A Social Distancing Monitoring System Using OpenCV to Ensure Social Distancing in Public Areas
1 Student, Department of Computer Science & Engineering, RKGIT Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, India

2 Student, Department of Computer Science & Engineering, RKGIT Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, India 5 Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science & Engineering, RKGIT Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, India ***
Abstract Social distancing measures are important to scale back Covid spread. To interrupt the chain of spread, social distancing must be strictly followed. This paper demonstrates a system that is useful in monitoring public places with regular, high people density like Banks, malls, and hospitals for any social distancing violations. With the assistance of this proposed system, it might be conveniently possible to watch individuals whether they are maintaining the social distancing within the area under surveillance and also to alert the individuals as and when there are any violations from the predefined limits. The proposed deep learning technology based system is installed for coverage within a particularly limited distance. The algorithm can be implemented on live images from CCTV cameras to perform operations. The simulated model uses a deep learning algorithm with the OpenCV library to estimate distances between people in frames, and a YOLO model trained on the COCO dataset identifies people within the frames. The system must be configured depending on where it is.
Keywords: YOLO model, COCO dataset, Image processing, Deeplearning,OpenCV,Social Distancing.
1.INTRODUCTION
InthecurrentscenariooftheCOVID 19pandemic,peopleareadvisedtotakecareofadistancetoconfirmthatvirusesdo not spread from one host to different [1]. Consideringthe sociocultural environment in India, enforcing the prescribed social distancing measures among varied categories of people could be a challenging task, where manual supervision is alsoimpossible.Tosearchforaremedyforthisissue,anautomatedmonitoringsystemhasbeendesignedthatmayanalyzea little area with the assistanceof2Dcamerasandinturn,willdetectanysocialdistance violations. We propose an automated monitoring system with 2D camera technology to detect and alert social distancing violations from a little area. It will calculatetherelativedistancebetweeneveryoneinitsviewand can give an alert if social distancing is violated. It willalso displaythefullnumberofindividualspresentinitssight.Thismonitoringsystemmaybeinstalledinplaceswithlessdense crowdslikeATMs,banks,smallshops,foodstalls,offices,etc.Thesystemmustbeconfiguredperthelocationtobeinstalledto supplybetterresults.
Corona Virus outbreak has proven to be deadly to everyone includingallage groups, gender, and people from differentclimateregions.Hence,it'svitaltoscalebackthespeedatwhichCOVID 19isspreading.Oneofthemost effective waystotrythat'sthroughsocialdistancing.Contagiousdiseasesandviruseslikecoronaspreadfrom contactwithinaspecific distance.Asingleaffectedpersoncouldaffectthespreadexponentially.
In this paper, a comprehensive Social DistanceMonitoringSystem(SDMS) provides atrue timesolution tokeep up and ensure social distancing publicly areas.Itensures thatnoone,whetherunintentionallyor intentionally, doesn't violatesocialdistancing.Thismethodwill be applied in places like malls, ATM lines, offices,shops,andothersmallplaces. ThismayhelpineffectivelystoppingthespreadingofcontagiousdiseasesandviruseslikeCovid 19[2][3].Fewexceptionsto SDMSexistsuchasthecaretakerfora physicallychallengedperson,children,patients, or the elderly. The algorithm may be extendedforsuchscenariosbydistinguishingthesortofdotswithinthevisualgraph.
2.LITERATURE REVIEW
SocialdistancingisoneofthecommunitymitigationmeasureswhichwillberecommendedduringCovid 19pandemics. Socialdistancingcanreducevirustransmissionbyincreasingphysicaldistanceorreducingthefrequencyofcongregationin sociallydensecommunitysettings,likeATMs, airports, or the marketplace. Covid 19 pandemicshavedemonstratedthat we cannot expect to contain geographically the subsequent influenza pandemic in the location it emerges, nor can we expect to forestall the international spread of infection over a brief period. COVIDvirusinfectionsare believedtospread mainlythroughclosecontactwithinthecommunity.Socialdistancingmeasures aimtoscalebackthefrequencyofcontact andincreasethephysical distance between persons, thereby reducingthe risks of person to person transmission. There
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
aretheoreticalmodelsexplainingthenecessityofsocialdistancing,whichmaymakeahugedifferenceinslowingthespread ofcoronavirus.
