International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
N.P.PATIL1 , RAHUL SHELAR2 , PARVEZ SAYYAD3, PRANAV WATILE4 , ANKUSH PATIL5 , LAXMIKANT JATHAR6
1.6Assistant professor in Mechanical Engineering Department, Imperial College of Engineering & Research, Pune, India
2 5UG Students, Mechanical Engineering Department, Imperial College of Engineering & Research, Pune, India ***
Abstract Bin Picking is a very popular topic in the scope of robotic applications. It usuallyinvolves components that require effective sorting. For many years, R&D facilities as well as the industries work on Bin Picking solutions. However, it is challenging to bring such systems into industrial shop floors mainly due to the design and economical calculability accompanied by the acceptance of stable Bin Picking systems without any downtime. This article presents a versatile interface based framework for the designing and in particular for the simulation of various Bin Picking applications. For that, the term ’Virtual Bin Picking’ has been introduced, which associates the simulation of Bin Picking scenarios in a virtual environment without the need for hardware components. Thus, it enables the design of Bin Picking work cells and it allows predicting the quality of such cells in an early virtual commissioning stage.
Key Words: Bin Picking, Robotics, Simulation, Material Handling.
Robotic bin picking is incredibly important as it is able to take the tedious, monotonous tasks off of workers hands [1]. It is able to effectively handle bulk parts sorting, dangerous operations, and/or labor intensive order fulfillment. Because of its complexity, random bin picking has yet to be perfected or completely grasped by automation systems. However, visionaries are pioneering their way into that uncharted territory. Many experts predict that robotic random bin picking will become mainstreamby2023asthereareavarietyofsubsets ofbinpickingarealreadycommonplace.
In general, bin picking can be divided into three differentcategories[2].Eachcontainsa specialamountof considerationsbasedonthepartpositionthatresultsinis a different level ofcomplexity,cost,andtime.Asonemay guess, the characteristics of parts often determine how easily they will be picked from a bin. The parts that have the greatest success in Bin Picking are geometrically symmetric parts. These parts don’t have strange features,
arenottooheavy,andhavesomesortofsufficientplanar surface in all of their random orientations. These few geometric surfaces are very easy to pick up with a robot andveryeasytogrip.
Recently, Innovative machine vision technologies have helped increase productivity and efficiency in many different industries, while allowing human workers to perform more meaningful work elsewhere within a company [3]. In manufacturing and e commerce settings, to deploy robotic bin picking solutions to automate material handling tasks such as pick, hold and release object, also the movement of robot respective of taught positions [4]. Doing so presents challenges but also adds tremendous value when successfully implemented. This article looks at the some of the latest advancements in bin picking, objectcheckingandsorting.
ThisprojectwasmotivatedbyaproblemthatRoyal Enfield Auto has faced in one of its factories. They are facing some issues while using wrongly dimension partswithvehicle Hence,theywantsystemsuchthatit will sort vehicle parts according to its Height, width, color, Barcode (Unique Identity) also system should workindependentlywithouthumanintervention.
Solving this task required collaborative effort from several industrialist in order to create a functional bin picking system with automation of sorting materials according to its Height, Width, Color, Barcode, which required building and connecting various hardware and software components. Our commitment to this project was simulating the ‘brain’ of this system, which is the simulation of visual recognition system, and simulating the behavior of the robotic arm. In this project, the developed components are described, implemented and tested.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Performance: To increase the pick and package global performance in terms of flexibility, dependability anderrorreduction.
Working Condition: Improvement of the working conditions of operators by a proper layout design and taskallocationbetweenworkerandrobot
Laboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench(LabVIEW)isasystem design platform and development environment for avisual programming languagefromNationalInstruments.
The graphical language is named "G"; not to be confused with G code. The G dataflow language was originally developed by LabVIEW, which is commonly used for data acquisition, instrument control, and
industrialautomationon a varietyofoperatingsystems (OSs), including Microsoft Windows as well as various versionsofUnix,Linux,andmacOS.
LabVIEW environment: The LabVIEW environment consists of LabVIEW VI manager (project explorer), the programming tools, debugging features, templates and ready built sample examples, and an easy interface to the hardware drivers. Read more about LabVIEW environment.
LabVIEW VIs: The LabVIEW VI is a “Virtual Instrument” that enables a user interface to be built and it contains the programming code. Read moreaboutLabVIEWVirtualInstruments,Vis.
LabVIEW G programming: This is the graphical programming language where the functional algorithms are built using “drag and drop” techniques. Read more about LabVIEW programming.
LabVIEW dataflow: This is the core concept that determinestherunningorderfortheprogram
This system has certain advantages and disadvantageswhicharelistedbelow:
Graphical interface is flexible and simple to use. Most engineers and scientistscanlearntouseit quickly.
LabVIEW provides a universal platform for numerous applications in diversefields.
LabVIEW is single sourced and some companies may not like to use a productthat is single sourced andnotstandardizedbytheindustry.
