dataset, with a validation accuracy of eighty four percent compared to seventy one percent for the InceptionV3model.ThismodelalsosurpassesallpriorCT scan basedmodels.
COVID 19victims mustbediscoveredassoonasavert the infection from spreading. Inception V3 with transfer learning, a DCNN based model for the diagnosis of coronavirus pneumonia patients using chest X ray radiographs, was created in 2020, with a classification accuracy of more than ninety eight percent. Transfer learning was found to be an effective, robust, and easily deployable technique for COVID 19 identification. By quickly training itself from a smaller number of photos, the Inception V3 model works brilliantly in identifying COVID 19 pneumonia. Researchers believe that using this computer aided diagnosis approach will increase the speed and accuracy of diagnosing COVID 19 patients significantly.[4].
According to the study detection of Covid chest Xray based on Multi Level Thresholding and Support Vector Machine, published in 2020, the early detection of SARS CoV 2, is currently a serious problem for clinical practitioners. The proposed method is widely recommended for using X ray images to detect COVID 19 infectedpeople.Theassistvectordeviceidentifiescorona affected X ray images from others by utilizing deep characteristics. The proposed multi level thresholding using SVM technique shown high precision in characterizing the affected lung with Covid 19. The pictures were all the same size and format, JPEG with a
resolution of 512 * 512 pixels. The average sensitivity, specificity,andaccuracywereninety five,ninety nine,and ninetysevenpercent,respectively[9].
A lung X ray is one of the most effective methods for detecting pneumonia, the most significant symptom of COVID 19. As a result, a minimalist model is essential since it enables the model to function on a number of services, including cell devices and conventional PCs, independent of flash volumes. To diagnose COVID 19 illness at various levels of severity, the proposed model employs fourteen layers of convolutional layers and a redesignedspatialpyramidpoolingmodule.Theproposed SPP COVID Net seems to have the highest accuracy correctness of 0.946 and the smallest mean error among thetraininglayersaccuracy,accordingtotheperformance data.It'sperfectforquickresults.[9].
In most cases, the ranges of symptoms of pneumonia andtheCovid 19virusarethesame.Bothareinfectionsof the lungs. Hence, the dataset consists of three separate datasetsofX raysofthechest(COVID 19patients,normal people,andpneumoniapatients).Thereare300photosin all(100COVID 19images,100pneumoniaimagesand100 healthy images). After that, the datasets are divided into two sections: training and testing the classifiers. Fig 1,2,3 showsanexampleofchestX rayimagecollections. Fig.1.
TransferLearningisakindofdeeplearningthatallows us to apply previously learned skills and knowledge to new learning or challenge circumstances. Because it allows you to train deep neural networks with relatively
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
littleinput,it'sapopulardeeplearningmethod.Totraina neural network from the start, a lot of data is usually required,butaccesstothatdataisn'talwaysfeasible.This iswhentransferlearningcomesinhandy.
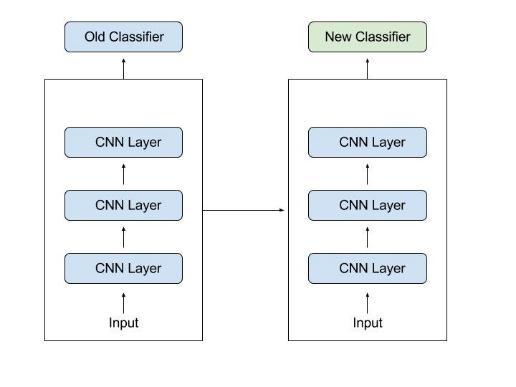
Because the model has been pre trained, transfer learning can produce an effective deep learning model withlesstrainingdata.Fig4showstheworkingoftransfer learningapproach.
Shortertrainingtimeframes,improvedneuralnetwork performanceinmostcircumstances,andtheeliminationof a large amount of data are few of the advantages of transfer learning. This is particularly valuable in the field ofmedicinebecausemostmedicalcasesdonothavemost ofthelabeleddataintheinitialdays.Forexample,COVID 19, for example, is an illness that has only recently been found. As a result, the covid chest image sample is insufficient. To detect this ailment, a transfer learning model was applied. In this situation, Inception V3 can be usedtoprovideresultswithasmallertrainingdataset.Itis alwayspreferabletodevelopadeeplearningmodelontop of a foundation of an established and tested model rather thanstartingfromscratch[14].
In this paper, a two section deep learning based neural network model is proposed. The initial component of this is a transfer learning model called Inception V3. second part of this network is a customized deep neural network(DNN)layer,whilethe
3.21)InceptionV3:
The Inception family's Inception V3 is a convolutional neural network. that includes factorized 7 x 7 convolutions.Youcansimplyimportapre trainedversion of the network from the ImageNet database, which has beentrainedonoveramillionphotographs. InceptionNet wasthefirstCNNclassifiertoapplypreciseapproachesto assure improved performance while balancing speed and accuracy. The Convolution Layer can be factorized in the Inception v3 model, lowering the number of parameters whilepreservingaccuracy.Itcancombinethemax pooling
and convolutional layers, allowing for more effective featurereduction[13].
