International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072
1MTech Student, Computer Science and Engineering, APJ Abdul Kalam Technological University, Kerala, India
2, 3Asst. Professor, Computer Science and Engineering, Mount Zion College of Engineering, Kadammanitta, Kerala, India
***
Abstract Currently, the detection of coronavirus disease (COVID 19) is one of the main challenges in the world, given the rapid spread of the disease. Recent statistics indicate that the number of people diagnosed with COVID 19 pandemic is increasing exponentially, withmorethan1.6millionconfirmed cases. The disease is spreading to many countries across the world. In this study, we analyses the incidence of COVID 19 distribution across the world. Machine learning is an innovative approach that has extensive applications in prediction. This technique needs to be applied for the COVID 19 pandemic to identify patients at high risk, their death rate, and other abnormalities. It can be used to understand the nature of this virus and further predict the upcoming issues
Key Words: COVID 19, Pandemic, Machine Learning, Convolutional Neural Network, Kaggle database
COVID 19isaglobalhealthcrisis,withmorethan51crore people infected and more than 63 lakhs deaths reported worldwide.Theresultingimpactonhealthcaresystemsis thatmanycountrieshaveoverstretchedtheirresourcesto mitigate the spread of the pandemic. In addition, a high degree of variance in COVID 19 symptoms has been reported, with symptomsrangingfroma mildflutoacute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or fulminant pneumonia.Thereisanurgentneedforeffectivedrugsand vaccinesforCOVID 19treatmentandprevention.Owingto the lack of validated therapeutics, most containment measurestocurtailthespreadofthediseaserelyonsocial distancing,quarantinemeasures,andlockdownpolicies.The transmission of COVID 19 has been slowed as a result of thesemeasures,butnoteliminated.
Moreover,withtheeaseofrestrictions,afearofthesecond waveofinfectionisprevalent.Topreventthenextpotential outbreak of COVID 19, there is a need for advanced containment measures such as contact tracing and identificationofhotspots.
Machine learning techniques have been employed in the health care domain on different scales ranging from the predictionofdiseasespreadtrajectorytothedevelopmentof diagnosticandprognosticmodels.
Impact Factor value: 7.529
AstudybyYeetalidentifiedandevaluatedvarioushealth technologies, such as big data, cloud computing, mobile health,andAI,tofightthepandemic.Thesetechnologiesand awiderangeofdatatypes,includingdatafromsocialmedia, radiologicalimages,omics,drugdatabases,andpublichealth agencies, have been used for disease prediction. Several studieshavefocusedonreviewingpublicationsthatdiscuss AIapplicationstosupporttheCOVID 19response.Oneofthe earlystudiesbyVaishyaetalidentified7criticalareaswhere AI can be applied to monitor and control the COVID 19 pandemic.However,giventhatthiswasanearlywork,this reviewlackedpublicationsinallthe7areas.Inalaterstudy, Lalmuanawmaetalbuiltuponthese7areasbyidentifying andperformingarapidreviewofthethenavailablestudies; however,consideringthiswasarapidreview,onlylimited studieswereincluded,andthequalificationcriteriawerenot clear. Furthermore, a study by Shi et al focused on AI applicationstoradiologicalimages,andastudybyWynants et al focused on critical appraisal of models that aimed to predict the risk of developing the disease, hospital admission, and disease progression. Nevertheless, the majority of epidemiological studies that aimed to model disease transmission or fatality rate, among other factors, wereexcludedinthisstudy.
Machine learning is an innovative approach that has extensiveapplicationsinprediction.Thistechniqueneedsto beappliedfortheCOVID 19pandemictoidentifypatientsat highrisk,theirdeathrate,andotherabnormalities.Itcanbe used to understand the nature of this virus and further predicttheupcomingissues.Thisliterature basedreviewis donebysearchingtherelevantpapersonmachinelearning for COVID 19 from the databases of SCOPUS, Academia, Google Scholar, PubMed, and ResearchGate. This research attemptstodiscussthesignificanceofmachinelearningin resolvingtheCOVID 19pandemiccrisis.Thispaperstudied how machine learning algorithms and methods can be employedtofighttheCOVID 19virusandthepandemic.It further discusses the primary machine learning methods thatarehelpfulduringtheCOVID 19pandemic.
