International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072
1Master of Technology, Civil Engineering, Institute of Technology and Management, Lucknow, India
2Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Institute of Technology and Management, Lucknow, India
***
Abstract In this research paper, we have created four models of the stone column and it is used in the RC structure. Model 01 has a simple stone column in the medium soil type, Model 02 have also a simple stone column but is used in the Hard soil, Model 03 has a stone column with reinforcement in the medium soil type, and Model 04 have also a stone column with reinforcement but it is used in the hard soil. All four models are used in the RC frame structure with different soil properties, and these models will be analyzed with help of the ETABS software by using the Time history analysis, and code is used for the analysis of these models is Indian Standard Code 1893 part 01:2016. We will analyze the structure by taking some important seismic parameters such as base shear, natural period, storey drift, Column force, and displacement.
Key Words: StoneColumn,RCColumn,RCframestructure, SeismicBehaviour, DynamicAnalysis,Timehistoryanalysis, ETABS
Stonecolumnsareatypeofgroundimprovementtechnology thatusesanetworkofcompactedstonecolumnstostabilise thesoil.Stonecolumnsareusedtodecreasesettlementand increase load bearing capacity, as do other ground improvement procedures. The drainage ability of the granular material within the columns, which function as poreorwaterpressureevacuationsites,alsohelpstospeed upsoilconsolidation.Byenhancingshearstrengthinsidethe soil,stonecolumnsareparticularlyefficientinstrengthening slopestabilityandpreventingliquefaction.
Theseverticalinclusions,whichcanbeformedofstoneor sand,arelaidoutinagridpatternbeneaththestructurein thesoftsoils.Stonecolumns,alsoknownasaggregatepiers, are ideal for improving soft or loose soils because they generateverticalinclusionsthatarestiff,shearstrength,and drainwell.TheStoneColumnsboostbearingcapacitywhile alsoloweringtotalanddifferentialsettlements.

1. AggregateColumn 2. GranularPiles
3. VibroStoneColumn 4. RammedStoneColumn 5. CompactedStoneColumn
6. AggregatePiers
7. SandCompactionPiles
8. GeotextileEncasedColumns 9. GroutStoneColumns
Fortheanalysisofthesefourmodels,weusedsomemethods such as Dynamic Analysis, ETABS Software and Indian Standard code 1893 part 1:2016. Dynamic Analysis is a methodoftheanalysisofthestructurewhenthevariationof the load concerning the time is more, according to the IS code 1893 part 1: 2016, clause 7.7.3 dynamic analysis is classifiedsintotwotypes:
i. TimeHistoryMethod
ii. ResponseSpectrumMethod
Accordingtoclause7.7.4fromIScode1893part 1:2016,the timehistorymethodshallbebasedonappropriateground motionandshallbeperformedusingtheacceptedprinciple of earthquake structural dynamics. The data of the time historyistakenfrom“ELCENTRO”.Thetimehistorymethod comesunderthedynamicanalysiswherethevariationofthe lateralforceconcerningtimeismaximum,ifthevariationof thelateralforceconcerningthetimeislowthenweshould usethestaticanalysismethod.Etabssoftwareisdeveloped
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net
by the CSI company and is used for both analysis and designingofthestructure.
In this paper, there are four models in the first model (Model 01) Stone Column without reinforcement in RC framestructureinthemediumsoiltype,inthemodelsecond (Model 02) Stone Column without reinforcement in RC frame structure in the hard soil type, in the third model (Model 03)StoneColumnwithreinforcementinRCframe structureinthemediumsoiltype,andinthefourthmodel (Model 04)StoneColumnwithreinforcementinRCframe structureinthehardsoiltype.
Allparameters(material,buildingconfiguration,seismic)of thisStoneColumninRCframestructurewithandwithout reinforcementatdifferentsoiltypeinthebuildingisgiven belowindetail:
In this parameter, we give the details about the material whichisusedin StoneColumninRCframestructurewith and without reinforcement at different soil types and the materialparameterisgivenbelowinthetable:
Table 1: MaterialParameter.
S. No Material Grade
Concrete M30&M25
1.0
2.0
3.0
LongitudinalBar Fe415
Stone
In this parameter, we provide the information about structure parameter such as size of beam, size of column, andslabisgivenbelowintable:
Table 2: BuildingParameter
S.No Building Parameter Value
01. Beam 240mm*360mm
02. Column 230mm*360mm
03. Slab 160mm
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072
SpanofBeam 3.25m 05. Heightofbuilding 39m 06. Floorheight 3m 07. Groundstorey 3m
04.
