Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072


Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

Dr.K.KALAISELVI 1, SATHYASRI R 2 , SAUMYA V 3, SIVAPRIYA S 4
1 Associate Professor Department of ECE, Hindusthan College of Engineering and Technology. 2, 3, 4 UG Students, Hindusthan College of Engineering and Technology. ***
ABSTRACT: Machinelearninghasbeenusedtoevaluatemedicaldatasetsfordecades.Oneofthemostcommon ailments among the elderly is stroke. The representation approach of these images is often used to diagnose stroke early. Deep learning technology has recently gained traction in a variety of fields, including computer vision, image identification, natural language processing, and, most notably, radiography. Using CNN and deep learning models, this study seeks to diagnose brain stroke images. The suggested method uses a Convolutional neuralnetworktoclassifybrainstrokeimagesintonormalandpathologicalcategories.Thebestalgorithmforall classification processes is the convolutional neural network. We discovered that deep learning models are not onlyusefulfornon medicalimagesbutalsoprovideaccurateresultsinmedicalimagediagnostics,particularlyin thedetectionofbrainstroke.
KEYWORDS: Strokedetection,Computervision,Imagerecognition,Deeplearning,CNN
Deeplearningisatypeofmachinelearningthatteachescomputerstomimichumanbehaviour.Itisalsoknownas deep structured learning and is part of a larger family of machine learning approaches based on representation learningandartificialneuralnetworks.Themajorityofmoderndeeplearningmodelsarebuiltonartificialneural networks,notablyconvolutionalneuralnetworks(CNNs),thoughtheycanalsoincludepropositionalformulasor latent variables structured layer wise in deep generative models like nodes in deep belief networks. So that by using CNN method it is possible to achieve the most accurate method of detecting brain stroke. With earliest detectionofstroke,itispossibletotreatthestrokeandtoreducedeathrate.
DeepLearningisasubsetofMachineLearningthatusesalgorithmstoprocessdataandconstructabstractions or replicate the thinking process. Deep Learning (DL) uses layered algorithms to process data, recognise human speech,andvisuallyassessobjects.Eachlayersendsdatatothenext,withtheoutputofthepreviouslayerserving asinputtothenext.Inanetwork,theinputlayeristhefirstandtheoutputlayeristhelast.Thelayersthatexist between the two are known as hidden layers. Typically, each layer is a simple, uniform algorithm with only one typeofactivationfunction.
AConvolutionalNeuralNetworkisaDeepLearningsystemthatcantakeinanimageasinput,assignpriority tovariousaspects/objectsintheimage,anddifferentiatebetweenthem.CNNapparentlyusesfourlayers: 1.Convolutionlayer 2.Poolinglayer
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072

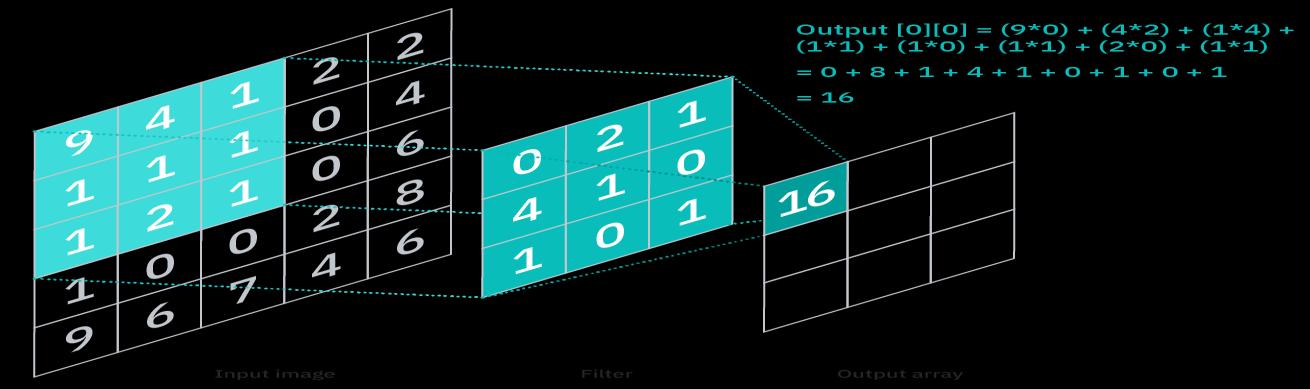
The input image is transformed using a convolution layer in order to extract features from it. The picture is convolved witha kernel inthis transformation.Akernel isa tinymatrixthatissmallerinheightand widththan theimagetobeconvolved.Aconvolutionmatrixorconvolutionmaskisanothernameforit.
