International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Anivesh Chaudhary1 , Purushottam sahu2
1BM College of technology Indore, RGPV, Bhopal
2Example: Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, BMCollegeoftechnologyIndore ***
Abstract This paper investigates how different tyre wheel designs affect the displacement distribution, equivalent (von mises) stress, strain, and safety factor of the tyre. It is difficult to estimate all of these data using basic mechanical approximations. Finite Element Model (FEA) is commonly used in the design stage of product development for this purpose. The 3 dimensional models of the wheel were created in the modelling software SOLIDWORKS 2019 and then imported into ANSYS 16.0 using the parasolid format. The model's finite element analysis was completed by meshing the models using solid mesh.Fortheanalysissystem,thestaticconditionwaschosen.Atthebolt,thewheelwasconstrainedinalldegrees offreedom.
Key Words: SOLIDWORKS,ANSYS,FEA,StaticAnalysis,FatigueAnalysis,WheelRim
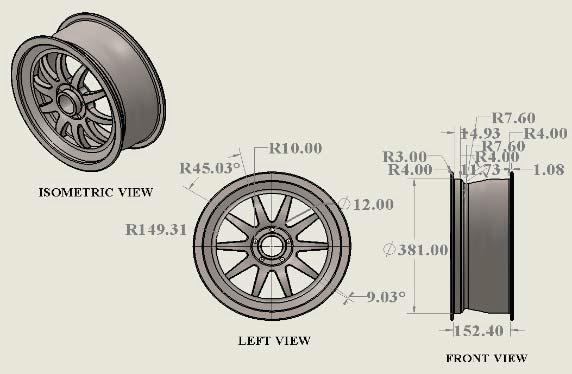
Awheelisacircularblockofhardanddurablematerialswithacircularholeboredthroughthecentrethroughwhichis placedanaxlebearingaboutwhichthewheelrotateswhenamomentisappliedtothewheelaboutitsaxisbygravityor torque.[1]
Thewheelsweusetodayarethe resultofcontinuousimprovementfrom3600B.C. tothepresentday,beginningwith woodendiscsandprogressingtomodernlightweightanddurablealloywheels.Thewheel'smainfunctionwastorollthe entirething.Itwasfirstusedasapotter'swheel,andthen300yearslateritwasusedtofitthechariot.Aftersuchalong period of development, there are now numerous options available, but those designs have a significant impact on the wheel'sperformance.
Theprimaryrequirementsofanautomobilewheelarethatitbeaslightaspossibleinordertoreducefuelconsumption whileincreasingoverall performanceandhandling.Itmustbe extremelystrongin orderto withstandtheload.Itshould besimpletomanufacture.Itsmaterialshouldnotdeteriorateovertimeandweathering.Ifthematerialcomesintocontact with corrosion, it must be given appropriate defensive treatment. [2] To overcome the weight and strength issues, the designandmaterialofthewheelshouldbeconsidered.
Steel or cast/forged aluminum alloys are used to make the wheels. Aluminum is a metal with excellent lightness, corrosionresistance,andotherproperties.Particularlynotablearethe rims,which aremadeofaluminumcastingdueto itslighterweightandlowercost.
Thispaperexaminesthebehaviourofsixdifferentwheeldesignsbycomparingtheirresultdata(weight,deformation, stress,strain,fatiguelife,andsafetyfactor).Thebestdesignoutofthesixhaslessdeformation,lessstressonthebody,and ahighersafetyfactor.
1.Rim:Thetyreisintroducedinthissection.
2.Disc:Apieceoftherimthatissecuredtothehubcentre.
3.Offset:Thisisthedistancebetweenthewheelmountingsurfaceandtherim'sfocusline.
4.Flange:Aribisapieceofrimthatholdsthetire'stwobedstogether.
5.BeadSeat:Abeadseatisapieceofrimthatholdsthetyreinanoutspreadmannerandplacesapproachesincontact withthedotface.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Table2.1showsthattheselectedmaterialforthewheel,whichislinearisotropicmaterialwhosepropertiesaresamein allofthedirections.