During the start of the pandemic, there was an interplay between age, contact patterns, social distancing, and susceptibility toinfectionwhich madethe pandemic dynamicstobeunclear.Afterthestudyofthetransmissionmodel,it wasconcludedthatbypracticingsocialdistancingalone, theoutbreakcouldbebroughtontopofthings,therebyreducing peak incidence by a greater percentage. There are algorithms reported in the literature for the detection of COVID 19 spread. Deep learning based CNN (ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks)appliedalgorithmtogetherwith geometric techniques combine to make a model covering three aspects such as detection, tracking, and validation of information. The study reportssocialdistancingdatatoauthoritieswitha91.7%precisionscore.
The modeling studies estimated that workplace social distancing measures produced a 23% median reduction in the cumulative influenza attack rate. Another study analyzes the effect of social distancing on the COVID 19 pandemic inKorea using a mathematical model. The transmission rate foreach epidemic stage by fitting into a model, especially for social distancingcriteria.Anaerodynamic basedCFDsimulationstudyinvestigateswhetherthegapis1.5morbeyondandthe possibilityofdroplet transfer.
3.METHODOLOGY
3.1System Architecture
TheobjectiveistouseobjectdetectionemployingaYOLOv3model trained on a COCO dataset that has 80 classes. YOLO uses dark net frameworks toprocessincomingfeedframe byframe. It returns the detections with their IDs, centroids, cornercoordinates,andalsotheconfidenceswithinthestyleofmultidimensionalarrays.Oncetheknowledgeisreceived,the IDs that aren't identified as a “person” are removed. Bounding boxes are drawn to highlight the detections in frames. Subsequently, centroids are calculated to search outthe Euclidean distance between required objects in pixels. The followingstepistocalculate,whetheracalculateddistancebetweentwocentroidsislessthantheconfiguredvalue.The systemwillthrowanalertwitha beepingsoundwhentheconditionis satisfiedwhich alsoturns thebounding boxesof violatorsred[7][9][10].
3.2 Experimental Model
Input: Videotobeaccessed
Output:DetectedinformationdisplayedinVideowithhighlightedboxes
Process: The detailed processing steps are listed below,fromwhichthealgorithmispresented.
Import
1. Importalltherequiredmodules,libraries,andmethods
2. Parseinput,output,YOLOmodel,threshold,Andconfidence
Load class names within the list Load trained YOLOobject detector and input the video
1. YOLOobjectdetectorisloadedwhichistrainedontheCOCOdataset(80classes)
2. Inputthevideowithappropriatevariables
3. Initializeoutputvideoandframe.Thenumberofviolationsarerecordedforallframes.
Determine the whole number of frames in the video
1. Loopovertheframesandskimeveryframeuntilthetip
2. Initializeagroupcalled”violate”,tostorethenumberofviolationsinanexceedingframeProcesstheframeand storethespecifiedoutput.
Process the frame and store the required output
1. Grabthescaleofthisframesay,widthandheight
2. Ablobisconstructedfromtheinputframe
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
3. Performan aerial of the YOLOobject detector returning with bounding boxes and associatedprobabilities ina list. 4. Timetakentoprocessoneframeiscalculatedandsaved 5. Initializeinternalliststostorethedataintheoutputlist 6. Loopovertheoutputlistforprocessingeachdetection 7. CollectclassIDsandcalculateprobabilitiesfromthedetectionwithinthearray,” scores”,forthepresentobject 8. From”scores”gettheclassIDandconfidenceassociatedwiththeclassID. 9. FilterdetectionsforclassID’person’asobjectandvalidconfidence 10. CalculateEuclideandistance Calculate Euclidean distance 1. Extractcoordinatesforcentroidsanddimensionsofboundingboxesfrom“detection”into”box” 2. Calculatecoordinatesforthetopleftcornerofboundingboxesusingcentroidsanddimensions 3. Verifythataminimumoftherearetwoidentifiableobjects 4. CalculateEuclideandistancebetweenthecentroidsofalltheobjectsdetected 5. Check if any set of centroids has but the adviseddistanceandaddthemtothe”violate”set. 6. Apply non maxima suppression to narrow downdetectionsinidxsarray 7. Ensure a minimum of one violation by the” if ”statement 8. oop over idxs after convertingittoa 1 dimensionalarray Processboundingboxentries.
Process bounding box entries
1. Extract boundingboxcoordinateswithrespectivecentroids. 2. RedcolorwillbeassignedtotheclassIDi.e.,(0,0,255)inBGRwhencurrentdetectionis”violates” 3. Centroidsaremarkedonthedrawnboxes 4. DisplayclassIDandconfidenceoverrespectiveboxes 5. Display the numberofviolations i.e.,length ofset ”violate”attheunderside of theframeWritefordisplay
Write
for
display 1. InitializeVideoWriter 2. Displaythetimetakenbyoneframetoprocess 3. Display the time tobetakenbyallframes 4. Writetheframetooutputthevideofile 5. finishoffandreleasethepointers
3.2 Algorithm
The following are the steps in the objection detection algorithm based on the detailed steps mentioned in an experimental model. 1. Inputthevideo 2. Determinethewholenumberofframesinthevideo 3. Loopovertheframesandskimeveryframeuntilthetip 4. Constructablobfromtheinputframe
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

3.3 Flowchart
The flowchart is depicting the complete algorithmic processis provided. The video is imported for processing. For the entire number of frames, the processing parameters are computedtocalculatethegap.Centroidiscalculated.Ifthereis a distanceviolationmarked,aboxismarkedasredotherwisegreen.Oncealltheframesareprocessedfortheirdistance,the programisendedafterthevideoiswrittenforitsviolationmarkings.
4. RESULT
If(p1,q1)and(p2,q2)arethecoordinatesoftheEuclideanDistance.Thesocialdistancethresholdisreportedas0.6.Table 1 presents the number of violations together with centroidanddistance.Thegapis giveninpixels.Distanceiscalculated based on the input frame image threshold in pixels. The violation is calculated supported by the centroidcalculation.All distancecalculationsareaggregatedtosearch outthe numberofviolations, which is reportedand writtenin video finally. Afterprocessingtheframesthey'reforwardedasreal timeoutput.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
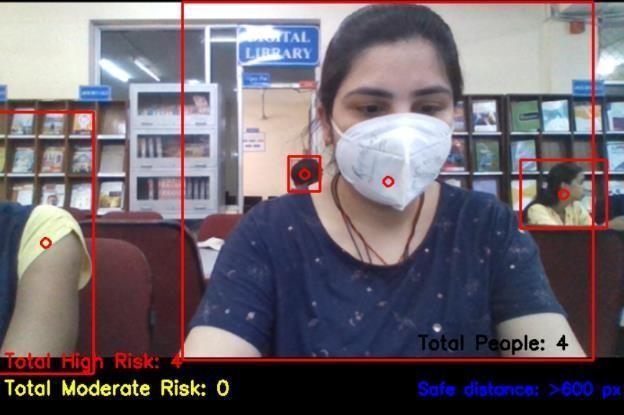
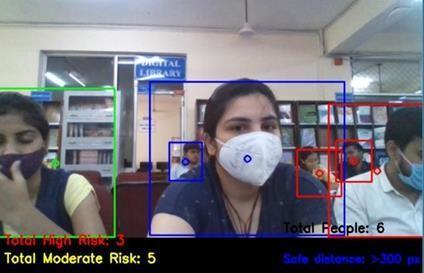
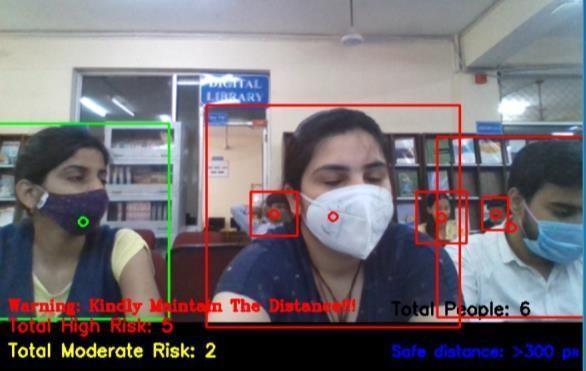
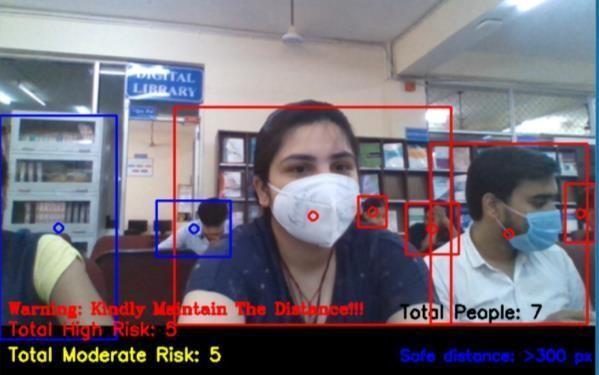
The Output displays all the pedestrians detected and highlighted with their Class IDs and therefore the confidence corresponding to detections. Also, every case in violation of social distancing i.e., when distance in pixelsis over the configured one, ishigh lighted in an exceedingly red color bounding box. The Total Number of violations detected is displayedatthebottomoftheframe.