Inthisfactor,weweregiventhefactoroftheseismicwhere the model is assumed to construct such as seismic zone factor,Importancefactor,etc
Table 3: SeismicParameter
S.No Seismic Parameter Value
01. SeismicZoneFactor(Z) 0.24(Forth Zone)
02. ResponseReductionFactor (R) 5 03. Importancefactor(I) 1.2 04. Soiltype 2nd or3rd 05. Eccentricratio 5%
TheloadwhichisactingonthemodelsuchasImposedload isgiveninthetable:
Table 4: LoadParameter
S.No Load Parameter Value
01. Liveload 3.0KN/m2
02. Deadload Automaticthrough software
03. Loaddistributionwall 14.0KN/m
Inthedetailsviewofthemodels,wewillseethedetailsplan, elevation,three dimensionalview,andcrossofeverystone column.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net
The plan, elevation and three dimensional view of the model 01(where)aregivenbelow:
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072
Theplan,elevationandthree dimensionalviewofmodel 02 arethesameasmodel 01.
The plan, elevation and three dimensional view of the model 03aresameasmodel 01,butthecross sectionofthe columnisdifferentwhicharegivenbelow:
The plan, elevation and three dimensional view of the model 04aresameasmodel 01,butthecross sectionofthe columnisalsothesameasmodel 03:
After analyzing all these four model, there are following result come out and we have taken some parameter to comparethevalueofthesethreemodels,suchparameteris thestoreydrift,baseshear,storeyoverturningmoment,and maximumstoreydisplacement.
AccordingtotheIndianstandardcode1893part 1:2016,the baseshearisdefinedasthelateralforceateverystoreydue toseismicforce.Thegraphofthebaseshearofeverymodel isgivenbelow:
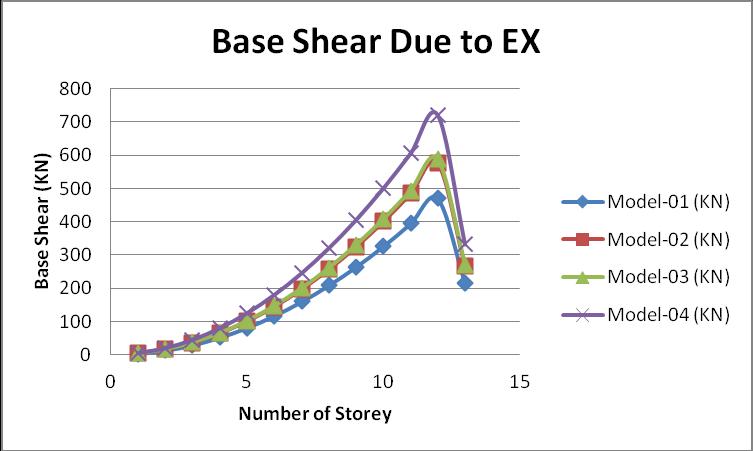
Fromtheabovegraph,themaximumvalueofthebaseshear isactinginmodel 04ascomparedtotheotherthreemodels.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
Page3666
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net
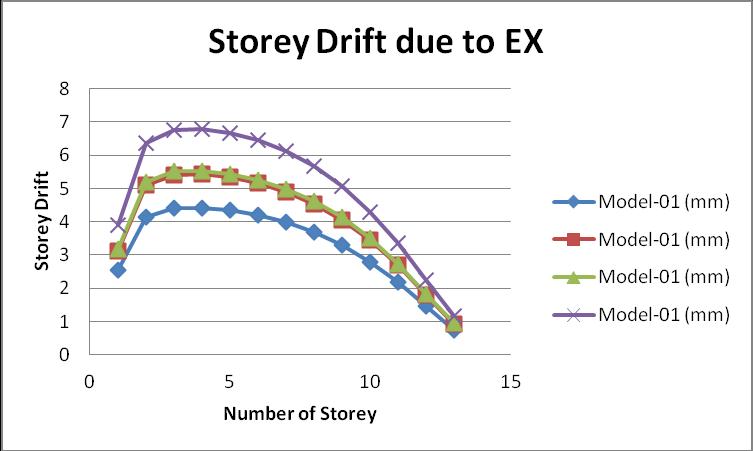
AccordingtotheIndianStandardCode1893part 01:2016, the storey drift is defined as the relative displacement betweentwofloorswhichmaybetheupperorlowerfloor. The maximum value of the storey drift should not exceed 0.004h,wherehistheheightbetweenfloors.Thegraphof thestoreydriftisgivenbelowattheloadcaseEX:
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072
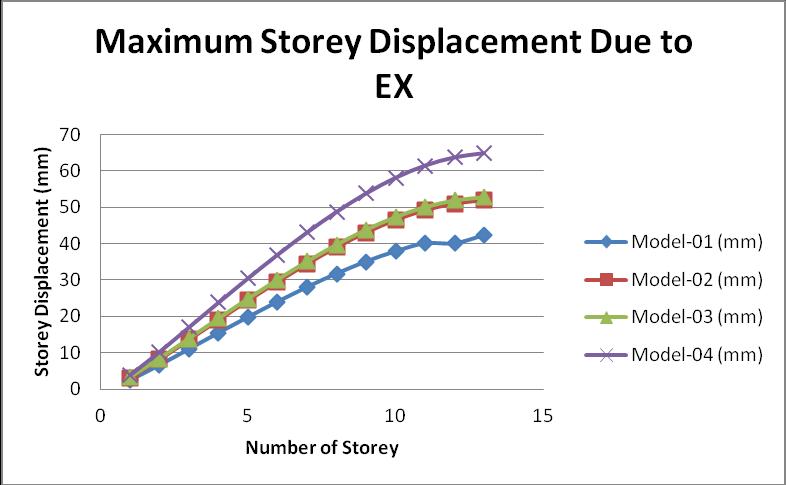
AccordingtotheIndianStandardCode,storeydisplacement isdefinedasthedisplacementoftheupperorlowerstorey concerninganotherstoreyduetoseismicforce.Iftheheight oftheflooris3m,thenthemaximumdisplacementshould not be greater than 12mm. The graph of the storey displacementofallmodelsatloadcaseEXisgivenbelow:
Themaximumvalueofthestoreydriftisactinginmodel 04 ascomparedtotheotherthreemodels.