Wefurtheridentifiedanddiscussedalgorithmsused inmachinelearningandtheirsignificantapplications. Machine learning is a useful technique, and this can be witnessed in various areas to identify the existing drugs, whichalsoseemsadvantageousforthetreatmentofCOVID
9001:2008
Chithra S. Prasad1 , Reshma Suku2 , Smitha C. Thomas3
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net
19 patients. This learning algorithm creates interferences out of unlabeled input datasets, which can be applied to analyzetheunlabeleddataasaninputresourceforCOVID 19. It provides accurate and useful features rather than a traditionalexplicitlycalculation basedmethod.Further,this technique is beneficial to predict the risk in healthcare duringthisCOVID 19crisis.Machinelearningalsoanalyses the risk factors as per age, social habits, location, and climates
The primary aim of this study was to conduct a comprehensivesystematicliteraturereviewontheroleofAI asatechnologytocombattheCOVID 19crisisandtoassess itsapplicationintheepidemiological,clinical,andmolecular advancements.Specifically,wesummarizedtheareasofAI application,datatypesused,typesofAImethodsemployed and their performance, scientific findings, and challenges experiencedinadoptingthistechnology.
Sincethelastdecade,digitaltechnologiesareplayingcritical roles in major health sector problems including disease prevention, the present worldwidehealthemergencyalso seeking technological support to tackle COVID 2019.The analysisanddetectionofCOVID 19havebeenextensively investigated in the last few months. The first part of this section addresses issues related to COVID 19 detection basedondeep learningapproachesusingCTscansandchest X rayimages.Thesecondpartreviewstherelatedliteratures to assess future estimates of the number of COVID 19 confirmations, recoveries, and deaths. COVID 19 has now become a global pandemic owing to its rapid spread. It is verychallengingtodetectexposedpersonsbecausetheydo notshowdiseasesymptomsimmediately. Thus, it is necessary to find a method of estimating the numberofpotentiallyinfectedpersonsonaregularbasisto adopttheappropriatemeasures.AIcanbeusedtoexaminea personforCOVID 19asan alternativeto traditional time consuming and expensive methods. Although there are severalstudiesonCOVID 19,thisstudyfocusedontheuseof
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072
AIinforecastingCOVID 19casesanddiagnosingpatientsfor COVID 19infectionthroughchestX rayimages.
One of the main advantages of AI is that it can be implementedinatrainedmodeltoclassifyunseenimages.In thisstudy,AIwasimplementedtodetectwhetherapatient ispositiveforCOVID 19usingtheirchestX rayimage.
The use of machine learning (ML) has been rapidly increasing in various fields including malware detection, mobile malware detection, medicine and information retrieval. A modern ML system called deep learning was introduced, which is based on a convolutional neural network (CNN). It won the ImageNet classification competition, the world’s best known computer vision competition.Deep learningalgorithmsenablecomputational modelscomposedofmultipleprocessinglayerstolearndata representation through several abstraction layers. They train a computer model to perform classification tasks directlyfrompictures,texts,orsounds.AccordingtoLeCun etal.,deep learningmodelsfeaturehighaccuraciesandcan improve human output in certain instances. Artificial intelligenceapproacheshaverepeatedlygivenaccurateand dependableoutcomesinapplicationsthatuseimage based data.Usingdeeplearningtechniques,researchershavebeen investigating and analyzing chest X ray images to identify COVID 19inrecentyears.
