Writer Identification via CNN Features and SVM
Mahmoud rahhal
Aleepo, Syria, Computer Engineering Department, College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Aleppo
Abstract Writer recognition is the process of identifying the author of a document based on his or her handwriting. Recent advances in computational engineering, artificial intelligence, data mining, image processing, pattern recognition, and machine learning have demonstrated that it is possible to automate writer identification. This paper proposes a writer recognition model based on Arabic handwriting.
This research presents the study and implementation of the stages of writer identification, starting from data acquisition by scanned images of handwritten text, and then augmented the data through studyofMaazet al. [1] thatgeneratealarge number of texts from the set of texts available within the database, and then building a convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Which is usually useful for extracting features information and then classification the data, but in this research it is usedfor feature extraction,finallysupportvector machine is used for classification.
The experiments in this study were conducted on images of Arabic handwritten documents from ICFHR2012 dataset of 202 writer, andeach writer have3 text. The proposedmethod achieved a classification accuracy of 97.20%.

Key Words: Arabichandwriting,dataaugmentation,writer identification,deeplearning,convolutionalNeuralNetwork, supportvectormachine.
1. INTRODUCTION
Identificationofpersonsismainlythroughthephysiological characteristicslikefingerprints,face,iris,retina,andhand geometry and the behavioral characteristics like a voice, signature, and handwriting. Writer identification is a behavioral approach of handwriting recognition, which offerswithmatchingunknownhandwritingwithadatabase ofsampleswithrecognizedauthorship.
Writeridentificationhasbeenalivelydisciplineoflookup overthepreviousfewyearsanditusedinmanyapplications asinbiometrics,forensicsandhistoricreportanalysis.
Identifying people involve a fields of Artificial intelligence (AI), image processing and pattern recognition, and it contributes in many applications: biometrics, forensics, security, and legal matters, and financial field etc. [2]. All methods of writer identification and verification can be
classified into two categories [3]: text dependent method andtext independentmethod Text dependentmethodsare methodswherethetextintestsamplesmustbethesameas intrainingsamples.Scaletoextractfeaturesfromtextimage. Text independentmethodsaremethodsinwhichthetextin test samples does not have to be the same in training samples and in which structural methods for extracting featuresfromacharactershapeareinvolved.
Writeridentificationisclassifiedintoon linewriterandoff line writer identification [3], in the case of on line writer identification, features are collected directly from signals sent from digital devices while writing, and in the off line case, and attributes are collected from written text Handwriting obtained from the scanned image . It is consideredasmorecomplexthanon linecaseduetomany dynamic features of handwriting are missing, for instance pen pressure,orderofstrokes,andwritingquickness[4].
Thetaskofclassificationinpatternrecognitionistoidentify thepatterntoaclassoftheknowngroupofclasses,inwhich features will be extracted from images of scanned texts handwritten and trained it by using a classification algorithm. This study proposed a system for identifying people through Arabic handwritten text by extracting features by deep learning, which required data augmentation. Because of limited number of handwritten text samples, it is impossible to gather a wide number of samplesfromdifferentwriters. Thetextisdividedintoparts and then Gathering all text structures randomly to obtain severallines,whichenablesustogeneratemanytextsfrom them,andthenusingaconvolutionalneuralnetwork[1]for feature extraction , finally using support vector machine (svm) for classification which proves its ability to achieve highaccuracyinwriteridentification.Thisresearchincludes a number of previous studies on handwriting features extraction,personidentificationtechniques,andsomedata augmentationtechniques.
2. RELATED WORKS
In this paragraph, the studies will be discussed that have beendoneonwriteridentificationandthetechniquesusedso far, with an overview of writer identification systems in severallanguages,suchasChinese,English,Arabic...etc.