The cornerstone of a CNN is the convolutional layer, which houses the majority of the computation. It requires,amongotherthings,inputdata,afilter,andafeaturemap.Assumetheinputisacolourimagemadeup ofa3Dpixelmatrix.Thismeansthattheinputwillhavethreedimensions,whichmatchtotheRGBcolourspaceof apicture.Afeaturedetector,alsocalledakernelorafilter,willscantheimage'sreceptivefieldsforthepresence ofthefeature.Thismethodisknownasconvolution.
Inthefeaturedetector,atwo dimensional(2 D)arrayofweightsrepresentsaportionoftheimage.Thesize ofthereceptivefieldisalsoaffectedbythefiltersize,whichcanvaryinsize.Afterapplyingthefiltertoasectionof theimage, the dot product oftheinput pixelsandthe filter iscalculated.The outputarrayis thenfilled withthe dotproduct.Thekernelisthensweptacrosstheentireimagebyshiftingthefilterbyastride.Theultimate result ofasuccessionofdotproductsfromtheinputandthefilterisafeaturemap,activationmap,orconvolvedfeature.
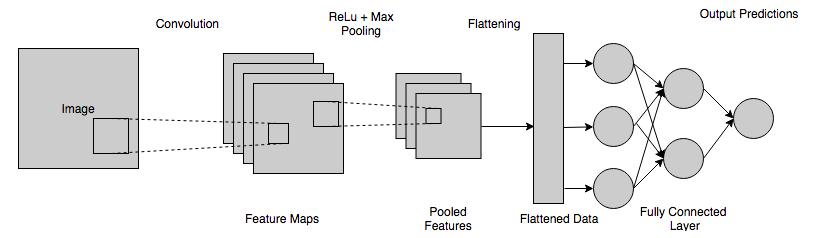
Pooling layers, also known as downsampling, is a dimensionality reduction technique that minimises the numberofcomponentsintheinput.Similartotheconvolutionallayer,thepoolingmethodsweepsafilteracross theentireinput,butthisfilterhasnoweights.Instead,thekernelpopulatestheoutputarraywithvaluesfromthe receptivefieldusinganaggregationfunction.
Therearetwomaintypesofpooling:
The filter selects the pixel with the highest value to transmit to the output array as it advances across the input.Incomparisontoaveragepooling,thisstrategyisemployedmorefrequently.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
Asthefilterpassesovertheinput,theaveragevalueinsidethereceptivefieldiscalculatedandtransferred totheoutputarray.
Whilethepoolinglayerlosesalotofinformation,itdoesprovidesomeadvantagesforCNN.Theyassist inreducingcomplexity,increasingefficiency,andreducingtheriskofoverfitting.
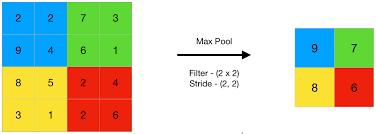
Max Pooling is a type of convolution in which the Kernel collects the maximum value from the area it convolves.MaxPoolingbasicallytellstheConvolutionalNeuralNetworkthatjustthatinformationwillbecarried forwardifitisthemostamplitude wiseaccessible.