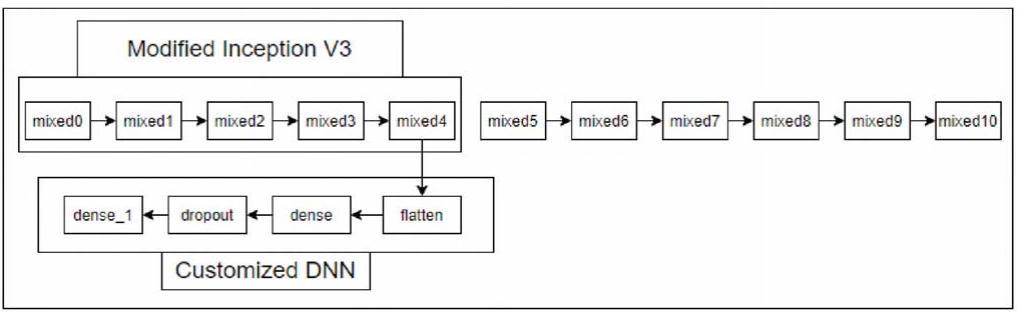
The model has the advantage of allowing output to be extracted from any concatenated node. There are 11 of them, and they're called mixed layers. Total number of layers in order to enhance the model's effectiveness, the model's general structure was changed as a result of the experiment. Fig.5 shows how to use only four of them. Otherwise,it's possibledue toourlimiteddatasetcausing overfitting.
Themodel'sfinallayerswerereplacedwithaDNNthat extracted the output using four customized layers, flatten to convert the mixed layer output to a one dimensional array, and a dense layer of 1024 layers. The following layerwasutilizedtodropout20%oftheneurons.Finally, a dense 1 layer with sigmoid activation function of 1 neuronwasemployed[13].
Class accuracy, sensitivity, and F1 score are the measures used to evaluate the overall efficiency of the suggestedtechnique,andtheyaredeterminedasfollows.:
Classificationaccuracy=TP+TN/TP+TN+FP+FN
Sensitivity=TP/TP+FN
F1Score=2×S×P/S+P
Where, TP denotes True Positive, FP denotes False Positive,FNisFalseNegative,andVolunteerStatedenotes True Negative, with S denoting sensitivity and P denoting accuracy.Wewilldrawaconfusionmatrixforthemodel,if the model gives a correct classification for Covid positive cases then it is correct positive and misclassified Covid negative cases then it is correct negative. Similarly, true negative participants are accurately identified as Covid
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
negative,whilefalsenegativesubjectsarewronglylabeled asCovidpositive.
Our Inception V3 model performs admirably and accuratelypredictsCovid 19.Tothatgoal,weconducteda number of trials. These experiments and their outcomes aredescribedinthefollowingsections:
We had given chest x rays as input for our model. where we split the dataset into an 8:2 ratio, with 80% of theimagesreservedfortrainingpurposesand20%ofthe images for testing purposes. By default, all set of data photosaredownsizedtothe(224,224)imagesize.
For the feature extraction component of Inception v3, the layers from the input layer to the last max pooling layer aretakenintoaccount[10].Figure6depictstheprocessof inceptionv3extractingfeaturesfromphotos.
To encourage a stable model, the parameter settings have been fine tuned. The learning rate, optimizer selection, loss functions, dynamic epoch variation, stack size, inspect dimensions, rotations span, and other parameters are all changed. We tried a variety of other optimizers and loss functions, but none had a substantial influence on the model's performance, so we stuck with Adamastheoptimizerandthebinarycrossentropyasthe lossfunctionthroughoutthemodel.Thenumberofepochs is defined by the number of times the model is applied to coaching data, and the batch size is determined by the number of samples in the network. Dropout could be a regularization strategy that requires training while ignoringcertainrandomneurons.Inmostcases,increased dropoutwillimproveaccuracy[10].
Initial Random callbacks were used to train all of the modelsfor50epochs. TheAdamoptimizer,whichisamix ofSGDwithmomentumand RMSProp,isusedfor quicker parameterdetermination.
Fig.7.TrainingandvalidationlossofInceptionv3
For the inception v3 model, model training takes 19 seconds each epoch. For the inception v3 model, the gradual change in loss (both training and validation/testing) during epoch was depicted in Fig.7. This shows that during training the models, Inceptionv3 hasthelowestloss.
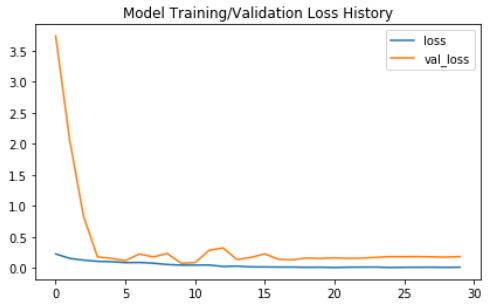
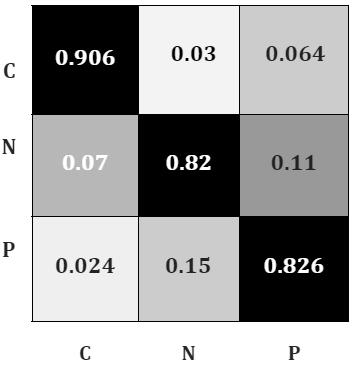
Figure8depictstheconfusionmatrixforthebehavior of several trained models over various layers where C is Covid, P is Pnuemonia, and N is normal chest Xrays. The suggestedinceptionv3modelproducesthemostaccurate results even while being one of the best, with significant
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
true positive and true negative counts for all COVID +ve andCOVID vepictures.
