International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Abstract A recommender system can be defined as a systemthat produces individual recommendations asoutput, based on previous decisions that the systemconsiders to be inputs. Book recommendation systems play an important role inbook searchengines,digitallibraries,orbookshopping sites. Inthe field of recommender systems, processing data, choosing the right data characteristics, and how toclassify them are challenges in determining the performance of recommender systems. This paper presents several solutions for data processing capabilities to build efficient book recommender systems. Book Crossing datasets examined in many book recommender systems are considered case studies. Many of the products we use today are theresult of recommender systems such as music, news, books and articles. However, inthispaperwewould be discussing about a book recommender system on Collaborative filtering and Content based filtering while comparing the accuracy of eachrecommendationsystem.
Key Words: Recommender System, Collaborative Filtering, Content Based Filtering, Hybrid Filtering, Nearest Neighbor.
The Current recommendation systems such as content based filtering and collaborative filtering use different information sources to make recommendations. Content based filtering, makes recommendations based on user preferences for product features in this case the genre of the Books, the authors, the ratings etc. Collaborative filtering impersonate user to user recommendations as a weighted and linear combination of other user preferences.Bothmethodshavelimitations.
Content based filtering recommends new entities byusing n or more custom data to absorb the best matches. Similarly, collaborative filtering requires alarge dataset of activeuserswhohavepreviously evaluatedtheproduct in order to make accurate predictions. The combination of these different recommender systems is called a hybrid system andallows you to combine item properties with other users' preferences. Existing services such as Goodreads personalize recommendations and use weighted averages to provide an overall rating for abook. This greatly enhances the value of each recommendation as it takes into account the user's individual book preferences. However, our recommendation engine employs a collaborative social networking approach that mixes your tastes with the wider community to produce meaningfulresults.
The complete RS contains three main components: user resources, article resources, and recommended algorithms. The user model analyzes consumer interests, and the item model analyzes the properties of items in a similarway.Itthencollatestheconsumer'scharacteristics withtheitem'scharacteristicsandusestherecommended algorithm to estimate the recommended item. The performance of this algorithm affects the performance of theentiresystem.
In memory based CF, book ratings are used directly to rank unknown ratingsfornew books.Thismethodcan be divided into two types: a user based approach and an item basedapproach.
1) User based approach: User Based Collaborative Filtering is a technique used to predict the items which looks for similar users that might like on the basis of ratings given to that item by the other users who have positively interacted with that item [12,11,5].
2) Item based approach: This method determines the similarity between a group of objects specifically evaluated by the buyer and the desired object. Items that are very similar will be selected. Recommended values are calculated by taking weighted average of userratingsforthesameobject.
3) Researchers have combined various recommendation techniques to obtain accurate and rapid recommendations, these are called hybrid recommendersystems.SomeHybridrecommendation approachesare:
Performseparateproceduresandconnectresults.
Use some content filtering directives with the CF communities
Use some CF principles in content filtering recommendations.
Use both content and collaborative filtering in the recommender
Inaddition,researchonsemantic based,contextual,cross language, cross domain, and peer to peer methods in progress[1].
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

A recommendation system generally depends upon the inputs of a user and their relationship between the products.
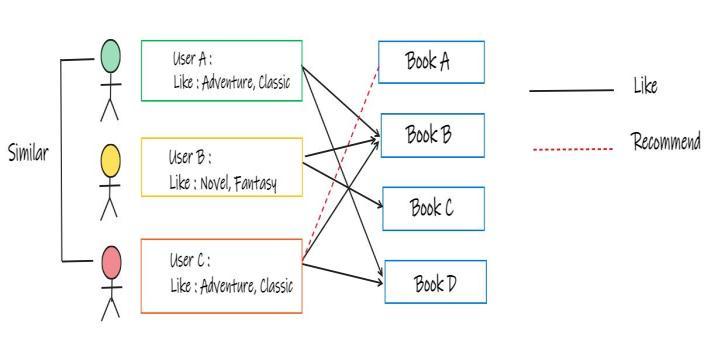
Thecollaborativefilteringalgorithm uses user's behaviour to recommend items. They exploit the behaviour of other users and factors of tracking history, ratings, and choices. Other users' behaviourand book preferences are used to recommendbookstonewusers.However,itcanbedifficult toincludesecondaryfunctionality,i.e.functionsbeyondthe query or ISBN. For book recommendations, extras may include genre and rating. The inclusion of available extra featuresimprovesthequalityofthemodel.