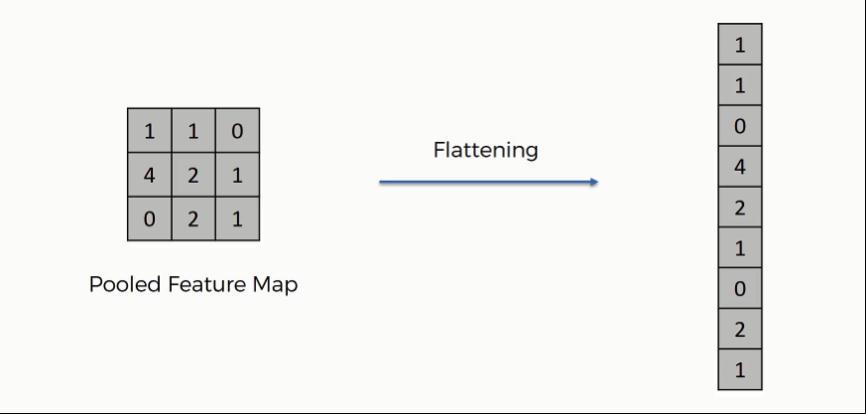
Theflattenfunctionlowersmulti dimensionalinputtensorstoasingledimension,allowingyoutomodelyour inputlayeranddesignyourneuralnetworkmodel,thenfeedthoseinputstoeachandeveryneuronproperly.
The name of the fully connected layer is self explanatory. The pixel values of the input image are not directlyrelatedtotheoutputlayerinpartiallylinkedlayers,aspreviouslyindicated.Inthefully connectedlayer, eachnodeintheoutputlayerconnectsdirectlytoanodeinthepreviouslayer.Thislayerperformsclassification tasks using the features and filters retrieved by the preceding levels. While convolutional and pooling layers utilise ReLu functions to categorise inputs, FC layers use a softmax activation function to generate a probability from0to1.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
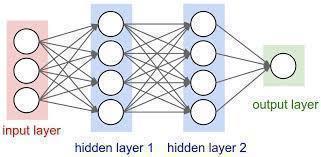
Eachneuroninafullyconnectedlayerislinkedtoeveryneuroninthepreviouslayer,andeachlink has its own weight. This is a completely generic connection pattern that makes no assumptions about the data's characteristics.
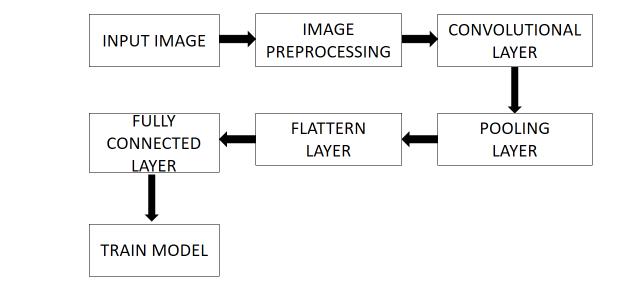
Fig.2.5 Fully connected layer
ThesoftwareemployedintheproposedincludesWindows10 OS,Pythonlanguage,PythonIDLEplatformand librariessuchasKeras,OpenCV,PickleandalsopackagessuchasMatplotlib,Scikitlearn,numpy,imultisand frameworksincludestensorflowandTkinter.
● CNNtakesessentialfeaturesintoaccountautomatically.
● Highprecision.
● CNN'sWorkingProcessisquitefast.
● Largedatasetsarebestsuited.
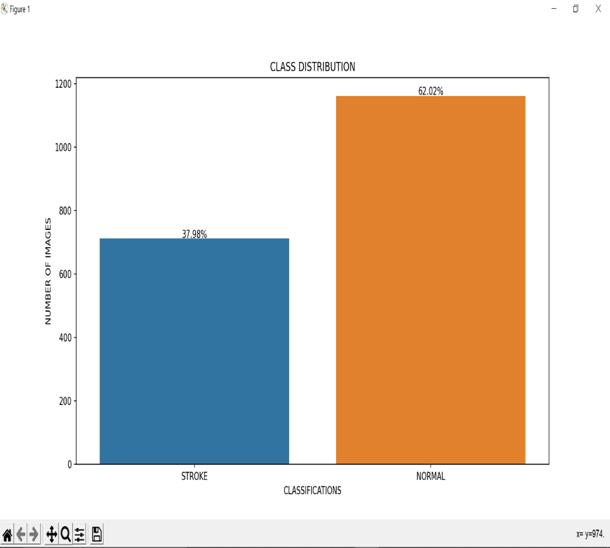
Fig.4.1 Training model
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
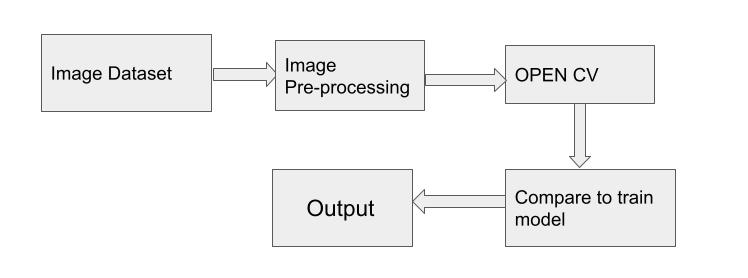
The project's major goal is to detect a stroke in the brain in advance with the highest level of accuracy. This will aid in lowering the death rate from brain stroke. The most traumatic one is a stroke of the brain. For classification, the suggested system employs a Convolutional Neural Network.This project can be carried out by developing a website where anyone can submit a CT brain image for classification. For the same dataset classification,differentMachineLearningAlgorithmscanbeemployed.
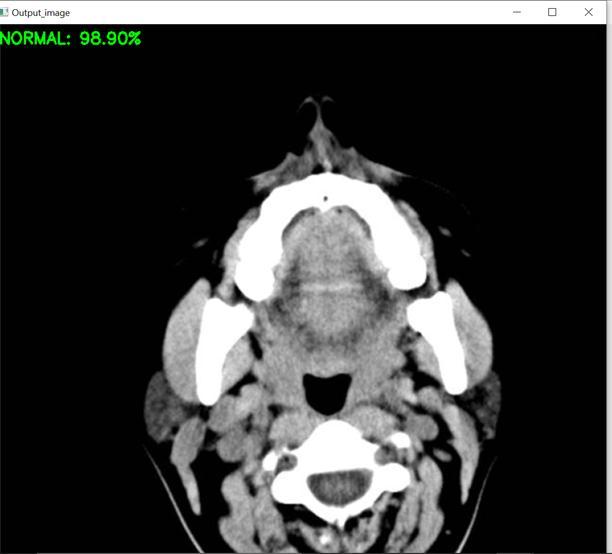
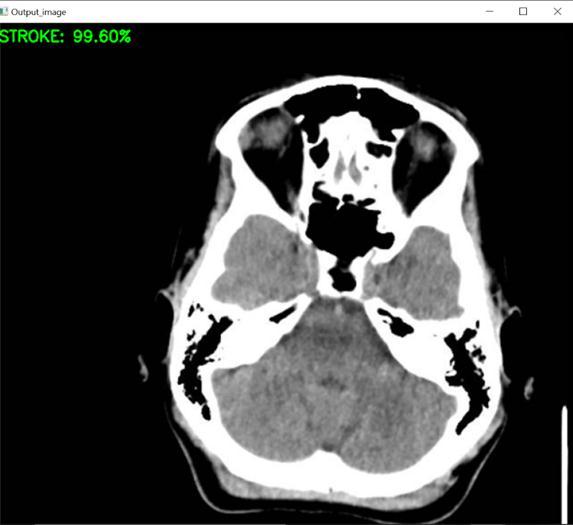
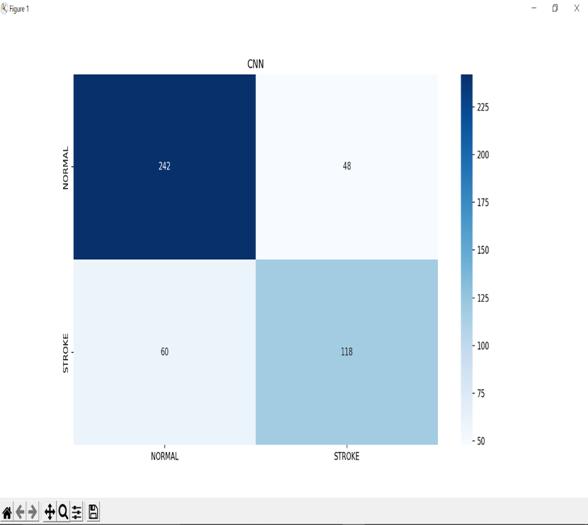
TheproposedsystemaccuratelydiagnosestheincidenceofahaemorrhageinthehumanbrainbyutilisingCT scanimages,andtheoutputissuccessfullyachieved.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

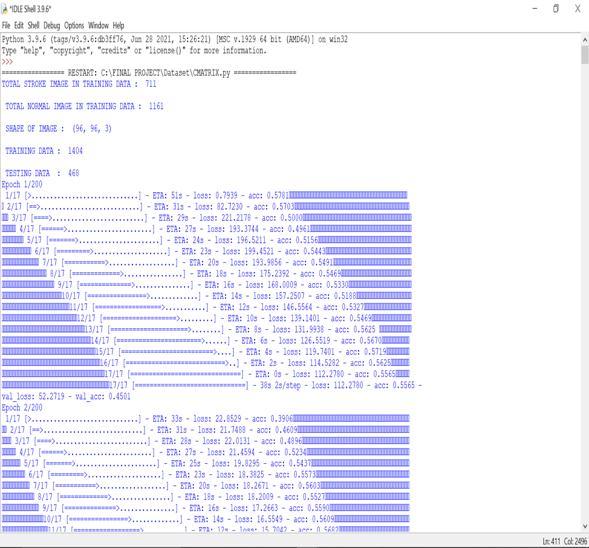
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
1. Deep learning iot system for online stroke detection in skull computed tomography images. Computer Networks,152:25 39.23Garg,R.,Oh,E.,Naidech,A.,Kording,K.,andPrabhakaran,S.(2019).
2. Automatingischemicstrokesubtypeclassificationusingmachinelearningandnaturallanguageprocessing. JournalofStrokeandCerebrovascularDiseases,28(7):2045 2051.
3. Ge, Y., Wang, Q., Wang, L., Wu, H., Peng, C., Wang, J., Xu, Y., Xiong, G., Zhang, Y., and Yi, Y. (2019). Predicting post strokepneumoniausingdeepneuralnetworkapproaches.InternationalJournalofMedicalInformatics, 132:103986.
4. Bentley,P.,Ganesalingam,J.,Jones,A.L.C.,Mahady,K.,Epton,S.,Rinne,P.,Sharma,P.,Halse,O.,Mehta,A.,and Rueckert, D. (2014). Prediction of stroke thrombolysis outcome using ct brain machine learning. NeuroImage:Clinical,4:635 640.
5. Bochniewicz, E. M., Emmer, G., McLeod, A., Barth, J., Dromerick, A. W., and Lum, P. (2017). Measuring functional arm movement after stroke using a single wrist worn sensor and machine learning. Journal of StrokeandCerebrovascularDiseases,26(12):2880 2887.
6. Dourado Jr, C. M., da Silva, S. P. P., da N´obrega, R. V. M., Barros, A. C. d. S., Rebou¸cas Filho, P. P., and de Albuquerque,V.H.C.(2019).
7. Asadi,H.,Kok,H.K.,Looby,S.,Brennan,P.,O’Hare,A.,andThorn ton,J.(2016).Outcomesandcomplications after endovascular treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations: a prognostication attempt using ar tificialintelligence.Worldneurosurgery,96:562 569.
8. Bacchi, S., Zerner, T., Oakden Rayner, L., Kleinig, T., Patel, S., and Jannes, J. (2019). Deep learning in the predictionofischaemicstrokethrombolysisfunctionaloutcomes:Apilotstudy.Academicradiology.
9. Barrett,A.,Boukrina,O.,andSaleh,S.(2019).Ventralattentionandmotornetworkconnectivityisrelevantto functionalimpairmentinspatialneglectafterrightbrainstroke.Brainandcognition,129:16 24