Theimageswerenormalizedtoextractenhancedfeatures, which were then fed into image classification algorithms utilizing deep learning techniques. Five cutting edge CNN systems, VGG19, MobileNetV2, Inception, Exception, and InceptionResNetV2, on a transfer learning scenario, were tested to detect COVID 19 from control and pneumonia images.Experimentswereconductedintwoparts:onewith 224 COVID 19 pictures, 700 bacterial pneumonia images, and504controlimages,andanotherwiththepriornormal andCOVID 19databut714instancesofbacterialandviral pneumonia.Inthetwo andthree classclassifications,the MobileNetV2nethadthegreatestresults,with96.78%and 94.72% accuracy, respectively. Both VGG16 CNN and Resnet50,whichweretrainedoncolorcameraimagesfrom ImageNet,wereutilizedtoperformtransferlearning.
ToassessthefeasibilityofutilizingchestX raysto diagnoseCOVID 19,10 foldcross validationwasperformed toobtainanoverallaccuracyof89.2%.
Three CNN architectures (ResNet50, InceptionV3, and InceptionRes NetV2)wereevaluatedinrelationtoCOVID 19 identificationinutilizingadatabaseofjust50controlsand 50COVID 19cases.ResNet50achievedthehighestaccuracy of98%.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008
Volume:
Inasuccessfulperformanceindiagnosisaccuracyfoundin thisresearchdemonstratesthatdeepCNNscouldcorrectly and efficiently distinguish 21,152 normal and abnormal chestradiographs.TheCNNmodelpre trainedondatasetsof adultpatientsandfine tunedonpediatricpatientsobtained an accuracy of 94.64%, a sensitivity of 96.5% and a specificity of 92.86% for normal versus pneumonia categorization. TheproposedmodelinwasbasedonanX rayimagedatasetandshowsthatCOVID CAPSoutperforms priorCNN basedmodels.COVID CAPSattainedanaccuracy of 95.7%, a sensitivity of 90%, and a specificity of 95.8% despite having a much lower number of trainable parametersthanothermodels.From400chestX rayimages, individualswithCOVID 19symptomswereidentifiedusing eight different deep learning techniques: VGG16, InceptionResNetV2, ResNet50, DenseNet201, VGG19, MobilenetV2, NasNet Mobile, and ResNet15V2. NasNet Mobile beat all other models in chest X ray datasets, attaininganaccuracyof93.94%.
The authors utilized a database of 127 COVID 19, 500 controls,and500pneumoniapatientscollectedfromvarious sources for the binary classification of COVID 19 and controls,aswellasthemulticlassclassificationofCOVID 19, controls,andpneumonia.TheDarknetmodelwasmodified fortransfer learningandfive foldcross validation,yielding 98%accuracyinbinaryclassificationand87%accuracyin multiclassclassification.
MachineLearningisthescienceoftrainingmachinesusing mathematicalmodelstolearnandanalyzedata.OnceMLis implemented in a system, the data are analyzed, and interestingpatternsaredetected. The validation data are thencategorizedaccording tothe patternslearnedduringthelearningprocess.AsCOVID 19 infection has rapidly spread worldwide and international action is required, it is important to develop a strategy to estimate the number of potentially infected people on a regularbasistoadopttheappropriatemeasures.Currently, decision makersrelyoncertaindecision makingstatistics suchasimposinglockdownsoninfectedcitiesorcountries.
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072
Therefore,MLcanbeusedtopredictthebehaviorsofnew casestostopthediseasefromspreading.Lietal.developeda predictionmodelusingMLalgorithmstocombatCOVID 19 in mainland China and in other infected countries in the world. The authors developed a model to estimate the numberofreportedcasesanddeathsinmainlandChinaand in the world. The data used to build the models were collectedbetween20January2020and1March2021.The authorsalsostatedthatCOVID 19wouldbecontrolledatthe beginningofApril2020inmainlandChinaandinmid June 2020acrosstheworld.Theyconcludedthattheestimated numberofCOVID 19caseswouldbeapproximately89,000 inChinaand403,000worldwideduringtheoutbreak.Asof 17April2021,theestimatednumberofdeathswas4000in mainlandChinaand18,300worldwide.Itisclearthattheir forecastwassimilartotheactualsituationinChinaasthe total numbers of infected cases and deaths had exceeded 82,367and3342,respectively.