1)ColdStartproblem:Collaborativefilteringsystemsoften requirea hugeamount of existing dataon which user can makeexactrecommendations[2].
2)Scalability: Collaborative filtering makes recommendations for various environments where billionsofproductsandusersexist.Hence,ahugeamount of computation power is rather essential to compute recommendations.
3)Sparsity:Onmajorwebsiteslikeamazonorflipkartthe number of items sold are enormously large. Because of that reason only a small subset of the entire database is ratedbymostactiveusers.Therefore,veryfewratingsare giventothemostpopularitems[3].
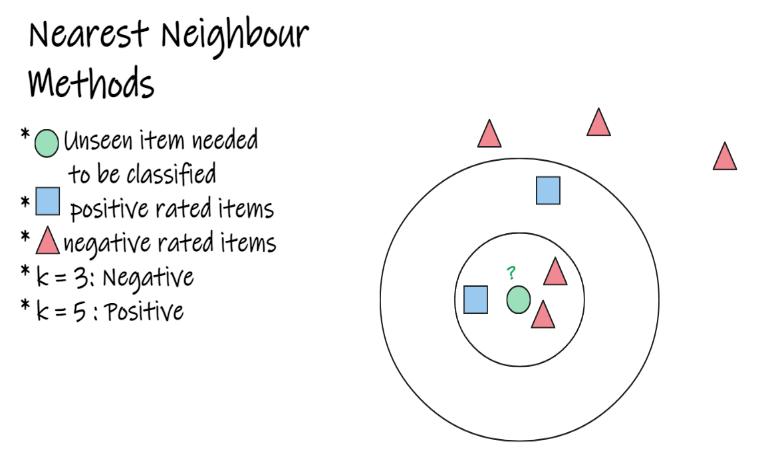
Themostwidelyusedalgorithmforcollaborativefilteringis the k Nearest Neighbors (kNN) [6, 5, 4]. It is very simple algorithm that stores all the available cases and classifies the new data or case based on a similarity measure. It was first introduced in the GroupLens Usenet article recommender[13].
User A prefers book genres A, B, C, and user C prefers to read books B, D, hence we can conclude thatthelikingsof userAanduserCareverysimilar.SinceuserAlikesbookD aswell,wecandeducethattheuserAmayalsolikebookD, therefore bookD would be recommended to the user The general idea of the algorithm is based on a review of previous ratings provided by the users. Find the neighbor userasalphawhoexhibitssimilarinterestwithtargetuser beta,andthensuggeststhe items which the neighbor user alpha preferred to target user beta, the predicted score whichthetargetuseramaygiveontheitemisobtained by thescorecalculationofneighboruseralphaontheitem.
Memory based collaborative filtering technology makes easierimplementationoftherecommendersystems.
1) Amemory basedcollaborativefilteringtechniquethat allowsyoutoaddnewdataeasilyandinstages[10].
2) Prediction performance gets improved when using Model BasedCollaborativefilteringtechniques.
TherearetwotypesofNearestNeighboralgorithms:
1) UserbasedNearestNeighbor
2) ItembasedNearestNeighbor.
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 2954
Inuserbasednearestneighbororusertouserversion,kNN executes three tasks to generate recommendation for a user:
(a) By using a selected similarity measure we can produce a set of k nearest neighbors for the active user alpha.Thekneighborsforalphaarethenearestk,similarto theuserbeta[10].
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
(b) Once a set of k users (neighbors) similar to active user alpha has been calculated, one of the average, weighted sum, and adjusted weighted aggregation (deviation from mean) to get the prediction of item i for useralpha.
(c) Togetthetopnrecommendation,wechoosenitems whichprovidemostsatisfactiontotheactiveuser.