ResearcherBangyLietalin2009proposedamethodbased on combining the static feature and dynamic feature, and
then the Nearest Neighbor Classifier was used as a classificationmethodology[5].In2009,researcherZhuetal presentedastudyinthisfieldusingtheShapeCodebookand MultiClassSVMClassifier,andtheirproposedmethodwas evaluated by collecting images of texts written in eight languages(Arabic,Chinese,English,Hindi,Japanese,Korean, RussianandThai).TheChineseidentificationratewasmuch lower(55.1%)comparedtotheeightotherlanguages[6].In 2013,researcherDjeddiandhiscolleaguesproposedawayto identify the identity of the text writer based on a set of featuresextractedthroughtheGrayLevelRunLength(GLRL) matricesmethodandcomparingthemwiththelatestknown features at the time, and good results were shown in identifyingthewriter’sidentity,andK Nearestwasalsoused. Neighbors and Support Vector Machines and their experiments were conducted on handwritten Greek and English texts of 126 writers and each writer 4 samples, achievinganinterestingperformanceinauthoridentification and verification in a multitext environment [7] A study presentedbytheresearcherAlaeietalin2014proposinga methodforidentifyingthewriterbasedonHistogram,using twodifferentsetsofhandwrittendatawritteninCanadian andEnglishlanguages. Theirexperimentswereconducted on228Canadian languagetextsfor57writerswith92.79% accuracy for F measure and 330 texts in English for 55 writerswith26.67%accuracyforF measure[8].Thendralet al conducted a 2015 study of person identification using imagesofTamilhandwritingof300writersandeachwriter 100samplesusingadiscriminantmodeltocategorizewith features aggregated from handwriting and use it in the SupportVectorMachine,usingthreekernelfunction:Linear TheRBFandPolynomialandtogetherwithPolynomialand RBF gave the highest prediction accuracy [9]. In 2015, researcherFielandSablatnig[10]presentedastudyonthe databasesICDAR2013,ICDAR2011andCVL,inwhichthey proposetousetheConvolutionalNeuralNetwork(CNN)to generatearayoftraitsforeachwriterthatiscomparedwith the rays of traits stored in the database. The method gave 98.6%onICDAR 2011,97.6%onCVLand40.5%onICDAR 2013might bebecauseofmissing Greektrainingdataand wrongsegmentation.
TheArabicwriteridentificationwasnotcoveredaswidelyas English or Chinese writer identification until the last few years, and the first study goes back to the proposal of the researcherAL Zoubeidyetal in2005usingmulti channel Gabor filtering and gray scale co occurrence matrices to distinguish writer from his writing style [11]. Fouad and Volke in 2014 proposed a system for Arabic writer identifition using only 21 feature, and Gaussian Mixture Models(GMMs)werealsousedasthekernelofthissystem, where GMMs provide a strong representation of the distribution of the extracted features using a fixed length slidingwindowItisconstructedandtrainedusingimagesof words and texts for writer [12]. Djeddi et al in 2014 conductedtheirstudyonhandwrittentextsof1,000writers
using three methods to extract features: run length distribution, edge hinge distribution, and edge direction features. They used Multiclass SVM (Support Vector Machine),andthenhadanidentificationrateof84.10%[13]. In2016,researcherElleuchandhiscolleaguespresenteda study based on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and SVM(SupportVectorMachine)forhandwritingrecognition. TheperformancewasevaluatedwithHACDBandIFN/ENIT database for character images. The results showed the effectiveness of the proposed method compared to CNN StandardClassifier[14].In2018,theresearcherAmarandhis colleaguesproposedadeeplearningmethodologyforslicing and recognizing printed and handwritten characters from words. An algorithm was proposed to slice the word into letters, and then extract the features using a wavelet transform, and these extracted features are exploited as connectionweightstobuildaconvolutionalneuralnetwork foreachlettershape,Theproposedmethodwastestedon APTIandIESKarDBdatabase,andtheirresultsshowedthe effectivenessandspeedoftheproposedmethodforeachof the databases [15]. Dengel et al presented the Arabic text recognitionsystemusingthe(KHATT)database Thisstudy mainly contributes to three aspects: preprocessing, deep learning, and data augmentation by creating copies of the data.Thefirstversionistheblurredversionofthedata,the second version defines the contours, the third version is enhancededges,andthefourthversionismakingeffectsand whereDataaugmentationwithadeeplearningapproachhas been shown to produce a better and more promising improvementinoutcomes.Thisstudyachievedarecognition accuracy of 80.02%, which is better compared to other studiesconductedonthesamedatabase[16].In2019,Aref andcolleaguespresentedastudybasedonintegratingOBI featureswiththecharactercodebookusingIAMdatabases for English texts and ICFHR 2012 for Arabic texts. The classificationaccuracywiththeKNNclassifierwas96%[17]. In 2019,Rehmanandhiscolleaguesappliedtheirstudyto identify the writer’s identity on the QUWI database that containsArabictextsandEnglishtextsfor1017writers,and eachwriterhas4texts,usingtechniquestoincreasethedata to improve performance, by obtaining from each original imageanimagecontainingtheboundariessurroundingthe words(Contours),aswellasobtainingnewsamplesfromthe originalimagesbyincreasingtheirsharpnessandtheimage unitobtainedinthefirststageofdataaugmentationwhen obtaining the bounding boundaries of words (Sharped Contours), and finally applying Negatives to the original images and images resulting from the previous steps to augmentthedata,AndusingtheAlexNetstructuretoextract attributes to then apply the Support Vector Machine as a classification method, the accuracy was 92.78% in English texts,92.20%inArabicand88.11%whencombiningArabic andEnglish,respectively[18].