Cost of ownership although in line with many other industry products of asimilar nature, itscostshouldbeconsideredbeforeitisintroduced
LabVIEW is a graphical programming environment. Each LabVIEW program is called a VI, or Virtual Instrument. The programming language is called “G”. The G language is similar to BASIC and C, in that it is intended for a wide variety of programming tasksandso itisconsideredgeneralpurpose.
The front panel is the graphical user interface (GUI), comparable to an HMI. It is thefront end of the
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
program. Here, various controls and indicators can be added depending on the application. The icons and graphical representations emulate those of the physical instrumentcounterpartsasmuchaspossible.
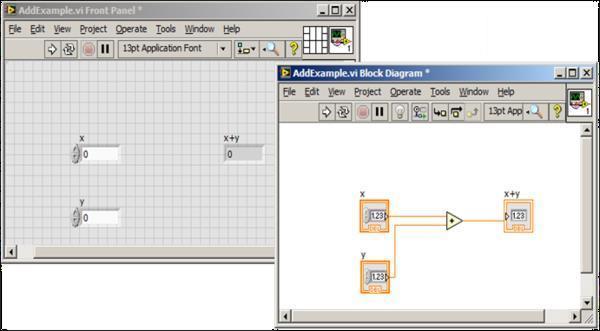
Theblockdiagramis,toputitsimply,thesourcecode of the VI. All the elements added in the front panel are includedintheblockdiagramasterminals.Eachterminal has the possibility to be connected (wired) to other terminalsintheVIusingnodestoformtheprogram
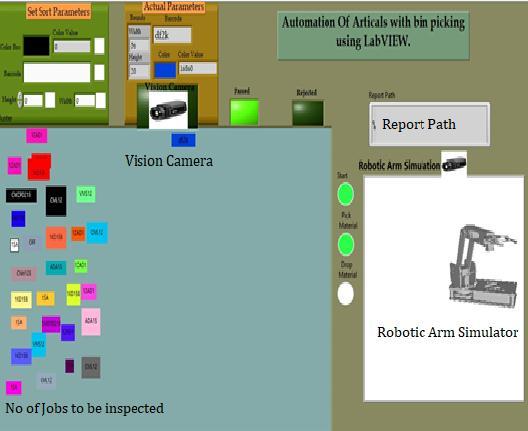
Fig 1:LabVIEWFrontpanelandBlockDiagram
In Fig 2, Number of jobs are stacked at left side with differentcolorsandbarcodes.Roboticarmisusedtopick different jobs and inspect its dimensions under vision camera. After inspection it decides whether the job is acceptedorrejected onthe basisofrequired dimensions and places it accordingly as Fig 3, shows the saved path result in form of excel sheet Parameter selection also available in Set Sort Parameters such that user can select any parameter and work pieces will be sorted accordingtoselectedparameters.
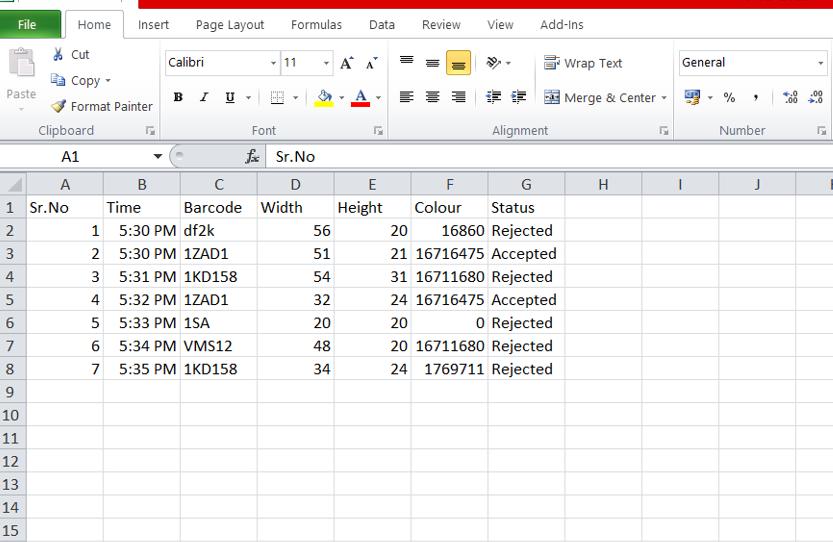
Fig 2: Checkingandsortingsystemsimulation
Fig-3: SavedpathResults(inexcel)
Inthissection,acontrolalgorithmforAutomation of article is explained. The main objective of bin picking is to recognize and acquire a part and sort it. In this framework, thisprocedureis donein multiple iterations, during which the part poseis determined moreprecisely.
Therearetwomainprocesseswhichrunparallel. 1. Roboticarmmovement
2. Checkingandsortingofwork piece
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Value of color, Height, Width, Barcode. By referringthis sheet operator can easily understand parameters wheneverrequired.
From Fig 6, we can understand that robots are more efficient than humans. Robots have better specialty, accuracy, exposure, and performance. Robots have heavy load lifting capacity and is more reliable than humans Table 1,shows the data comparison between Human and Robot.