The increase in the number of users increase the scalability problems in User to user based kNN. To overcomethisdrawbacknewmethodisintroducedItemto item kNN, it is introduced by Sarwar et al.[7] and karypis. This item based nearest neighbor investigates the set of items rated by target users and calculates their similarity with the target item i and then chooses k most similar items {i1, i2, i3…., ik} and the representing similarities_{si1,si2,si3,……,sik}arealsocalculatedatthe same time. The most similar items are discovered early and then predictions are calculated by taking a weighted averageofthetargetuser'sratingsforthosesimilaritems. Similarity computation and prediction generation are two key factors that make item based recommendation more powerful. Different types of weighted sum, similarity measures and regression used for prediction computation forsimilaritycomputation.
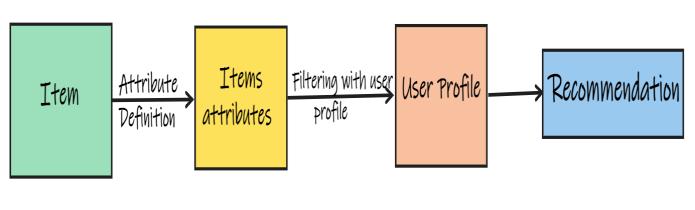
Content based filtering uses books characteristic to recommendbooksthataresimilartowhatuserslike,based ontheirpreviousactionsorexplicitcomments.Thismakes scaling easier for a large number of users. The model can capture a user's specific interests and based on that, can recommendnichebooksthatfewotherusersareinterested in. However, since the characteristic representation of elements is designed by hand in some respects, this methodology requires a lot of domains. That's why, this model can only be as good as manual features. The model can only recommend anything based on already existing userpreferences.Ingeneralterms,themodelhasalimited ability to evolve existing user preferences [8]. When we talk about book recommender system, content based recommender system can recommend books based on explicitly provided user data, then user profile is created. This background knowledge is then used to make recommendationsthatbecomemoreaccurateovertime.In a content based system, the concepts of (TF IDF) term frequency and inverse document frequency are used for information retrieval and filtering systems. The prime use of these terms is toacquire the importance of any book. Termfrequencycanbedescribedasthenumberoftimesor thefrequencyofthewordinadocument.
1) CBF recommender system provide user independence through exclusive ratings which are used by the active usertobuildtheirownprofile.
2) CBFrecommendersystemprovidetransparencyto theiractiveuserbygivingexplanationhow recommendersystemworks.
3) CBF recommendersystemareadequateto recommend items not yet placed by any user. This will be a benefit fornewuser.
Here comes the most crucial step for your research publication.Ensurethedraftedjournaliscriticallyreviewed by your peers or any subject matter experts. Always try to get maximum review comments even if you are well confidentaboutyourpaper.
1) It is difficult to create item characteristics in some areas.
2) CBF recommend the same types of items because of thatitsuffersfromanoverspecializationproblem.
3) It is harder to get feedback from users in CBF because usersdonottypicallyranktheitemsascomparedtoCF and hence, it is not possible to determine whether the recommendationiscorrect.
Hybrid based recommender system proved to be more effectiveinsomecases.Basicallycontentbasedfilteringand Collaborative based filtering approaches are used more extensively in information filtering application. The main objective of hybrid approach is to aggregate content based and collaborative based filtering to improve recommendation accuracy. Hybrid approach can be implementedasfollows:
I) Implement content and collaborative based methods separatelyandthenaggregatetheirprediction.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

2) Include some content based attributes into a collaborativeapproach,
3) Integrate some collaborative attributes into a content basedapproach
4) Build a general integration model to integrate both content basedandcollaborativebasedfeatures.
Sparsity and cold start are common problems in recommendersystemwhichareofsomedegreeisresolved by using these methods. Good example of hybrid recommender system in amazon, they make recommendations by comparing the exploring habits of similar users (collaborative filtering) as well as by providing items that share features with items that a user has rated highly (content based filtering). Some organizations, like Facebook, use this hybrid filtering methodtodisplaymessages thatareimportanttoyouand othersinyournetwork,andthesameisusedforLinkedIn.
CBF and CF can be accumulated in different ways [6].Below given figures shows the different choices for accumulatingCBandCBF.
Fig-6: showsthemethodsforconstructingaunifiedutility systemwithbothCFandCBFattributes.Inthismethodby combiningsomefeaturesofCFandCBFoneunifiedmodel is constructed that can improve performance of recommendationprocess.