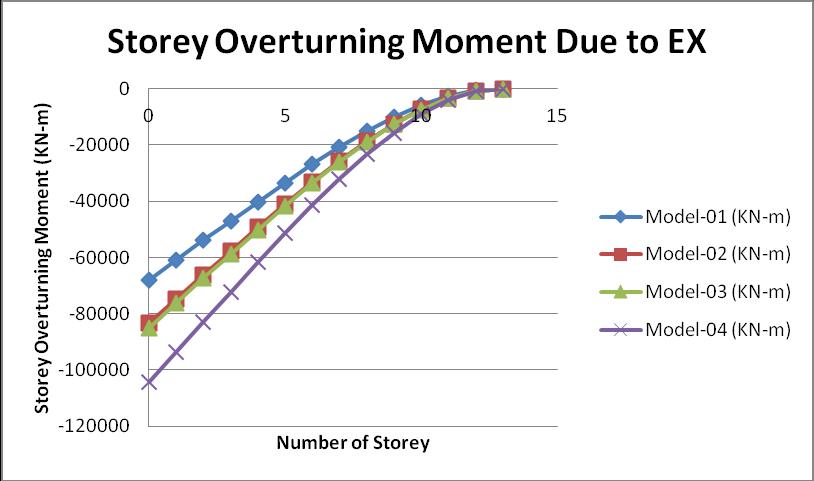
AccordingtotheIndianstandardcode1893 part01:2016, the storey overturning moment is defined as the moment generatedateachstoreyofthebuildingduetotheeffectof seismic force. At the top storey, the value of the storey overturningmomentalwayszeros.
Fromtheabovegraphofthestoreydisplacement,wefound that maximum displacement occurs in model 04 as comparedtotheotherthreemodels.
AfteranalysingallthesemodelswiththehelpoftheETABS softwarebyusingTimehistoryanalysis,andIScode1893 part 01:2016,wefoundsomeresultswhicharegivenbelow:
Thevalueofthebaseshearismaximuminmodel 04where thereinforcementprovided inthestonecolumninthe RC framebuildingatthehardsoil,whichisapproximate19% higherthanmodel 03,20%higherthanmodel 02,and35% approximately higher than model 01. The stability of the resistingthelateralforceduetoseismiceffectinthebuilding isinthemodel 04.
Fromtheabovegraphofthestoreyoverturningmoment,the maximumvalueofthestoreyoverturningmomentactingin model 04ascomparedtotheotherthreemodels.
AccordingtotheIndianStandardcode1893part 01:2016, thevalueofthestoreydriftshouldnotexceed0.004h,where “h”relativeheightbetweentwofloors.Inthisresearchwork, taketheheightofeveryflooris3m,sostoreydriftshouldnot exceed12mmrelativebetweentwofloors.Allvalueofthe storeydriftislessthan12mmsowecansaythatallmodels are in the safe condition, but the maximum value of the storeydriftexistsinthemodel 04wherethereinforcement providedinthestonecolumnintheRCframebuildingatthe hardsoil,thatis6.782mm.
AccordingtotheIndianStandardcode1893part 01:2016, thevalueofthemaximumstoreydisplacementshouldnotbe exceedingthanH/250,where“H”isthetotalheightofthe
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3667
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net
building.Inthisresearchwork,takethetotalheightofthe building is 39m, so the maximum storey displacement shouldnotexceed156mmfromthegroundtothetopfloor. Thevalueofthemaximumstoreydisplacementislessthan 156 mm so we can say that all models are in the safe condition, but the maximum value of maximum storey displacement exists in the model 04 where the reinforcementprovidedinthestonecolumnintheRCframe buildingatthehardsoil,thatis64.845mmatthetopfloor.