Theviolationsaremarkedinredbetweentwopersonsandthedistanceisdisplayed.Otherwise,thecalculateddistanceis additionallygiven.Thefullvideowillbeanalyzedforeveryandeachframeforitscontentsandcalculatedviolationsusing centroidcalculations.Theimportanceofthisalgorithmisveryusefulinthepandemicperiodstoimplementincrowded areas, schools, parks, and other public places. The performance parameter such as detection which there's high as per the extensive testing.Fig.presentsthefiguresrepresentingbeforeandaftertheimplementationoftheSDMSalgorithm.Fig6b shows fourdistancing violations highlighted. Similarly, the results maybe interpreted for Fig. where two violations are reportedbased.Thesocialdistancethresholdissetas0.6.Thespaceiscalculatedsupportedequation.Theresultclearlyimplies the detection of violation scenarios for various real time images. The objective of highlighting the social distancing regulationandidentifyingpeoplewithintheframeiseffectivelyattained.
4. CONCLUSION
Thisconcludesthesystemforsocialdistancingandhelpingworldfightcoronavirusthroughnon medicalmeasure.
5. REFERENCES
[1] DeVos,J.,“TheeffectofCOVID 19andsubsequentsocialdistancingontravelbehavior,”Transportation Research InterdisciplinaryPerspectives,A247,pp.100121.,2020
[2] A. H. Ahamad, N. Zaini and M. F. A. Latip, “PersonDetection for Social DistancingandSafetyViolation Alert basedon Segmented ROI,” 2020 10th IEEEInternational ConferencEon Control System, Computing andEngineering(ICCSCE), Penang,Malaysia,pp. 113 118., doi: 10.1109/ICCSCE50387.2020.920493 4, 2020
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
[3] M. Cristani, A. D. Bue, V. Murino, F. Setti and A. Vinciarelli “The Visual Social Distancing Problem,” in IEEE Access, vol. 8,pp. 126876 126886.,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3008370 ,2020
[4] Reluga, T.C., “Game theory of social distancing in response to an epidemic,” PLoS Comput Biol, 6(5), pp. 1000793.,2010
[5] De Vos, J., “Nyabadza, F., Chirove, F., Chukwu, W.C.andVisaya,M.V.,”Modellingthepotentialimpactofsocial distancing on the COVID 19 epidemic in South Africa,medRxiv, 2020 Choi, S. and Ki, M., “Analyzing the effects of socialdistancing on the COVID 19 pandemic in Korea usingmathematical modeling.Epidemiologyandhealth,’42, pp.2020064.,2020
[6] Zhang, J.,Litvinova, M., Liang, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, W., Zhao, S., Wu, Q., Merler, S., Viboud, C., Vespignani, A. and Ajelli, M., “Age profile of susceptibility, mixing, and socialdistancing shape the dynamics of the novel coronavirus disease2019outbreakinChina.medrxiv,’42,pp.2020064.,2020,preprint
[7] Li, K.K., Jarvis, S.A. and Minhas, F., “Elementary Effects Analysis offactors controllingCOVID 19 infectionsin computational simulation reveals the importance of Social Distancing and Mask Usage, 2020, arXiv preprint arXiv:2011.11381.
[8] Yadav,S.,“DeepLearningbasedSafeSocialDistancingandFaceMaskDetectioninPublicAreasforCOVID 19 Safety Guidelines Adherence,” International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology, 8(7),pp.1368 1375.,2020
[9] Ahmed, F., Zviedrite, N. and Uzicanin, A., “Effectivenessofworkplacesocial distancing measures inreducing influenzatransmission:asystematicreview,”InternationalBMCpublichealth,18(1),pp.1 13,2018