The COVID 19 outbreak has undoubtedly endangered human life. The healthcare system is being strained as a result of measures to contain the disease's spread. The cost of testing for the existence of the virus is high, and it maynot besufficienttoreach a broaderpopulation. Deep learning algorithms have shown to be an effective technique for sifting enormous volumes of data. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate that deep learningtechniquesmightbeutilisedtoidentifyCOVID 19 infection. Deep neural network (DNN) models, according to the study's findings, can be utilised in the healthcare industry to screen for and detect the presence of COVID 19 in chest X rays. Transfer learning has been demonstratedtoimprovethemodel'slearningability.The model Inception V3 with DNN correctly identified and classified COVID 19 chest X rays with 90.64 percent, whereas from other types of chest abnormalities it was 85.06percent.Thisstudyillustratesthatbyproperlyusing AI technology, the burden on medical institutions may be reduced. Because no physical exams are required of doctors or patients at the screening level, the use of this technologyminimizesthedangerofdiseasedissemination whileincreasingthenumberofcases.
Our key objective for the future is to train this model on a huge trustable data set so that we can train it properly and therefore raise the accuracy, as training the machinelearningonmoredataresultsinthemodelbeing much better on invisible data shuts off. This may also be improved to forecast the chance of the affected person surviving.
[1] Rajagopal,Rekha."ComparativeAnalysisofCOVID 19 X ray Images Classification Using Convolutional Neural Network, Transfer Learning, and Machine Learning Classifiers Using Deep Features." Pattern RecognitionandImageAnalysis31.2(2021):313 322.
[2] Zhou, Changjian, et al. "COVID 19 Detection based on Image Regrouping and ResNet SVM using Chest X ray Images."IEEEAccess(2021).
[3] Eljamassi,DuaaF.,andAshrafYunisMaghari."COVID 19 Detection from Chest X ray Scans using Machine Learning." 2020 International Conference on Promising Electronic Technologies (ICPET). IEEE, 2020.
[4] Asif, Sohaib, et al. "Classification of COVID 19 from Chest X ray images using Deep Convolutional Neural Network."2020IEEE6thInternationalConferenceon ComputerandCommunications(ICCC).IEEE,2020.
[5] Thepade, Sudeep D., and Ketan Jadhav. "Covid19 Identification from Chest X Ray Images using Local Binary Patterns with assorted Machine Learning Classifiers." 2020 IEEE Bombay Section Signature Conference(IBSSC).IEEE,2020.
[6] Qian, Yan, et al. "Safety management of nasopharyngeal specimen collection from suspected cases of coronavirus disease 2019." International JournalofNursingSciences7.2(2020):153 156.
[7] Scohy,Anaïs,etal."Lowperformanceofrapidantigen detection test as frontline testing for COVID 19 diagnosis." Journal of Clinical Virology 129 (2020): 104455.
[8] Ella, Hassanien Aboul, et al. "Automatic X ray COVID 19 Lung Image Classification System based on Multi Level Thresholding and Support Vector Machine." https://www. medrxiv. org/content/medrxiv/early/2020/04/06/2020.03. 30.20047787.full.pdf(2020).
[9] Abdani, Siti Raihanah, Mohd Asyraf Zulkifley, and NuraisyahHaniZulkifley."Alightweightdeeplearning model forcovid 19detection."2020IEEESymposium onIndustrialElectronics&Applications(ISIEA).IEEE, 2020.
[10] Das, Amit Kumar, et al. "Automatic COVID 19 detection from X ray images using ensemble learning with convolutional neural network." Pattern Analysis andApplications24.3(2021):1111 1124.
[11] Haritha, D., N. Swaroop, and M. Mounika. "Prediction of COVID 19 Cases Using CNN with X rays." 2020 5th International Conference on Computing, CommunicationandSecurity(ICCCS).IEEE,2020.
[12] Minaee, Shervin, et al. "Deep COVID: Predicting COVID 19fromchestX rayimagesusingdeeptransfer learning."Medicalimageanalysis65(2020):101794.
[13] Dutta, Pramit, Tanny Roy, and Nafisa Anjum. "COVID 19 detection using transfer learning with convolutional neural network." 2021 2nd International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and SignalProcessingTechniques(ICREST).IEEE,2021.
[14] Rashid, Nayeeb, et al. "Transfer Learning Based Method for COVID 19 Detection From Chest X ray Images." 2020 IEEE REGION 10 CONFERENCE (TENCON).IEEE,2020.