Fig 4: Shows the methods that estimate CBF and CF recommendations individually and afterwards combine themtoyieldbetterrecommendations.
Fig 7:ItshowsthemethodsthatincorporateCFattributes intoaCBFapproach





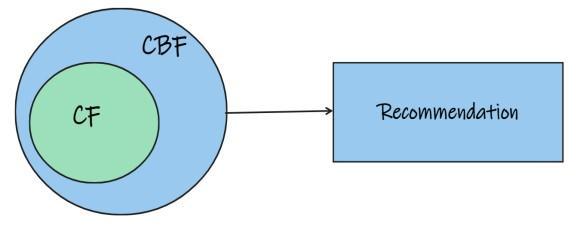
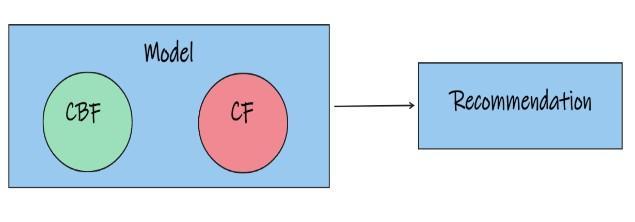
Fig 5: shows the methods that integrate CBF attributes intotheCFapproach,sothatitwillovercomethecoldstart problemincollaborativefilteringofcontent basedfiltering.
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 2956
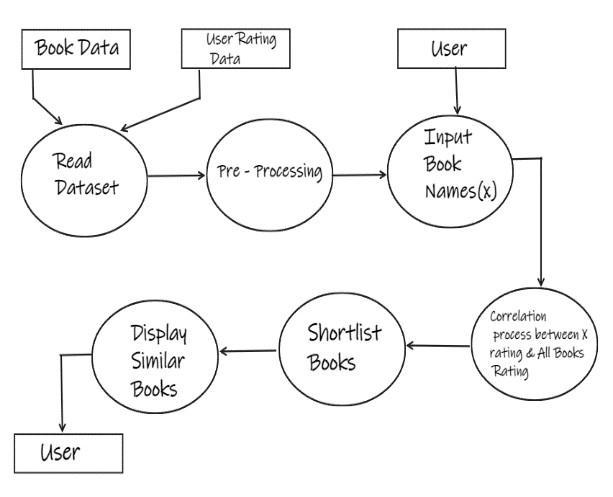
Inabookrecommendersystem,abookisthatentitywhich is considered and recommendation is done using similar entities. Based on the user's query, you can make recommendations using the most relevant similar entities from a large number of datasets. Books are rated, which helps in retrieving other entities that are more relevant

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

based on popularity, relevance, etc. Below stating output, inputanddataoftherecommenderandproblem.
4.1.1 Average Weighted Rating Formula:
Where:
W=WeightedRating
R=averageforthebookasanumberfrom0to10(mean) =(Rating).
v=Numberofvotesforthebooks=(votes)
m=minimumvotesrequiredtobelistedintheTop200
C=themeanvoteacrossthewholereport
The above formula is a variation of the formula used by Goodreads to rate its Book lists. It’s an effective formula that involves the consideration of a user’s perspective to provideaclearrecommendationthereafter.
1)KNNisasupervisedmachinelearningalgorithmusedfor solving classification and regression problems. The K stands for the number of nearest neighbours. In this algorithm the number nearest neighbours to an unknown variable that needs prediction or classification is representedbyk.
2)Algorithmtriestolocatetheclosestneighbourarounda new unknown data point in order to figure out which category the unknown data point belongsto. It assumed that the nearest neighbour to and by unknown data point possessthesamecharacteristics.
3) Algorithm calculates the distance between the allthe data point in the space around the unknown datapoint whichareclosesttotheunknowndatapointandthentries topredictthesimilardataset.