Our proposed deep learning based COVID 19 detection comprisesseveralphases,asillustratedinthebelowFigure.
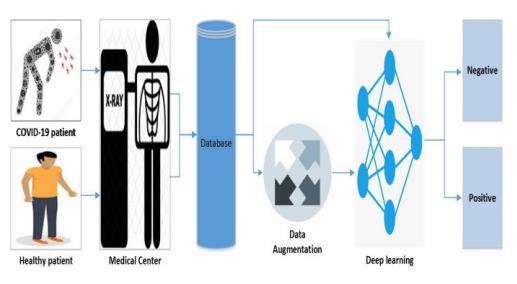
Thephasesaresummarizedinthefollowingfivesteps:
Step1:CollectthechestX rayimagesforthedatasetfrom COVID 19patientsandhealthypersons.

Step 2: Generate 1000 chest X ray images using data augmentation.
Step3:Representtheimagesina featurespaceandapply deeplearning.
Step4:Splitthedatasetinto twosets:a trainingsetand a validationset.
Step 5: Evaluate the performance of the detector on the validationdataset
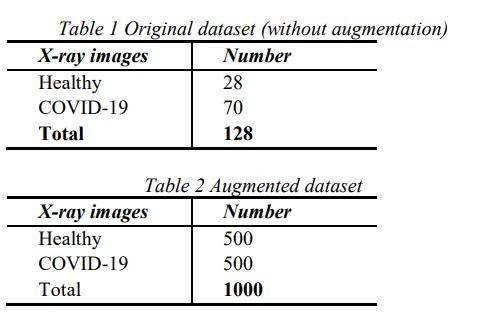
Two types of datasets were used in the evaluation, the originaldataset(withoutaugmentation)andtheaugmented dataset, which are summarized in Tables. The dataset contained the following: a) a healthy dataset containing chest X ray images of healthy persons and b) a COVID 19
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net
datasetcontainingchestX rayimagesofCOVID 19patients. TheoriginaldatasetwasobtainedfromtheKaggledatabase. wegeneratedourdatasetusingdataaugmentation.
DataaugmentationisanAImethodforincreasing the size and the diversity of labelled training sets by generatingdifferentiterationsofthesamplesina dataset. Data augmentation methods are commonly used in ML to addressclassimbalanceproblems,reduceoverfittingindeep learning, and improve convergence, which ultimately contributestobetterresults.Thetotalnumberofimagesin the dataset became 1000 after applying augmentation, as presentedinTable.
A computer with Microsoft Windows 10 was used for the experiment.Ithasthefollowingspecifications:IntelCorei7 8565U1.80 GHzprocessor,16GBofDDR4RAM,and1TBof hard disk. We installed the virtual machine tool VMware WorkstationProversion14.1.8build 14921873onit. Then, we installed Ubuntu 18.04.4 (64 bit) on the virtual machineandthefollowinglibrariesandsoftware:
Python
NumPy
ARMIA
ImageDataGenerator
Fbprophet
Matplotlib
KERAS
LSTM
Pandas
Alltheresultsandpredictionsmadeinthisstudyhavebeen uploadedtotheKaggledatabase.Webelievethatbymaking the system and solution publicly available, we draw attentiontothemostaffectedareas,therebypreventingthe spread of the COVID 19 outbreak and fostering the use of deep learningtechniquesinCOVID 19research.
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072
Duringthetimesofpandemics,fasterdiagnosisplaysakey roleintheresponseeffortstocontainthediseaseaswellas reducingitsspread.Computer aideddetectionwouldsave time and increase the quality of diagnosis in comparison withmanualhumandiagnosis.