Fig 4: ControlAlgorithm
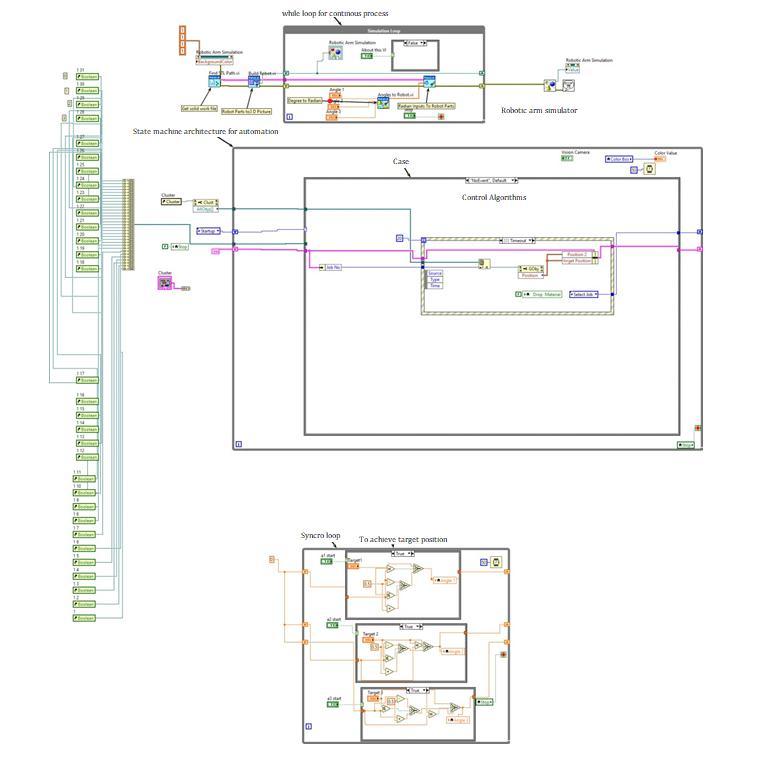
InBlockdiagramwholecontrolalgorithmiswritten.
StatemachineisusedasControlAlgorithm.
Case Structure is used to operate specific logic from program
Local variables are used to transfer data between twoloops.
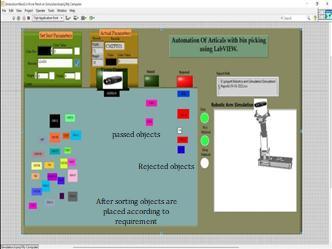
As shown in Fig 5, work pieces will be sorted in two areas.workpiecewhichmatchesselectedsortparameters itgetspassedofanyparameterdoesnotmatchesitwillbe rejected. It shows Excel sheet where result is stored. ResultconsistsofJob number,DateandTimeofchecking,
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Parameter Human Robot
Adaptivity Medium as compared to robots
Specialty Generic (depending ontraining)
Accuracy Mightbework error as compared to robots
Exposure Workers might get affected to radiation and movingparts
Performance
The efficiency of some parts may be more thanrobotbut in long term the robot is moreefficient
High as compared to humans on selective designs
Specialized for certain partsandindustry
[2]S.T.Mortensen,D.Chrysostomou,O.Madsen, A novel framework for virtual recommissioning in reconfigurablemanufacturingsystems,in:201722nd IEEEInt.Conf.onEmergingTechnologiesandFactory Automation(ETFA),IEEE,2017,pp.1 4(2017).URL https://doi.org/10.1109/ETFA.2017.8247744
High accuracy and moreefficient
[3] R. E. Andersen, E. B. Hansen, D. Cerny, S. Madsen, B. Pulendralingam, S. Bøgh, D. Chrysostomou, Integration of a skill based collaborative mobile robot in a smart cyber physical environment, Procedia Manufacturing 11 (2017) 114 123 (2017). URL https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.07.209
Unsusceptible to environmental hazardsandradiation
[4] M. Alonso, A. Izaguirre, M. Grana, ˜ Current research trends in robotgrasping and bin picking, in: The 13th Int. Conf. on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications, Springer, 2018,pp.367 376(2018).
The efficiency of the robot is more as compared to humans and can literally work 24hrscompared
This article represents simulation study of industrial bin picking application. The developed framework includessimulationmodelsforestimationofposition andorientationandforocclusiondetection
The part that has been used for testing the system was a geometrical square work piece. However, the proposed system does not require hard coded knowledge of the part, and uses trained models to determine key attributes of the object, and the application of the proposed system is not limited to the tested part. These models are based on automation and their implementation and testing procedureweredescribed
[1] J. F. Buhl, R. Grønhøj, J. K. Jørgensen, G. Mateus, D. Pinto, J. K. Sørensen, S. Bøgh,D. Chrysostomou, A dual arm collaborative robot system for the smart factories of the future, Procedia Manufacturing 38 (2019) 333 340 (2019). URL https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2020.01.043
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3068