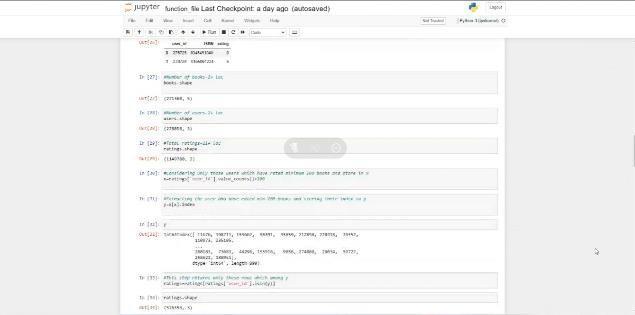
4) In our book recommendation system we used this algorithm to find out the cluster of similar user basedon common book ratings and make predictions based thetop valueofk nearestneighbour.
5)Inthismodelonlythoseuserhavebeenconsideredonly those rated minimum 200 books, this is done to make the recommendation highly relevant. The book ratings have beenpresentedinamatrixwithmatrixhavingonerowfor each book and one column for each reader (user) and a pivottableiscreated.
6)Thepivottableoftheuserratingisconvertedintoasparse matrixmeaningthemissingvaluesarefilledwith a 0 this is done because the distance between the rating vectors will be calculated. The sparse matrix makes the computation fastandcalculationefficient.
7)TotraintheNearestNeighbours model,wehave created acompressedsparserowmatrixtakingratingsofeachBook by each User individually. Thismatrix is used to train the Nearest Neighbours model and then to find n nearest neighborsusingthecosinesimilaritymetric.
Anaconda Navigator, Jupyter Notebook, PyCharm, Python3.9
Data cleaning by using Python libraries like NumPy andPandas.
DataandOutputVisualizationbyStreamlit.
Python Libraries like pickle are used to take data as cache and provide Streamlit with instantaneous result astherecommendationsareprovidedbythebackend.
Wehavetestedmodelusingsimulationofthefollowing requirements.
System with minimum requirement of 8 GB RAMand inteli5coreprocessor.
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 2957
UnderthismoduleweareimportingpythonlibrariestoBook Crossing dataset [9] has shown. The given book dataset is provided byInstitut für Informatik,UniversitätFreiburg
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056

6.2 MODULE 2:
Data cleaning module comprises of the removal of those columns that are not required for calculation of our recommendations.Inthismodule,aswecanseethefactors like Image URL M, Image URL L, Image URL S do not play anyrole nor giveany idea about the interests of our users hence we have dropped such columns. Therefore we have separated those columns of use and merged with user’s database which consists of columns like user ID, Location, Age.Thecodeisgivenbelow:
6.5 MODULE 5:
Fig-12
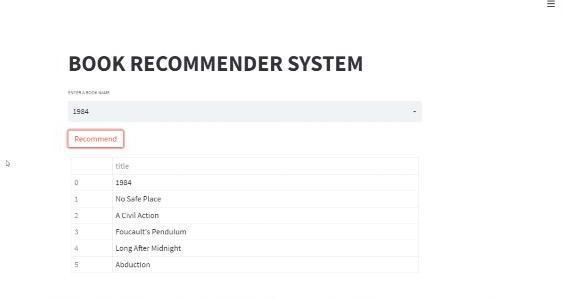
In this module we are training the model on nearest neighbouralgorithmandwhenthemodelistrained,ifasked thequerybygivinganameofabook,recommendersystem providesuswiththenamesofrecommendedbooks.
Fig-10
6.3 MODULE 3:
In this module we are cleaning book rating dataset which have duplicates and redundant data. We are cleaning the databytakingdataofonlyuserswhohaveratedminimum of200books.
Fig 11
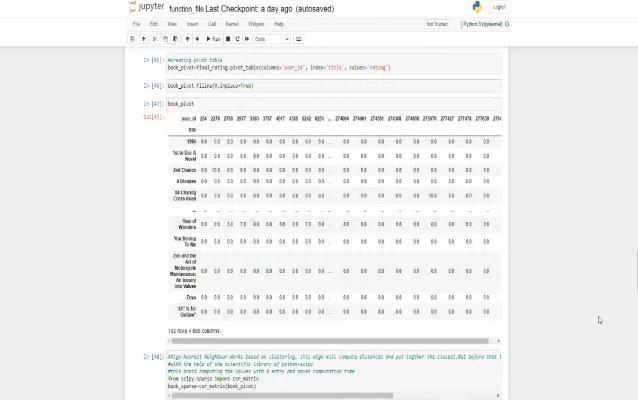
6.4 MODULE 4:
Merging those dataset and then we created pivot table between user ID, index and ratings. It is also shown that using sparse matrix, by using it we can avoid computing time as the value with 0 is not considered and the remaining data creates a pivot table. Also, by using cosine similarity we are going to find the similarity in tastes of users by which ourmodel get to know how similar one user’stastetoanotheruseris.
6.6 MODULE 6:
Fig 13
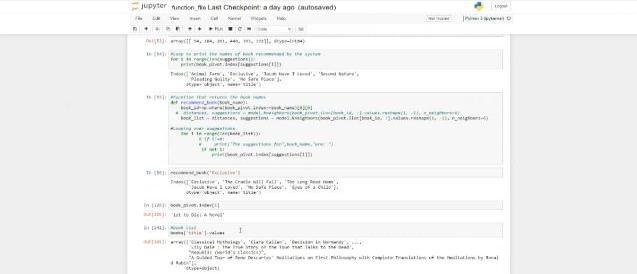
Under this module we are showing the recommendation producedbythemodelusingvisualizationlibraryStreamlit ofPython.
Fig 14
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 2958
Undertheconditionofmassiveinformationavailability,the requirements of Book recommendation system from book amateur are increasing. This article designs and implements a complete book recommendation system prototype based on the Nearest Neighbour classification, collaborative filtering algorithm and recommendation systemtechnology.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
[1] P.K. Singh, P.K.D. Pramanik, A.K. Dey and P. Choudhury, Recommender systems: an overview, research trends, and future directions,Int. J.Business Syst.Res.15(1)(2021)14 52.
[2] K. Heung Nam, E.S. Abdulmotaleb, J. Geun Sik, “Collaborative error reflected models for cold start recommendersystems”, DecisionSupportSystems 51 (3)(2011),pp.519 531
[3] J. Bobadilla, F. Serradilla, “The effect of sparsity on collaborative filtering metrics”, in: Australian DatabaseConference,2009,pp.9 17.
[4] J. Bobadilla, A. Hernando, F. Ortega, J. Bernal, “A framework for collaborative filtering recommender systems”, Expert Systems with Applications 38 (12) (2011)14609 14623.
[5] J. B. Schafer, D. Frankowski, J. Herlocker, S.Sen,“Collaborative filtering recommender systems”, in: P.Brusilovsky, A. Kobsa, W. Nejdl (Eds.), The AdaptiveWeb,2007,pp.291 324
[6] Adomavicius, G.; Tuzhilin, A., "Toward the next generation of recommender systems: a survey of the state of the art and possible extensions," Knowledge and Data Engineering,IEEE Transactions on , vol.17, no.6,pp.734,749,June2005.
[7] B. M. Sarwar, G. Karypis, J. A. Konstan, and J.Reidl, “Item based collaborative filtering recommendation algorithms,” in ACM www ‟01, pp. 285 295, ACM, 2001.
[8] C. Basu, H. Hirsh, W. Cohen, “Recommendation as classification: using social and content based information inrecommendation”, in: Proceedings of the Fifteenth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence,1998,pp.714 720.
[9] Book Crossing Dataset by apl. Prof. Dr. Cai Nicolas Ziegler http://www.informatik.uni freiburg.de/~cziegler/BX
[10] Thorat, Poonam B., R. M. Goudar, and Sunita Barve. "Survey on collaborative filtering, content based filtering and hybrid recommendation system." International Journalof Computer Applications 110, no.4(2015):31 36.
[11] M. Balabanovic, Y. Shoham, “Content based, collaborative recommendation”, CommunicationsoftheACM40(3)(1997)pp.66 72.
[12] M. Pazzani, “A framework for collaborative, content based, and demographic filtering”, Artificial Intelligence Review Special Issue on Data Mining on theInternet13(5 6)(1999)pp.393 408.
[13] Konstan, Joseph & Miller, Bradley & Maltz, David & Herlocker, Jon & Gordon, Lee & Riedl, John. (2000). GroupLens: Applying collaborative filtering to Usenet news. Communications of the ACM. 40. 10.1145/245108.245126.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN:2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN:2395 0072