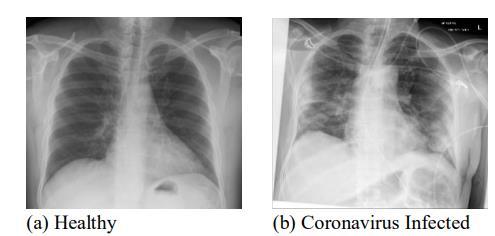
This study developed a CNN based COVID 19 detectionmodelthatwastestedwithboththeoriginaland the augmented datasets. All the chest X ray images used were resized to 224×224 pixels while ignoring the aspect ratio.Figures14a andbpresentthechestX rayimagesof healthy and COVID 19 infected patients, respectively. The collected dataset was randomly split into a training data subsetandatestingdatasubset.TheCOVID 19detectorwas trained and tested on the collected dataset, 80% of which wasusedfortrainingandtheremaining20%wasusedfor testing.TheweightsoftheCNNwererandomlyinitialized, andthebatchsizewasvariedupto25andempiricallysetto 25toavoid overfitting andtoachieve thehighest training accuracy.
Basedonthestudyresults,thefollowingresultsweredrawn:
PA delivered the best performance for COVID 19 prediction over 7 days, compared to LSTM and ARIMA.
Thepredictionswillenablepeopleinbothcountries to predict their medical needs for tackling the spreadofCOVID 19.
ARIMAcannotmakepredictionsoverthenext 1,2,and3days.
After investigating the number of COVID 19 confirmations, recoveries, and deaths in various countries, we found that coastal areas are significantlyimpactedbythedisease.
TheuseofchestX rayimagesisrecommendedfor diagnosing COVID 19 because X rays are easily obtainedatnearbyhospitalsorclinicsfairlyquickly andatlowcosts.
Our CNN based COVID 19 detector delivered superiorperformanceintermsofprecision,recall, andF measure.
The application of ML techniques for COVID 19 diagnosisusingourCNN basedCOVID 19detector isrecommended.
OurCOVID 19detectorobtainedbetterresultswhenusing augmentation.Abettertrainingprocesswasachievedasthe gapbetweenthetrainingandvalidationbecamesmaller.
The world is under the grasp of COVID 19 virus. Early prediction of the transmission can help to take necessary actions.Thisarticleproposedtoutilizethemachinelearning anddeeplearningmodelsforepidemic.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net
Future prediction of potential infections will enable authorities to tackle the consequences effectively. Furthermore,itisnecessarytokeepupwiththenumberof infectedpeoplebyperformingregularcheck ups,anditis oftenvitaltoquarantineinfectedpeopleandadoptmedical measures
Prediction models such as the PA, ARIMA, and LSTM algorithms were used to predict the number of COVID 19 confirmations,recoveries,anddeathsoverthenext7days. PA delivered the best performance and a diagnosis model usingVGG16wasproposedtodetectCOVID 19usingchest X ray images. The model allows the rapid and reliable detectionofCOVID 19,enablingittoachieveanF measure of99%usinganaugmented dataset.Ina future study, we willconsiderdiagnosingCOVID 19inchestCTscanimages usingtheVGG XXversionsandcomparetheirperformances usinglargerdatasets.
A further contribution of this study is the analysis of the COVID 19spreadanditsrelatedstatisticaldatabasedonits global regional distributions. Thus, two main conclusions weredrawnusingourAI basedanalysis:(i)themosthighly infected areas have similar characteristics, and (ii) the spreadofthediseaseincoastalareasissignificantlyhigher thanthatinothernon coastal areas.Therefore,extra care andattentionshouldbegiventocoastalcities.Inourfuture work, we will investigate the effects of temperature, humidity,andterrainontheCOVID 19spreadincitiesand countries.
[1] Wang L, Wong A (2020) COVID Net: a tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID 19casesfromchestradiographyimages.
[2] Beck BR, Shin B, Choi Y, Park S, Kang K. Predicting commerciallyavailableantiviraldrugsthatmayacton the novel coronavirus (SARS CoV 2) through a drug targetinteractiondeeplearningmodel
[3] Cohenetal(2020)COVID 19imagedatacollection
[4] Ting,DanielShuWei,LawrenceCarin,VictorDzau,and TienY.Wong.“DigitaltechnologyandCOVID 19.”