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

3. PROPOSED SYSTEM
In this paragraph, the Arabic writer identification is presented.First,ImageAcquisitionofhandwrittentextsin Arabic, Secondly, the data augmentation technique for increasing the input data images, third, finally, training processandtheexperimentalarepresented.
3.1. Image Acquisition
The study was conducted on an ICFHR2012 database downloaded from Kaggle for 202 writers, each writer had threedifferenthandwrittentextsinArabic,andtheimages wereataresolutionof600DPPbinary[19].
3.2. Pre processing
The database did not need to be pre processed so it was binaryimageswithwhitebackgroundandtextinblack,this datajustneedtobeincreased.
3.3. Data Augmentation
Handwrittendocumentsmaybelimited,whichprompteda numberofresearcherstoincreasedatatechniques,anditwas necessarytotraintheneuralnetworkfromthepresenceofa large number of samples. This prompted us to use an algorithm that seeks to increase the number of images for handwrittentextsinArabic[1],especiallythatthedatabase The data on which the study was conducted (ICFHR2012 dataset) contains onlythreetextsfor each writer,and this numberisnotenoughtotraintheproposedneuralnetwork in the research, in addition to the images of large and different sizes, which does not fit with the nature of the proposed network and to avoid the problem of out of memory. To solve this problem, huge local image patches centeredonthecontourofthehandwritingimages[20]or insidetheslippingwindowsontextlines[21]areextracted bypastapproaches,whichonlyconsiderthelocalstructural informationofhandwriting.
After reviewing some research in this field, the method of researcherMaaz etal.wasappliedtoincreasethedata[1], andthroughthefollowingstagesasshownin"Figure1":
ISSN: 2395 0056
ISSN: 2395 0072
1) Consequently,theproposedmethodfordividingthetext intowordsorwordstructureswasadoptedtoavoidthe problemsofusingthetechniquesfordividingthetext into lines and then into words, in proportion to the databasethroughthefollowingstages:
a) Readoriginal picturesandfindtheirNegativeand thendeterminingtheconnectedcomponents(CCs: connected components)fromthebinaryimage.
b) Applyingthe(LoG:LaplacianofGaussian)filterto the matrix of connected components, which resultingfromphase(a).
c) Filling the filtered image based on morphological reconstruction.
d) Determining the connected components (CCs: connected components) from the output image of phase (c). Then, determining the connected components,whichresultingontheoriginal.
e) Deletingtheconnectedcomponentsthatarewithin larger connected components and make the interconnectedcomponentsasinglecomponentthat includesthem.
2) Collecting all the words or word structures randomly,whichresultingfromthepreviousstage in one line and repeat this step to get several differentlines.
3) Forminganimageofafive linetextgeneratedfrom stage(c)inthesecondstage.
4) Croppingeachimagegeneratedfromthethirdstage intoanumberofimageswithasizeof400*R,where (R) represents the height of the image generated from the third stage, as shown in "Figure 10", and then the size of all images was standardized whenenteredintothedeeplearningnetwork.
Hundredsofpicturesofhandwritingtextsforeachwriterare got from this stage; the first 200 handwriting images resultingfromDataAugmentationstageforeachwriterwere takentoobtainadatabaseof40400handwritingscriptsfor 202writersandforeachwriter200texts.
Fig 1:Dataaugmentationprocess:(a)Negativeoriginalimage.(b)Imageafterfiltering.(c)Fillingimageregionsandholes afterfiltering.(d)Determiningconnectedcomponentsonimageshownin(a).(e)Deleteconnectedcomponentsthatare amongothercomponents.(f)Sampleofwordpicturesandwordstructuresforawriter.(g)Sampleofgeneratedtextline image.(h):sampleImageofa5 linegeneratedtext.(i)Sampleofthetextimagesaftercropping.

3.4 Convolutional neural network
After increase the data, a wide number of images are generatedfromthetrainingdataset,groundedonwhich,the comingstepistoextractsomedistinctfeaturestorepresent theircharacteristic.AsdonebyChristleinetalandFieletal [20, 21], the Convolutional neural network is employed to reckonthefeaturesinthiswork.
Convolutional neural network’s architecture has several famousdesigns,including:LeNet,AlexNet[22],GoogLeNet [23],andVGGNet[24].
Three types of A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN): Convolutional Layer (CONV), Pooling Layer (POOL), and Fully ConnectedLayer(FC).
3.4.1ConvolutionalLayer(CONV)
ThislayeristhemostsignificantinanyCNNstructuredueto thefactfiltersareutilizedtolearnthefeaturesfromtheenter image. The 2D function map consists of the fold product between the filter values and the scanned area with the
correspondingfilterdimensionoftheenterimage,i.e.every neuron of this layer will join to a precise enter location accordingtoforfiltersize.
InaCONVlayer,theinputvolumeisrepresentedas[D1xM1x P1]correspondingtothedimensionsoftheinputimage.Four hyperparameters are represented as (N, L, Z, W) corresponding to the number of pollutants, the size of the filter,thestrideandthequantumofzeropadding.Theoutput volumeisrepresentedas(W2xH2xD2)correspondingto:
D2=(D1 L+2W)/Z+1 (3.4.1.1)
M2=(M1 L+2W)/Z+1 (3.4.1.2)
P2=N (3.4.1.3)
3.4.2PoolingLayer(POOL)
It is an intermediate layer in the network that reduces or compressesthespatialdimensionsoftheincominginputtoit, andthisreducesthecomputationswithinthenetwork.

Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

2395
2395
Poolinglayersdecreasethedimensionsofdatabycombining the outputs of neuron clusters at one layer into a single neuron in the subsequent layer. Pooling acts on all the neurons of the feature map, by combining small clusters, tilingsizessuchas2x2arefrequentlyused. Therearetwo commontypesofpoolinginfamoususe:maxandaverage. Maxpoolingusesthemaximumvalueofeachlocalclusterof neuronsinthefeaturemap,whileaveragepoolingtakesthe averagevalue.
InaPOOLlayer,theinputvolumeisrepresentedas[D2xM2x P2] corresponding to the dimensions of the input volume, two hyperparameters are represented as [L1, Z1] correspondingtothereceptivefieldorsizeofthefilterand thestride,andtheoutputvolumeisrepresentedas[D3xM3 xP3]correspondingto:
D3=(D2 L)/Z+1 (3.4.2.1)
M3=(M2 L)/Z+1 (3.4.2.2)
P3=P2 (3.4.2.3)
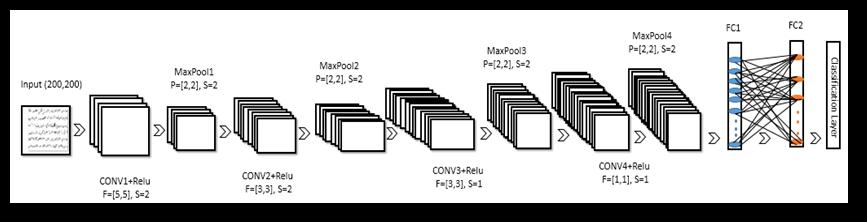
1. Theinputlayerreceivestrainingsamples,whichis binaryimagesandsize[400,400].
2. ConvolutionalLayer(CONV1):Inthislayer,96filters of size F = [5,
applying
=
3. BatchNormalizationLayer:Itnormalizestheinput via mini batch, speeds up the training of convolutional neural networks, and reduces the sensitivity of network initialization, so batch normalization layers are used between convolutional layers and nonlinearlayers, suchas ReLUlayers.
The layer first normalizes the activations for its inputbysubtractingthemeanoftheminibatchand dividingbythestandarddeviationoftheminibatch. [26]:
3.3.3Fully ConnectedLayer(FC)
The FC layer in a CNN like in ANNs has neurons that are connectedeveryneuronsinonelayertoeveryneuroninthe pastlayer.ThislayerisoftenkeptasthefinallayerofaCNN with “SOFTMAX” as its activation function for multi class classificationproblems.TheFClayerisresponsibletopredict thefinalclass.Thus,ithasanoutputdimensionof[1x1xD] where D represents the number of classes or labels consideredforclassification[25].
The network architecture that was used in this research consists of 4 convolutional layers, 4 pooling layers, and 2 FullyConnectedLayer(FC).[1]Eachconvolutionallayeris followedbyaBatchNormalizationLayer(BN)andRelulayer. ThisnetworkalsoincludesaSoftmaxlayer,whichisusedfor Classificationproblems.
Thedescriptionofthisarchitectureconvolutional network layersisasfollowsandillustratedaccordingto"Figure2":
4. ReluLayer:Thislayerappliesathresholdtoallits incomeitemsfromthepreviouslayeraccordingto thefunctionshownbelow:
(3.4.2)
5. Thepoolinglayer:(Pool1)InthislayerMaxPooling hasbeenusedinthemaximumpoolandthesizeof the area from which the maximum value will be chosenissizeP=[2,2],andstep(S=2).
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

6. Convolutional Layer (CONV2): In this layer, 128
ISSN: 2395 0056
ISSN: 2395 0072
of sizeF = [3,3],
stride(S= 2) without applyingzeropadding.
7. BatchNormalizationLayer.
8. ReluLayer.
9. Thepoolinglayer:(Pool2):Thesizeoftheareafrom whichthemaximumvaluewillbechosenisofsizeF =[2,2],andastride(S=2).
10. Convolutional Layer (CONV3): In this layer, 256 filters of size F = [3,3], and stride (S = 1) without applyingzeropadding.
11. BatchNormalizationLayer.
12. ReluLayer.
13. Thepoolinglayer:(Pool3):Thesizeoftheareafrom whichthemaximumvaluewillbechosenisofsizeF =[2,2],andastride(S=2).
14. Convolutional Layer (CONV4): In this layer, 300 filters of sizeF = [1,1],andstride(S= 1) without applyingzeropadding.
15. BatchNormalizationLayer.
16. ReluLayer.
17. Thepoolinglayer:(Pool4):Thesizeoftheareafrom whichthemaximumvaluewillbechosenisofsizeF =[2,2],andastride(S=2).
18. FullyConnectedLayer(FC1):TheFClayercontains neuronscompletelyconnectedtotheneuronsinthe previous layer, the output volume of this layer is defined(4500).
19. ReluLayer.
20. Dropout Layer: This layer effectively changes the
underlyingnetworkstructurebetweeniteratorsand helps prevent the network from over fitting by setting the input elements randomly to zero accordingtotheprobabilitythatwasdefinedwhen building the network and the most appropriate probabilityvalueforournetworkis(0.5)[27],[28]
21. Fully Connected Layer (FC2): The output size has beenspecifiedforthislayer(202),whichrepresents thenumberofclasses.
22. Softmax Layer Activation Function: It is used in classification problems of several classes. In classification problems, the last connected layer must be followed by a softmax layer and a classificationlayer,wheretheactivationfunctionof theoutputunitisthesoftmaxfunction
23. ClassificationLayer.
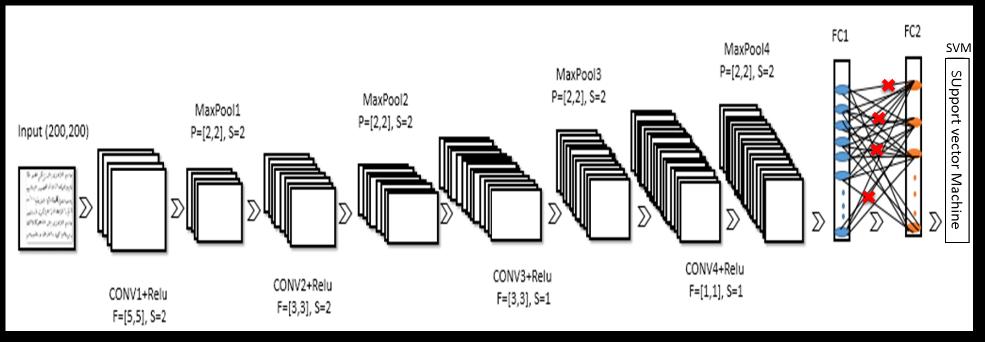
3.5 Feature extraction using CNN
This section shows how to extract learned image features fromapertainedconvolutionalneuralnetwork,andusethose featurestotrainanimageclassifier.Featureextractionisthe easiestandfastestwaytousetherepresentationalpowerof pertained deep networks. Because feature extraction only requiresasinglepassthroughthedata,itisagoodstarting pointifyoudonothaveaGPUtoacceleratenetworktraining with.WeshowedthenetworkarchitectureoftheCNNbased SVMmodelin"Figure.3".
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
It is observed that it looks as follows. First, load the data. Second, load a pre trained network. Third, the network creates a hierarchical exemplification of the input images. Deeperlayerscontainhigher levelfeatures,whicharebuilt
using the lower level features of past layers. To get representations of training features and test images, use activations on the fully connected layer 'FC1'. For a lower level exemplification of the images, use a past layer in the grid. Fourth, from the training images has been used the featuresextractedaspredictorvariablesandfitamulti class
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

Volume: 09 Issue: 04
2022 www.irjet.net
supportvectordevice(SVM).Finally,fromthetestimagesthe trainedSVMmodelandfeaturesextractedareusedtoclassify thetest
TheexperimentswereconductedonMatlabversionR2020a. The database includes 202 writers and each writer has 3 texts to be increased by using the Data Augmentation techniquesproposedinthisresearch,sothateachwriterhas 200 texts and the dataset becomes 40400 handwriting images. The dataset was divided into 3 groups 90% as a trainingset,chose5%ofthemasavalidationset,and10%as atestset.
To know the effectiveness of the proposed method, the accuracy was measured using relationship (4.1) to obtain 96.5099%classificationaccuracy.
(4.1)
Table 1: TablecompareresultbetweenProposedSystem andMaazetal.
Maazetal.
System
96.51%
SVM 97.20%
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
Writer identification by handwriting is a relatively new biometric method that has received significant research interestinrecentyears.Handwritingbiometricscanbeused inforensicapplicationstoidentifyindividualsbasedonthe characteristics of their writing by comparing unsorted handwritten texts with written samples Handwritten and categorized.
Handwritten texts were used to verify the identity of the authorofadocument.Thefontanalyzerusuallydependson studying some features of the writing style of each writer. Thisresearchpresentusingaconvolutionalneuralnetwork, whichrequiredtheuseofadataaugmentationmethodthat fitsthecharacteristicsofthetextwritteninArabictoextract thefeaturesandthenUsingsupportvectormachine(SVM).
In the future, experiments will be focused interest on applyingthisstudytoanewandmorediversedatabaseof texts that contain structures in Arabic and English and numbers,inordertodeterminetheidentificationaccuracy withthesecasesinthetext.
6 REFERENCES
ISSN: 2395 0056
ISSN: 2395 0072
[1] MAAZ, SH., ISSA, H., 2020 Using Deep Learning For Arabic Writer Identification.International Journal of CoputerApplications.Vol.175,No25.
[2] SREERAJ, M., IDICULA, S., 2011 A Survey on Writer Identification Schemes. International Journal of ComputerApplications,(26).
[3] SHAHABINEJAD,F.,RAHMATI,M.,2009 ANewMethod for Writer Identification of Handwritten Farsi Documents,ICDAR2009,Spain,pp.426 430
[4] SARANYA, K., VIJAYA, M. S., 2013 Text Dependent Writer Identification using Support Vector Machine. InternationalJournalofComputerApplications,(65).
[5] Li,B., Sun, Z., Tan,T.N., 2009 Hierarchical Shape PrimitiveFeaturesforOnlineText independentWriter Identification. 2009 10th International Conference on DocumentAnalysisandRecognition,pages201 210.
[6] ZHU, G., YU, X., LI, Y., DOERMANN, D. 2009 Language identificationforhandwrittendocumentimagesusinga shapecodebook.PatternRecogn.(42),3184 3191.
[7] DJEDDI, C., SIDDIQI, I., MESLATI, L., ENNAJI, A., 2013 Text independentwriterrecognitionusingmulti script handwrittentexts.journalhomepage,1196 1202.
[8] ALAEI,A., ROY, P.P., 2014 A New Method for Writer Identification based on Histogram Symbo lic Representation. 14th International Conference on FrontiersinHandwritingRecognition, 2167 6445.
[9] THENDRAL,T.,VIJAYA,M.S.,KARPAGAVALLI,S.,2015 Prediction of Writer Using Tamil Handwritten Document Image Based on Pooled Features. International Journal of Computer, Electrical, Automation,ControlandInformationEngineering,(9).