[1] Ahmet Yakut (2003) “REINFORCEDCONCRETEFRAME CONSTRUCTION”1AppliedTechnologyCouncil(ATC),1996. Seismic Evaluation and Retrofit of Concrete Buildings. Vol.1, ReportNo.SSC96 01,(ATC 40).
[2]Kimetal(2012)“SiteResponseandShearBehaviorof Stone Column Improved Ground under Seismic Loading” WCEE 12.
[3] Davide Forcellini1 and AngeloMarcello Tarantino2 (2014) “Assessment of Stone Columns as a Mitigation Technique of Liquefaction Induced Effects during Italian Earthquakes” Hindawi Publishing Corporation Scientific World Journal Volume 2014, Article ID 216278, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/216278
[4] C. Cengiz, E. Güler (2018) “Seismic behaviour of geosyntheticencasedcolumnsandordinarystonecolumns” GeotextilesandGeomembranes46(2018)40 51
[5] Su Won Son, Pouyan Bagheri and Jin Man Kim * “Dynamic Behavior of Ground Improved Using a Crushed Stone Foundation Wall” Sustainability 2019, 11, 2767; doi:10.3390/su11102767
[6] Alexander et al (2019) “A case study of stone column ground improvement performance during a sequence of seismic events” Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering for Protection and Development of Environment and Constructions Silvestri&Moraci(Eds)
[7]ISafkan,SDerogar,andJAnywar(2020)“Theeffectof stonecolumnareareplacementratioonseismicbehaviourof foundation” IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering 800 (2020) 012041 IOP Publishing doi:10.1088/1757 899X/800/1/012041
[8] S. D. Futane, A. I. Dhatrak, S. W. Thakare (2020) “Assessment of Group of Stone Column under Seismic Condition” International Journal of Engineering and AdvancedTechnology(IJEAT)ISSN:2249 8958(Online), Volume 9Issue 4,April2020
[9] Elsiragy,M.N.(2021)“Utilizationofstonecolumnfor improvingtheseismicresponseoffoundationonsoftclay Numerical study” Journal of Petroleum and Mining Engineering 23(1)2021 DOI: 10.21608/jpme.2021.58911.1069
[10]AdityaKumarTiwary1,SandeepSingh1,Jasgurpreet Singh Chohan 2, Raman Kumar 2, Shubham Sharma 3,*, Somnath Chattopadhyaya 4, Farid Abed 5 and Mislav Stepinac 6,* (2022) “Behavior of RC Beam Column Joints Strengthened with Modified Reinforcement Techniques”
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072
Sustainability 2022, 14, 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031918
[11] Myeong Ho Choi 1 and Chang Hwan Lee 2,* (2022) “SeismicBehaviorofExistingReinforcedConcreteColumns withNon SeismicDetailsunderLowAxialLoads”Materials 2022,15,1239.https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031239
[12] Alexiew, D., Brokemper D. and Lothspeich S. (2005), “GeotextileEncasedColumns(GEC):Loadcapacity,geotextile selection, and pre designed graphs”, Geotechnical Special Publication, No. 130 142. Geo Frontiers,pp.497 510.
[13] Ali,K.,Shahu,J.T.,Sharma,K.G.(2012),Performance of Geosynthetic Reinforced Stone Columns,ProceedingsofIndianGeotechnicalConferenceDec13 15, 2012, Delhi,396 399.
[15] Ambily,A.P.andGandhi,S.R.(2006),EffectofSandPad ThicknessOnLoadSharingInStoneColumn, Proceedings of Indian Geotechnical Conference Dec14 16,2006, Delhi,555 556.[16]Ambily,A.P.,andGandhi,S.R.(2007),Behaviourof Stone Columns Based on Experimental and FEM Analysis, Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, ASCE/APRIL2007,405 415.
[17]Ayothiraman,R.andSoumya,S.(2011),Useofshredded tire chips as aggregates in the stone column: An experimental study, Proceedings of IGC December 15 17, 2011, Kochi,711 714.
[18]Beena,K.S.,andShukoor,T.P.A.(2012),Useoflocally availablematerialsinthestonecolumn, Proceedings of IGC December 13 15, 2012, Delhi,592 595.
[19] Castro, J. and Sagaseta, C. (2011), Deformation and consolidationaroundencasedstonecolumns, Geotextiles and Geomembranes,vol.29,268 276.
[20]Dutta,S.andMandal,J.N.(2012),Behaviorofsoftsoil reinforcedwithencasedstonecolumns, Proceedings of IGC December 13 15, 2012, Delhi,420 423.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified