Neural Network Based Automatic Classification of ECG Signals with Wavelet Statistical Characteristics
Arjun Choudhary
1Research Scholar,
Prakash Choudhary
Department, Bhagwant University, Ajmer, Rajasthan 305001, India

2HOD & Assistant Professor, Computer Science and Engineering Department, Bhagwant University, Ajmer, Rajasthan 305001, India
Assistant Professor, Computer Science and Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology Hamirpur, HP 177005, India
Abstract Cardiac abnormalities are the most common threat to human life. An electrocardiogram is the most common way to examine a heart abnormality. We present automatic detection of two typesofECGsignals withstatistical wavelet features using a Multilayer Perception Neural Network as the classifier. The database used for the heart abnormality detection is the MIT BIH arrhythmia database. The Butterworth and Chebyshev Type II filters have been introduced for de noisingthesignal.Thewaveletfeatureshave been extracted from the preprocessed ECG signal by using DWT (discrete wavelet transform) and 3600 samples have been taken from each signal and split into frames. The total number of samples of the signal is split into 4 windows, and each window contains 900 samples. DWT is applied in each frame or window to get wavelet coefficients which determine the characteristics of the signal. This wavelet coefficient is the input feature of the classifier for training and testing the model, which gives up to 100% accuracy for normal cases and 90% abnormality detection. This has been achieved.
Key Words: MIT BIH Arrhythmia, DWT, ECG, LDA, MLP, ChebyshevType II,NeuralNetwork,Perceptron
1. INTRODUCTION
TherearemainlythreesortsofcomponentswithintheECG signals.Eachwavecontainsdifferentinformation,whichhas includesamplitudes,durations,andmorphology.ThenHigh bloodpressure,cholesterol,smoking,beingoverweight,etc. arethevariouscausesthatincreasethegeneralriskofheart disorder. During long term monitoring, an automatic analysis of the ECG signal is vital to classify the various diseases of the heart. Manually analysing an oversized amountofinformationcouldbeaverytime consumingtask for doctors and analysts. Hence, there's a necessity for computationalmethodsandmachinelearningtechniquesfor the classification of the ECG signal. ECG analysis tools require knowledge of the location and morphology of the variedsegmentsintheECGrecordings[1],[2].
Karpagechilvi et al. [3] proposed a sentimental analysis method where it's necessary to extract vital information fromtheECGsignaltodetectnewfeaturesforhisuseasan inputwithintheartificialneuralnetworktoclassifytheECG
signal.Inpaststudies,manyresearchershaveworkedwith the ECG signal to detect the heart disorder. Several algorithmsarebeendevelopedfortheclassificationofECG signals.
Stalin Subbiah et al. [4] proposed a method for preprocessing to cancel the noise using Gaussian filters, medianfilters,FIR filters,andButterworthfilters.Theseare usedforfeatureextraction,wavelettransformation,andQRS componentfeaturesareusedasaclassifierinputtospotthe conventionalandabnormalheartbeat.
EduardoJosedaS.Luzetal.[5]performedresearchbywhich away isproposedwhichusesa10secECGsignalfornormal andarrhythmiaorabnormalECGclassification.Thedatabase hasbeentakenfromtheMIT BIHnormalsinusdatabaseand supraventriculararrhythmiadatabase.
SharmaandBhardwajetal.[6]proposedthemodeltotrain the neural network.TheLevenberg Marquardt functionis usedwith100%accuracyforthenormalSinusDatabase.
Ayub,J.P.Sainietal.[7].Researchperformedbyhimusesthe ANFIS (Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Interface System) model to identify normal and abnormal ECG signals. The MIT BIH normalsinusandMIT BIHsupraventriculardatabasesare used for training and testing the neural network. A feed forward and back propagation algorithm are accustomed minimisetheerrors,andatrapezoidalmemberfunctionis employedasaninputandoutput.
Mondal,S.,Choudhary,P.,etal.[8]usedthisMIT BIHnormal sinusdatabase.TherecordsfromtheMIT BIHArrhythmias and Apnea ECG databases from Physionet are used for training and testing our neural network based classifier. Fromwhich90%healthyand100%abnormalrecordsare detectedwithintheMIT BIHArrhythmiasdatabasewithan overallaccuracyof94.44%.WithintheApnea ECGdatabase, 96% of normal and 95.6% of abnormal ECG signals are detected, achieving a 95.7% classification rate. From this MIT BIHnormalsinusdatabase,18samplesaretakenand 61samplesaretakenforabnormalitiestotrainandtestthe model.Theproposedmodelgivesanaccuracyof100%for normaland91%forabnormal.
Kalpna
Journal of Engineering and Technology

KulkarniandLaleetal.[9]proposedhisworkforextracting the morphological and statistical features like RR interval heartrate,arithmeticmean,median,variance,skewness,and kurtosis, respectively, for ECG analysis using discrete wavelettransformation(DWT).Heproposedclassificationof theECGsignalwiththeKNNclassifier,whichistobeusedto achieveaclassificationaccuracyof86.95%.Thesensitivity and specificity results of ECG are 87.09% and 86.66%, respectively.
The inability to pick features using the correct feature extractiontechniquecouldbeasignificantdisadvantagefor ECGclassification.Tobeatthematter,awindowmethodis employedforapplyingthediscretewavelettransformand extractingstatisticalfeaturesforeverywindow.
2. TRANSFORMATION OF DISCRETE WAVELETS
Wali, Mousa K and colleagues et al. [10]. DWT is that the mathematical tool used for various signal and image processing applications, which are employed in both continuousanddiscrete timesignals.It'susedforde noising thesignalsandhavefeatureextractiontechniques.It'smade fromvarietyoffilterseries(highpassandlowpassfilters) similarlyassub sampling.
They proposed a multilevel task that's distributed using DWT. We have two styles of coefficients in each level: approximationcoefficientsanddetailcoefficients,whichare obtained after DWT is applied to the preprocessed signal. Theseapproximationcoefficientscontain a low frequency component, and also the detailed coefficients contain the high frequencycomponents.Theapproximationcoefficient continuously passes through the varied filters until the specified level of decomposition has been achieved or reached.
ForECGsignalclassification,LDAandMLPclassifierswere proposed.Duringthiscase,theelectrocardiogramsignalmay containnon stationarycharacteristics.Hence,efficientand instantaneousseparationoftheECGrhythmsisoftendone supported on the decomposition of the EEG signals into wavelet coefficients. The Wavelet transform may be a powerful spectral estimation technique for the time frequency analysis of a signal. Commonly, Haar wavelets, Daubechies wavelets, coeiflets, etc., with various different waveletfamiliesareused.Duringthisstudy,Dabechies(DB) waveletsareused.
3. METHODS
ThetaskofclassificationforECGsignalsisbroadlydivided into three parts: preprocessing, feature extraction, and classification.Fig.1.showsthetecticduringthiswork.
2395
2395
Fig. 1. MultidimensionaldiagramoftheECGclassification.
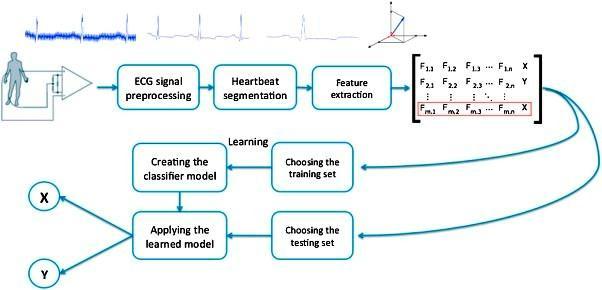
3.1 Datasets
The database provided by MIT BIH Arrhythmia is from PhysionetATM[13].Thedatabasecontains48recordings, includingmaleandfemale.Eachrecordingishalf hourlong andsampledat356Hz.FortheclassificationofECGsignals,a 10 seconddurationsignalhasbeenusedandsplitintotwo parts:normalandarrhythmia(orabnormal).
3.2 Preprocessing
In the electrocardiogram (ECG) signal, various styles of noises are present, like baseline drift noise, power cable noise, electrode contact noise, and other kinds of noises. Hence,thisstageisextremelyvitalforECGsignalprocessing. To get rid of the noise, we use the band pass filter, the Butterworthfilter,andtheChebyshevType IIfilterdesigned forthiswork.ThefrequencyoftheECGsignalisin between 0.5 Hz and 100 Hz. It's necessary to preprocess the ECG signals before performing feature extraction and classificationtourgehigheraccuracy.
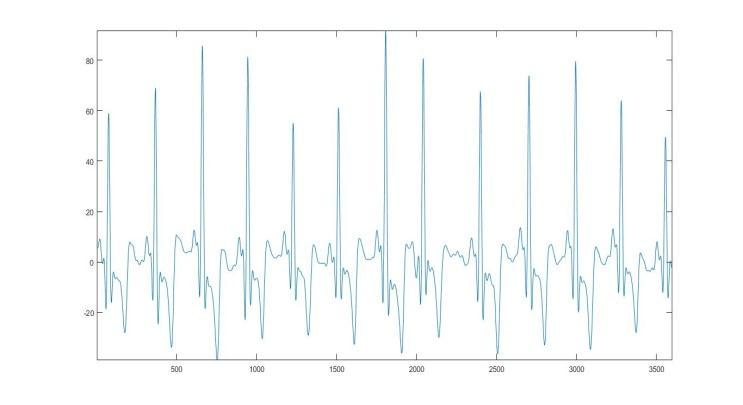
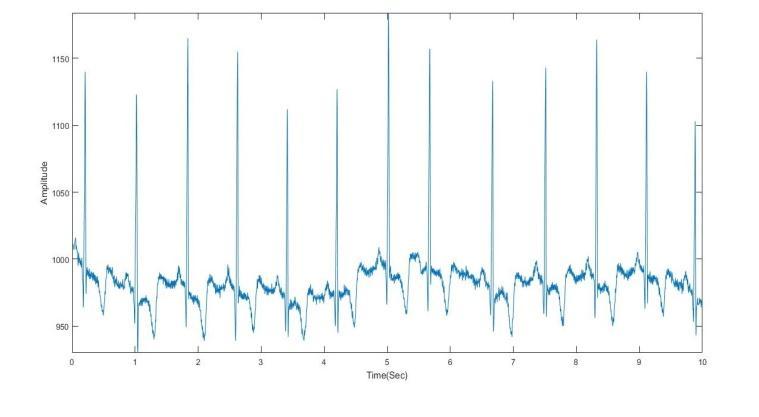
Sonal K et al. [14] used Butterworth to get rid of baseline drift noise. Chebyshev Type II filters are wont to remove higherfrequencies.Fig.2andFig.3showtherawandpre processedECGsignals,respectively.
Fig. 2. UnfilteredECGsignals
3.3 Extraction of Characteristics
Theprocessoffeatureextractionisextremelyimportantfor the classification of ECG signals. Within the first start, the features are extracted from the preprocessed ECG signal using DWT (Discrete Wavelet Transformation) using 10 seconds of ECG signal from the MIT BIH Arrhythmia database[15].Thedesiredstatisticalfeaturesareextracted from the DWT coefficient. The extracted features are as follows: • Energy • Entropy • Mean • Median • Standard Deviation In this study, the features are extracted using DWT. The waveletsused areDaubechies(db3), which are applied to the 3600 samplesfor the 10 secondECGsignal anddividethesignalinto4windowsofequalsamples,900 samples per window. The DWT is performed out at four levelstogetthedetailedandapproximatecoefficients.From each window, 20 statistical features are calculated to representtheECGsignal[16].
3.4 Classification
This is the ultimate step where the ECG signals are recognizedwiththeassistanceofaclassifier.Theextracted features are the inputs of the classifier to spot the conventionalandabnormalECGsignals.Aneuralnetwork (NN)classifierisemployedduringthiswork.Withinthenext section,theclassificationprocessisdescribed[17].
4. NEURAL NETWORK
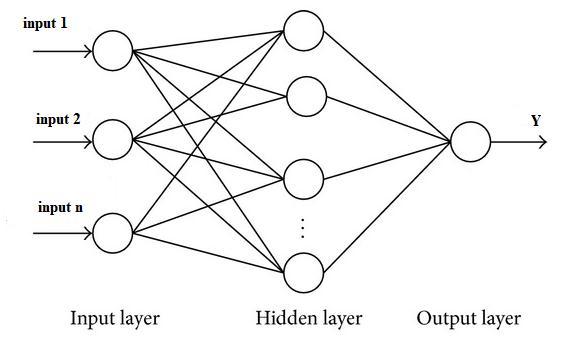
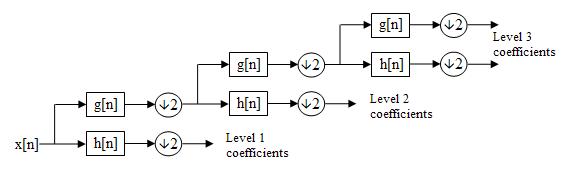
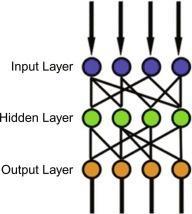
Amulti layerperceptron(MLP)neuralnetworkclassifieris used as a classifier to check the features of two types of signals[18]and[21].Amulti layerperceptron(MLP)could beaclassoffeed forwardartificialneuralnetwork(ANN). Sometimes the term "MLP" is employed ambiguously to meananyfeed forwardANN,butsometimesitstrictlyrefers to networks composed of multiple layers of perceptrons (with threshold activation). Multilayer perceptrons are sometimesco laterallystatedas"vanilla"neuralnetworks aftertheyhaveaonehiddenlayer[22] [26].1.Asproposed byAtanganaetal.[27],aselectedproblemisthatanartificial neuralnetworkconsistsofthreelayersofneuralnetworks: input,output,andahiddenlayer.Theneuralnetworkfirst trainsthenetworkbytrainingtheinformationtosearchout the link or relationship between the features of the ECG signal and therefore the properly trained algorithm. The trained algorithm is employed as a back propagation algorithm with the connection of weights between layers. The algorithm calculates the mean square error, during which the minimum mean square error is chosen to differentiatebetweenthetwovarietiesofECGsignals.
Fig. 4. Thethree leveltreeofDWT.

Fig. 5. ThearchitecturalmodelofMLP.
Multi layer perceptrons are designed to make approximationsofanycontinuousfunctionandmaysolve problemsthatarenotlinearlyseparable.Theforemostuses ofMLParepatternclassification,recognition,prediction,and approximation. The computations going down at every neuronwithintheoutputandhiddenlayerareasfollows:
(1)Ox=Gb2+W2hx
(2)Hx=x=sb1+W1x
Withbiasvectorsb(1)andb(2),weightmatricesW(1)and W(2),andactivationfunctionsGands,Theparametersare W(1),b(1),W(2),b(2)
TypicalchoicesforsincludetheTanhfunctionwith Tanh(a)=(ea ea)or(ea +ea)
Thelogisticsigmoidfunction,with Sigmoid(a)=1/1(+ea)
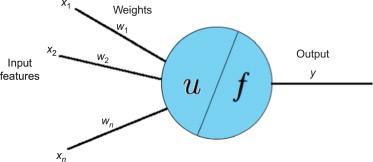
MLPs are neural network models that work as universal approximators, i.e., they'll approximate any continuous function.TheaboveMLPiscomposedofneurons,whichare called perceptions. So, before explaining the overall structureofMLPs, the overall structureofa perceptron is going to be explained. As shown in Figs. 6 and 7, A perceptronreceivesnfeaturesasinput(x=x1,x2,...xn),and everyofthosefeaturesisrelatedtoaweight.Inputfeatures mustbenumeric.So,non numericinputfeaturesshouldbe converted to numeric ones so as to use a perceptron. A categoricalfeaturewithppossiblevaluesisconvertedintop inputfeaturesrepresentingthepresenceorabsenceofthese values.Thesearecalleddummyvariables.Forinstance,ifthe inputfeatureoftheeventtypecantaketheworthofrecent development,enhancement,orre development,itmaywell be replaced by the three dummy variables of new development,enhancement,andredevelopment,whichtake thevalueof1ifthecorrespondingvalueispresentand0if it'sabsent.
Ifu(x)>0,Y=f(u(x))=1,otherwise,
Wherei, isathresholdparameter.
An example of a step function with a value of 0 is shown inFigure 24.2a. Thus, we can see that the perceptron determineswhether w1x1 + w2x2 ++ wnxn >0istrueorfalse. The equation w1x1 + w2x2 + + wnxn = 0 is the equation of ahyperplane.Theperceptronoutputs1foranyinputpoint abovethehyperplaneand0foranyinputonorbelowthe hyperplane.Forthisreason,theperceptronisnamedalinear classifier,i.e.,itworkswellfordatathatislinearlyseparable. Perceptronlearningconsistsofadjustingthe weightssoa that a hyperplane separates the training data that 's determined.
5. RESULT WITH DISCUSSION
In this study, the MIT BIH Arrhythmia database has been used,fromwhich45recordsweretakenof10secondsignals of 3600 samples [13], [15]. The above datasets are first preprocessed using a Chebyshev type II filter to cancel various types of noise. Then the preprocessed signal is divided into windows, where each window contains 900 samples. Then, for feature extraction, a discrete wavelet transformwasappliedineachwindow,andweobtained20 attributes. A total of 80 attributes are obtained from all windows to represent the ECG signals. The statistical featuresthatwereextractedaretheinputsoftheartificial neuralnetwork.Thedatabaseisseparatedintonormaland abnormalclasses.Thereare25and20recordsfromnormal andabnormal,respectively.Table1.showsthetotalnumber oftrainingandtestingrecordsusedfortheclassificationof ECG.Itshows100%accuracyfornormalECGsubjects.
Fig. 7. PerceptronSchemawithNinputfeatures
Theinputfeaturesarepassedtotheinputfunctionu,which computestheweightedsumoftheinputfeatures:
1nwixi u(x)=I
The result of this computation is then passed onto anactivationfunction f,whichwillproducetheoutputofthe perceptron. In the original perceptron, the activation functionisastepfunction:
Table1showstheMIT BIHArrhythmiaDatabase'straining, testing,andaccuracy.
6. CONCLUSION
Inthisexperiment,theMIT BIHarrhythmiasdatabasefor10

signals of 3600 samples has been used for the classificationofECGsignals,andthesignalsarepartitioned into 4 windows, each of which contains 900 samples per window. Then, we extract some statistical features by applying a discrete wavelet transformation (DWT). The features that were extracted are energy, entropy, median, mean,andstandarddeviation,andthesefeaturesarepassed through the artificial neural network with a back propagationalgorithm.Theresultsshowthat100%accuracy fornormal
subjectswasachieved.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Editor in Chief and anonymous referees for their suggestions and helpful comments that have improved the paper's quality and clarity.
REFERENCES
[1] RashkovskaA,DepolliM,TomaicI,AvbeljV,Trobec R, (2020): Long term monitoring with a medical gradeECGsensor.Sensors,20,1695.
[2] Miquel Alfaras, Miguel C. Soriano, and Silvia Ortn (2019): A Fast Machine Learning Model for ECG Based Heartbeat Classification and Arrhythmia Detection. http://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2019.00103.
[3] Karpagachelvi S, Arthanari M, Sivakumar (2010): ECG Feature Extraction Techniques A Survey Approach. International Journal of Computer ScienceandInformationSecurity,Vol.8,No.1.
[4] Subbiah S, P Rajkumar, and P Subbthai (2015): Artificial Neural Network and Machine Learning ApproachforFeatureExtractionandClassification in ECG Signal Processing.Vol. I. ISBN: 978 81 929742 5 5.
[5] Eduardo Joseda S. Luz, William Robson Schwartz, Guillermo Cámara Chávez, and David Menotti (2016): A survey of computer methods and programmesinbiomedicine127,144 164.
[6] Sharma, A., and K. Bhardwaj (2015): Detection of normal and abnormal ECGs using a neural network.International Journal of Information ResearchandReview,Vol.2(05),pp.695 700.
[7] S. Ayub and J.P. Saini (2011): Using a cascaded forwardneuralnetworkforECGclassificationand abnormalitydetection.
DOI:10.4314/ijest.v3i3.68420.
[8] Sourav MondalandPrakash Choudhary (2019): DetectionofNormalandAbnormalECGSignalUsing
ANN: Selected Revised Papers from the Joint InternationalSymposiumonArtificialIntelligence andNaturalLanguageProcessing(iSAI NLP2017).
T.Theeramunkong, et.al.(2017).Advances in Intelligent Informatics, Smart Technology, and NaturalLanguageProcessingiSAI NLP.Advancesin IntelligentSystemsandComputing,Springer,Cham. Vol.807.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978 3 319 94703 73
[9] KulkarniA,LaleS,IngoleP,andGengajeS(2016): ECGsignal analysis,SSRGInternational Journal of ElectronicsandCommunicationEngineering(SSRG IJECE), Vol. 3. DOI: 10.14445/23488549/IJECE V3I4P104.
[10] Wali, Mousa K et al. (2012): Development of a Dicerete Wavelet Transform (DWT) toolbox for signal processing applications, International Conference on Bionedical Engineering (ICoBE), Penang,pp.211 216, DOI:10.1109/ICoBE.2012.6179007.
[11] S. Hemchandra and Y. Dileepkumar (2020): Realtime analysis of an ECG signal using the DiscreteWaveletTransform,InternationalJournal ofAdvancedScienceandTechnology,Vol.29.
[12] Romain Atangana et al. (2020): Djoufack/ publication/339789817.ECGSignalClassification usingLDAandMLP.
[13] https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Laurent.
[14] http://www.physionet.org/physiobank/ database/mitdb.
[15] Sonal K Jagtap and Mahadev Dattatraya Uplane (2012): A Real Time Approach to ECG Noise Reduction Using a Chebyshev Type II Digital Filter.49(9), International Journal of Computer Applications, DOI:10.5120/7659 0763.