Name: StructuralSteel
Model type: LinearElasticIsotropic
Default failure criterion: Unknown
Yield strength: 3.51571e+08N/m^2
Tensile strength: 4.20507e+08N/m^2
Elastic modulus: 2e+11N/m^2
Poisson's ratio: 0.3
Mass density: 7,850kg/m^3
Shear modulus: 7.7e+10N/m^2
Thermal expansion coefficient: 1.5e 05/Kelvin
Figure 4.1(a)WheelDesign1and(b)WheelDesign2
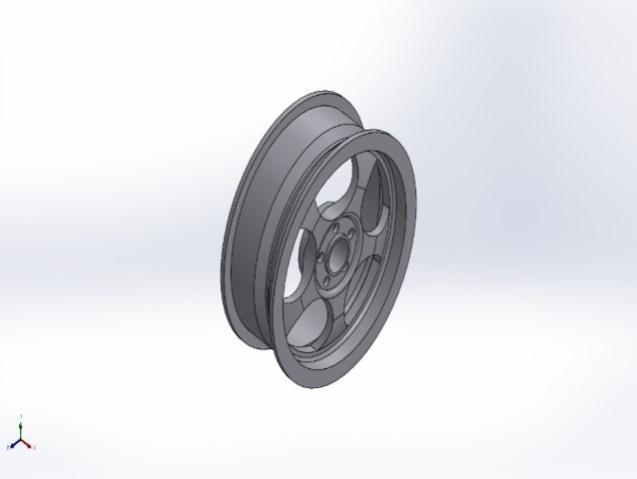
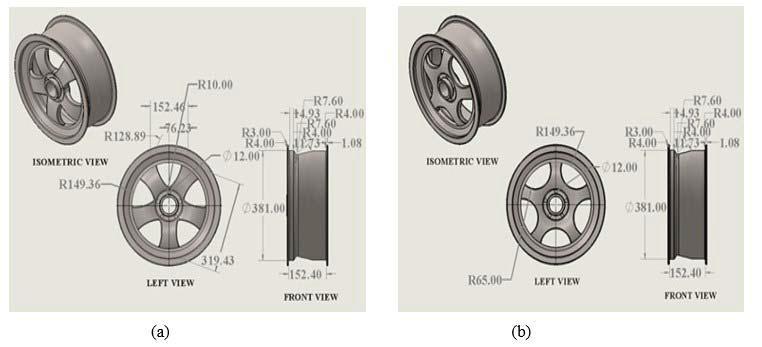

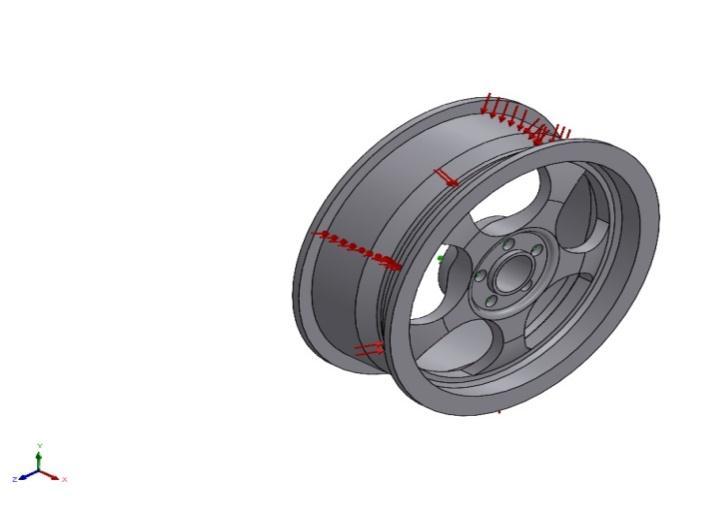
Figure 4.2(a)WheelDesign1(b)meshedmodel
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Name Type Min Max
Figure 4.4 (c)TotalDeformation(Design1)
Name Type Min Max
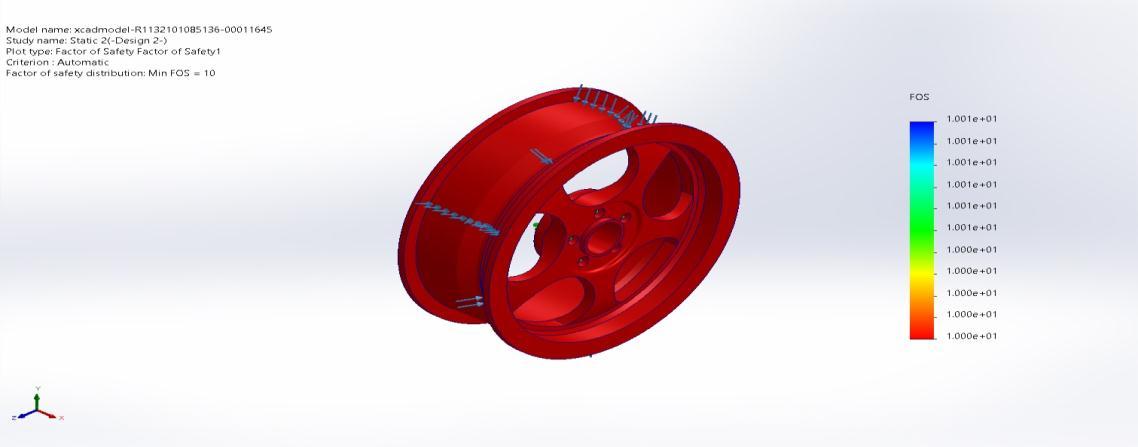
Factor of Safety1 Automatic 8.000e+00Node:1 8.000e+00Node:1
Master Model Wheel Static 1 Factor of Safety Factor of Safety1
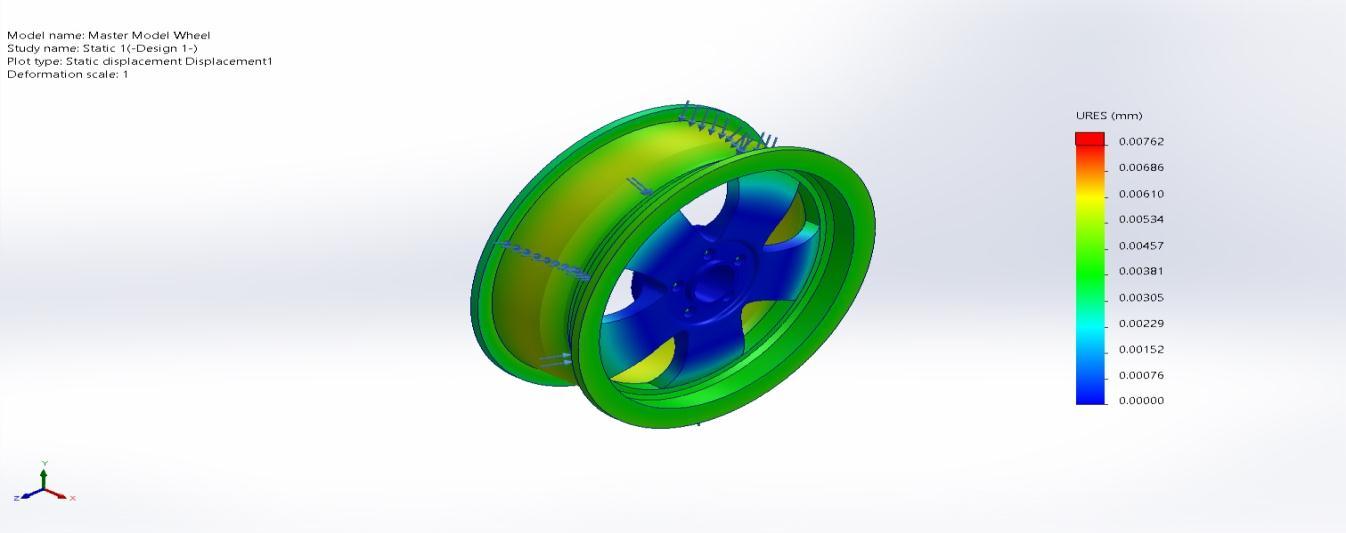
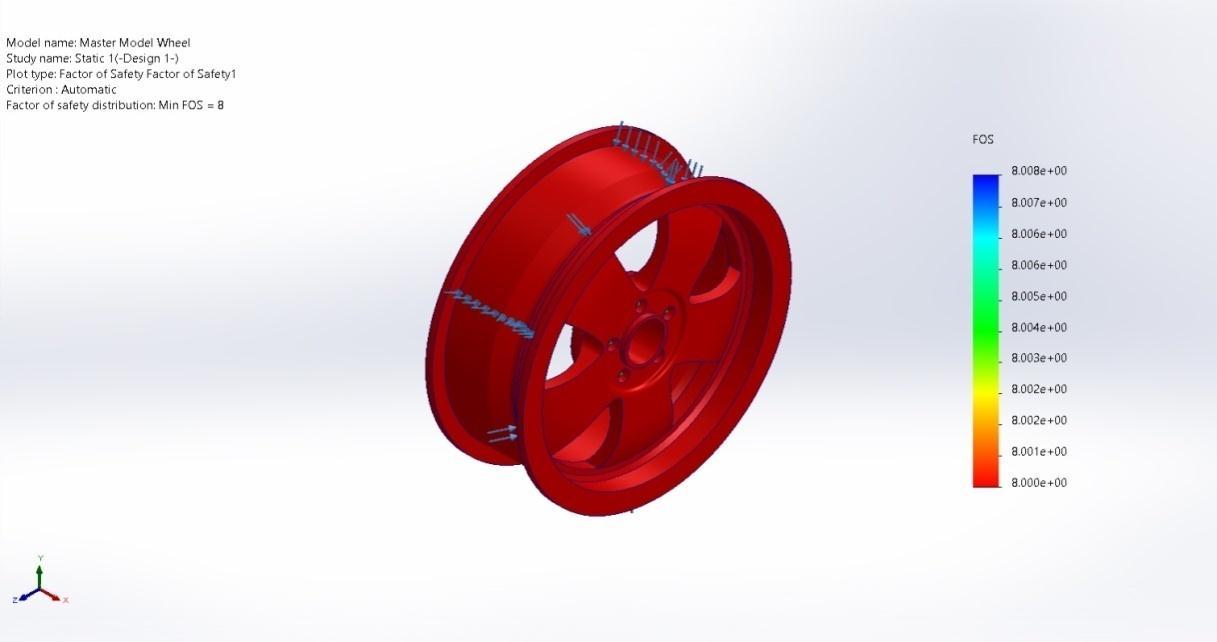
Figure 4.5 (c) Factor of Safety Design 1
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
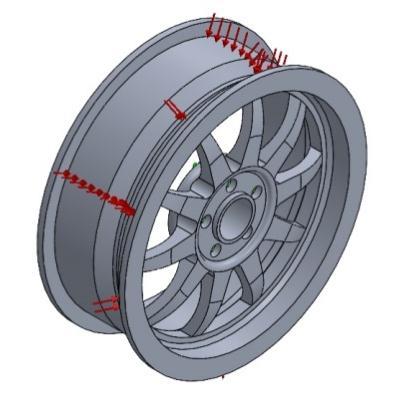
Loadname LoadImage LoadDetails
Entities: 5 face(s)
Pressure 1
Type: Normal to selected face Value: 0.241317 Units: N/mm^2 (MPa) Phase Angle: 0 Units: deg
Figure 4.6 (c) Pressure MPa
Model Reference Properties Components