[10] Fiel,S.,Sablatnig,R.,Writeridenti_cationandretrieval usingaconvolutionalneuralnetwork, inProc.Int.Conf. Comput. Anal. Images Patterns. Cham, Switzerland: Springer,2015,pp.26_37.
[11] AL ZOUBEIDY ,L. M. AL NAJAR ,H. F., 2005 Arabic writer identification for handwriting images, International Arab Conference on Information Technology, pp.111 117.
[12] SLIMANE ,F., MARGNER, V., 2014 A New Text IndependentGMMWriterIdentificationSystemApplied toArabicHandwriting.14thInternationalConferenceon FrontiersinHandwritingRecogniti.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
09 Issue: 04
www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

[13] DJEDDI,CH.,MESLATI,L.,SIDDIQI,I.,ENNAJI,A.,ABED,H., GATTAL,A., 2014 Evaluation of Texture Features for Offline Arabic Writer Identification. 11th IAPR InternationalWorkshoponDocumentAnalysisSystems.
[14] ELLEUCH,M.,MAALEJ,R.,KHERALLAH,M.,2016 ANew Design Based SVM of the CNN Classifier Architecture with Dropout for Offline Arabic Handwritten Recognition. Procedia Computer Science. Volume 80, 2016,Pages1712 1723.
[15] ELADEL,A., ZAIED,M., AMAR,CH., 2018 Trained convolutional neural network based on selected beta filtersforArabicletterrecognition.WIREsDataMining KnowlDiscov.2018;e1250.
[16] DENGEL,A., LIWICKI,M., RASHID,S., AFZAL,M., NAZ,S., AHMAD,R.2018 ADeepLearningbasedArabicScript Recognition System: Benchmark on KHAT. The InternationalArabJournalofInformationTechnology, Vol.17,No.3,May2081
[17] Durou,A., Aref,.I., Al Maadeed,S., Bouridane,A., 2019 Writeridentificationapproachbasedon bagof words withOBIfeatures.ScienceDirect,InformationProcessing & Management, vol 56 issue (2) pp. 354 366. ISSN 0306 4573.
[18] REHMAN,A.,NAZ,S.,RAZZAK,M.,2019 AutomaticVisual Features for Writer Identification: A Deep Learning Approach.IEEEVolume7,2019.
[19] www.kaggle.com/c/awic2012/leaderboard
[20] Christlein,V.,Bernecker,D.,Maier,A., Angelopoulou,E. 2015 OfflineWriterIdentificationUsingConvolutional Neural Network Activation Features, Proc. German ConferenceonPatternRecognition,pp.540 552.
[21] Fiel, S., Sablatnig, R. 2015 Writer Identification and RetrievalUsingaConvolutionalNeuralNetwork,Proc. ComputerAnalysisofImagesandPatterns,pp.26 37.
[22] Krizhevsky,A.,Sutskever,I.,Hinton,G.E.2012 Imagenet classificationwithdeepconvolutionalneuralnetworks, Proc.NeuralInformationProcessingSystems,pp.1097 1105.
[23] Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S. , Anguelov, D.,Erhan,D.,Vanhoucke, V., Rabinovich, A. 2014 Goingdeeper withconvolutions, arXivpreprint arXiv:1409.4842
[24] Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A. 2014 Very deep convolutional networks for large scale image recognition,arXivpreprintarXiv:1409.1556
[25] Gogul.,Kumar,S., 2017 Flower Species Recognition System using Convolution Neural Networks and Transfer Learning. 2017 IEEE, 2017 4th International ConferenceonSignalProcessing,Communicationsand Networking.
[26] IOFFE, S., SZEGEDY, CH., 2015 Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing InternalCovariateShift.reprint,arXiv:1502.03167
[27] SRIVASTAVA,N., HINTON , G., KRIZHEVSKY, A., SUTSKEVER,I.,SALAKHUTDINOV,R.,2014 Dropout:A Simple Way To Prevent Neural Networks From Overfitting.JournalofMachineLearningResearch.Vol. 15,pp.1929 1958,2014.
[28] KRIZHEVSKY,A.,SUTSKEVER,I.,HINTON,E.,G.,2012 ImagenetClassificationWithDeepConvolutionalNeural Networks.AdvancesinNeuralInformationProcessing Systems.Vol.25,2012.