[16] https://archive.physionet.org/physiobank/databas e/html/mitdbdir/intro.htm.
[17] MuhidinA.Mohamed,Mohamedet.al.(2014):An approach for ECG Feature Extraction using the Daubechies4(DB4)Wavelet.Volume96 No.12of theInternationalJournalofComputerApplications (0975 8887).
[18] Mohamed Hammad, Asmaa Maher, et. al. (2018): DetectionofabnormalheartconditionsusingECG signalcharacteristics.Pages634 644inVolume125, September, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.05.0 33.
[19] S. Abirami and P. Chitra (2020): Advances in Computers TheDigitalTwinParadigmforSmarter SystemsandEnvironments:IndustryUseCases,
[20] Vijay Kotu and Bala Deshpande (2019): Data Science (Second Edition). K Gurney (2018): An introductiontoneuralnetworks
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3364

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 04 | Apr 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
http://www.macs.hw.ac.uk/~yjc32/project/refNN/ Gurneyetal.pdf.
[21] Awaysheh,J.Wilcke,F.Elvinger(2019):Reviewof Medical Decision Support and Machine Learning Methods.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985819829524
[22] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multilayer perceptron.
[23] Flora Amato, Nicola Mazzocca, et.al. (2017): An Intelligent Model for Classification and Intrusion Detection, 31st International Conference on AdvancedInformationNetworkingandApplications Workshops(WAINA)
DOI:10.1109/WAINA.2017.134.
[24] https://towardsdatascience.com/multilayer perceptron explained with a real lifeexampleand python code sentiment analysis cb408ee93141.
[25] MW Gardnel, R Dorlingal (1998): Artificial neural networks(themultilayerperceptron) Areviewof applications in the atmospheric sciences in AtmosphericEnvironmentVol.32,Issues14 15,1, Pages2627 2636.
[26] Yildirim, P Pławiak, R S Tan and U R Acharya (2018): Arrhythmia Detection Using Deep ConvolutionalNeuralNetworkWithLongDuration ECGSignals.ComputersinBiologyandMedicine DOI:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.09.009
[27] Romain Atangana, Laurent Chanel et.al.(2020): Formalized paraphrase EEG Signal Classification usingLDAandMLPClassifiers,HealthInformatics. An International Journal (HIIJ), Vol. 9, No. 1. Djoufack/publication/339785382.MotherWavelet SelectionforEEGSignalAnalysisFrequencyBand Decomposition and Discriminative Feature Selection/links/5ebda54492851c11a867c14a.
BIOGRAPHY OF AUTHORS
1. Arjun Choudhary, Research Scholar, ComputerScienceDepartment, Bhagwant University, Ajmer, Rajasthan 305001, India, Place:Jodhpur(Rajasthan),DOB:30 08 1976, Sr. Technical Assistant, Government Engineering College, Ajmer since12Dec.1999 tilldateandhaving22 years of experience. Field of Research is Adhoc Networks, Document Image Analysis, Medical Image Processing, ComputerVisionandPatternRecognition, MachineLearning,NeuralNetworksandAI.


2. Dr.Kalpna Sharma, HOD & Assistant Professor, Computer Science and Engineering Department, Bhagwant University, Ajmer, Rajasthan 305001, India, Place: Ajmer (Rajasthan), 21stJuly ,2016 tilldate.AssistantProfessor,Pacific Institute of Management & Technology PacificUniversity,Udaipur(Rajasthan)1st Jan. 2012 31st June 2013. Lecturer (IT) Savitri Institute of Management, Savitri Girls’College,Ajmer,AffiliatedtoRajasthan TechnicalUniversity,Kota,(Rajasthan)1st Oct.2009 31st Dec.2011. Research experience in Document Image Analysis, Image Processing, Computer Vision and PatternRecognitionetc.

3. Dr.Prakash Choudhary, Assistant Professor, Computer Science and Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology Hamirpur, Himachal Pradesh,Hamirpur, HP177005, India, Place:Hamirpur,HP.DOB: 01 01 1987,21stDec.2018 tilldate.HOD &AssistantProfessor,NationalInstituteof Technology Manipur, India 795004, 30th Dec.2013 20th Dec.2018. Research experience in Document Image Analysis, Bioinformatics, Algorithms in Distributed Systems, Medical Image Processing, ComputerVisionandPatternRecognition, MachineLearningandAI.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page3365