Name: StructuralSteel
Model type: LinearElasticIsotropic Default failure criterion: Unknown
Yield strength: 3.51571e+08N/m^2
Tensile strength: 4.20507e+08N/m^2

Elastic modulus: 2e+11N/m^2
Poisson's ratio: 0.3
Mass density: 7,850kg/m^3
Shear modulus: 7.7e+10N/m^2
Thermal expansion coefficient: 1.5e 05/Kelvin
Solid Body 1(CirPattern5)(xcadmodel R1132101085136 00011645)
Curve Data/A
WheelDesign2

2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal




International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072


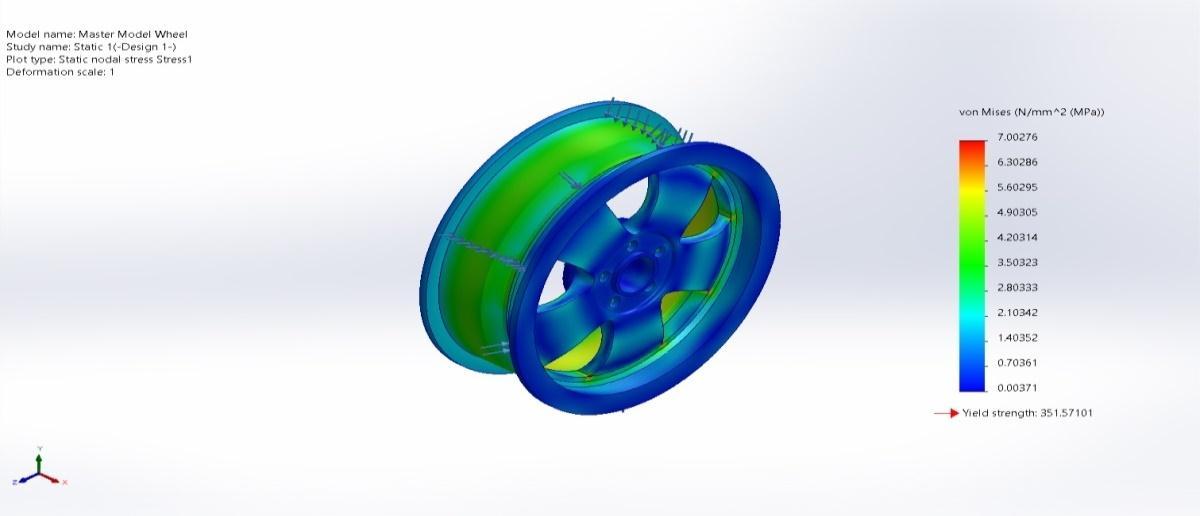
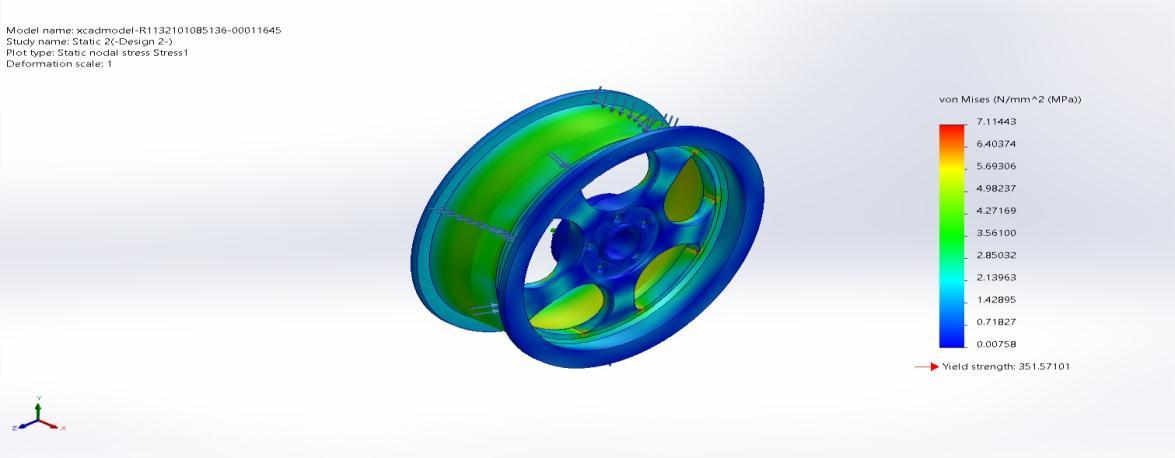
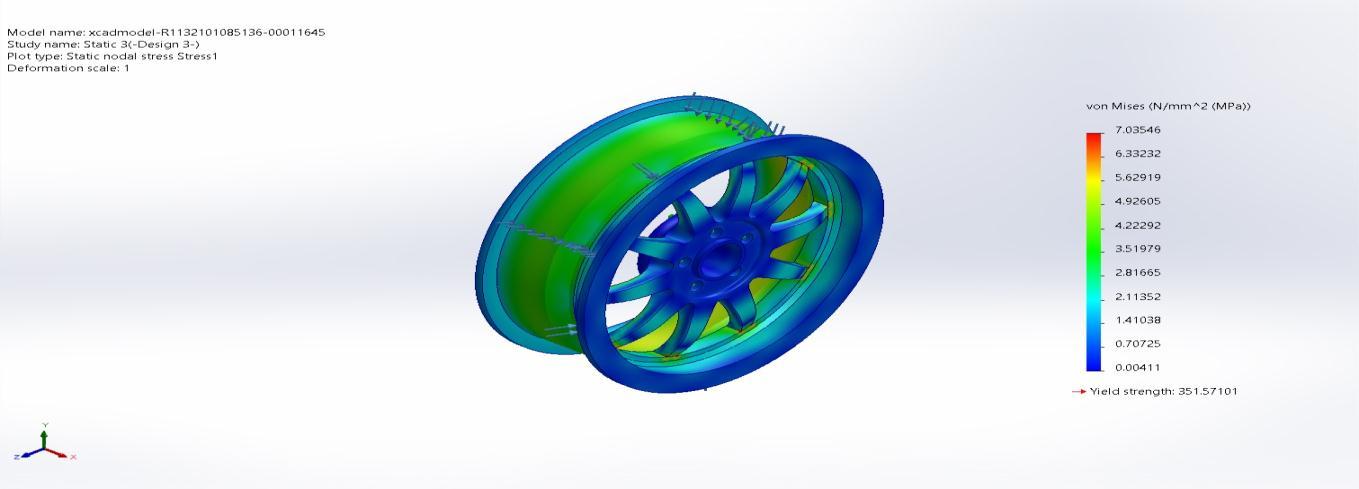
Name Type Min Max Stress1 VON:vonMisesStress 0.00411N/mm^2(MPa) Node:128719
7.03546N/mm^2(MPa) Node:125
xcadmodel R1132101085136 00011645 Static3 Stress Stress1
Figure 4.13 (c)Equivalent(von mises)stress(Design3)
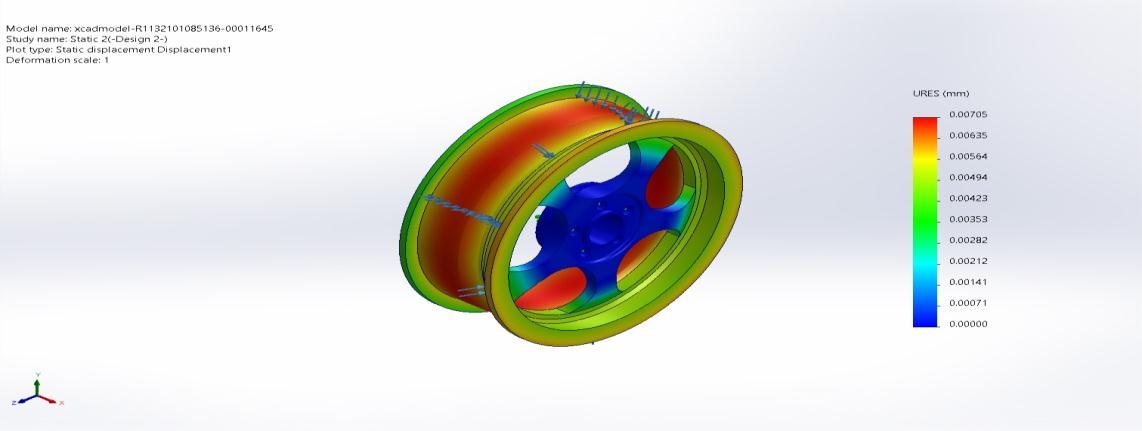
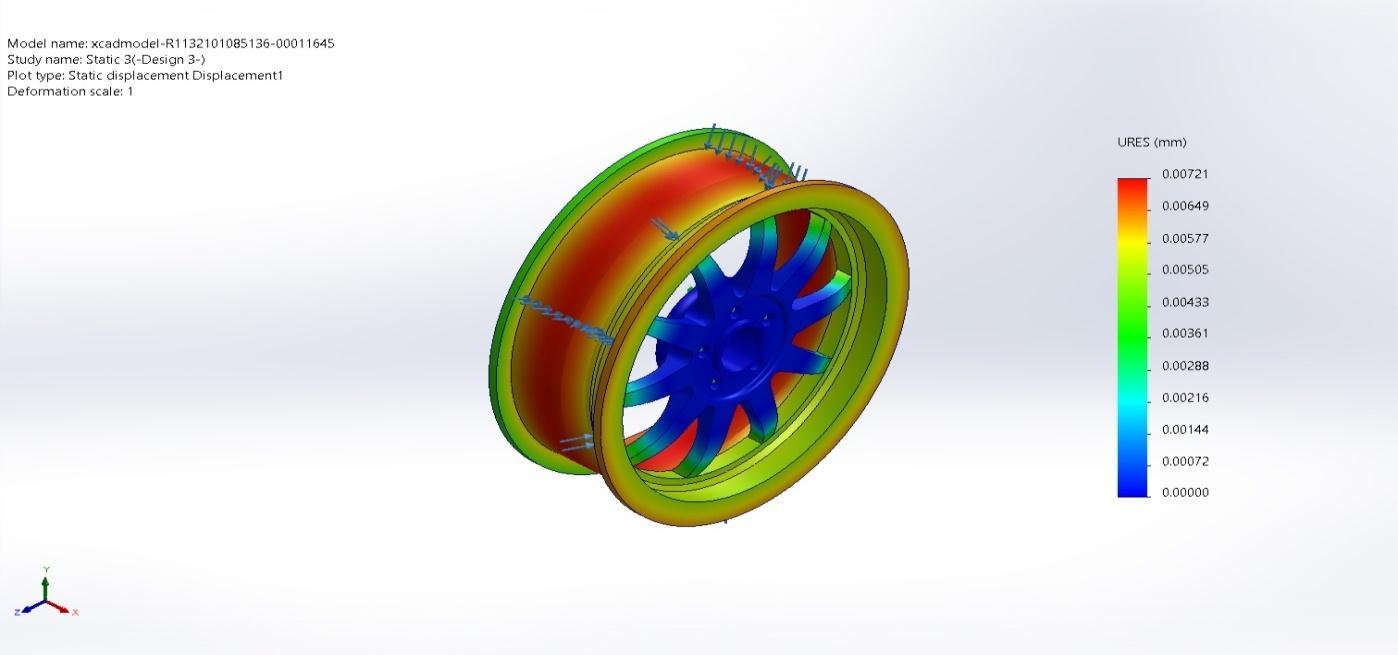
Name Type Min Max Displacement1 URES: ResultantDeformation 0.00000mmNode:135 0.00721mm Node: 98823
xcadmodel R1132101085136 00011645 Static3 Displacement Displacement1
Figure 4.14 (c)TotalDeformation(Design3)
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2812

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

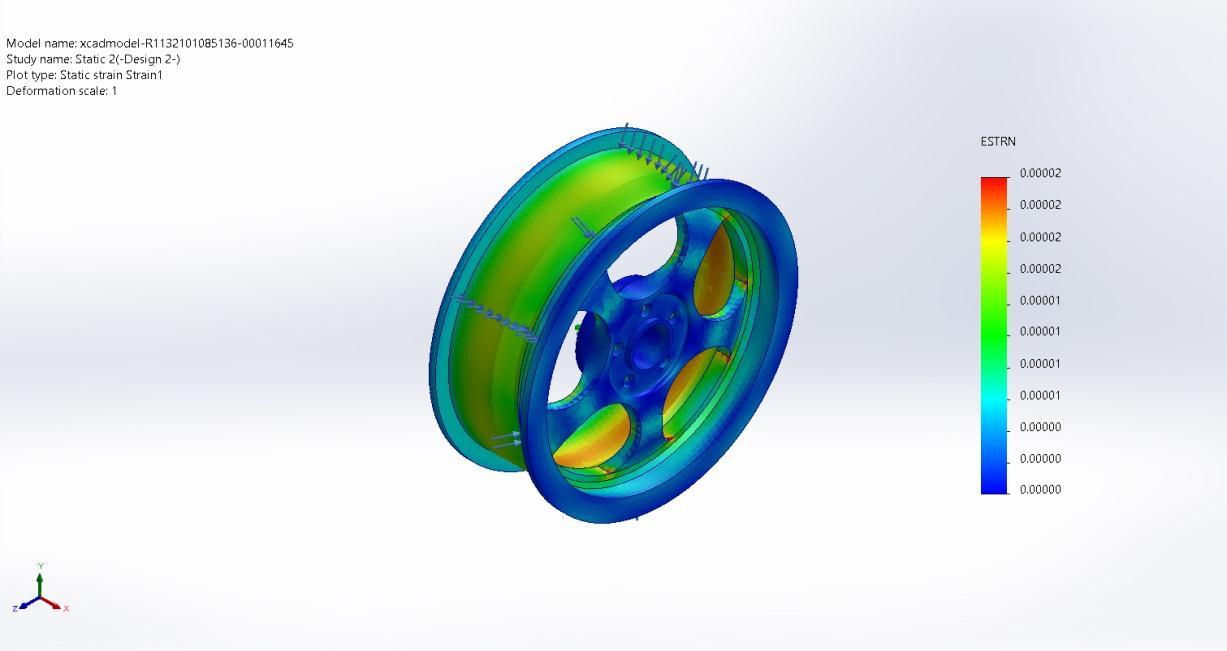
Name Type Min Max Strain1 ESTRN:EquivalentStrain 0.00000Element:79259 0.00002Element:63607
xcadmodel R1132101085136 00011645 Static3 Strain Strain1
Figure 4 .15(c)EquivalentStrain
Name Type Min Max
Factor of Safety1 Automatic 3.677e+00 Node:119
7.282e+04 Node:612715
xcadmodel R1132101085136 00011645 Static 3 Factor of Safety Factor of Safety1
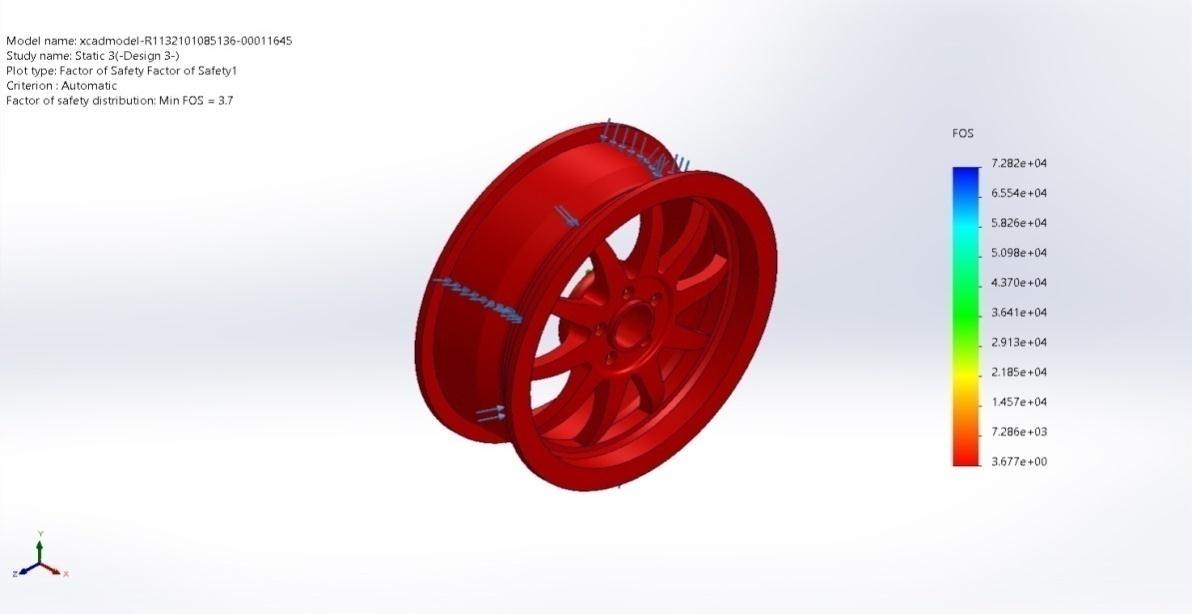
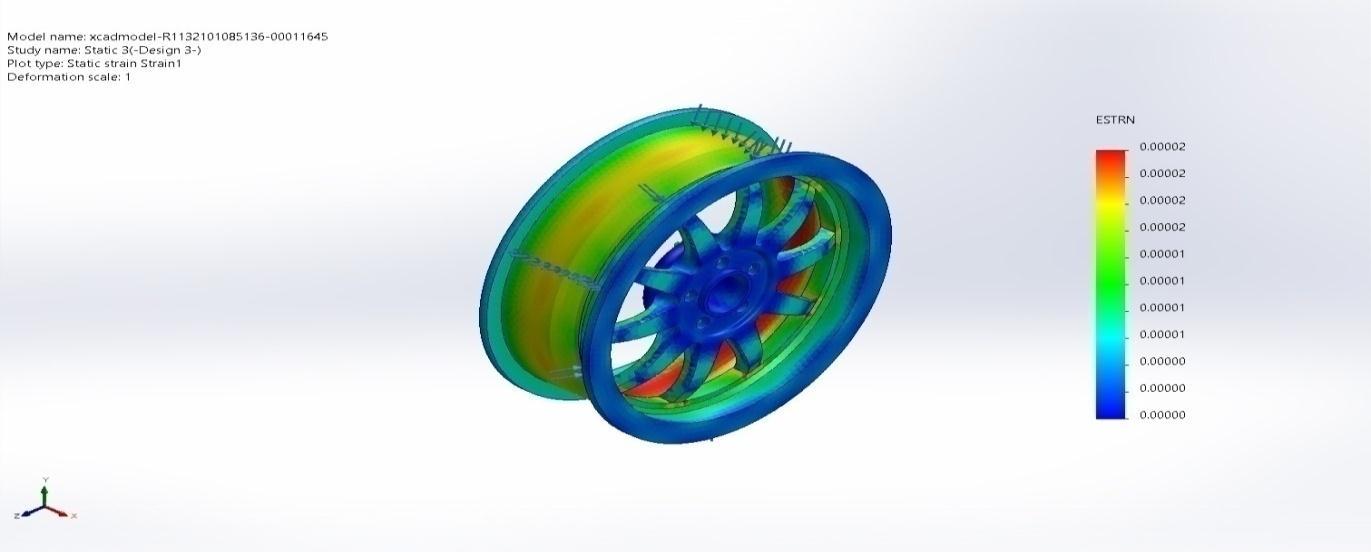
Figure 4.16 (c) FactorofSafetyDesign3 WheelDesign4
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Structural Steel Design 1 Design 2 Design 3 Design 4 Design 5 Design 6
Weight(Kg) 29.76 kilograms 26.95 kilograms 26.85 kilograms 26.23 kilograms 25.45kilograms 25.12 kilograms
Deformation(mm) 0.00762mm 0.00705mm 0.00721mm 0.00717mm 0.00831mm 0.00703mm Stress(MPa) 7.00276N/mm ^2 7.11443N/mm ^2 7.03546N/mm ^2 9.98752N/mm ^2 14.38969N/mm ^2 6.13956N/mm ^2
Factor of Safety Distribution >8 >8 >10 >10 >12 >15 Pressure(Mpa) 0.241317 0.241317 0.241317 0.241317 0.241317 0.241317
Mesh Element Size (mm) 8 8 8 8 8 8
1.Theweightofthewheelisreducedfrom29.76kilogram’sto25.12kilogram’swithoutcompromisinganyofthewheel's physicalpropertiesorperformance.
2.Amassreductionof4.64kgperwheelisachieved,bringingthetotalmassofthecarto27.84kgwhenthesparewheelis included. This mass reduction has the advantages of lowering the total weight of the car and lowering the cost of production.
3.Lessweightleadstoimprovedperformanceandfuelefficiency.Therearemanyindirectbenefitstotheseresults,suchas reducedairpollutionduetolowerfuelconsumption,savingcrudeoilmeanssavingnaturalresources,andsoon.
4. According to Ansys data, wheel design 6 is the most appropriate of the six models because it is lighter in weight (27.192kg) and has less deformation (0.00703mm), as well as the highest factor of safety (>15) and the least equivalent stress(6.13956Mpa)
1) Abijit Dani, P., Ghosh, A., Ajithkumar, G., Dua, A., Kannan, C., & Vijayakumar, T. (2019). Influence of Material and Spoke Pattern on the Performance of Automotive Wheels. Materials Today: Proceedings, 22, 1452 1459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.01.503
2) Arunkumar, S., Girimurugan, R., Vairavel, M., Deenadhayalan, M., Dhineshkumar, C., Sivaramakrishnan, N., & Santhoshsivam,S.(2020). Design and Material Optimization of an Automobile Wheel Rim by Finite Element Analysis 1* XII(Iv),1286 1300.
3) Bao, Y., & Zhao, X. (2017). Research of Lightweight Composite Automobile Wheel. World Journal of Engineering andTechnology, 05(04),675 683.https://doi.org/10.4236/wjet.2017.54056
4) Choudhary, V. S., Akram J, W., Yaseen S, M., & Saifudheen, M. (2016). Design and Analysis of Wheel Rim With Magnesium Alloys ( Zk60a ) By Using Solidworks and Finite Element Method. International Research Journal of AutomotiveTechnology, 1(3),16 29.
5) Dharani,V.,Mahalingam,S.,SanthoshKumar,A.,Scholar,P.G.,&Professor,A.(2014).ReviewonFatigueAnalysis ofAluminumAlloyWheelunderRadialLoadforPassengerCar. International Journal of Engineering Development andResearch, 3(1),2321 9939.www.ijedr.org
6) FiniteElementAnalysis ofAlloyWheel1,2,3.(2015). 2,544 550.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
7) Hafeezasif, A., Jayakumar, V., Kumar, D. S., Reddy, M., Sciences, T., & Nadu, T. (2018). A Review on Selection , Manufacturing and Testing of COMPOSITE MATERIALS FOR ALLOY WHEELS. International Journal of Pure and AppliedMathematics, 118(9),331 343.
8) Kancheti,N.,ReddyVemula,A.,ReddyGudibandla,G.,Krishna,H.,&BalaSubramanyam,P.N.V.(2019).Modeling and analysis of wheel rim using ansys. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 8(8),415 418.
9) Kumar, K. A. (2017). Analysis and Optimization of Material For KTM Motorcycle (Duke 390) Front Alloy Wheel. International Journal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology, 8(2), 113 130. https://doi.org/10.21172/ijiet.82.017
10) Kumar,R.A.,Amarnath,G.,&Raj,K.P.|S.K.|I.J.A.(2019).ExperimentalStudiesofOptimizationofAutomotive wheelRimusingANSYS. International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development, Volume 3(Issue 3), 311 316.https://doi.org/10.31142/ijtsrd22778
11) Loi, C. Y., & Choy, H. Y. (2019). Modelling and Fatigue Analysis of Automobile Wheel Rim 2019 5th International Conference on Control, Automation and Robotics, ICCAR 2019, 696 701. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCAR.2019.8813410
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