[5] AbedMH,Al RammahiAHI,RadifMJ(2019)Real time color image classification based on deep learning network
[6] Deb,Soudeep,andManidipaMajumdar.“Atimeseries method to analyze incidence pattern and estimate reproduction number of COVID 19.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.10655(2020).
[7] Jia, L., Li, K., Jiang, Y., Guo, X. (2020). Prediction and analysis of Coronavirus Disease 2019. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.05447.
[8] Sujath R, Chatterjee JM, Hassanien AE. A machine learning forecasting model for COVID 19 pandemic in India. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess. 2020 May 30;34(7):959 972.doi:10.1007/s00477 020 01827 8
e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072
[9] CohenJP,BertinP,ChesterVF,Awebdeliveredlocally computedchestx raydiseasepredictionsystem.
[10] Ivanov,D.Predictingtheimpactsofepidemicoutbreaks onglobalsupplychains:Asimulation basedanalysison thecoronavirusoutbreak(COVID 19/SARS CoV 2)case. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp.Rev. 2020, 136, doi:10.1016/j.tre.2020.101922.
[11] Fu L, Li Y, Cheng A, Pang P, Shu Z. a novel machine learning derivedradiomicsignatureofthewholelung differentiates stable from progressive COVID 19 infection:aretrospectivecohortstudy.JThoracImaging. 2020Jun16;doi:10.1097/RTI.0000000000000544
[12] HickJL,HanflingD,WyniaMK,PaviaAT.Dutytoplan: health care, crisis standards of care, and novel coronavirusSARS CoV 2. NAM Perspectives. 2020Mar5; doi:10.31478/202003b.
[13] Liu C, Wang X, Liu C, Sun Q, Peng W. Differentiating novelcoronaviruspneumoniafromgeneralpneumonia based on machine learning. Biomed Eng Online. 2020 Aug19;19(1):66.doi:10.1186/s12938 020 00809 9.
[14] ClarkK,VendtB,SmithK,FreymannJ,KirbyJ,KoppelP, MooreS,PhillipsS,MaffittD,PringleM,TarboxL,Prior F.TheCancerImagingArchive(TCIA):maintainingand operating a public information repository. J Digit Imaging. 2013 Dec;26(6):1045 57. doi:10.1007/s10278 013 9622 7
[15] SedikA,IliyasuAM,AbdEl RahiemB,AbdelSameaME, Abdel RaheemA,HammadM,etal.DeployingMachine andDeepLearningModelsforEfficientData Augmented Detection of COVID 19 Infections. 2020;12(7):769. PMID:doi:10.3390/v12070769
[16] CyranoskiD.'Weneedtobealert':Scientistsfearsecond coronavirus wave as China's lockdowns ease. Nature. 2020Mar30.PMID:32231319.doi:10.1038/d41586 020 00938 0.
[17] Sear RF, Velasquez N, Leahy R, Restrepo NJ, El Oud S, Gabriel N, et al. Quantifying COVID 19 Content in the Online Health Opinion War Using Machine Learning. IeeeAccess.2020;8:91886 93.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008
International
Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr
Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e ISSN: 2395 0056
p ISSN: 2395 0072
Chithra S Prasad, currently pursuing MTech degree in ComputerScienceandEngineering from APJ Abdul Kalam Technological University, Kerala, India at Mount ZionCollege of Engineering, Kadammanitta, Kerala,India.
Smitha C Thomas, received the MTechdegreeinComputerscience and Engineering. She is currently workingasAssistantProfessorin the Department of Computer scienceandEngineeringatMount Zion College of Engineering, Kadammanitta,Kerala,India.
ReshmaSuku,receivedtheMTech degree in Computer science and Engineering. She is currently workingasAssistantProfessorin the Department of Computer scienceandEngineeringatMount ZionCollegeofEngineering, Kadammanitta,Kerala,India.


