International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
1,2,3 Information Technology, Usha Mittal Institute of Technology, Mumbai, India
4Assistant Professor, Usha Mittal Institute of Technology, Mumbai, India
Abstract In digital image processing and computer vision, image segmentation is a process that involves separating a wide variety of images into various segments. The goal of this procedure is to simplify and improve the representation of an image. The role of image segmentation is very important in image processing. The partitioning of an image into multiple segments makes it easier for further process. Thus, after completing the operations, the image will be re joined. Segmentation increases the accuracy of recognizing the object in an image and reduces the loss. Semantic segmentation and Instance segmentation are the types of image segmentation established on the problem we use image segmentation.
OpenCV, NumPy, TensorFlow, Keras, Scikit Image, Python ImageLibrary(Pillow/PIL),andotherpythonlibraries,that would help detect and identify the objects present around one’ssurroundingsandcomparetheirresults.
An image contains a lot of useful information. Understanding the image and extracting information from the image to accomplish something is an application of digital image technology. Therefore, the start in understanding the image is Image Segmentation. In practice, it’s often not inquisitive about all parts of the image, butjust forsomecertainareaswhichhaveidentical characteristics. Image segmentation is a vital basis for image recognition. It is based on the group to divide an inputimageintoa numberofthesamenatureofthegroup in order to obtain the area in which people are interested. Andit’sthe idea behindImageAnalysisandunderstanding of Image Feature Extraction and Recognition. Image Segmentationisawaytopartitionanimageintonumerous segments(subgroups)thathelpinreducingtheintricacyof the image, hence making the analysis of the image easier. Various algorithms are used to allocate a certain set of pixelstogethertoformanimage.Wearebasicallyassigning labelstothepixelsbydoingso.Pixelswiththesametagfall under a category where they have some or the other thing familiar in them. Using these labels, we are able to specify boundaries,drawlines,andseparatetheforemostrequired objects in a picture from the remainder of the not so importantones.
The aim of this project is to compare various Image Segmentation techniques with Machine Learning, using
In[1],theK meantechniquewasusedtoimplementimage segmentationontheimage.AnRGBimagewastransformed into l*a*b* colour space because the RGB image was very large. They concluded that in the K mean algorithm, the number of clusters was very important. If the number of clusterswasveryhighorverylow,thentheresultwas not so good. K mean showed every cluster in a new window, and it made it easier to analyse the image for further information. In Köhler’s method [2], Adaptive thresholding was one of the most frequently used techniques in many applications because it was fast to evaluate and when merged with previous filters, it gave sturdy decision rules for pattern recognition. In [3], the proposed segmentation systemprovidedacompletesolutionforbothunsupervised and supervised segmentation of colour images built on neuralnetworks.Inthesystem,unsupervisedsegmentation was implemented by SOM based colour reduction and SA based colour clustering. The supervised segmentation was achieved by HPL learning and pixel classification. The system proposed in [4], presented and compared different criteria to optimize segmentation parameters, when examples are available. They also exposed another way to takeadvantageof groundtruth,in changingthe data space before applying the segmentation algorithm. It was shown that using this knowledge to guide the segmentation enables to produce better results, even better than manually produced segmentation by an expert. The paper [5] mainly focused on the study of the soft computing approach to edge detection for image segmentation. The soft computing approaches namely, fuzzy based approach, Genetic algorithm based approach, and Neural network based approach were applied on a real life example image of a nature scene and the results showed the efficiency of image segmentation. In [6] they proposed a conceptually easy, pliable, and general framework for object instance segmentation.Theirapproachefficientlydetectedobjectsin an image while at once generating a high quality segmentationmaskforeachinstancebyusingMaskR CNN. Mask R CNN extends Faster R CNN by appending a branch for predicting an object mask aligned with the existing branch for bounding box recognition. The paper [7]
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

Volume:
proposedthatthehistogramthresholdingwasproposedto enhance image segmentation. Thresholding of the final histogram is done relatively easy with the definition of a lowpassfilterandtheamplificationandattenuationof the peaksandvalleys respectivelyor thestandard deviationof thepresumedGaussianmodes.
Westartedourimplementationbyinstallingandimporting some very important modules namely NumPy, Matplotlib, Scikit image,TensorFlow,KerasandOpenCV.
We then imported the Mask RCNN or the MRCNN model. And then we imported the Coco dataset. COCO signifies Common Objects in Context. It is wide ranging object detection,segmentation,andcaptioningdataset.Itpresents a thoroughstatistical analysisofthedatasetincomparison to PASCAL, ImageNet, and SUN. And it also provides baseline performance analysis for bounding box and segmentation detection results. We then defined the path for the pretrained weights and the images on which we performedthesegmentation.
We then created an inference class that was used to infer the Mask R CNN model. The inference is the method of takinga model and implementing it ontoa machine, which will then process inbound data to look for and classify whatever it has been trained to perceive. The inference is the step in which a trained model is used to foresee the testing.
We can see the various specifications of the Mask R CNN model that we have used. The backbone is Resnet 101. ResNet, is an ideal neural network used as a backbone for variouscomputervisiontasks.

ResNet 101 isa convolutional neural network that is 101 layers deep. The pretrained network can classify

e
p
2395
2395 0072
imagesintomany groups,suchaskeyboard,mouse,pencil, andmanyanimals.Asaresult,thenetworkhaslearnedrich feature representations for a variety of images. The networkhasanimageinputsizeof1024 by 1024.
Themaskshapethatwillberestoredbythemodel is28X28,asitistrainedontheCOCOdataset.Andwehave an overall 81 classes (including the background). We can also see various other statistics as well, like the input shapes, the Number of GPUs to be used, and Validation steps,amongotherthings.
Next, we created our model and loaded the pretrained weights.Themodelispre trainedontheCOCOdataset.This dataset includes overall 80 classes (plus one background class)thatyoucandetectandsegmentfromaninputimage (with the first class being the background class). We then definedtheclassesoftheCOCOdatasetwhichwillassistus inthepredictionphase.

A random image was loaded and then the objects were detected within that image. An abounding box was created aroundeachobjectandeachobjectwasidentifiedcorrectly withgreataccuracy.

Volume:
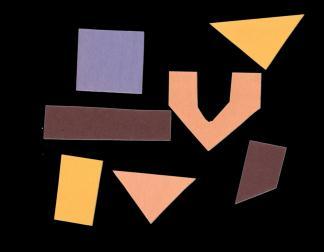
We started off the implementation by importing a few modules:NumPy,matplotlib,andSkimage. Wethenloaded theimageanddisplayedit.
We want the pixels belonging to the shapes to be “on,” while turning the remaining pixels “off,” by setting their colour channel values to zeros. The skimage library has several different methods of thresholding. We started withthe onlyversion, which involves a crucialstep, i.e., human input. Specifically,during thissimple, fixed level thresholding, we must provide a threshold value t. We then loaded the original image, converted it to grayscale, andde noisedit.
Grayscale images contain pixel values within the range from 0 to 1, so we aretrying to finda thresholdthereinclosed range and the geometric shapes are “darker” than the white background so,a methodto work outa “good” value for t isto refer the histogram of the image andinspectto identify what grayscale ranges correspond to the shapes within the image or the background. Since the imagefeatures awhite background, most of the pixelswithin theimage are white. This corresponds nicely to what we see within the histogram:thereisapeaknear1.0
Ifwe mightwish topick the shapes and not the background,we would liketo showoff the white background pixels, while leaving the pixels for the shapes turnedon

e
p
2395
So, we should always choose the value of ‘t’ somewhere beforethemassivepeak.So,wechosetas0.9.Toapplythe threshold, we used the comparison operators to make a mask. We want to show “on” all pixels which have values smallerthanthethreshold,soweusethelessthanoperator and the operator returns a mask. It has just one channel, andeveryoneofitsvaluesiseither0or1.Theareaswhere the shapes werewithin theoriginal image are now white, whilethe remainderof the mask image is black. We can now apply the binary mask to the original coloured image andwhatweareleftwithisonlythe colouredshapesfrom theoriginalimage
As ahead, we started off by importing the same modules. Wealsoloadedtheimageanddisplayedit.Wealsousedthe Gaussian blur to denoise the image and colluded a histogram of the denoised image. The histogram has a significant peak around 0.2 and an alternate, lower peak veritably near1.0. So,we willsay that this imagemay be agood candidate for thresholding with Otsu’s system. The Otsu’ssystemfindsathresholdvaluelinkingthe 2peaksof agrayscalehistogram.
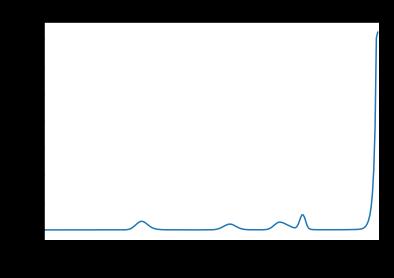

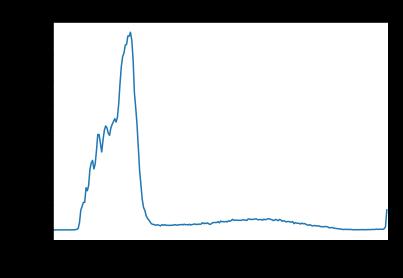
We'veautomaticthresholdingstrategiesthatcandetermine the threshold automatically for us. One similar system is Otsu’s system. It's particularly useful for situations where the grayscale histogram has two or further peaks that resemblethebackgroundandobjectsofinterest.
The Otsu function from the Skimage library can be used to ascertain the threshold automatically through Otsu’s method.Also,comparisonoperatorscanbeusedtoapplyit. Forthisimage,theestimatedthresholdvalueis0.4113.Now wecanproduceabinarymask.Aswe'veseenahead,pixels above the threshold value are going to be turned on, and thosebelowtheedgearegoingtobeturnedoff.Eventually, weusethemasktochoosethefocus.

We started off the implementation by importing a few modulesnamelyNumPy,MatplotLib,andOpenCV.Wethen read the image and transformed it to an RGB image. We thenorganisedthedatafortheK Meansprocess.Theimage wasa 3 dimensional butto utilizek meansclustering onit werequiredtoreformittoa2 dimensionalarray.Weused theNumPyreshape()functionforthis.

We designed a criterion for the algorithm to stop executing,whichwilloccurif100iterationsareexecutedor the epsilon (which is the required accuracy) inclines to 85%.Wethenperformedthek meansclusteringwith total number of clusters as 3, and random centres were randomly chosen for k means clustering. We then convertedthedatainto8 bitvalues,reshapedthedatainto theoriginalimagedimensions,andplottedit.

In Fuzzy c means clustering we started off the implementation by importing a few modules namely NumPy, MatPlotlib, PIL, Skimage, Skfuzzy, and Google.Collab.PatchesandOpenCV.Wethenreadtheimage andtransformedittoanRGBimage.
The image was a 3 dimensional but to utilize k means clusteringonitwerequiredtoreformittoa2 dimensional array, similar to k means clustering. We used the NumPy reshape()functionforthis. Weusedthetransposefunction to focus the cluster prediction based on the colour pixels whichisRGBformatratherthanotherfeatures.

Under Gradient based segmentation, we first implemented the Sobel operator followed by the Prewitt Operator. We startedofftheimplementationbyimportingafewmodules: NumPy,MatplotLib,OpenCV,andPIL.
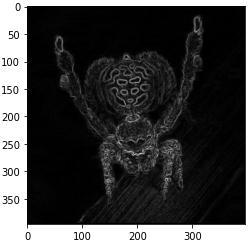
Wethenloadedtheimageandconvertedittograyscale.We then rounded the pixel values to their nearest integers, in thiscase,0sand1s.Wethenassignedvariablesh,wtothe image’s respective height and width. And defined the Gx andGykernels.
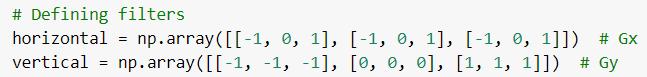
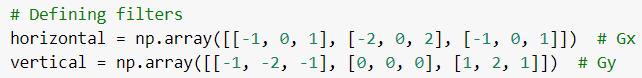
Then by using loops, we applied both the horizontal and vertical filter to the image. And, with the new Gx and Gy values,wecalculatedthegradientmagnitudeanddisplayed theimage.


We then organised the data for the Fuzzy c means algorithm. We created a change_color_fuzzycmeans() function to predict the features of particular pixels and appendthemtoanarray.
We then performed the fuzzy c means clustering with a number of clusters defined as 6, and various other parameters were chosen for fuzzy c means clustering. Finally, we reshaped the finalized data into the original imagedimensionsandplottedit.
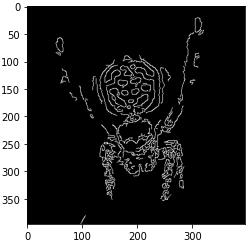
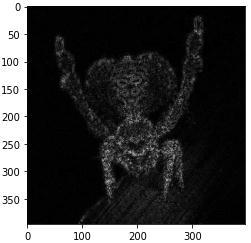
Under Gaussian based segmentation, wefirst implemented theLaplacianoperatorfollowedbytheCannyOperator.We started off by importing the cv2 and MatplotLib modules andreadingtheinputimage.WethenappliedtheGaussian filter to denoise the image and converted the de noised image to grayscale. Using the in built Laplacian and Canny filters,wedetectedtheedges.
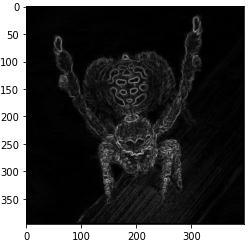
Weimplemented4typesofImagesegmentationtechniques i.e.

Region based segmentation where we learned how to use MaskR CNNtoperforminstancesegmentation.Contraryto objectdetection,whichonlygivesyoutheboundingbox(x, y) coordinates for an object in an image, instance segmentation takes it a step further, complying with pixel wise masks for each object. By applying instance segmentation,weactuallysegmentanobjectfromtheinput picture One of the most prominent applications of region basedsegmentationisobjectiondetectionandrecognition.
Thresholding based segmentation is used to convert a multilevel/grayscale image into a binary image. The advantage of acquiring first a binary image is that it minimizes the complexity of the data and simplifies the processofrecognitionandclassification.Thebinaryimages acquired by thresholding are held in two dimensional NumPy arrays as they need just one colour value channel. they're Boolean, and accordingly contain the values 0 (off) and 1 (on). Thresholding based segmentations are used in caseswheretheforegroundneedstobeseparatedfromthe background, therefore, they are mostly used for object detection.
Clustering basedsegmentationduringwhichweused(a)K means algorithm which is an iterative algorithm that tries to divide the dataset into K pre defined clear non overlapping subgroups (clusters) where each data point belongs to just one group. It aims to form the intra cluster data points as alike as possible while also keeping the clustersascontrasting(far)aspossible. (b)Fuzzy Cmeans an algorithm that works by assigning membership to each datapointcorrespondingtoeachclustercentreonthebasis of the distance between the cluster centre and the data point.Themorethedataisnearbytotheclustercentre,the
Fig.4.5:OutputimageafterapplyingLaplacianfilterFig.4.6:OutputimageafterapplyingSobelfilter
International
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net

closeritsmembershipisclosetotheprecisecluster centre. Clustering based segmentation are primarily used for patternrecognitionanddataanalysis.
Edge based segmentation remits to the process of identifying and locating sharp discontinuities in an image. The discontinuities are instantaneous changes in pixel intensity that distinguish the boundaries of objects in a scene. In this technique, we implemented the Sobel Operator,Prewitt Operator, CannyOperator,andLaplacian of Gaussian. From the experiment performed, it was observed that the Canny result is the superior one when compared to the other detectors for the selected image since different edge detectors work better under different conditions. Edge based segmentation techniques are used where finding out edges is important such as fingerprint sensors.
[1] B. Tanwar, R. Kumar, and G. Gopal, ”Clustering Techniques for Digital Image Segmentation”, vol. 7, no. 12, pp.55 60,2016.
[2] Ralf Kohler, “A segmentation system based on thresholding, Computer Graphics and Image Processing”, Volume15,Issue4,ISSN0146 664X,1981.
[3] Guo Dong and Ming Xie, ”Learning for image segmentation based on neural networks,” in IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, vol. 16, no. 4, pp., July 2005
[4] I. Levner and H. Zhang, ”Classification Driven Watershed Segmentation,” in IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol.16,no.5,pp.,May2007.
[5] N Senthilkumaran and Rajesh, Reghunadhan, “Edge DetectionTechniquesforImageSegmentation ASurveyof Soft Computing Approaches”, International Journal of RecentTrendsinEngineering,November2007.
[6] Kaiming He, Georgia Gkioxari, Piotr Doll´ar, and Ross Girshick,”Mask RCNN” ,IEEE International Conference on ComputerVision(ICCV),2017.
[7] P.Daniel Ratna Raju and G.Neelima, ”Image SegmentationbyusingHistogramThresholding”,2012.
[8]K.SimonyanandA.Zisserman,”Verydeepconvolutional networksforlargescaleimagerecognition”,2015.
[9]KaimingHe,XiangyuZhang,ShaoqingRen,andJianSun, “DeepResidualLearningforImageRecognition”, December 2015
e ISSN:2395 0056
p ISSN:2395 0072